PCOL:3102 Marijuana & Cannabis
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
what are marijuana and hemp?
they are 2 subspecies of the cannabis sativa plant that differ in their utility as well as their THC and CBD content
difference between marijuana and hemp THC and CBD content
hemp contains 20%+ CBD and less than 0.3% THC
marijuana contains 10%+ CBD and more than 20% THC
what are THC and CBD?
they’re plant derived cannabinoids but THC cannabinoid is what is responsible for the euphoric and addictive properties of marijuana as it acts on the DA reward pathway
health benefits of marijuana/cannabis
cannabis/marijuana has been ascribed many health benefits encompassing both mind and body. however, most of the evidence pointing towards these health benefits are anecdotal. the only conditions for which there is reliable evidence that cannabis/marijuana may be of some therapeutic benefit are: chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting, AIDs-related appetite stimulant, epilepsy, and chronic pain
what’s used for chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting?
THC
what is used for AIDs - appetite stimulant?
nabilone
what is used for epilepsy in dravet & lennox gastaut syndromes?
CBD
what is used for chronic pain?
CBD
most valuable part of the marijuana plant
resin which is a gooey substance heavily concentrated on buds where the THC and CBD cannabinoids are
3 main forms of marijuana you can acquire
dried buds (smoke)
hashish (inhaled/smoked)
hash oil (oral)
in all these forms, the THC content is determined by how much resin you are ingesting relative to plant material
dried buds
burned and smoked
inhaling THC thru the vapors
contains <1% THC but since it’s inhaled it reaches peak plasma concentration quickly so as a result, you feel euphoric effects of smoked marijuana quickly
hashish
dried resin that can inhaled or smoked
contains 5-14% THC and since it’s inhaled/smoked, it reaches peak plasma concentration quickly
hash oil
resin is removed and goes thru purification process → oil form
not inhaled and taken orally, so it takes longer to reach peak plasma concentration (0.5 - 2 hr)
contains at least 20% THC
where is THC stored?
THC is highly lipid soluble so it’s readily absorbed into those fat storages throughout the body. as a result it can be stored in your body’s adipose tissue for prolonged periods of time.
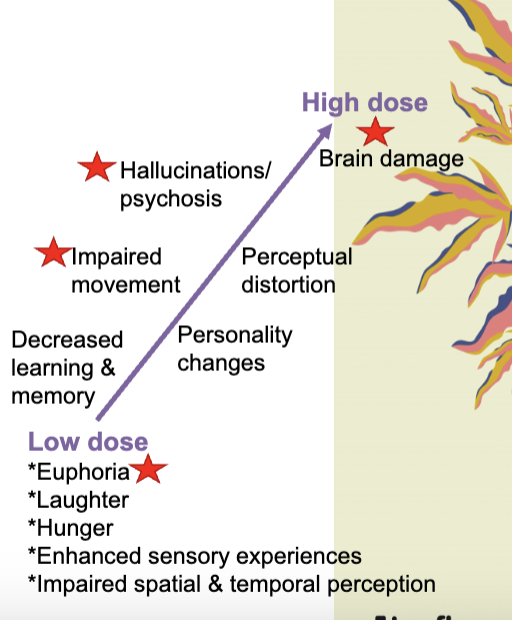
THC’s side effects on CNS
variety of side effects on CNS ranging from euphoria, laughter, hunger, enhanced sensory perception, etc. at low doses
at high doses, you get impaired movement, hallucinations, psychosis, and brain dmg
THC’s side effect on PNS
the cannabinoid receptors are not only expressed in the brain but also in other body tissues
therefore, THC use can also increase HR, decrease BP, suppress the immune system, decrease fertility, and cause lung damage
prolonged marijuana use and THC exposure can cause what?
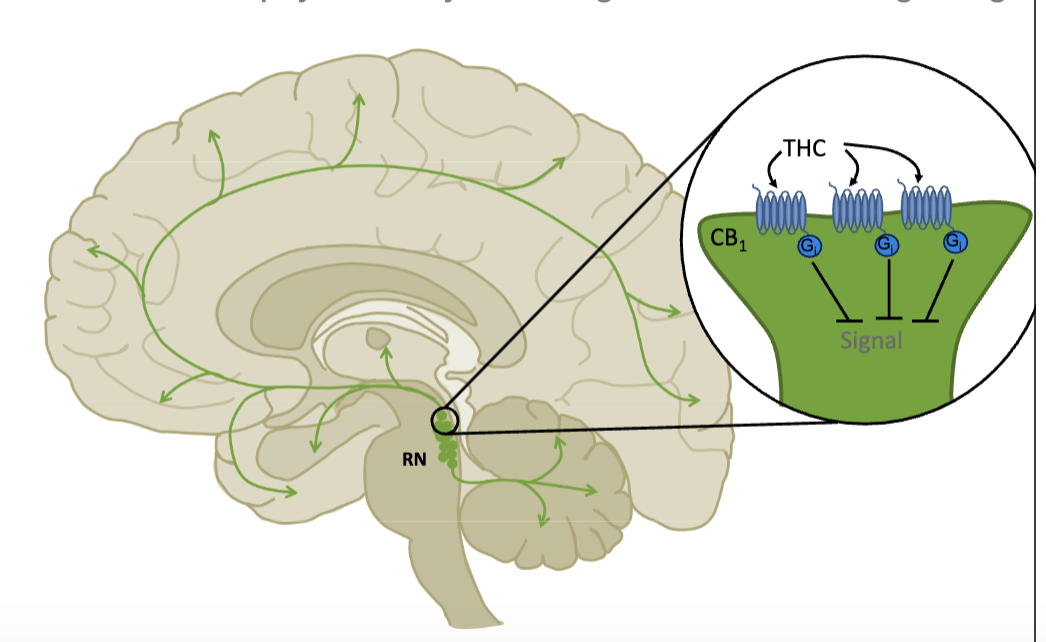
hallucinations and psychosis by removing breaks on SER signaling
initial use isn’t common with hallucinations since THC decreases SER signaling thru the Gi-linked CB1 receptor
but prolonged use causes SER neurons to realize that they’re abnormally quiet cuz THC is always present to silence them thru the CB1 receptors
so to correct for this, CB1R is removed and THC is no longer able to regulate the SER neurons BUT the cannabinoid receptors are there as a natural brake for SER signaling so without them, neurons fire at higher levels → hallucinations!
