Pulmonary Drug Delivery- Miroshnyk
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Pulmonary drug delivery are drugs being delivered to the lungs via the __________ or ____________________.
via the NOSE or an ORAL INHALATION
All drug formulations being delivered to the lungs must be _______________.
aerosolized
Pulmonary drug delivery provides a local, systemic, or both effect?
both!
local (to the lungs only)
systemic
What are the 4 obstacles to pulmonary drug delivery?
airway geometry (hard for drug to move between all the twists and turns of the airway system)
mucus
mucociliary clearance
alveolar macrophages
What are the 3 mechanisms of deposition of inhaled particles?
inertial impaction
sedimentation
diffusion
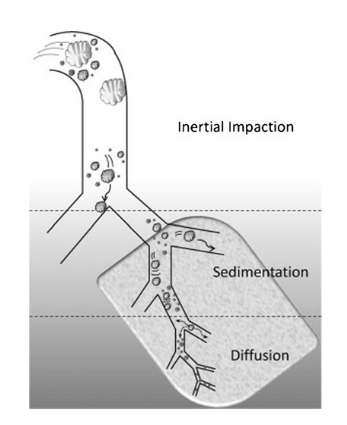
What mechanism of deposition is this?
mechanism for particles >5 um in diameter
deposition increases w/ velocity, diameter, and density
occurs in larger airways (highest airflow velocity)
inertial impaction
What mechanism of deposition is this?
occurs when particles follow gravity
deposition depends on particle diameter and density
occurs in smaller airways (low airflow velocity)
sedimentation
What mechanism of deposition is this?
SMALL particles
independent of density
deposition decreases with increasing particle size
SMALL airways
diffusion
All mechanisms of deposition are dependent on what?
particle size
What is the relationship between physical diameter and aerodynamic diameter of particles?
physical diameter provides the straightforward size of the particle, aerodynamic diameter reflects how the particle interacts with the gas during its movement.
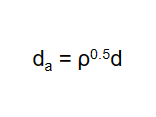
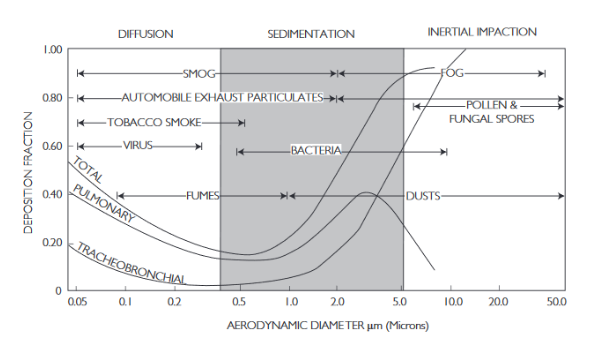
What is the effect of aerodynamic diameter on drug deposition in the lungs?
you can look at the chart and see with each deposition mechanism, how diameter effects the deposition fraction or rate
with diffusion: small diameter= more deposition
with sedimentation and inertial impaction: large diameter= more deposition
What is the advantage of pulmonary drug delivery for local/ respiratory disease treatment?
targeted delivery
rapid onset of action
avoid 1st pass metabolism
avoid GIT
minimized ADRs
enables a similar/superior therapeutic effect at a fraction of the systemic dose
What is the advantage of pulmonary drug delivery for systemic disease treatment?
non-invasive, needle free
drugs can be self-administered
patient compliance
suitable for both small/large molecules
enormous absorptive surface area and high permeable membrane in the lung region
less harsh, low enzymatic environment that avoids 1st pass metabolism
reproducible absorption kinetics
What are the 3 major types of pulmonary drug delivery devices?
nebulizers
pressurized metered dose inhalers (pMDI)
dry powder inhalers (DPIs)
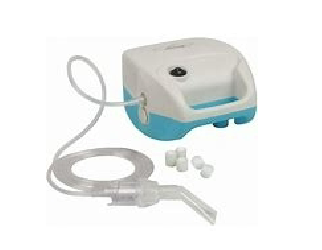
Describe nebulizers:
device that takes solutions/suspensions and turns them into aerosols
3 major kinds (air-jet, ultrasonic, and modern)
How do air-jet nebulizers create an aerosol?
