Anatomy Block 2 ASL Clinical Applications (ALL)
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
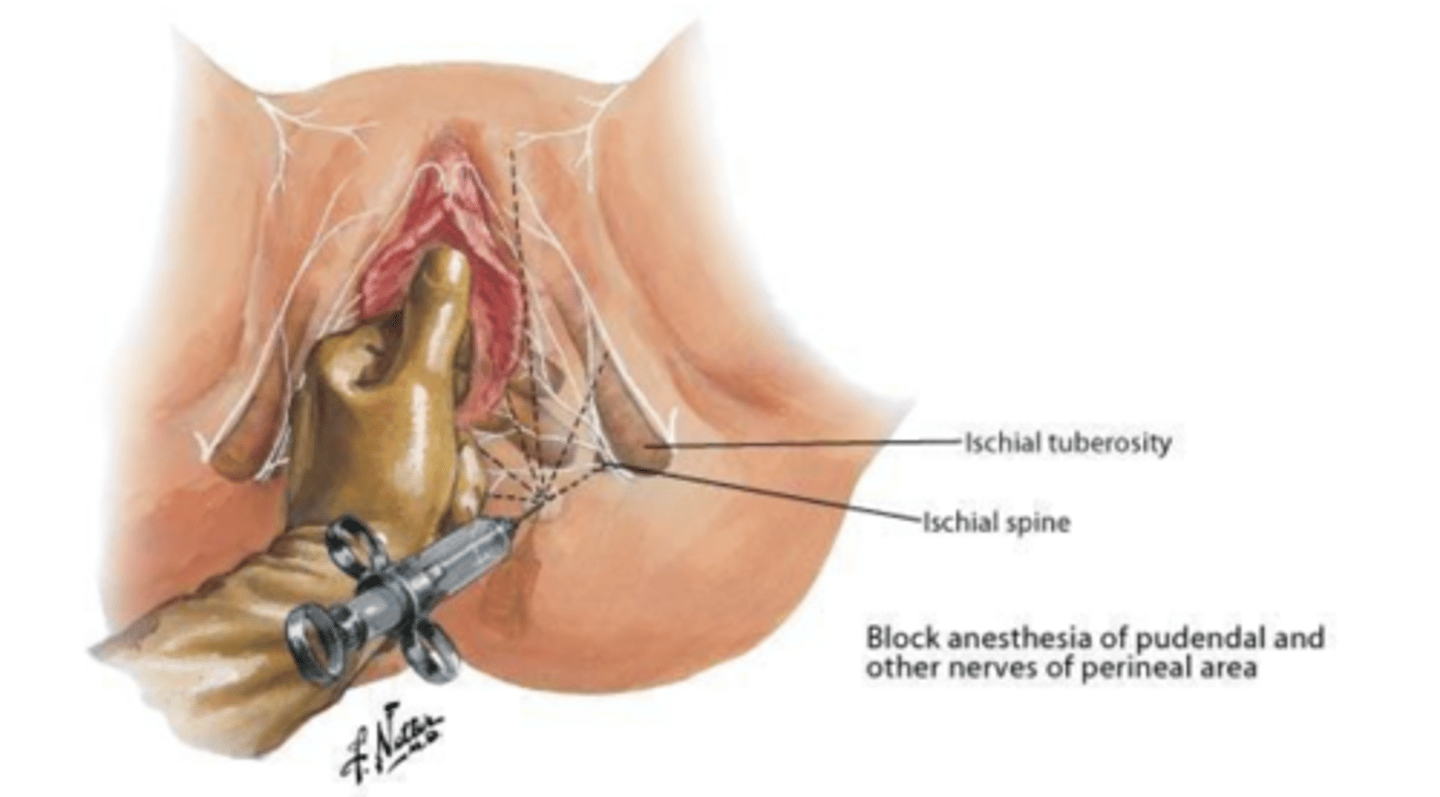
pudenal nerve block
Given in second stage of labor
Doesn't relieve pain from uterine contractions, but relieves pain in vagina, vulva, and perineum
