AP chem unit 6 study
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Endothermic
Requires energy to be added to the system
Exothermic
Releases energy to the surroundings
Energy
Heat is
Temperature
The measure of the average kinetic energy
Hot to cold
Heat transfers from
Kinetic energy
Heat transfers from the collisions of the particles until both substances have the same -
Heat capacity
The amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of all of the substance by 1 degree C
Specific heat (capacity)
The amount of energy needed to increase the temperature of 1 gram of the substance by 1° C
Calorimetry
The measure of the amount of heat transferred between a system + the surroundings
Calorimeter
Measures the change in temperature in calorimetry
4.18
Heat capacity of water (J/g ° C )
75.2 J / mol °C
Molar specific heat for water
Forces of attraction
Heat is required to break -
Released
When forces of attraction are formed, heat is
Freezing + condensation
Forces of attraction are formed during
High
Gaseous systems are at a relatively —- potential energy
Low
Solids systems are a relatively ___ potential energy
Molar enthalpy of fusion
The energy required to melt a substance
Molar enthalpy of vaporization
The energy required to vaporize a substance
6.01 kj / mol
Water-molar heat of fusion
40.65 kj / mol
Water- heat of vaporization
36.6 J / mol °C
Specific heat for water (gas)
75.4 j /mol °C
Specific heat for water (liquid)
37.7 J / mol °C
Specific heat of water (solid)
Endothermic
Broken bonds -
Exothermic
New bonds -
A
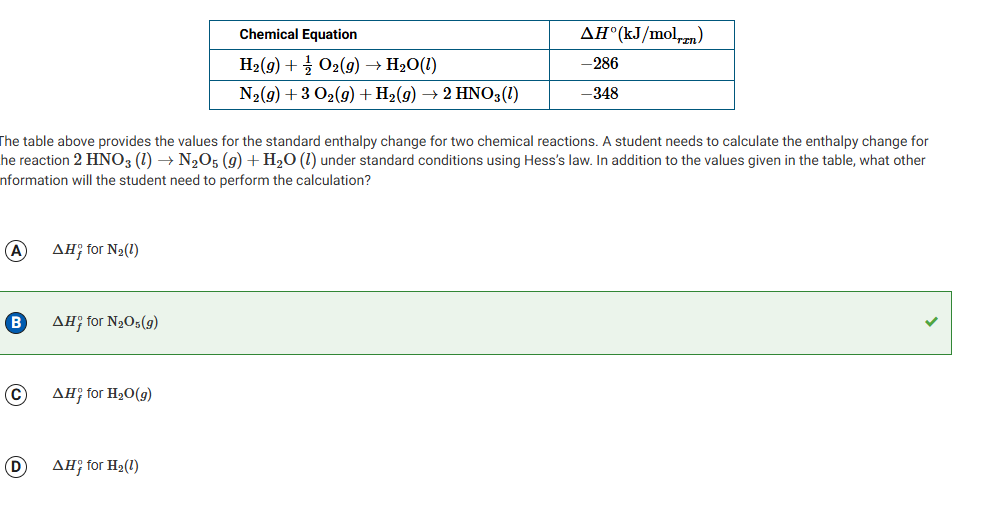
The heating curve for a sample of pure ethanol is provided above. The temperature was recorded as a 50.0 g sample of solid ethanol was heated at a constant rate. Which of the following explains why the slope of segment T is greater than the slope of segment R?
Responses
A
The specific heat capacity of the gaseous ethanol is less than the specific heat capacity of liquid ethanol.
B
The specific heat capacity of the gaseous ethanol is greater than the specific heat capacity of liquid ethanol.
C
The heat of vaporization of ethanol is less than the heat of fusion of ethanol.
D
The heat of vaporization of ethanol is greater than the heat of fusion of ethanol.
C
Which of the following best helps to explain why the value of ΔH° for the dissolving of CaF2 in water is positive?
Responses
A
CaF2(s) is insoluble in water.
B
CaF2(s) dissolves in water to form CaF2(aq) particles.
C
Ca2+ ions have very strong ion-ion interactions with F- ions in the crystal lattice.
D
Ca2+ ions have very strong ion-dipole interactions with water molecules in the solution.
electron emission is
endothermic
adding an electron is
exothermic
A
The enthalpy of vaporization of water is 40.7 kJ/mol. Which of the following best explains why the enthalpy of vaporization of methane is less than that of water?
Responses
A
Methane does not exhibit hydrogen bonding, but water does.
B
Methane has weaker dispersion forces.
C
Methane has a smaller molar mass.
D
Methane has a much lower density.
