18- Bacteriophages
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Bacteriophages
Viruses that infect bacterias. They cannot infect us.
Phage = eat in latin
Prokaryotic viruses
must bind to host cell receptor
must cross a cell wall
gram- hosts also cross two membranes
must not damage host initially
Prokaryotic virus
use host nucleotides, amino acids, ATP
replicate viral genome, build capsid, build new viruses
Exit through cell wall
usually lyse host cells
Bacteriophage Life Cycle
Attachment to host cell proteins
Normal bacterial cell surface receptors (sugar uptake, signaling, conjugation)
viruses takes + uses host proteins
Injects genome through cell wall into cytoplasm
like shooting bacteria
Lytic Cycle
bacteriophage quickly replicates, killing host cell. It explodes, gets out fast, T4
Lysogenic cycle
Bacteriophage is dormant
Integrates into cell chromosome as a prophase
can reactivate and become lytic
less violent, chills after inserting DNA, lambda
The Lytic Phase (life cycle)
Use cell components to synthesize capsids
assemble progeny phases
exit from cell
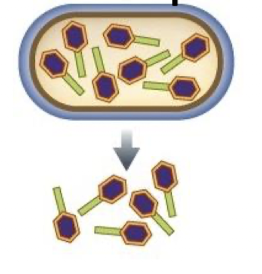
The Lytic Phase, Lysis
Makes protein to break peptidoglycan
Bursts host cell to release progeny phase