what kind of tolerance is THC?
pharmacodynamic due to insensitivation of receptors
endocannabinoid system
body system composed of endocannabinoids that bind to cannabinoid receptors expressed in numerous body tissues. system is involved in various functions
two main receptor types in the endocannabinoid system
CB1 and CB2 which are both Gi-linked GPCRs
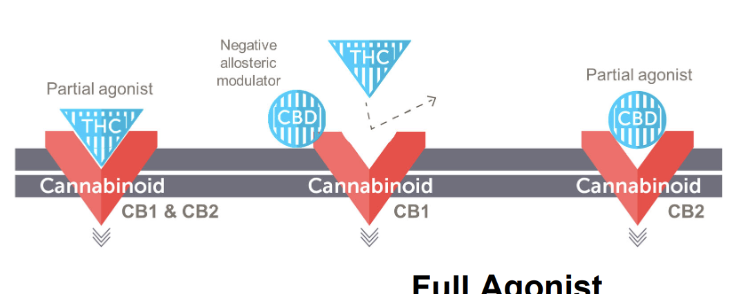
how does THC and CBD interact with the CB1 and CB2 receptors?
these receptors have very different patterns of expression in the body
while CB1 is the primary target of THC and is highly expressed in CNS + GI tract, CB2 the primary target of CBD is not
this difference is why THC has euphoric effects and CBD doesn’t
THC is a partial agonist of CB1 and CB2 receptors but CB1 is negatively allosterically modulated by CBD which prevents THC from binding to CB1.
CBD is a partial agonist of CB2
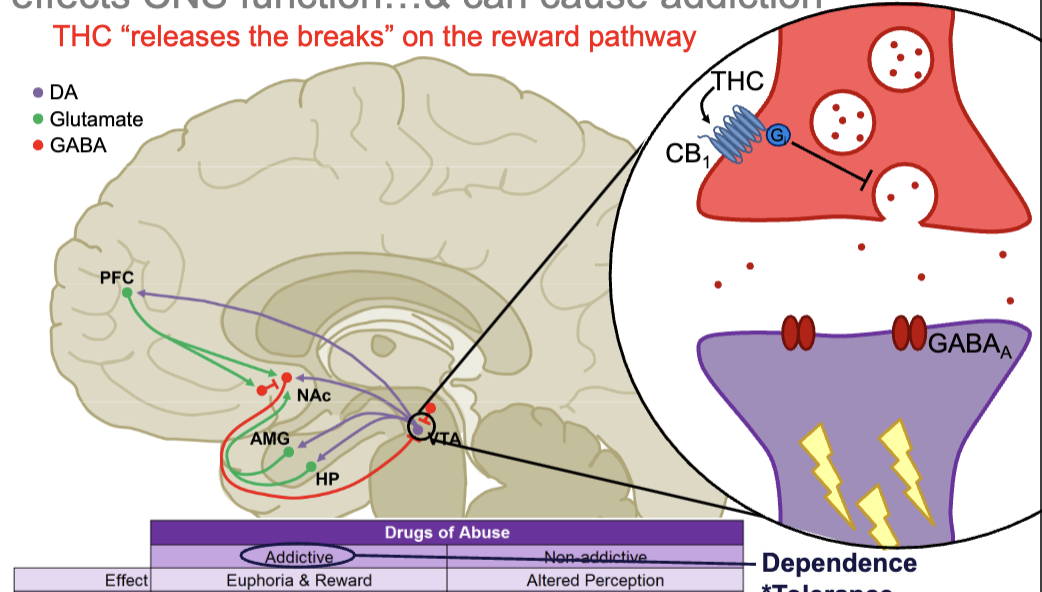
how does THC cause addiction?
THC promotes mesolimbocortical DA signaling by activating the CB1 autoreceptor expressed presynaptically on GABA interneurons present in the VTA
essentially releases the brakes on the reward system by activating CB1 to inhibit GABA release onto presynaptic neuron to the post-synaptic VTA DA neurons
no stop signal for DA to stop
indirect activation of DA pathway
synthetic marijuana
not real marijuana
composed of man-made cannabinoids that have sprayed onto plant material
why is synthetic marijuana bad?
most synthetic marijuana is made in asia under no specific regulations/standards so that means that every batch of synthetic marijuana is going to have a different cannabinoid at a different concentration
most man-made synthetic cannabinoids tend to be more potent than THC and therefore more likely to produce negative side effects