given for forceps of vacuum delivery
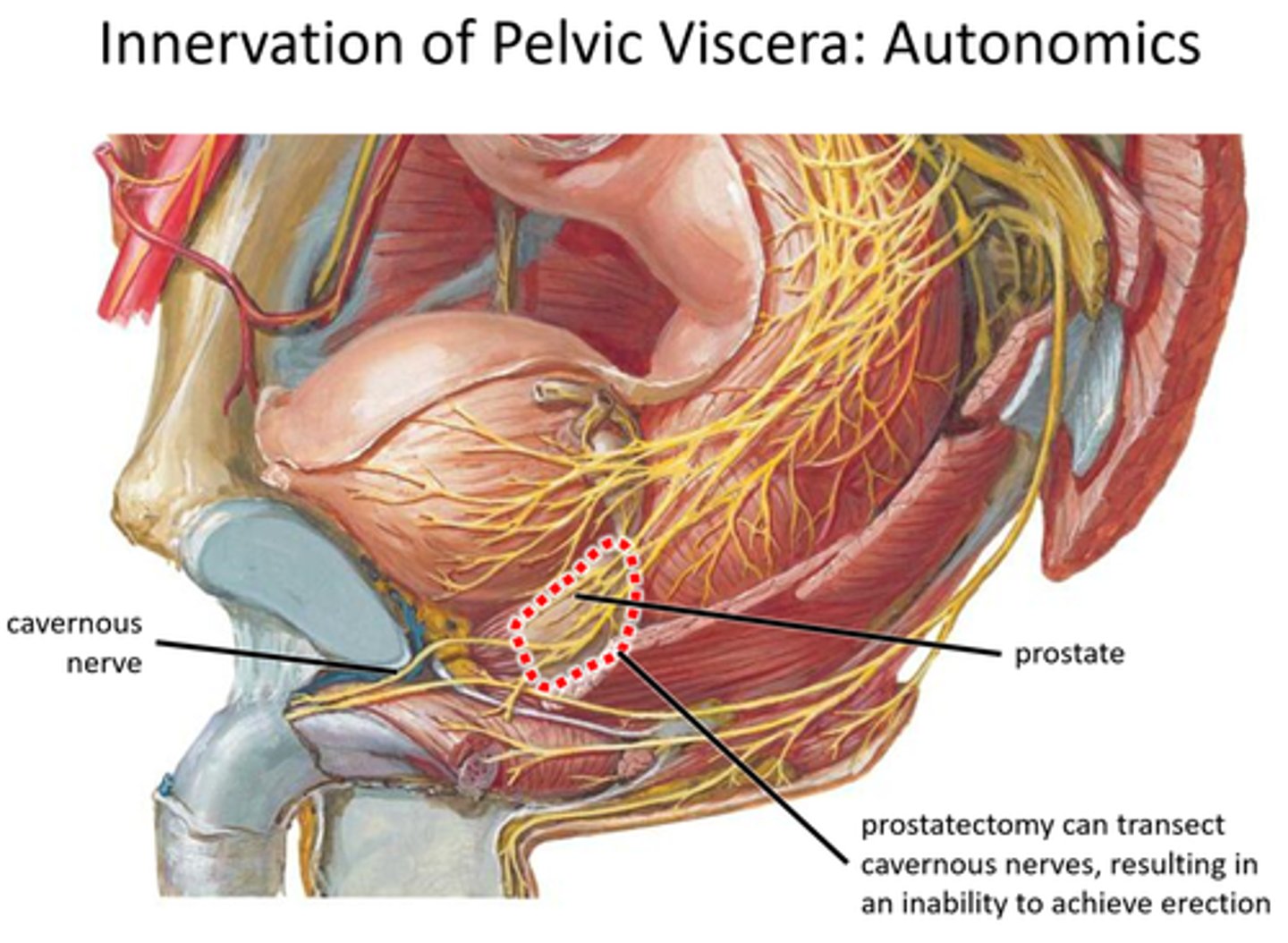
prostatectomy and impotence
surgical removal of the prostate
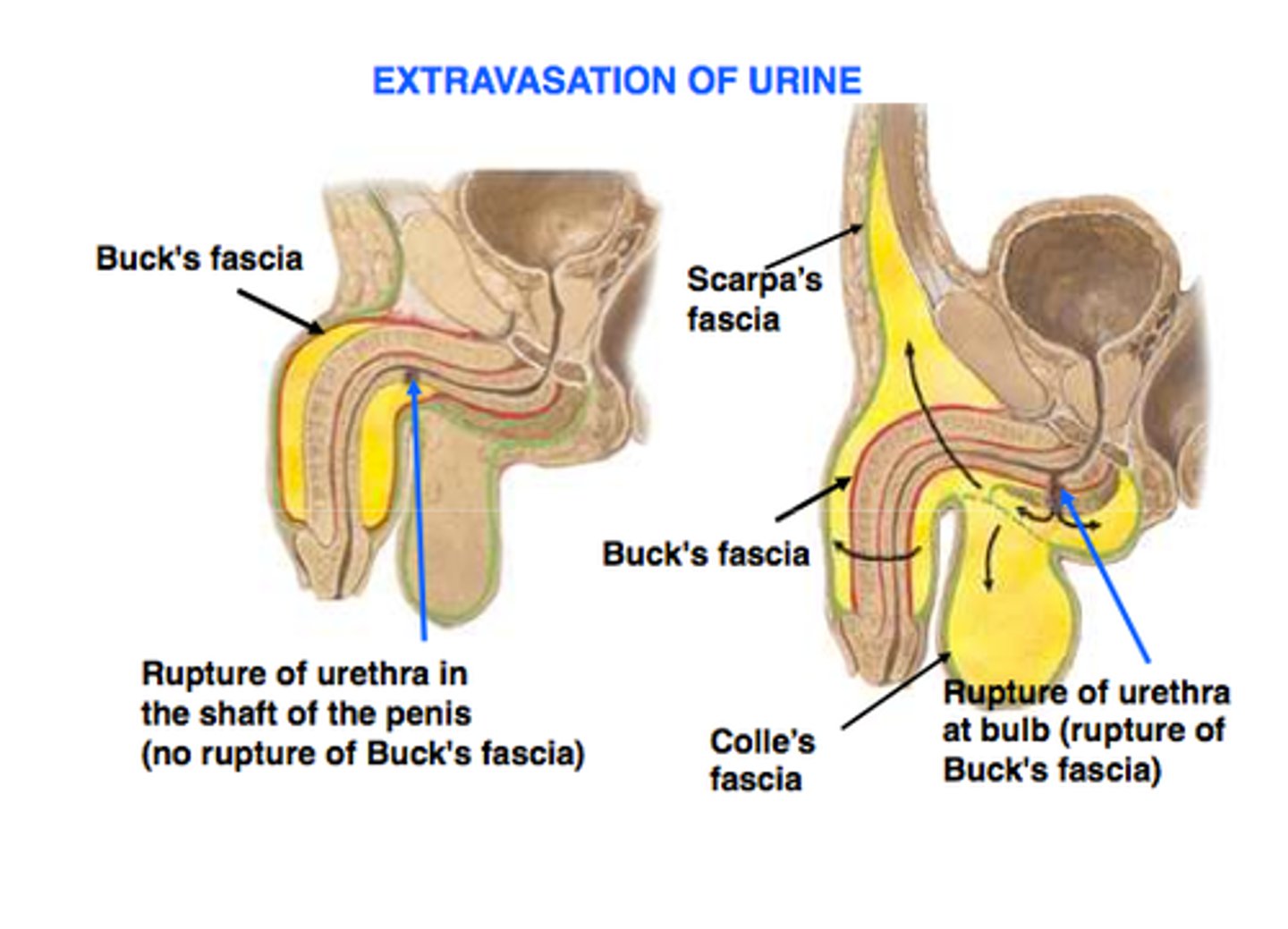
urethral rupture
straddle injury (males)