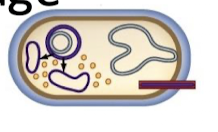
The Lytic Phase, Slow release
Filamentous phages can slip individual progeny out through cell envelope
Coliphages
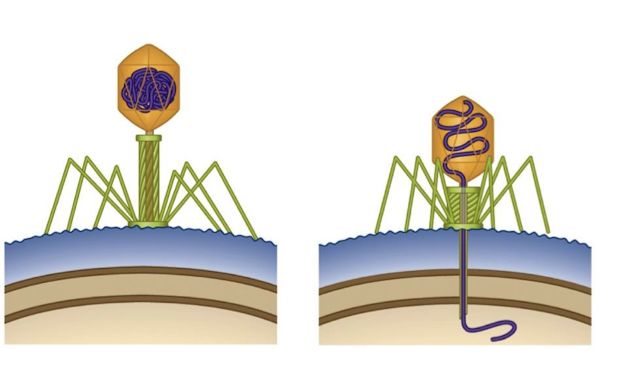
Viruses that infect E. coli (T4 and lambda)
T4 and lambda
double-stranded linear DNA genome
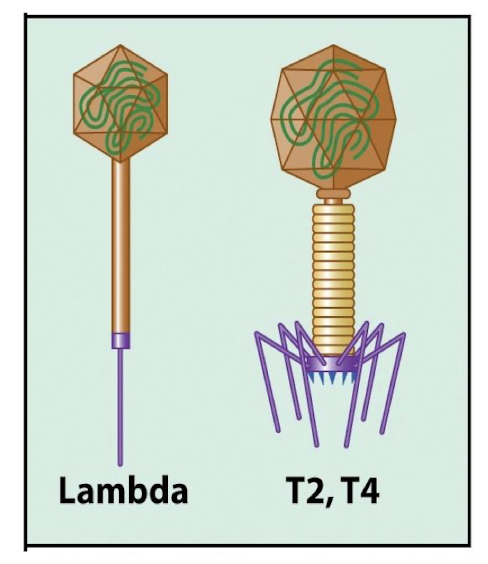
T4 phage
lytic
capsid head, tail
virulent lytic (intemperate)
Lambda phage
lysogenic (temperate)
capsid head, tail
Bacteriophage T4
complicated structures
170 genes
10 capsid proteins
tail fibers bind the host
receptor = OmpC porin, outer membrane protein
long tail injects DNA
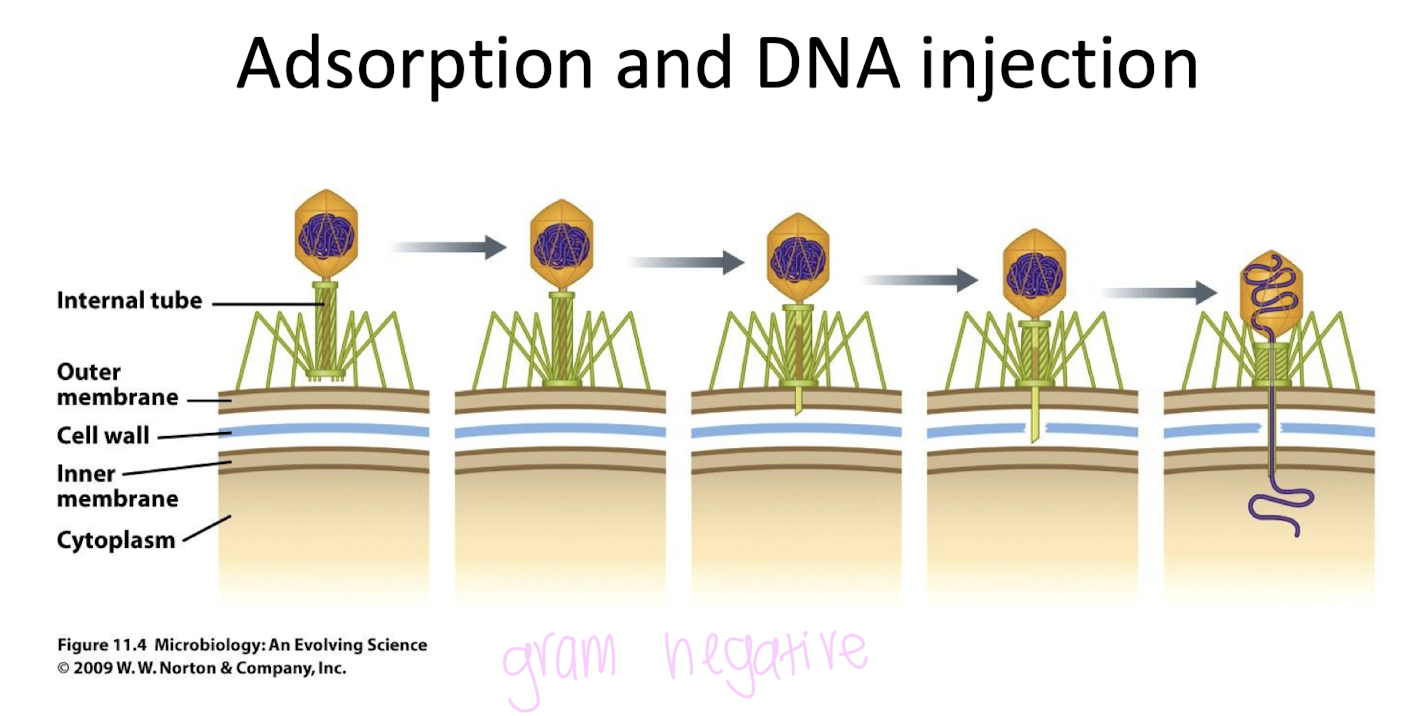
Absorption and DNA injection
DNA is injected through outer membrane, cell wall, inner membrane, and finally into the cytoplasm (in gram negaice)
Phage T4 genome replication
upon entry, a phage genome forms a circle
early genes transcribed
take control of the cell, destroy chromosome
use cell nucleotides to replicate genome
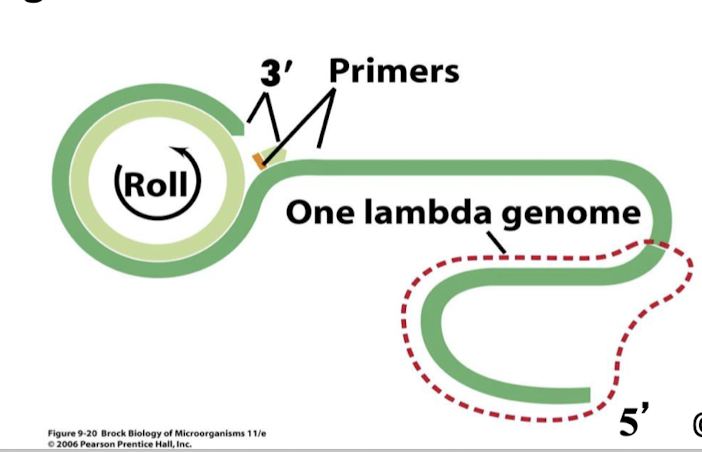
“rolling circle replication”
continuous replication of many copies of the genome. Replicates as it rolls
Phage T4 genome replication
progeny genomes are linked in a concatemer (several genomes linked together)
