Global Marketing Strategies and Research Insights
1/367
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
368 Terms
Information Technology (IT)
Processes for managing organizational information.
Management Information System (MIS)
System for analyzing and reporting market data.
Big Data
Large datasets analyzed for patterns and trends.
Intranet
Internal network for information sharing within an organization.
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI)
Computer-to-computer exchange of business documents.
Efficient Consumer Response (ECR)
Strategy to improve supply chain efficiency.
Electronic Point of Sale (EPOS)
System for processing sales transactions electronically.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
Tools for managing company interactions with customers.
Latent Market
Undiscovered market segment with potential.
Incipient Market
Emerging market based on trends.
Qualitative Data
Non-numerical information for understanding concepts.
Quantitative Data
Numerical data used for statistical analysis.
Primary Data
Data collected firsthand for specific research.
Secondary Data
Existing data collected for other purposes.
Market Research Process
Steps to gather and analyze market information.
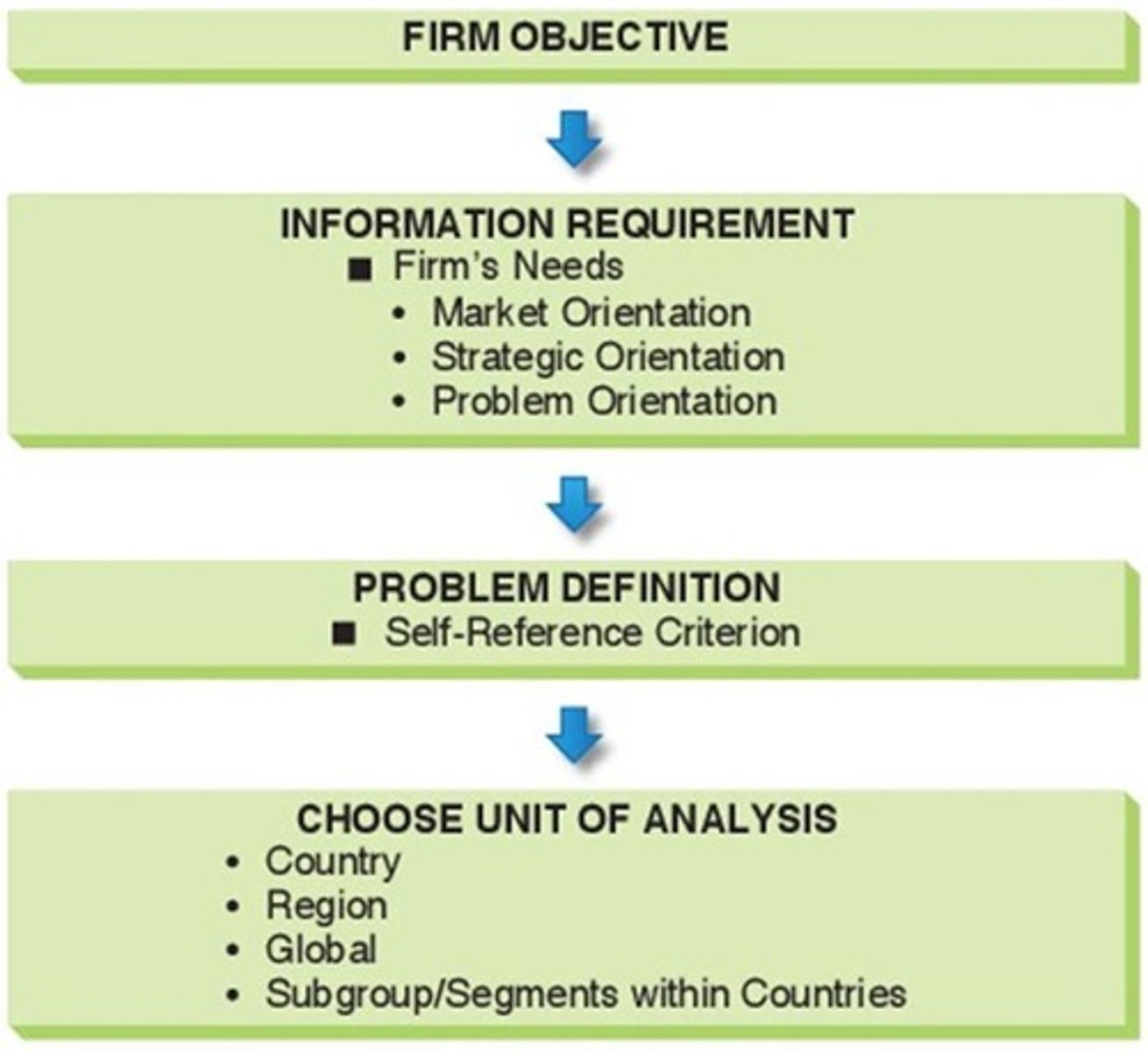
Information Requirement
Identifying necessary data for decision-making.