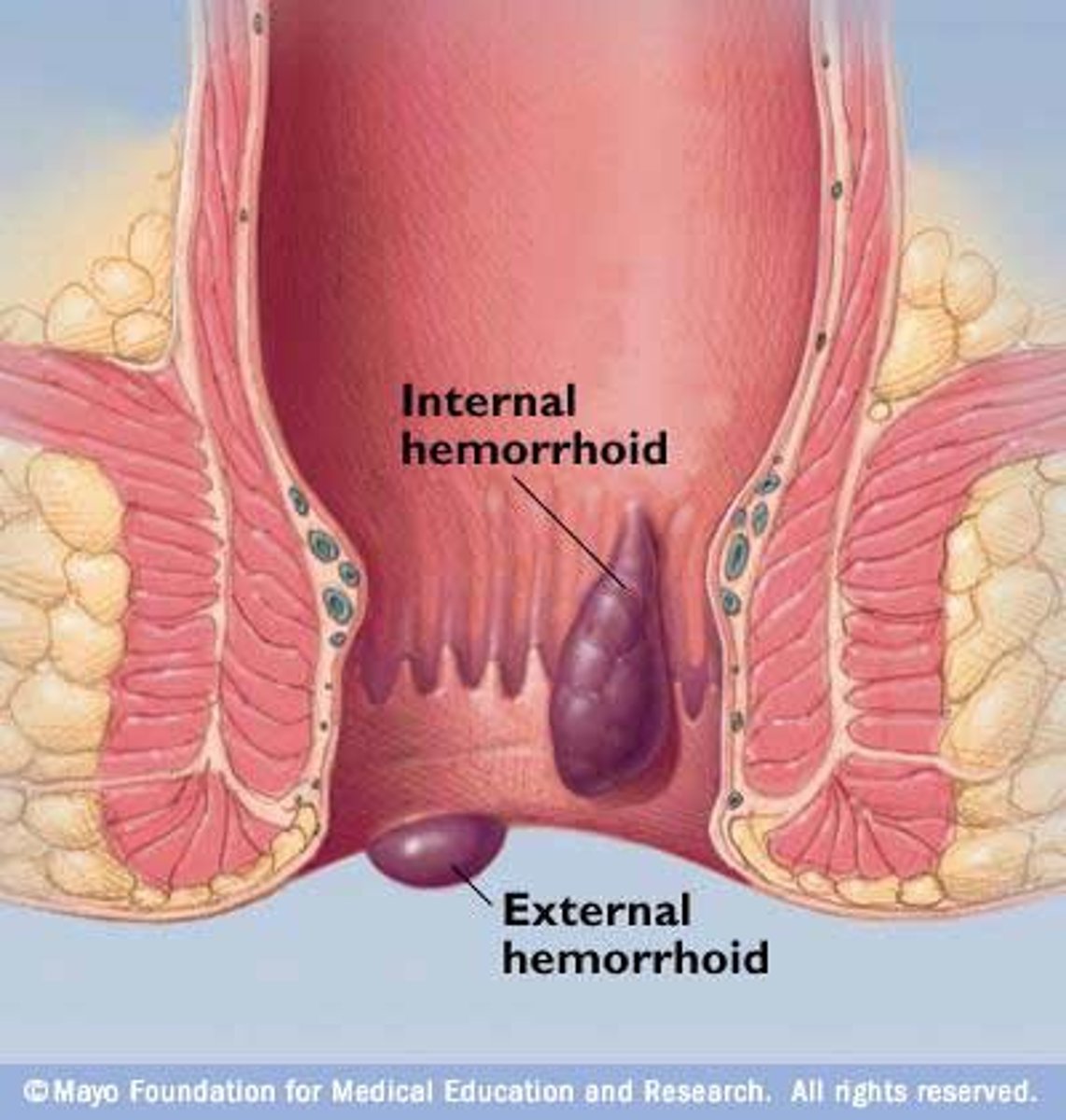
hemorrhoids
Swollen, painful rectal veins; often a result of constipation
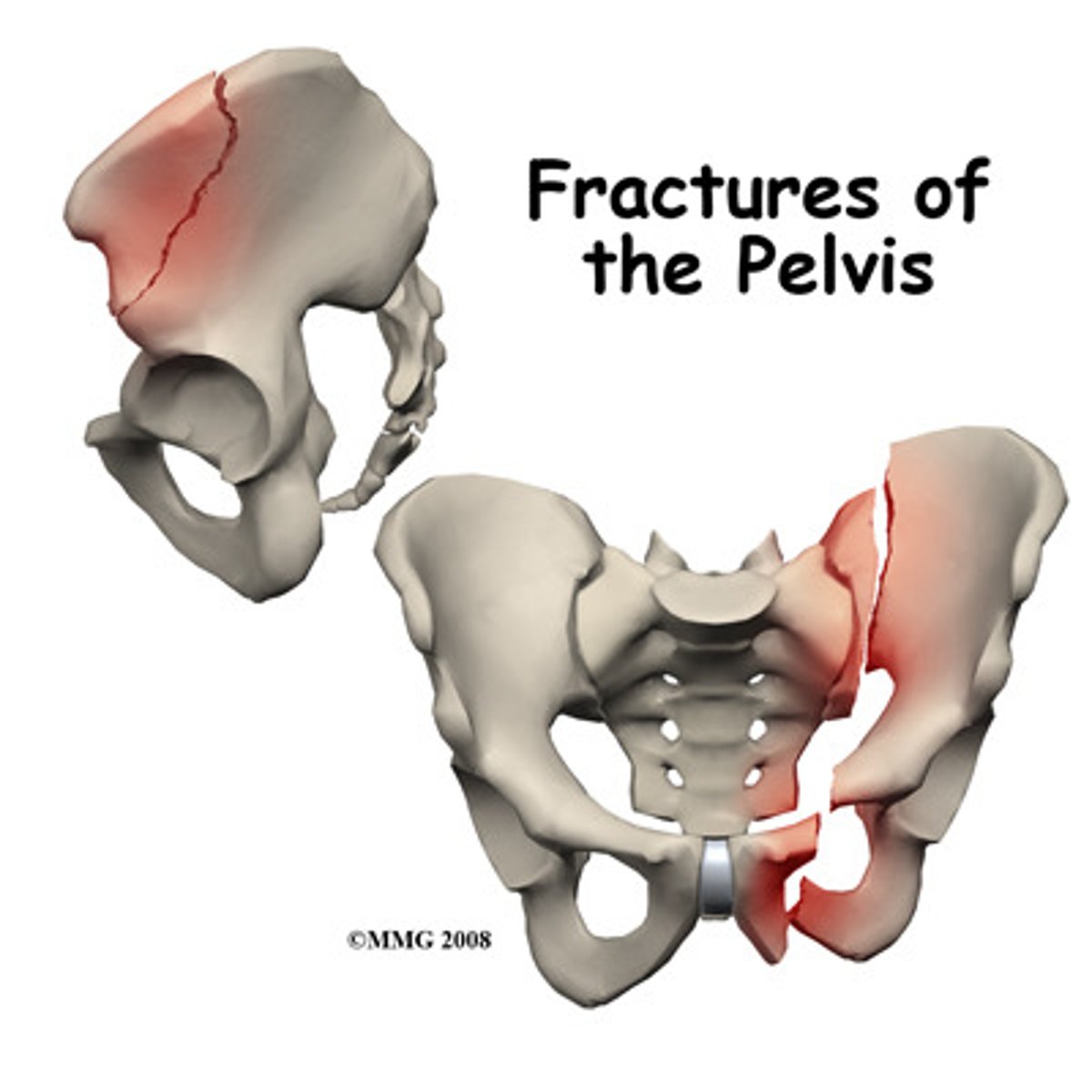
Pelvic fracture
mostly from MVC< motorcycle
pelvis has highly vascular stuff and abd, pelvic organs