cut with an offset, so that individual linear genomes have slight overlaps
Packaging of T4 DNA into virus heads
genome is packaged slightly longer than the complete phage chromosome (103%)
Sequence begins and ends at different points in different virions
start and end are not static, order does not matter
Phage Particles Self-Assemble
Late genes transcribed
capsid particles”
head polymerizes around progeny DNA
Tail fibers, long tail made
head, tail, tail. fibers assemble
Lysis protein made
destroys cell wall, releases progeny
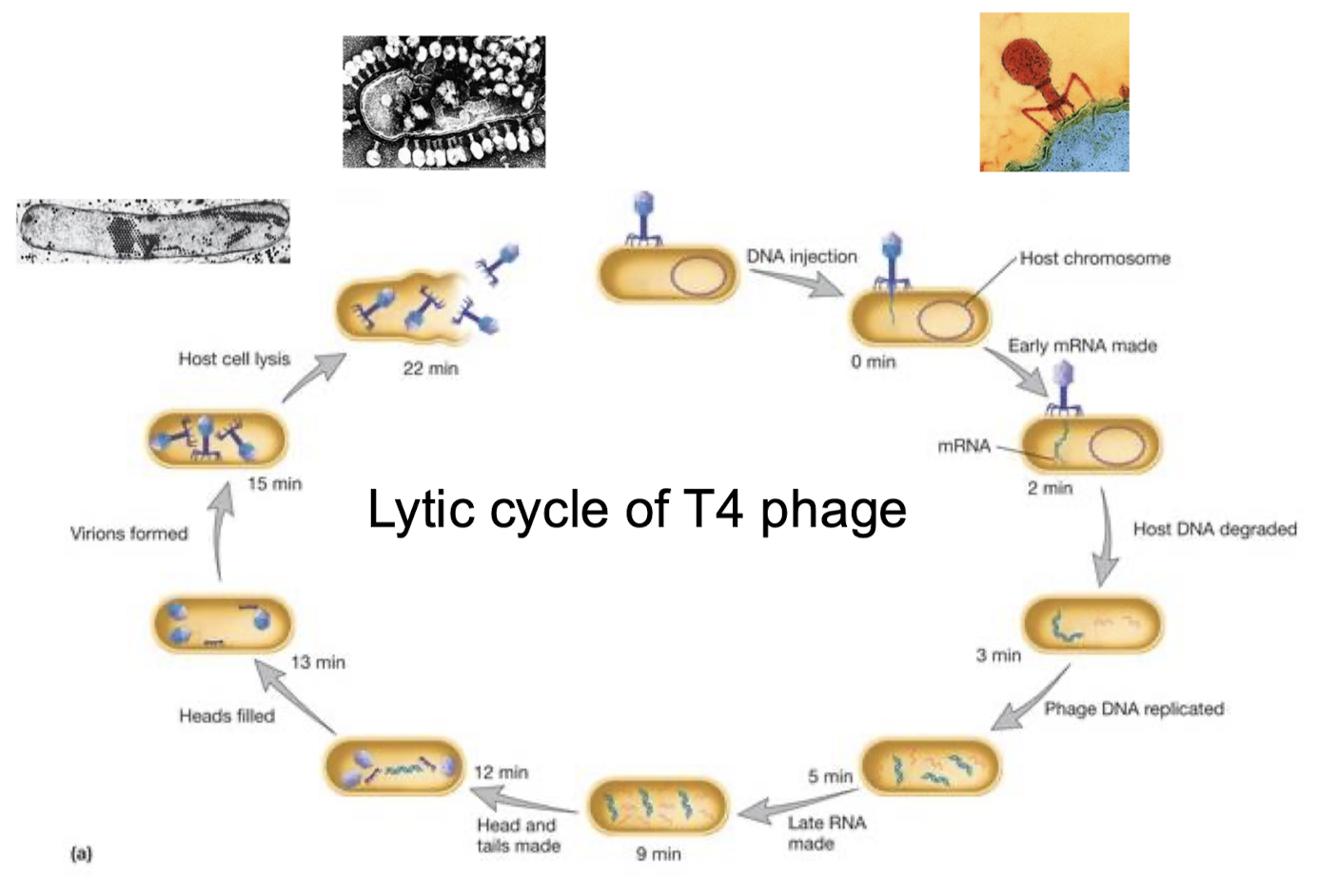
Lytic cycle of T4 phage
DNA injection
degrades host DNA
mRNA of phage made and replicated
heads and tails made
heads filled with DNA
virions form
host cell lysis
Lysogenic Bacteriophage
Some phages maintain a stable relationship with the host cell where they don’t kill and stay with the host: temperate phages
Temperate phages are capable of lysogeny
Integrate viral genome (prophage) into host DNA (a bacterium harboring a prophage is called lysogen)
prophage DNA is mostly dormant
doesn’t enter the lytic cycle until induced (DNA damage/ very bad environment)
only a single lysogenic virus of a particular type can be present in a host cell