use a pressurized jet air stream delivered by a compressor
this air is then forced through an opening called a “venturi”
this air then hits the liquid and turns it into an aerosol
Think: air-jet nebulizer= air
What is the venturi effect?
fluid speed increases when the fluid is forced through a narrow or restricted area
How do ultrasonic nebulizers create an aerosol?
piezo-electric crystals produce high frequency sound waves in the nebulizer solution
Think: ultrasonic nebulizer= sound waves

Advantage of ultrasonic nebulizers to air-jet nebulizers:
ultrasonic are lighter and quieter compared to air-jet
Disadvantage of air-jet nebulizers:
change in drug conc due to crystallization of drug or evaporation of solvent
Disadvantage of ultrasonic nebulizers:
cannot nebulize high-viscosity liquids
increase in temp causes degradation of thermolabile drugs
What should a patient using a nebulizer be counseled on?
keep nebulizers upright!
pt should breathe slow and deep for better med delivery
do not mix any other meds with the nebulizer
What do metered dose inhalers depend on to deliver the medication?
depend on the functioning of the container and propellant (gases) to deliver the medication
(you can see in the picture that the actual drug product is just a small portion)
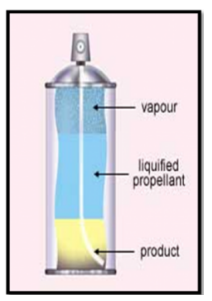
How do pressurized metered dose inhalers work in general?
drug is dispersed in propellants (like HFA)
the device aerosols the drug
“metering valves” allow for multiple dosing of the drug+propellant aerosol
FYI: this is what we commonly think of when someone has an inhaler
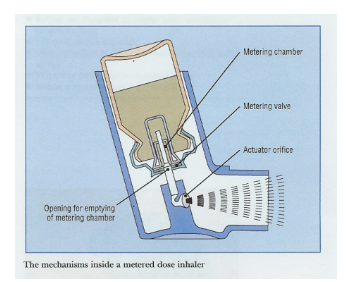
What is the role of metering valves in pressurized metered dose inhalers?
big picture: determine drug dose
Function: to expel contents at the desired rate and in the proper amount
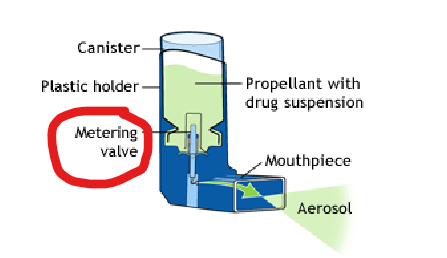
What is the role of HFA in pressurized metered dose inhalers?
propellant
What volume is dispensed from a pressurized metered dose inhaler (pMDI) each time it’s used?
30-100 uL
How should patients be counseled on how to use a pDMI?
shake well
wait 1 minute between if multiple dosing
hold breath for 10 seconds
explain importance between firing the device and breathing
like make sure they know to breath and hit the button releasing the drug at same time
Breath actuated MDIs are pDMIs that…
sense the patient’s inhalation through the actuator and fire the inhaler automatically
(like a vape)
What are some examples of propellant-free MDIs?
Respimat
Drug Formulations for Aerosol systems may be _______________ in the propellant system.
SATA
a. dissolved
b. suspended
c. emulsified
d. solutioned
a, b, c
A main issue with pMDIs is…
hand-breath coordination
What was developed to address the main issue of pMDIs?
dry powder inhalers (DPIs)
What is the major disadvantage of Dry powder inhalers?
efficient drug delivery depends on the patients own inspiratory effort (how hard they can breathe in)
Co-solvents used in inhaled products:
water
ethanol
propylene glycol
Surfactants/Lubricants used in inhaled products:
sorbitan
lecithin
magnesium stearate
Carrier Products used in inhaled products:
lactose
mannitol
dextrose
preservatives/antioxidants used in inhaled products:
parabens
BAC
EDTA
ascorbic acid
Flavoring agents used in inhaled products:
menthol
Sweeteners used in inhaled products:
saccharin