so assess INTERNAL HEMORRHAGE, paralytic ileus, Neurovascular deficit
assess abd distension, absent bowel sounds
Defecation
elimination of feces from the digestive tract through the anus
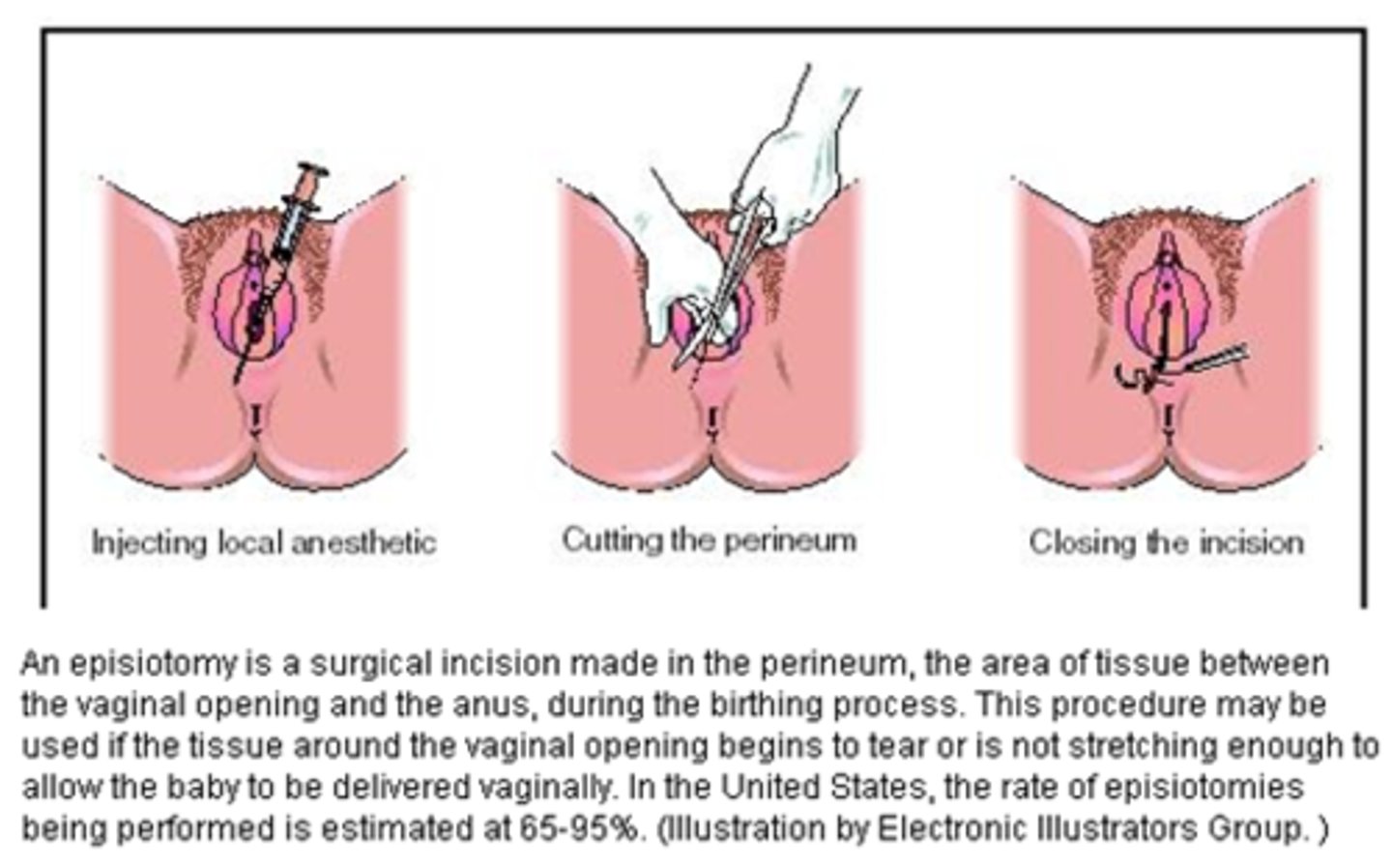
Episiotomy
