HN220 Midterm 2
1/451
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
452 Terms
What are the anatomical divisions of the nervous system?
1) Central nervous system (CNS)
2) Peripheral nervous system (PNS)
What does the CNS consist of?
brain and spinal cord
- its the integrating centre
What does PNS consist of?
All neural tissue outside the CNS
What are the 2 different neurons the PNS consists of?
1) afferent neurons
2) efferent neurons
What are afferent neurons?
Sensory neurons
-Carry information towards the CNS
What are efferent neurons?
Motor neurons
-Carry information away from the CNS
What are neurons
cells that send and receive electrical signals rapidly and over long distance if needed
The CNS is ncessary for the maintenance of _________________
homeostasis
What is cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)?
clear watery fluid bathing the CNS
Where is cerebrospinal fluid produced?
choroid plexus
- produces 400-500 mL/day
How many times is cerebrospinal fluid recycled every day
3 times
What is the function of CSF?
- cushions the brain
- maintains a stable interstitial fluid environment
How much oxygen does the brain use at rest?
20% of oxygen consumed by body
How much oxygen does the brain use at rest?
50% of oxygen consumed by body
What method do neurons depend on for oxygen?
aerobic glycolysis
True or false: there are no glycogen stores in the brain at all
False: there are some in glial cells
True or false: fatty acids are used for energy
False: they are not used for energy
True or false: ketones are used for energy during extreme conditions
true
What structure maintains the blood brain barrier
Capillaries
What are capillaries?
sites of exchange between the blood and the interstitial fluid
What are capillaries made of?
a single layer of endothelial cells
What type of transport occurs in capillaries?
diffusion
How are the capillaries in the CNS different from the capillaries in the rest of the body?
- capillaries in the CNS do not have pores
- they have tight junctions
What kind of cell junctions do the capillaries in the brain have?
TIGHT JUNCTIONS
How do hydrophilic solutes move in and out of the brain capillaries?
Carrier mediated transport
True or false: the spinal cord is continuous with the brain
true
The spinal cord is surrounded by the _______________
vertebral column
A nerve is a bundle of ____________
axons
What is a mixed nerve?
One that has both efferent and afferent neurons
- carries both sensory and motor information
What is a dermatome?
specific segment of skin supplied by a single spinal nerve
What are two functional parts of gray matter?
dorsal and ventral
What are dorsal roots?
sensory input to spinal cord
- afferent
What are ventral roots?
motor output from spinal cord
- efferent
True or false: spinal nerves are not mixed
false: they are mixed
White matter forms ______________
tracts (ascending and descending)
What are ascending tracts?
tracts that conduct impulses to the brain
- sensory, dorsal tracts
What are descending tracts?
tracts conduct impulses down the cord away from the brain
- motor, ventral
What are reflexes?
Automatic patterned responses to certain stimuli
What is the reflex arc?
1) sensory receptor
2) afferent neuron
3) integration center
4) efferent neuron
5) effector organ
What are the 3 different reflexes?
1) stretch reflex
2) withdrawal reflex
3) crossed extensor reflex
What is the muscle spindle stretch reflex?
a tap on the knee's tendon causes a change in the muscle fibre length in your quads
Explain the communication between the afferent and efferent neurons during the muscle spindle stretch reflex
- spindles detect the change in muscle fibre length and send afferent information to the spinal cord
- theres a direct excitatory connection with efferent neurons and then this response innervates the quads to extend your knee and (the kick)
true or false: the muscle spindle stretch reflex is a monosynaptic reflex
true
What does the muscle spindle stretch reflex do to the hamstrings?