Defining the Problem
Clarifying issues to guide research efforts.
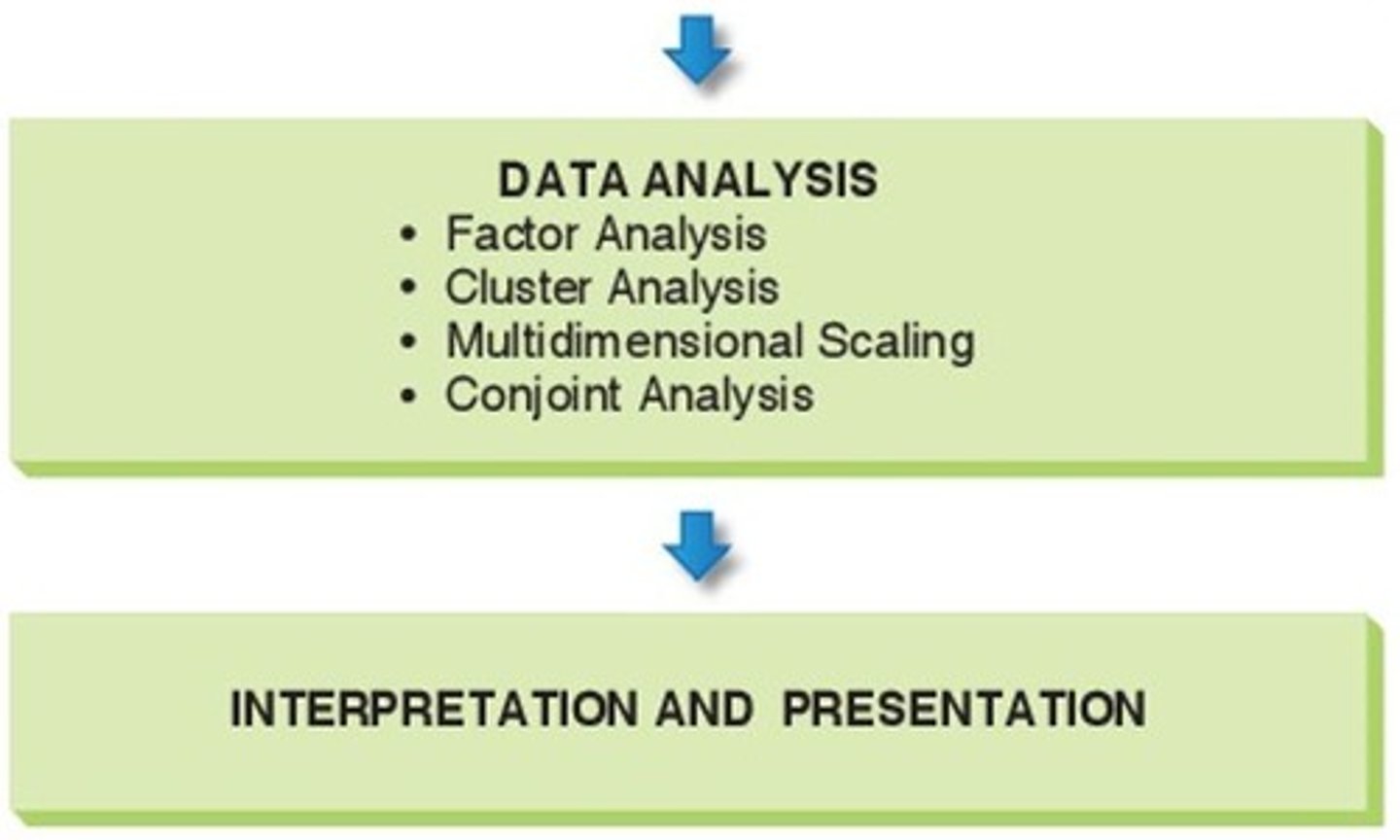
Data Analysis
Interpreting collected data to draw conclusions.
Recommendations
Suggestions based on data analysis outcomes.
NAICS Codes
Classification system for industry sectors.
Market Potential
Estimates of demand and consumer behavior.
Competitor Information
Insights into competitors' strategies and capabilities.
Foreign Exchange
Currency values affecting international trade.
Prescriptive Information
Legal and regulatory guidelines for operations.
Resource Information
Data on availability of necessary resources.
General Conditions
Overview of sociocultural and political environments.