surgical incision of the perineum to enlarge the vagina and so facilitate delivery during childbirth
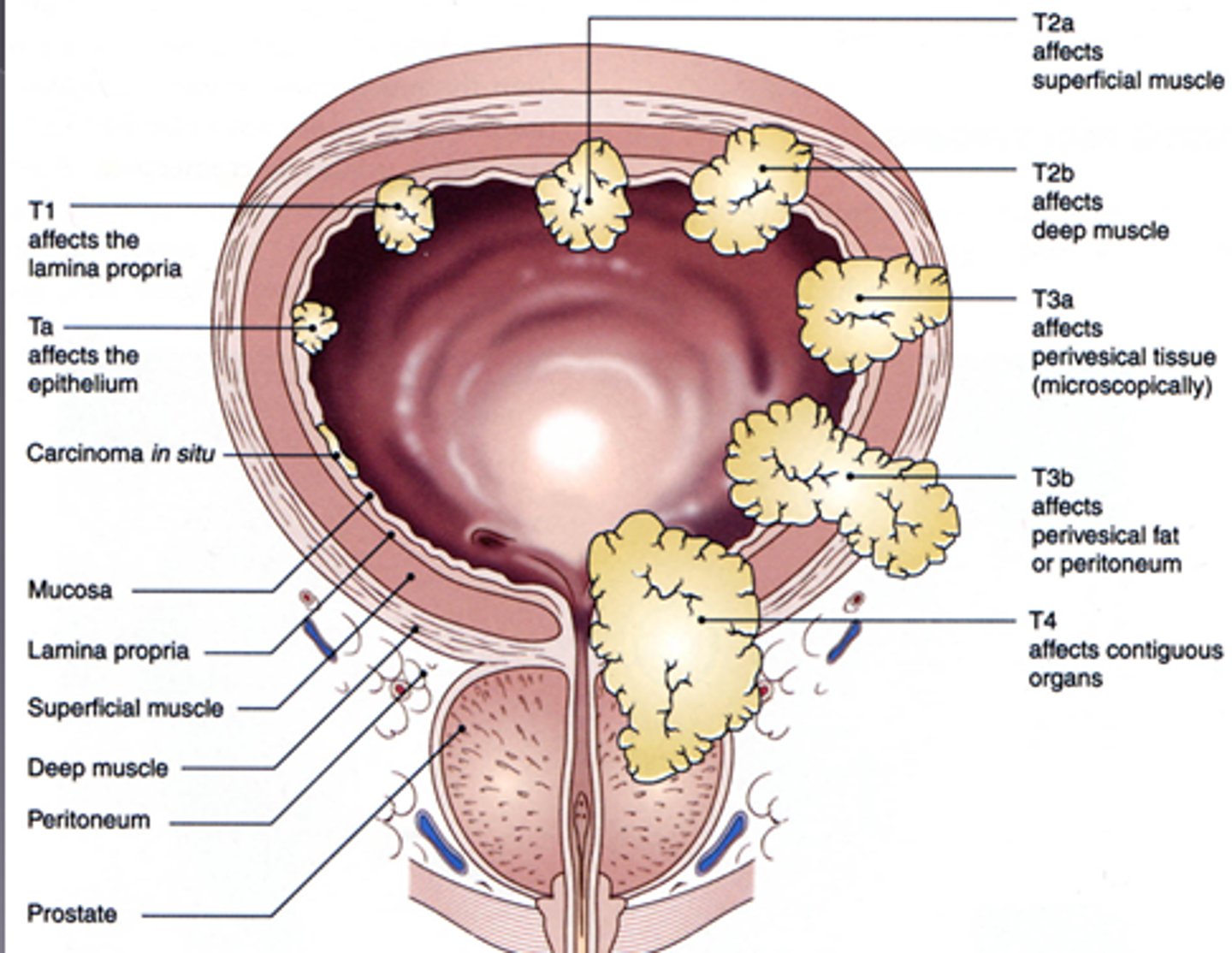
Bladder cancer
cancerous tumor that arises from the cells lining the bladder; major sign is hematuria
Bladder infection
Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)
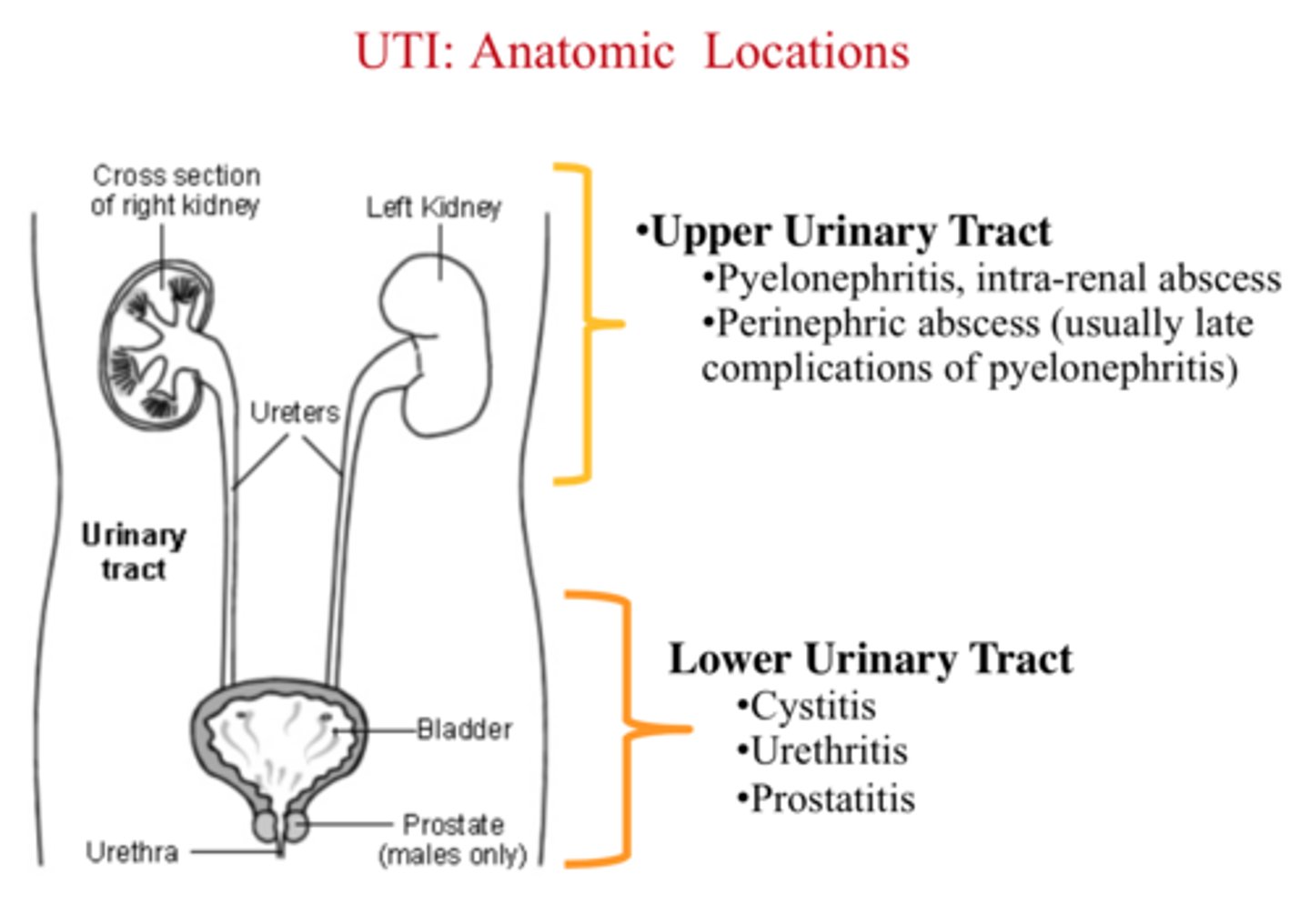
Urethral catheterization
peformed by inserting a tube along the urethra and into the bladder
Undescended testes
failure of one or both testes to move from the abdomen