Module 1: Organic Chemistry - Part 7 - Isomers
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Compounds with the same molecular formula but different structure.
a. Isomers
b. Isotones
c. Isobars
a. Isomers
Isomer that differ in their attachment.
a. Constitutional isomer
b. Stereoisomer
a. Constitutional isomer
Constitutional isomerism is difference in
a. Branching
b. Locant
c. Functional group
d. a and b
e. b and c
f. all
f. All
Constitutional isomer that differ in branching.
a. Skeletal isomer
b. Positional isomer
c. Functional isomer
d. a and b
e. b and c
f. all
a. Skeletal isomer
Constitutional isomer that differ in locant.
a. Skeletal isomer
b. Positional isomer
c. Functional isomer
d. a and b
e. b and c
f. all
b. Positional isomer
Constitutional isomer that differ in functional group.
a. Skeletal isomer
b. Positional isomer
c. Functional isomer
d. a and b
e. b and c
f. all
c. Functional isomer
Isomer that have same attachment but can have temporary reversible or permanent irreversible arrangement; conformational or configurational.
a. Constitutional isomer
b. Stereoisomer
b. Stereoisomer
Temporary reversible difference in arrangement.
a. Conformational
b. Configurational
a. Conformational
Permanent and irreversible difference in arrangement.
a. Conformational
b. Configurational
b. Configurational
Cis and trans isomers are what type of isomers?
a. Conformational
b. Configurational
b. Configurational - specifically geometric isomers
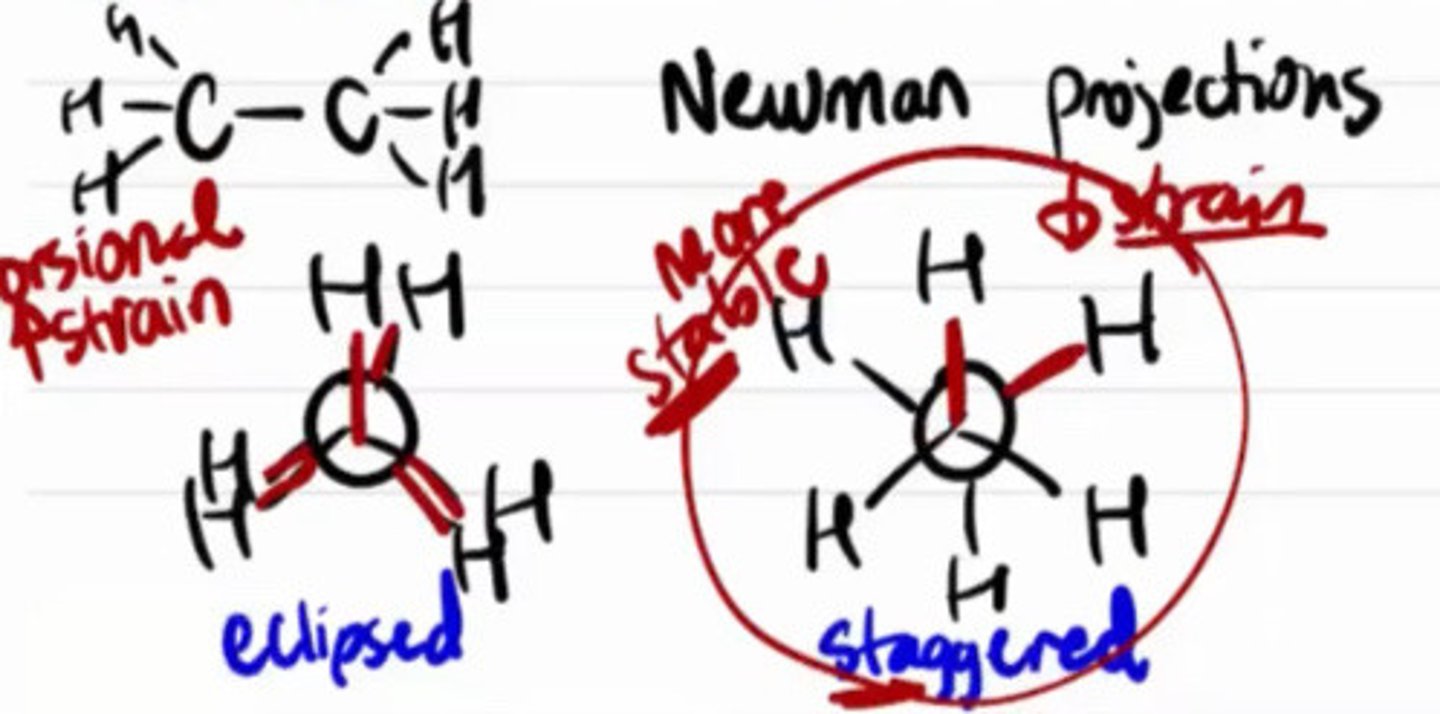
Visualizes the conformation of a chemical bond from front to back, with a line representing the front atom and a circle representing the back carbon.