inhibits it using inhibitory neurons
- decreases its activity
- allows for knee to contract
Explain the withdrawal reflex
1) Leg in pain: Stimulation of the afferent fibers causes excitatory stimulus in the hamstrings and inhibitory stimulus in the quads (reciprocal innervation)
Other leg: Excitatory neurons on quads, and inhibitory neurons on hamstrings (allows you to balanc)
2) efferent neurons cause knee flexion
What is perception
- Conscious interpretation of the world based on sensory systems, memory, and other neural processes
True or False
We perceive info solely based on the effector responses that occur due to afferent/sensory responses
False
We perceive info is a combo of previous experiences (memories) and effector responses that occur
What are some senses that are associated with the skin
Touch, pressure, temperature
What is proprioception
Perception of limb and body positions
What are examples of special senses
-Balance + equilibrium
-Vision
-Hearing
-Taste
-Smell
Sensory neurons have sensory ______
Sensory receptors
What do sensory receptors detect
Detect specific form of E in the external environment
What are some examples of modality
-Light
-Sound
-Pressure
-Temperature
-Chemicals
What is the Law of Specific Nerve Energies
A given sensory receptor is specific for each modality
Ex. Thermoreceptors are sensitive to their specific modality (temp)
Sensory receptors require an adequate ________, which leads to depolarization of that particular type of neuron
Adequate stimulus
What is sensory transduction
Conversion of stimulus E into electrical E
What are receptor/generator potentials
-Similar to a graded potential
-Opening or closing of ion channels
-Triggered by sensory stimuli
If a receptor potential exceeds threshold, it can generate an ___ _______
action potential
How do specialized nerve endings work
Swelling at dendritic end which forms at the sensory receptor end
Pressure at the end opens mechanically gated channel
What is receptor adaptation
-Decrease in amplitude of receptor potential over time in the presence of a constant stimulus
-Corresponding decrease in frequency of action potentials
-Decreases perception of stimulus
What's the difference between slowly adapting receptors and rapidly adapting receptors
-Rapidly adapting receptors respond only at the moment when the stimulus is applied
-Slowly adapting receptors continue to respond as long as the stimulus is applied
What are labelled lines
-Specific neural pathways transmitting information of a specific modality
What is a sensory unit
-Single afferent neuron, plus all receptors associated with it
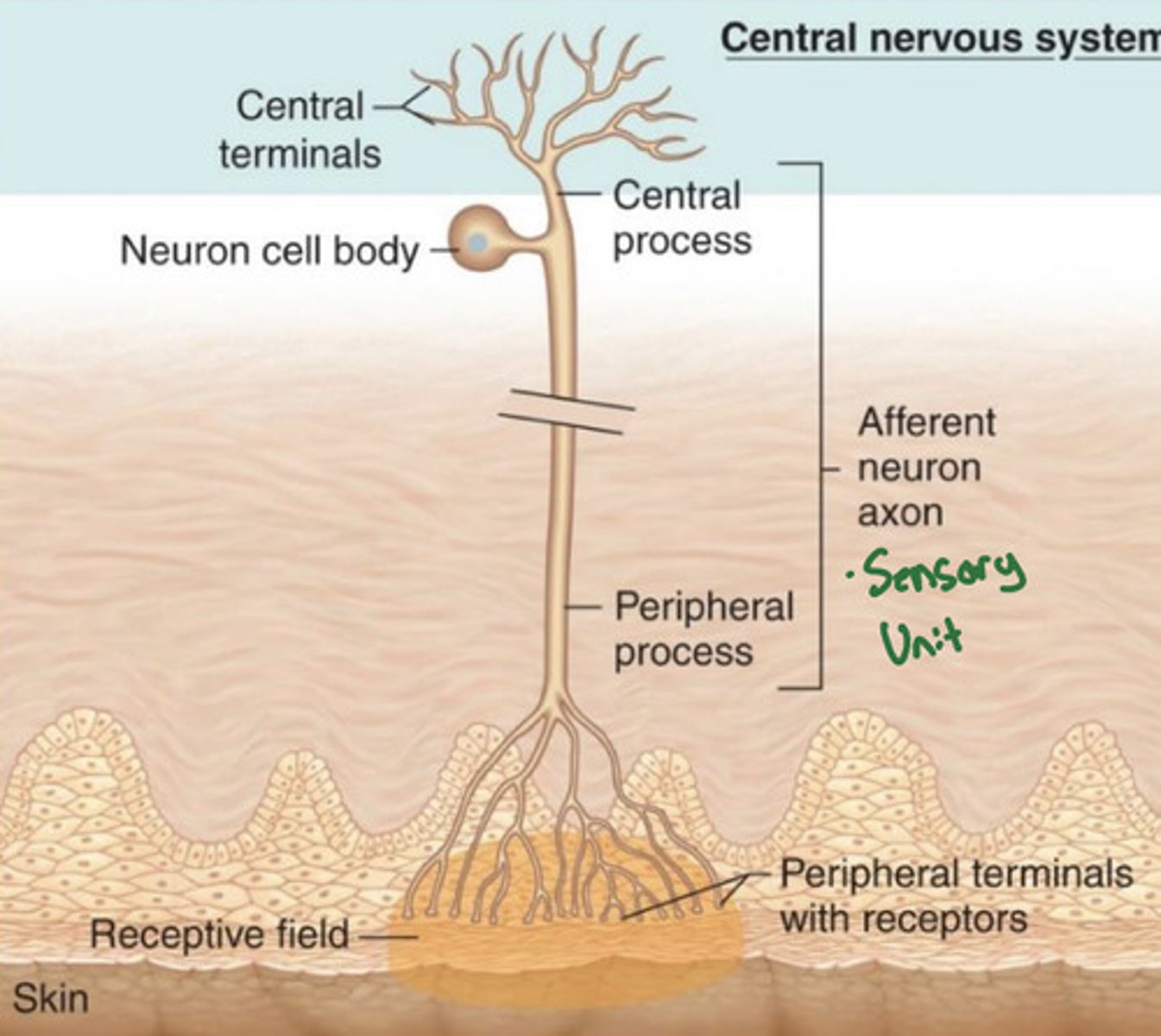
What is a receptive field
Area in which a sensory unit is activated
Touching anywhere within a receptive field activates the __________ _________
sensory neuron
Explain the generalized pathway for sensory systems
-Stimulus picked up receptors and travels to spinal cord or brain stem via afferent neuron (1st order)
-Travels to thalamus via 2nd order neuron
Travels to cortex via 3rd order neuron
What are the 3 factors of sensory coding
-Stimulus type
-Stimulus intensity
-Stimulus location
Describe stimulus type as a factor of sensory coding
Combination of receptor type and pathway activated
True or False
If you increase the stimulus,
AP frequency increases
# of receptors activated increases
True
What is acuity
Precision with which a stimulus is perceived
What is 2 point discrimination
Two-point discrimination is the ability to discern that two nearby objects touching the skin are truly two distinct points, not one