A
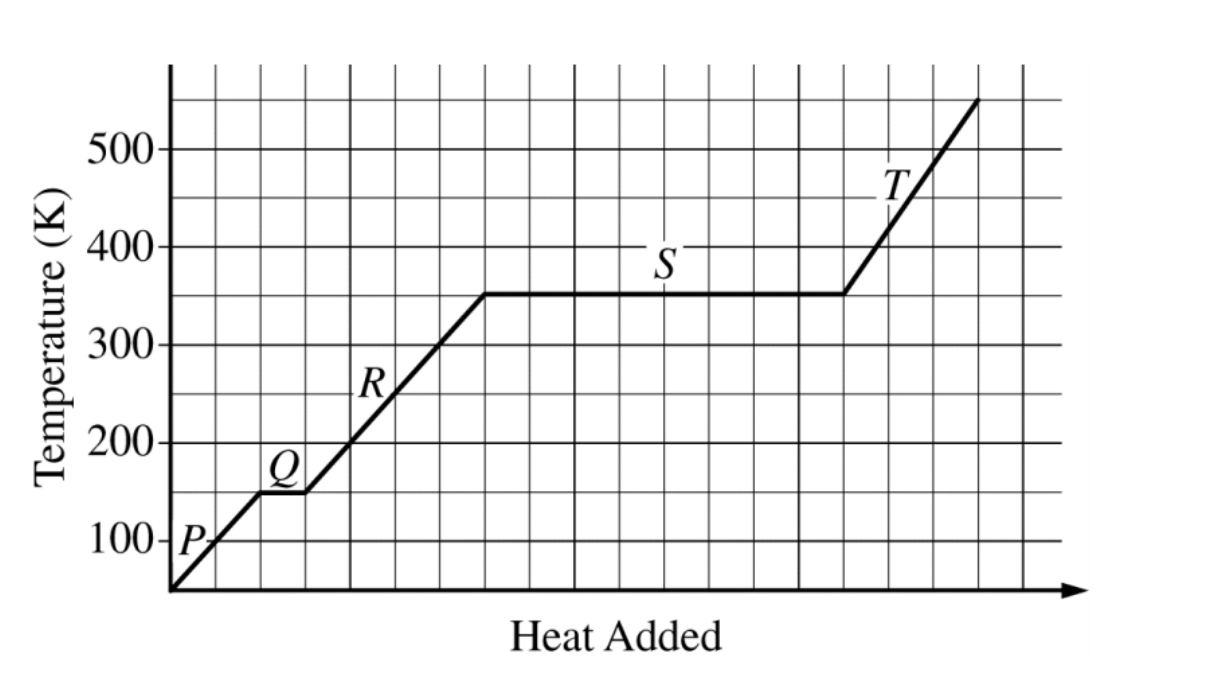
A → X
The enthalpy change for the reaction represented above is ΔHT. This reaction can be broken down into a series of steps as shown in the diagram:
A relationship that must exist among the various enthalpy changes is
Responses
A
ΔHT – ΔH1 – ΔH2 – ΔH3 = 0
B
ΔHT + ΔH1 + ΔH2 + ΔH3 = 0
C
ΔH3 – (ΔH1 + ΔH2) = ΔHT
D
ΔH2 – (ΔH3 + ΔH1) = ΔHT
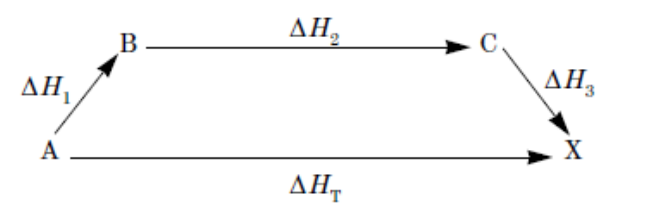
B
The first ionization energy of an element is the energy required to remove an electron from a gaseous atom of the element (i.e., X(g) → X+(g) + e−). The values of the first ionization energies for the third-row elements are shown in the graph above. On the basis of the information given, which of the following reactions is exothermic?
Responses
A
Cl(g) + Mg+(g) → Cl+(g) + Mg(g)
B
Al(g) + Mg+(g) → Al+(g) + Mg(g)
C
P(g) + Mg+(g) → P+(g) + Mg(g)
D
S(g) + Mg+(g) → S+(g) + Mg(g)
B
A student carefully drops a 9.0g solid Zn pellet initially at 50.0°C into an insulated cup containing 30.0g of water at 27.8°C. The student predicts that the temperature of the water will increase after the pellet is added. Which of the following statements is the best justification for the student’s prediction?
Responses
A
The metallic bonds between Zn atoms will break when the Zn is exposed to the water molecules, releasing energy that will be absorbed by the water molecules.
B
Collisions between the water molecules and the surface of the Zn pellet will result in the transfer of energy, increasing the average kinetic energy of the water molecules.
C
The strength of the hydrogen bonds between the water molecules will increase when the Zn pellet is added, decreasing the average kinetic energy of the water molecules.
D
Collisions between Zn atoms in the solid will increase in frequency when the Zn is exposed to the water molecules, resulting in the transfer of energy to the surroundings.
B