to the scrotum during fetal development
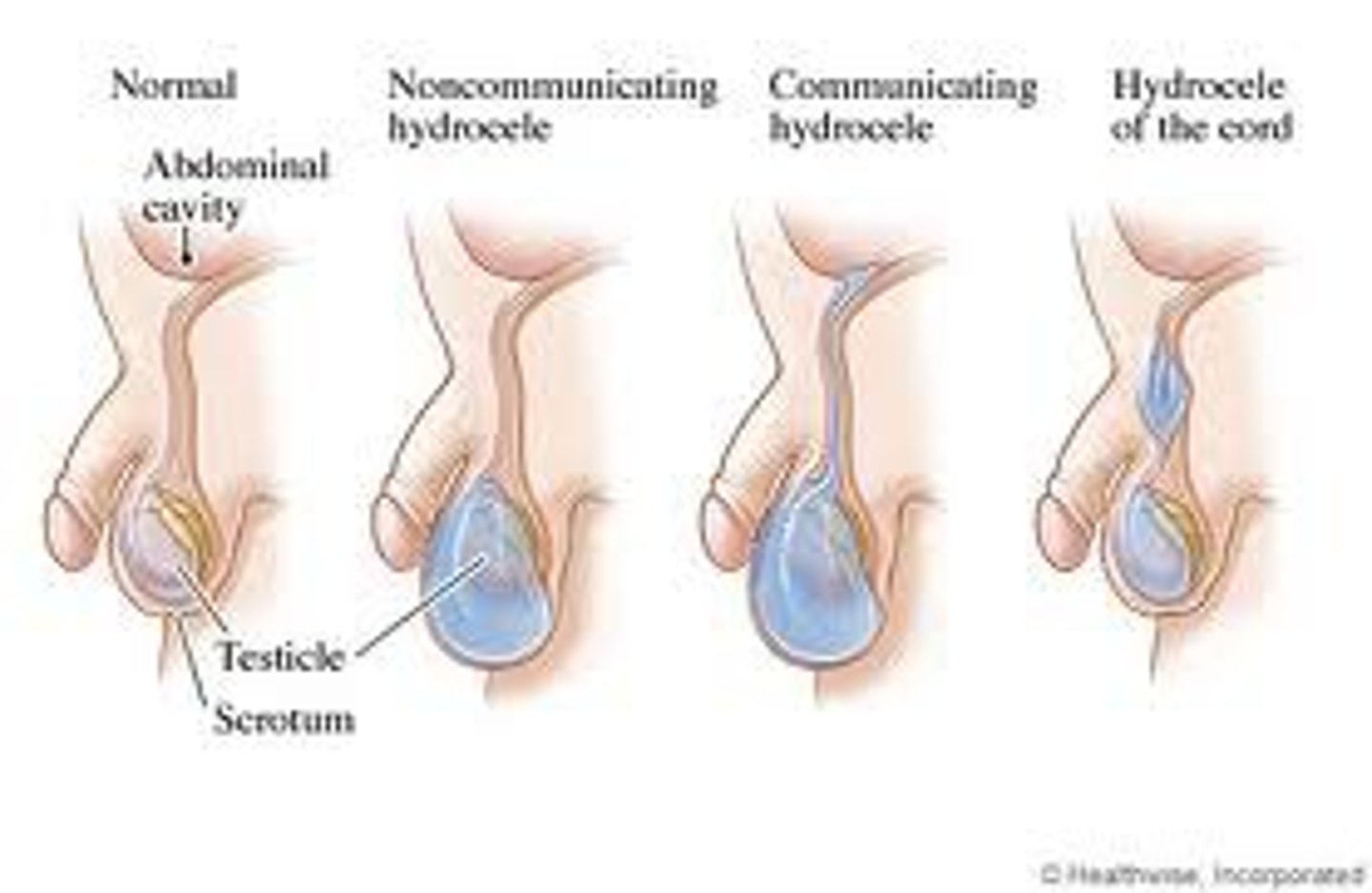
Hydrocele
a fluid-filled sac in the scrotum along the spermatic cord leading from the testicles
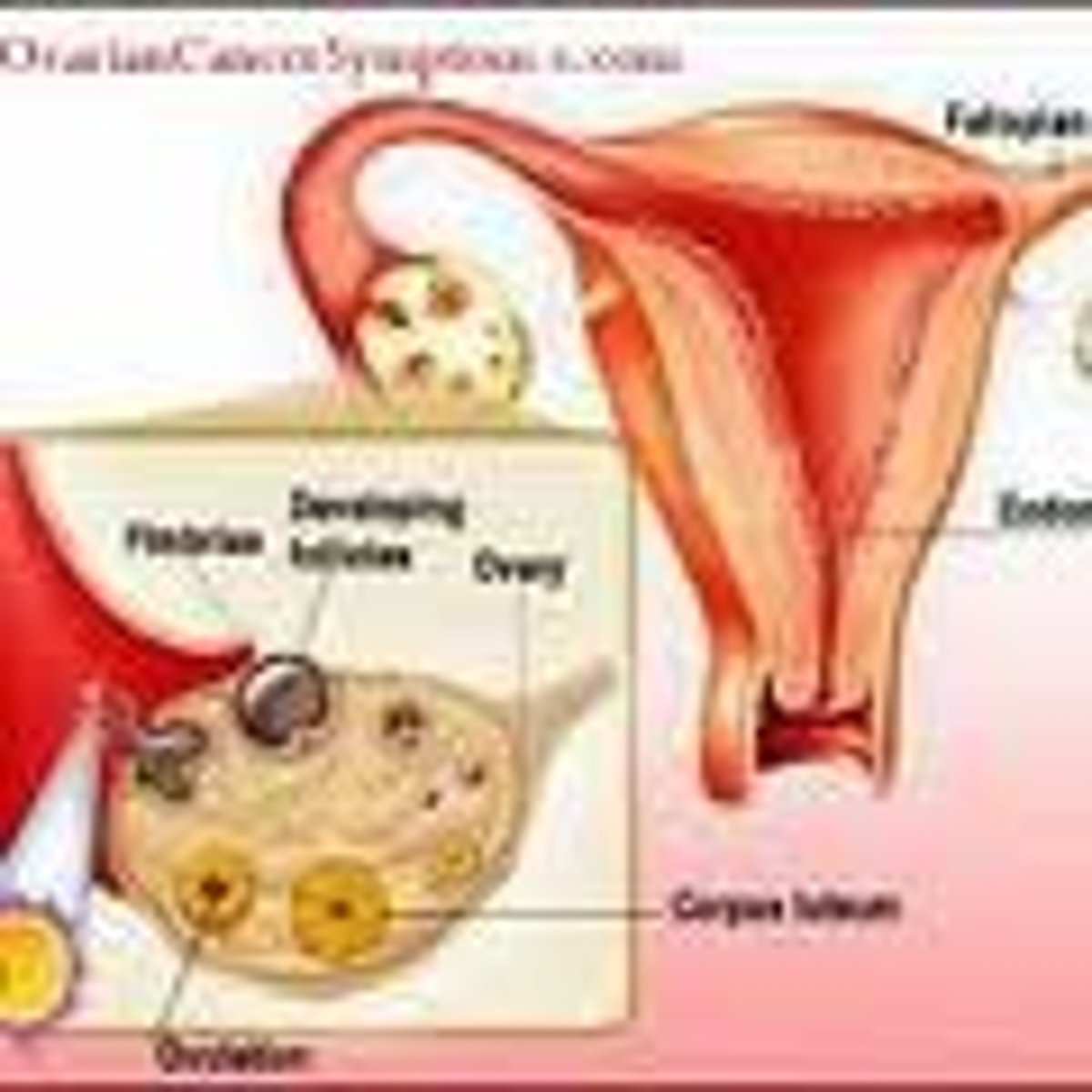
Ovarian cancer
cancerous tumor formed within ovary