a. Newman projection
b. Dalton projection
c. Huckle projection
d. Steric projection
a. Newman projection
More stable conformational isomer of ethane
a. Eclipsed
b. Staggered
c. Similar stability
d. Cannot be compared
b. Staggered
Relative more stable conformational isomer of cyclobutane.
a. Planar
b. Butterfly
c. Enveloped
d. Boat
e. Chair
b. Butterfly
Butterfly conformation:
• Not eclipsed, less torsional strain
• Still with angle strain
Relative more stable conformational isomer of cyclopentane.
a. Planar
b. Butterfly
c. Enveloped
d. Boat
e. Chair
c. Enveloped - also known as puckered
Most stable conformational isomer of cyclohexane.
a. Planar
b. Boat
c. Chair
c. Chair

Configurational isomer can be due to:
a. Bond rigidity
b. Chirality
c. Both
d. None of these
c. Both
Configurational isomerism due to bond rigidity or restriction in motions; 2D isomerism.
a. Geometric isomerism
b. Optical isomerism
a. Geometric isomerism
Configurational isomerism due to optical activity; 3D isomerism.
a. Geometric isomerism
b. Optical isomerism
b. Optical isomerism
Geometric isomerism can be due to
a. Formation of rings
b. Double bonds
c. Branching
d. a and b
e. b and c