temperate phages
integrate into host DNA. replicated bc the virus is part of the chromosome
lysogen
a bacterium harboring a prohage
Temperate coliphage lambda
capsid head, tail
double stranded DNA genome (50 genes)
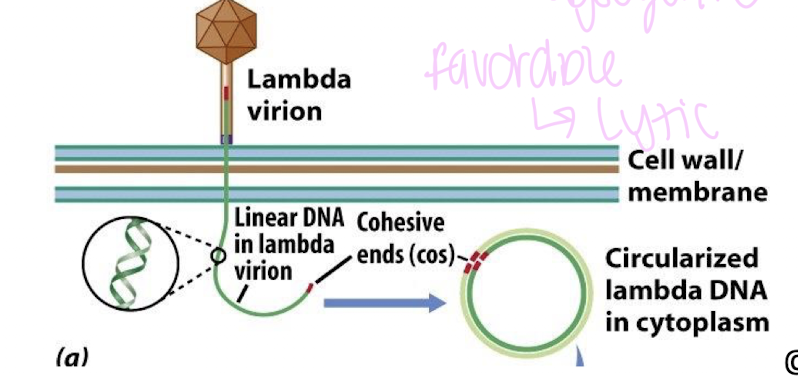
linear DNA with cohesive sends (cos sites)
DNA circularizes inside the host
lambda phase receptor in e.coli is porin

Lambda phage DNA
ds linear in phage head, circular in host
tandem repeating ends combine in host to give a circular configuration at the ligated cos sire
cos recognition site determine where the genome is cut and packaged
Replication of lambda genome
Theta replication (theta; circle-to-circle)
at the beginning
initiates at the ori site
bi-directional replication
Rolling circle replication
continuous replication of many copies of the genome
rolls in 2 directions always
long chains of concatenated genomes
cutting occurs at cos sites to generate linear form for packaging
temperate
lambda
Lambda
cuts a cos sites
lysogenic, lytic when induces
T4
always lytic
cuts according to DNA lengths (103% of genome size)
Transduced cell
contains host DNA and phage DNA
Specialized Transduction
Some viruses can integrate their viral genome into the bacterial chromosome (lysogeny) at att sites