In large receptive fields, 2 stimuli within close distances of each other are often perceived as _______
One point
Smaller 2-point discrimination distances indicate greater ________ ________
Greater tactile acuity
What body region has the greatest tactile acuity
Lips
What body region has the lowest tactile acuity
Calf
What is pain perception
Sensation produced by potentially tissue damaging stimulus
What is involved in the pain response
-Activation of nociceptors
-Autonomic responses (sweating)
-Emotional responses (fear)
-Reflexive withdrawal
True or False
Pain perception depends on past experiences
True
Ex. Big pain at dentist when little, little pain at dentist when big= big pain
What is visceral pain
- Pain originating in internal organs (not limited to body surface)
What is referred pain
Sensation referred to body surface
Ex. Heart attack victim complains of pain in left side of chest, not heart
Why does referred pain occur
Nociceptors are following along a similar neural tract to cerebral cortex as other parts of our body
True or False
Signals can be modulated as they transmit along sensory pathways
True
What's a specific example of how pain can be modulated as it transmits along a sensory pathway
Gate control theory
What is the gate control theory?
Non-painful sensations can override and reduce painful sensations
If you rub your toe after you stub it, it'll hurt less
How does gate control theory work
Many nociceptors share synapses with interneurons and communication can occur
These interneurons are inhibitory interneurons, so activating them will communicate with 2nd order neurons, which will dull the pain perception
What are 2 parts of the Peripheral Nervous System
1. somatic nervous system
2. autonomic nervous system
What is the somatic nervous system?
Controls voluntary movement
- controls skeletal muscle
What is the autonomic nervous system?
Controls involuntary movement
- controls smooth muscle, cardiac muscle glands, and adipose tissue
What other systems does the autonomic nervous system work with to maintain homeostasis?
1) endocrine system
2) behavioural state system
What are the two parts of the Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)?
1) sympathetic
2) parasympathetic
What is the sympathetic nervous system?
fight or flight
What is the parasympathetic nervous system?
rest and digest
True or false: if one part of ANS is working the other is not
false: the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems work together, so one may be more active than the other, but they are both always working
True or false: the parasympathetic nervous system innervates more effector organs than the sympathetic nervous system
false: both divisions of the autonomic nervous system innervate most effector organs
- known as dual innervation
What is the primary function of the dual innervation by the ANS
regulate organs to maintain homeostasis
Parasympathetic and sympathetic activities tend to be _________________
antagonistic
What parts of the brain initiate autonomic, endocrine, and behavioural responses?
1) hypothalamus
2) pons
3) medualla
How does the ANS work with the endocrine system to maintain homeostasis?
- sensory information goes to the homeostatic control centres (hypothalamus, pons, medulla)
- the centres monitor and regulate bodily functions
(blood pressure, temperature control, and water balance)
What is the "centre for homeostasis"?
hypothalamus
What are the different kinds of motor outputs from the integrating centres
1) autonomic
2) endocrine
3) behavioural