f. All
d. a and b
Formation of rings
Double bonds
Example of geometric isomers except:
a. Cis isomer
b. Trans isomer
c. E isomer
d. Z isomer
e. None
e. None
Geometric isomer descriptors used when the alkene is disubstituted.
a. Cis isomer
b. Trans isomer
c. E isomer
d. Z isomer
e. a and b
f. c and d
e. a and b
Geometric isomer descriptors used when the alkene is tri or tetra substituted.
a. Cis isomer
b. Trans isomer
c. E isomer
d. Z isomer
e. a and b
f. c and d
f. c and d
Carbon holding a double bond is technically called:
a. Vinylic carbon
b. Alpha carbon
c. Chiral carbon
d. Terminal carbon
a. Vinylic carbon
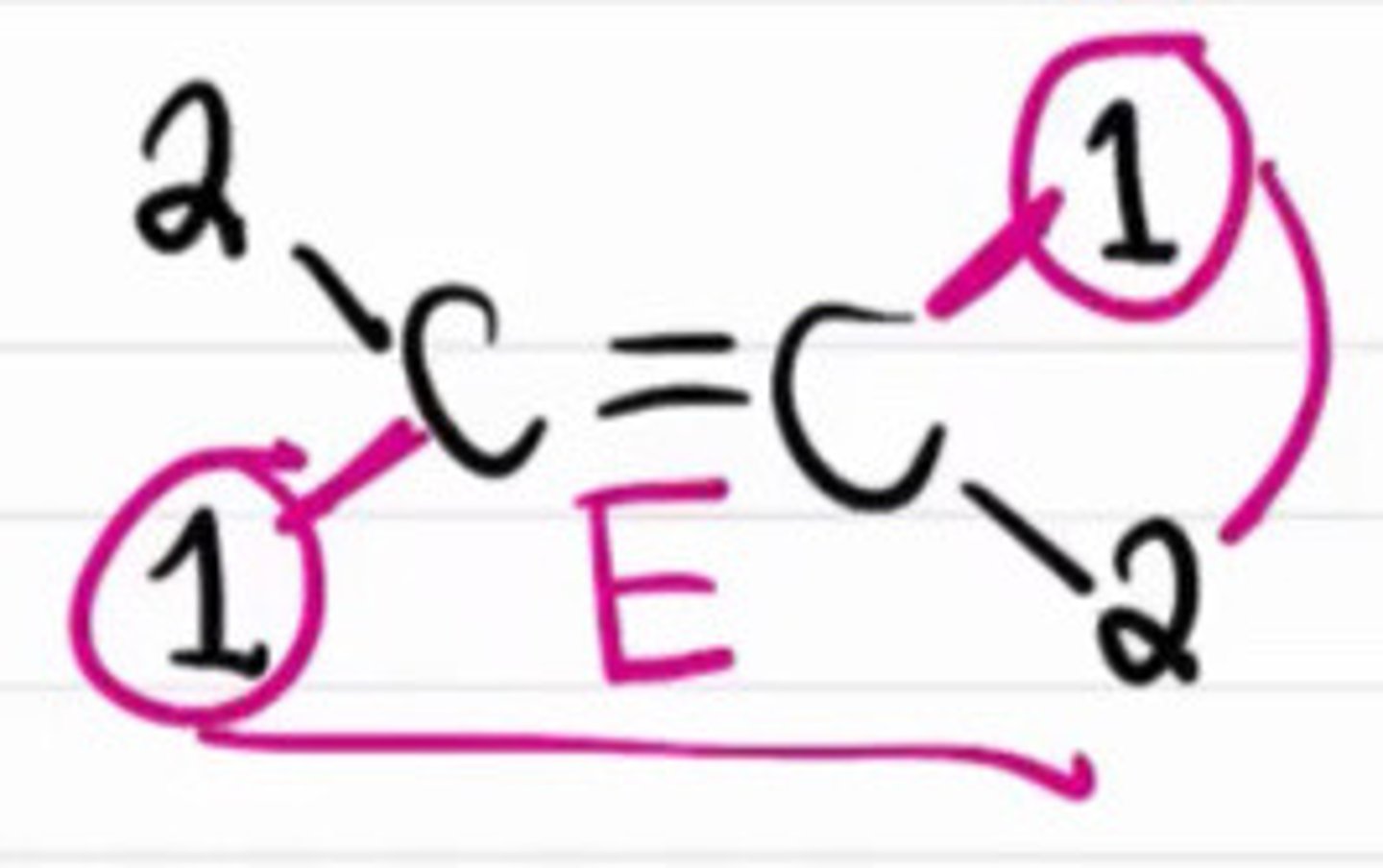
True about determining E/Z geometric descriptors except:
a. First find the vinylic carbon
b. Assign high or low priorities
c. Use E if high priorities are on the opposite sides
d. Use Z if high priorities are on the same sides
e. None
e. None
Help to determine how to rank the substituents of a stereocenter using priority rankings.
a. Cahn Ingold Prelog
b. Henderson Hasselbalch Prelog
c. Newman Prelog
d. Noyes Prelog
a. Cahn Ingold Prelog
The higher the atomic number, the more prioritized in Cahn Ingold Prelog.