when entering lytic cycle, bacterial genes adjacent to the viral attachment (att) sites are sometimes picked
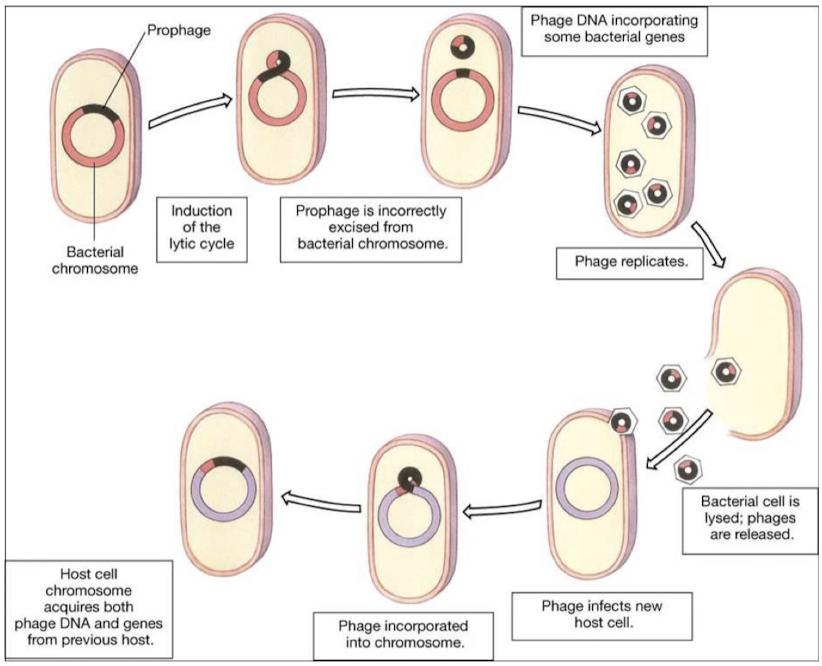
lytic transduction
in the induction of the lytic cycle sometimes prophage is incorrectly excised from bacterial chromosome
phage DNA incorporates some bacterial genes
when the bacterial cell is lysed, phages are released including the host DNA
the new host acquires both phage DNA and genes from the previous host
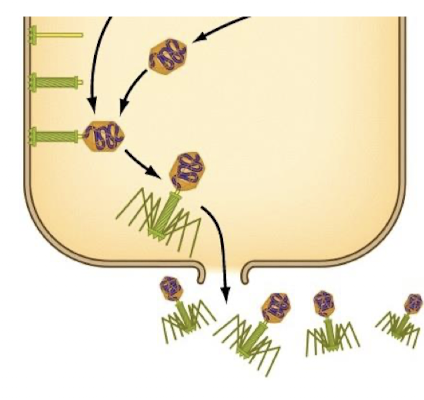
Slow-release replication
some phages can push individual through the cell envelope
host cells grow slowly but don’t die
Culturing Bacteriophage
pour agar + E. coli mixture onto petri dishes containing bottom agar
plates are incubated overnight
E. coli grows
phage infect E. coli cells and multiply
plaques formed (containing virions)
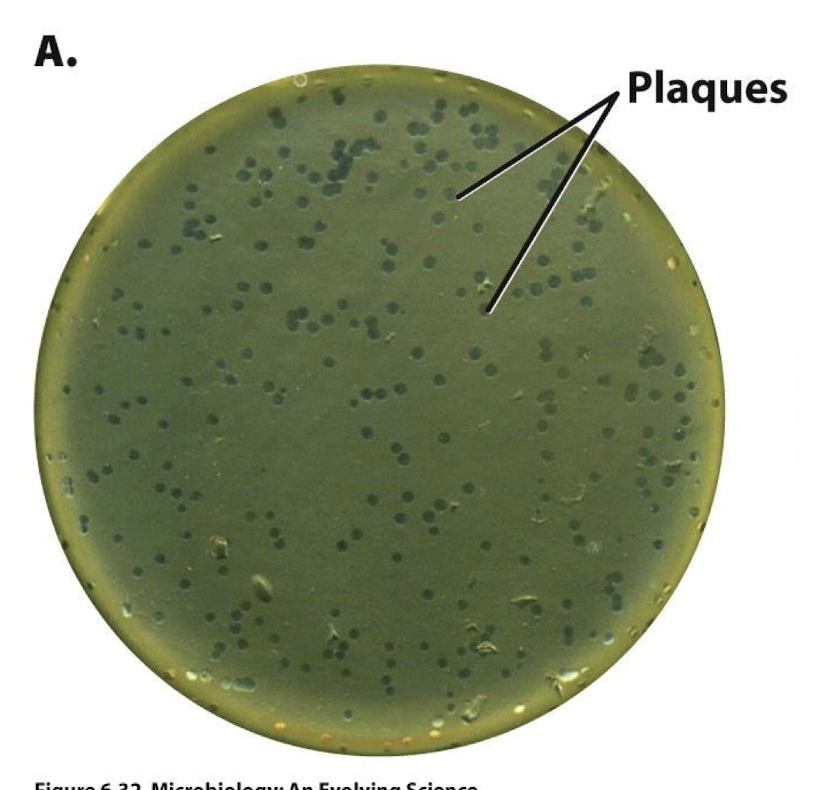
results of culture
Cloudy area: growth of E.coli
Cleared areas: plaques (E. coli killed by phage). spots where a virus has entered and ruptured
virions infect E. coli cells
plaques are formed upon the lysis of E. coli cells
one plaque is formed from infection of one virion: plaque forming units (pfu)