Survey Research
Qualitative or quantitative data collection method.
Back Translation
Technique ensuring accuracy in survey translations.
Parallel Translation
Simultaneous translation method for accuracy verification.
Consumer Panel
Longitudinal tracking of respondents' behavior.
Nielsen Media
Tracks television audience measurement (TAM).

Observation
Recording consumer behavior via trained observers.
Focus Groups
Moderated discussions with 6-10 participants.
Likert Scale
Rating scale measuring attitudes or opinions.
Bias in Scale Development
Systematic error affecting survey results.
Convenience Samples
Non-random sampling based on easy access.
Quota Samples
Sampling ensuring specific characteristics are represented.
Data Cleaning
Process of correcting or removing inaccurate data.
Factor Analysis
Statistical method reducing data to underlying factors.
Cluster Analysis
Grouping similar data points for analysis.
Multidimensional Scaling
Visualizing data in multiple dimensions for insights.
Conjoint Analysis
Evaluating consumer preferences for product features.
Comparative Analysis
Evaluating differences between two or more entities.
Market Estimation by Analogy
Estimating market potential using similar markets.
Emic Analysis
Studying culture from an insider's perspective.
Etic Analysis
Detached study of culture for cross-country comparisons.
Business Intelligence (BI)
Interactive data access for informed decision-making.
Intranet
Private network for secure information sharing.
Real Time Enterprises (RTE)
Companies leveraging big data for operations.
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI)
Systems enabling standardized data exchange.
Efficient Consumer Response (ECR)
Supply chain optimization initiative for customer benefit.
Electronic Point of Sale (EPOS)
Data from checkout scanners for sales analysis.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
Philosophy emphasizing two-way communication with customers.
Touchpoints
Points of contact between company and customer.
360-degree View of Customer
Comprehensive understanding of customer interactions.
Sales Force Automation (SFA)
Software automating sales and marketing tasks.
Direct Sensory Perception
Firsthand experience of consumer behavior.
Global Market Segmentation
Dividing world markets into distinct customer subsets.
Demographic Segmentation
Segmenting based on income, age, gender, etc.
Geographic Segmentation
Segmenting based on location and regional factors.
Psychographic Segmentation
Segmenting based on attitudes, values, and lifestyles.
Behavioral Segmentation
Segmenting based on user behavior and usage rates.
Benefits Sought Segmentation
Segmenting based on the benefits consumers seek.
Pluralization of Consumption
Theory stating consumers seek variety in products.
Forecasting Purposes
Using segmentation to predict market trends.
Market Potential Assessment
Evaluating market size and growth opportunities.
Lean Start-up Methodology
Framework for assessing market segments: TAM/SAM/SOM.
TAM
Total Addressable Market; overall revenue opportunity.
SAM
Serviceable Available Market; segment of TAM targeted.
SOM
Serviceable Obtainable Market; realistic sales target.
Competition Analysis
Evaluating competitors' strengths in potential markets.
Negative Factors in Feasibility
Regulatory and marketing issues affecting market entry.
Regulatory Factors
Government rules impacting market entry and operations.
Marketing Issues
Challenges in distribution and product adaptation.
Import Restrictions
Barriers to importing goods into a market.
High Tariffs
Taxes imposed on imported goods affecting pricing.
Market Need Assessment
Identifying unmet needs in the market.
Product-Market Profile
Framework for analyzing target market characteristics.
Target Market Strategy Options
Different approaches to selecting target markets.
User Status Segmentation
Classifying users as potential, regular, or competitors.
Current Market Size
Existing size of a market segment.
Growth Potential
Expected future increase in market segment size.
Management's Network
Contacts influencing market targeting decisions.
Screening Criteria
Guidelines for evaluating market segments.
Product-Market Decisions
Assess products for country market suitability.
Product-Market Grid
Matrix showing product availability by country.
Lexus I S Model
Available in all countries.
Lexus H S Model
Available only in North America.
Standardized Global Marketing
Mass marketing globally with minimal adaptation.
Target Market Strategy
Options for targeting specific market segments.
Differentiated Global Marketing
Targets multiple distinct global markets.
Concentrated Global Marketing
Focus on a single global market segment.
Niche Marketing
Targeting a specific, smaller market segment.
P&G Old Spice Example
Illustrates differentiated global marketing strategy.
Chanel and Estee Lauder
Examples of concentrated global marketing.
Cost Leadership Strategy
Offering lowest prices in the market.
Differentiation Strategy
Creating unique product attributes for competition.
Focus Strategy
Targeting a specific market niche.
Positioning
Brand placement in consumer's mind relative to competitors.
Attribute Positioning
Based on product features and benefits.