a. True
b. False
a. True
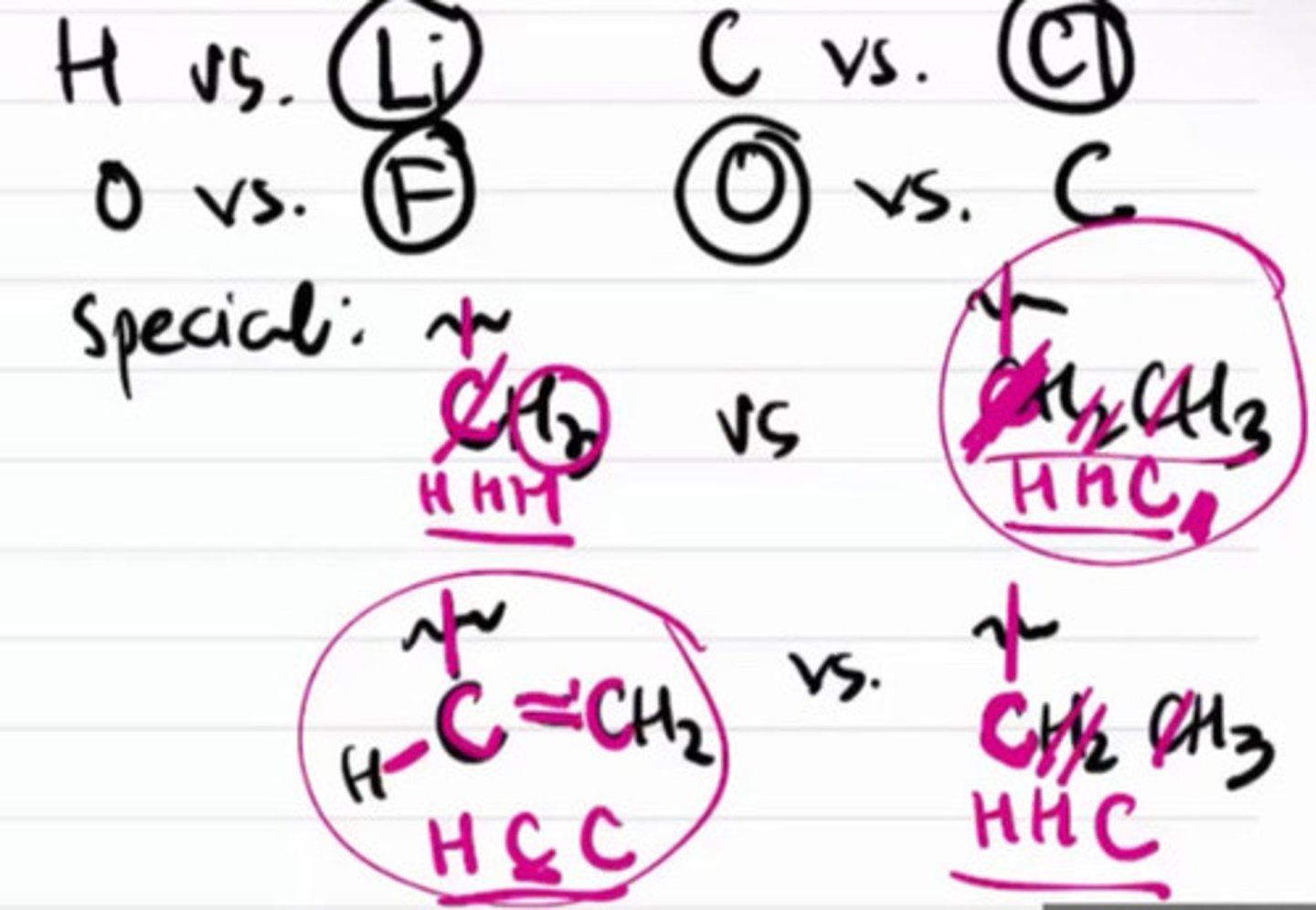
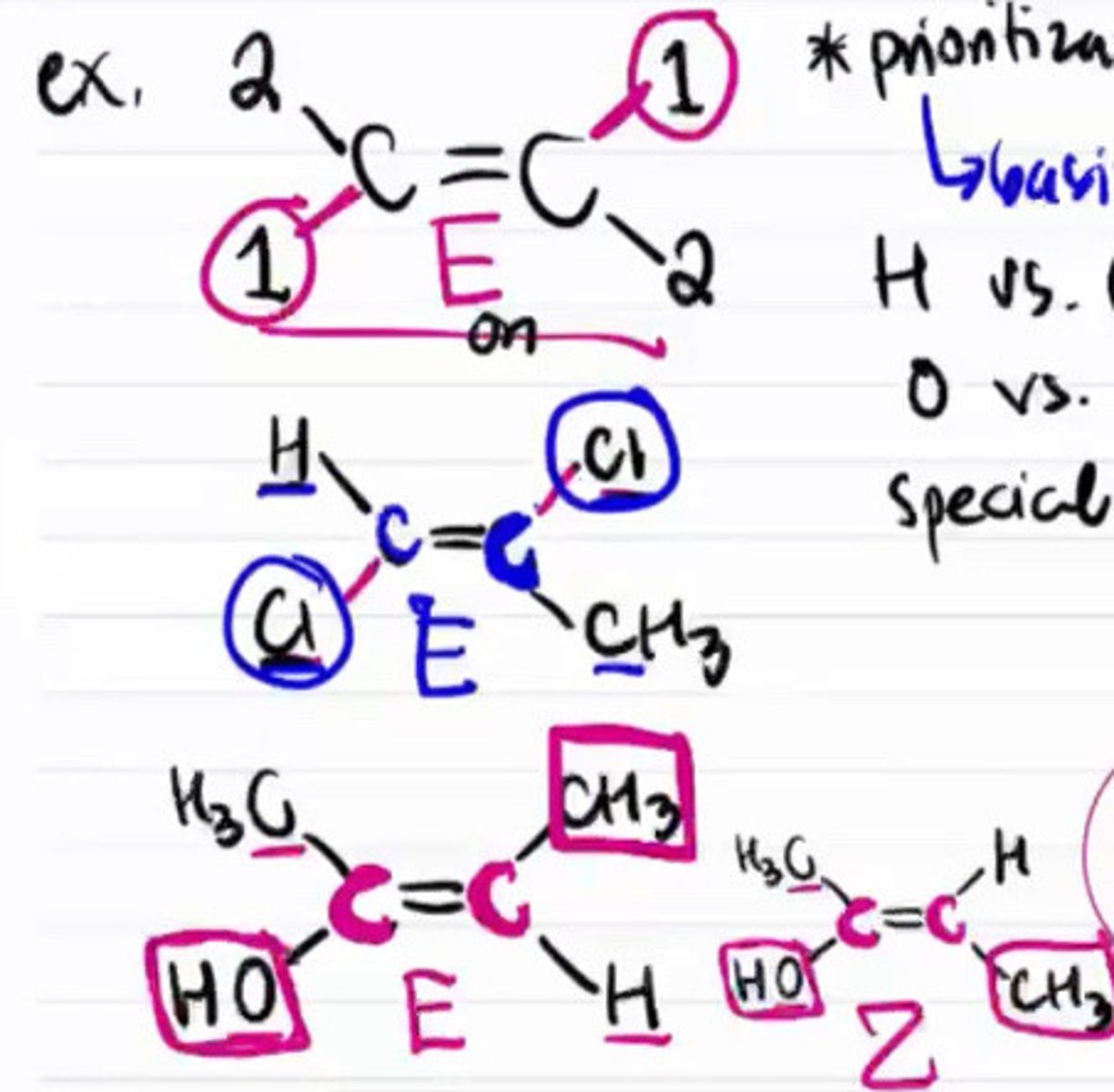
E/Z isomer example
E/Z isomer example
True about optically active compounds.
a. Has chiral carbon
b. Nonsuperimposable
c. Has important isomers
d. a and b
e. All
e. All
Descriptor for optical isomers.
a. cis-trans
b. E-Z
c. R-S
d. a and b
e. All
c. R-S
R - for clockwise
S - for counterclockwise
R and S configuration does not equate to dextro and levo spin.
a. True
b. False
a. True
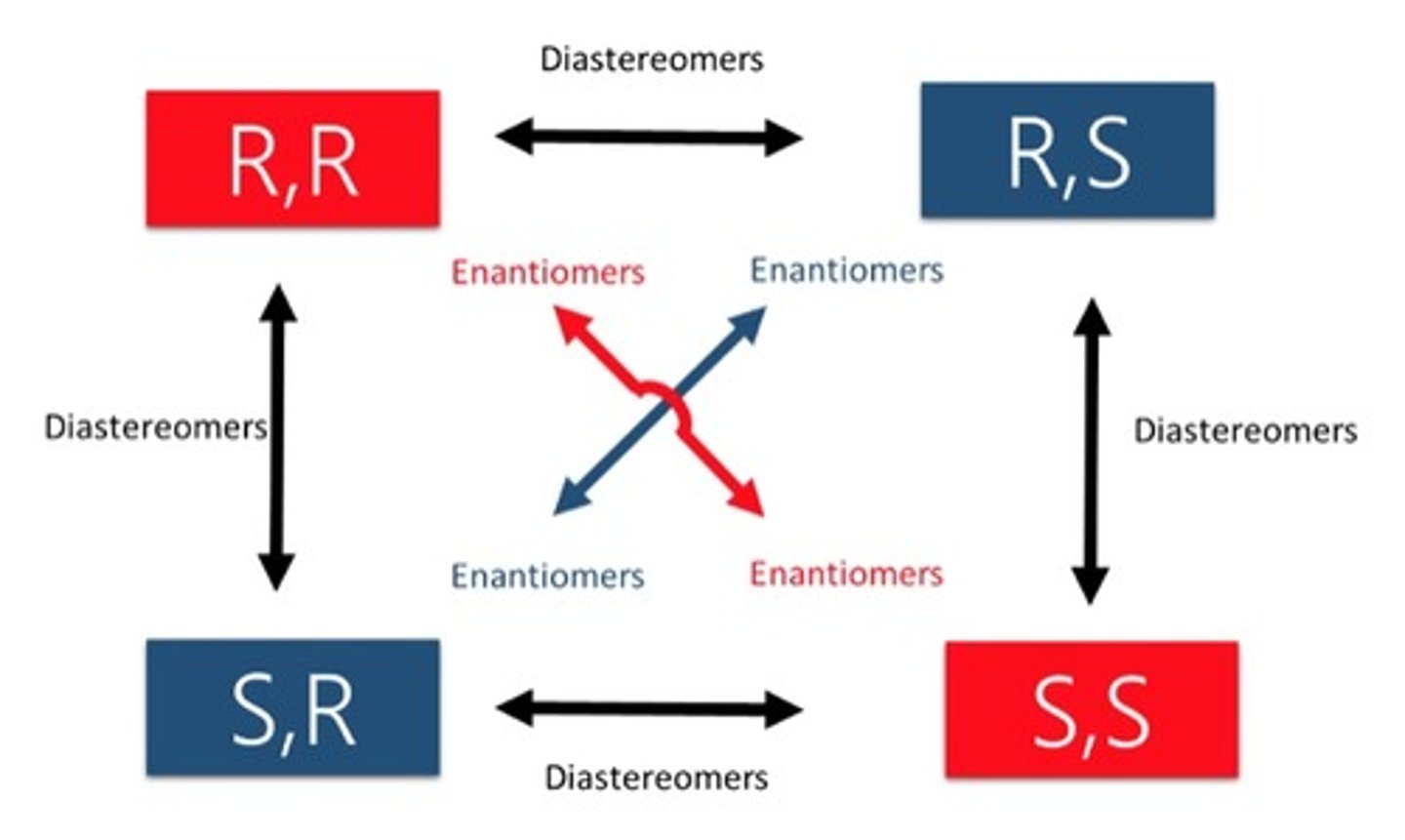
Enantiomers and diastereomers are what type of configurational isomer?
a. Geometric isomer
b. Optical isomer
b. Optical isomer
All chiral carbons are inverted thus are real mirror images.
a. Enantiomer
b. Diastereomer
a. Enantiomer
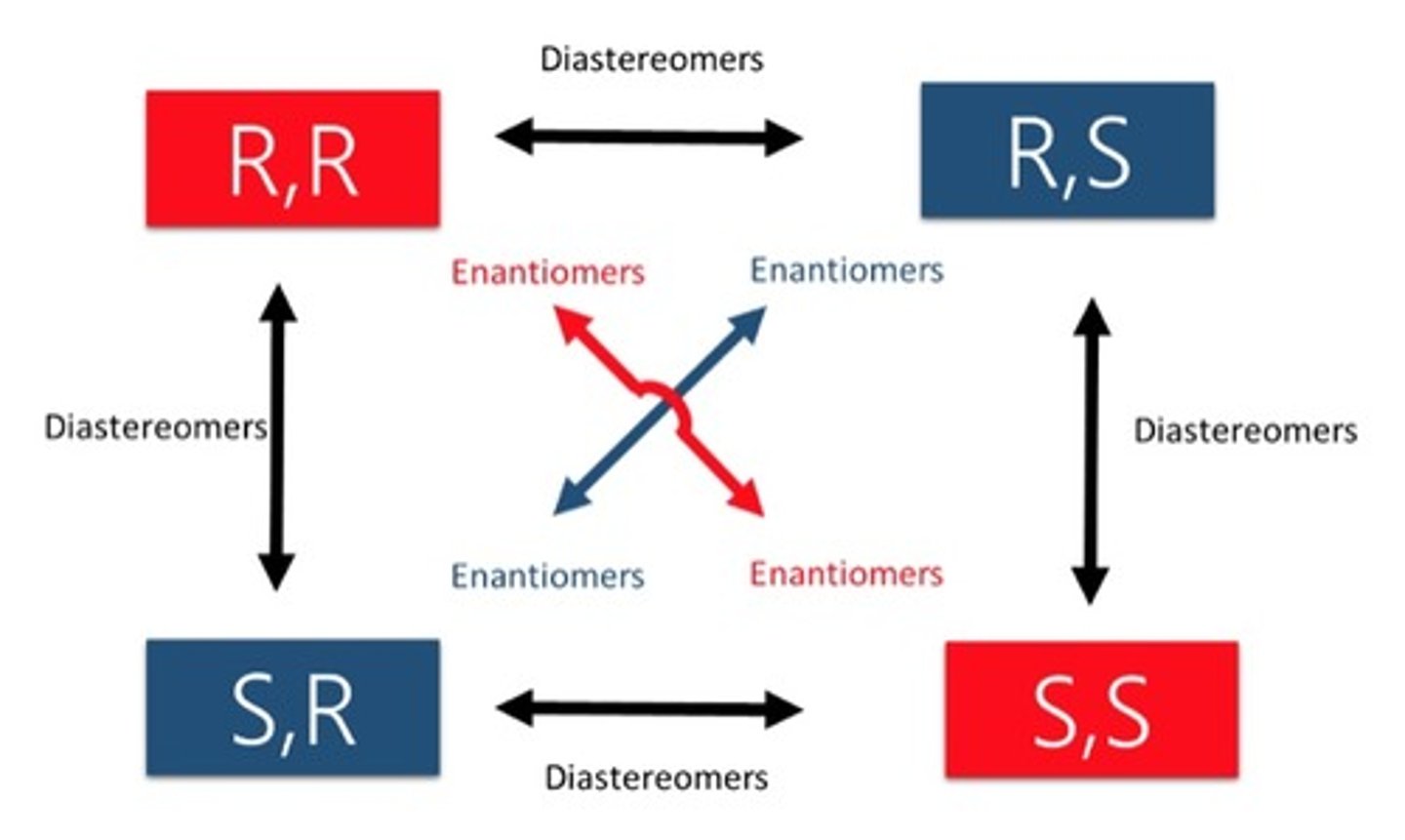
Only some of the chiral carbons are inverted.
a. Enantiomer
b. Diastereomer
b. Diastereomer