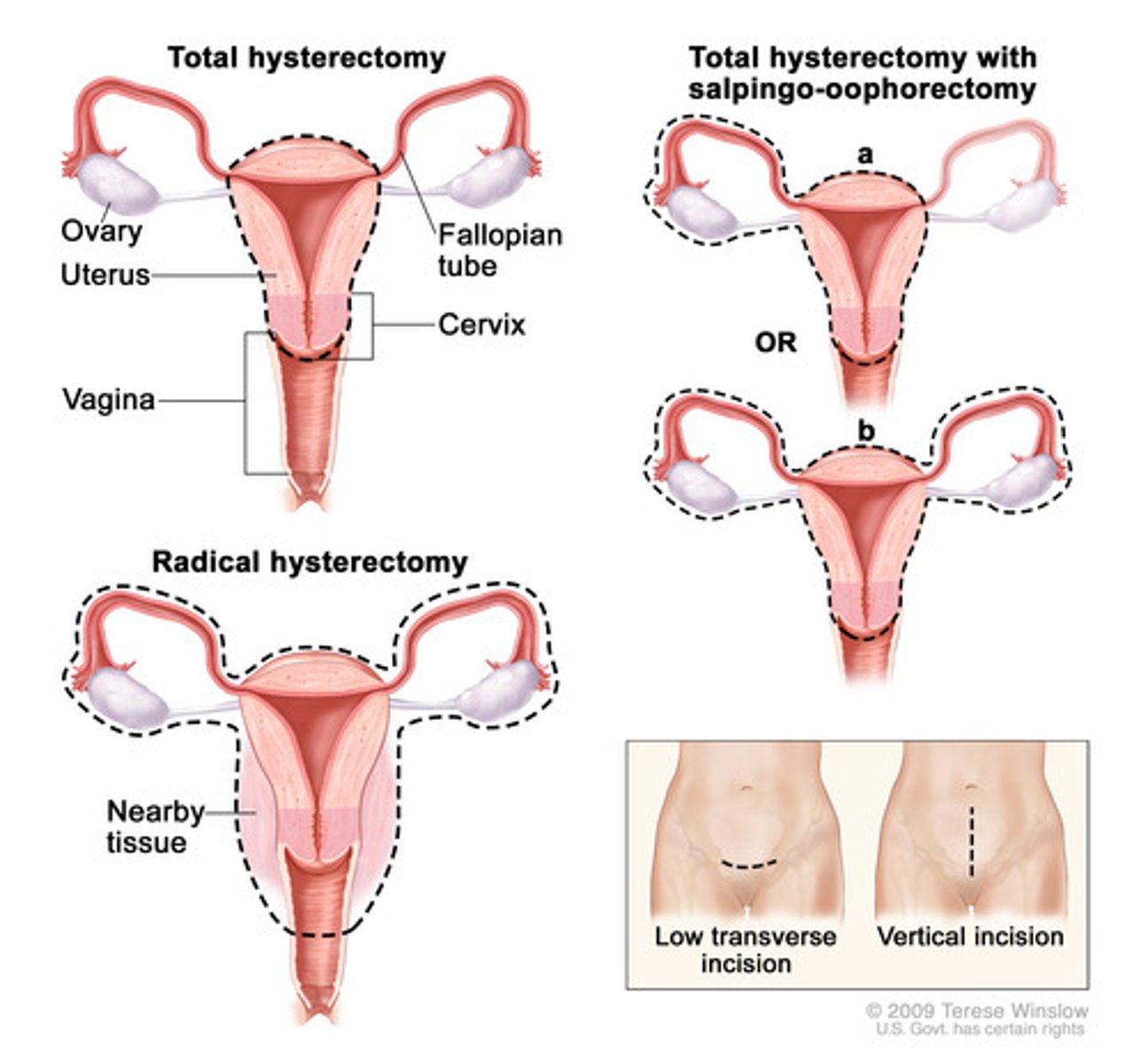
Hysterectomy
surgical removal of the uterus
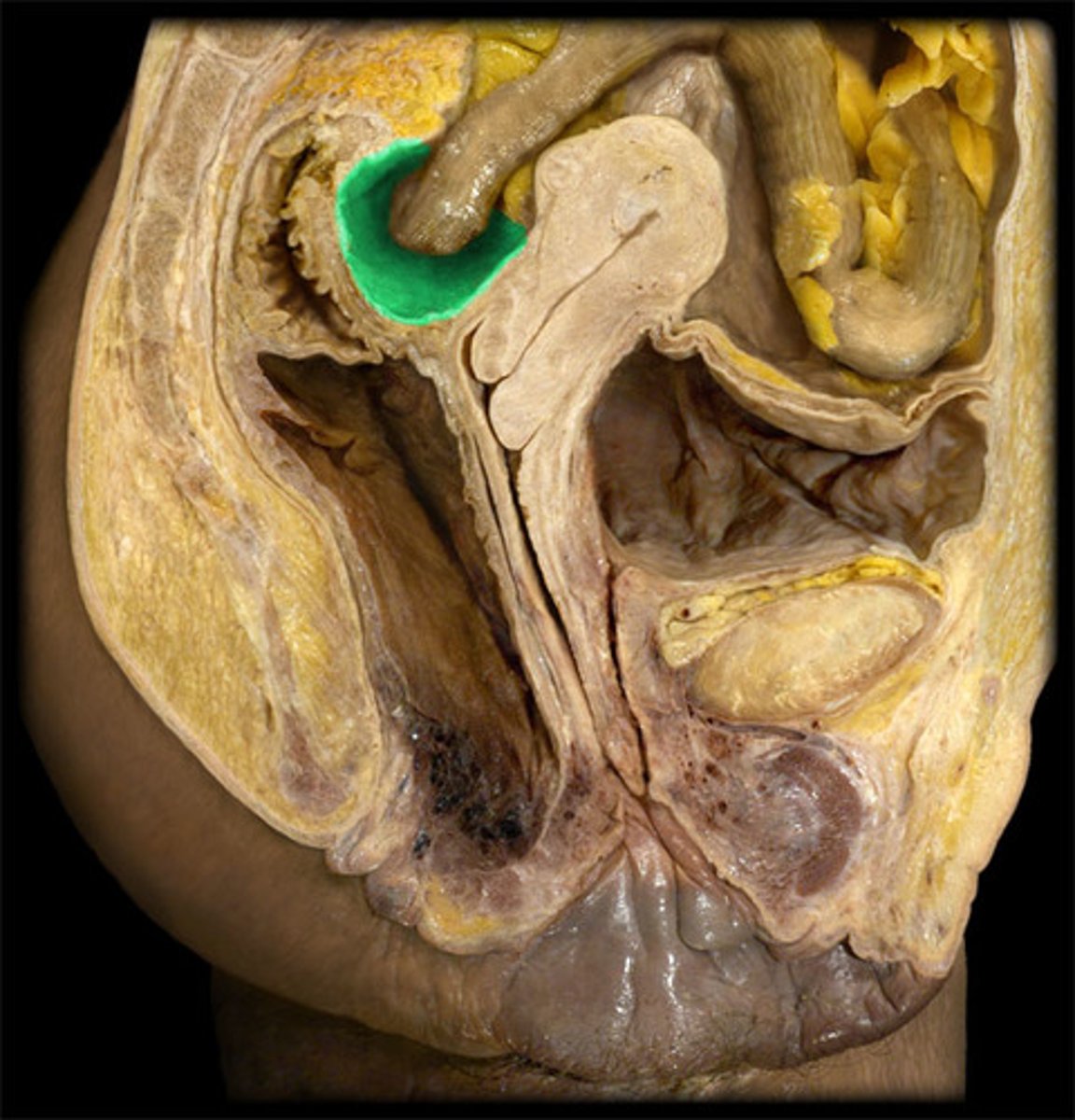
Recto-uterine pouch
the pocket formed between the posterior wall of the uterus and the anterior surface of the colon
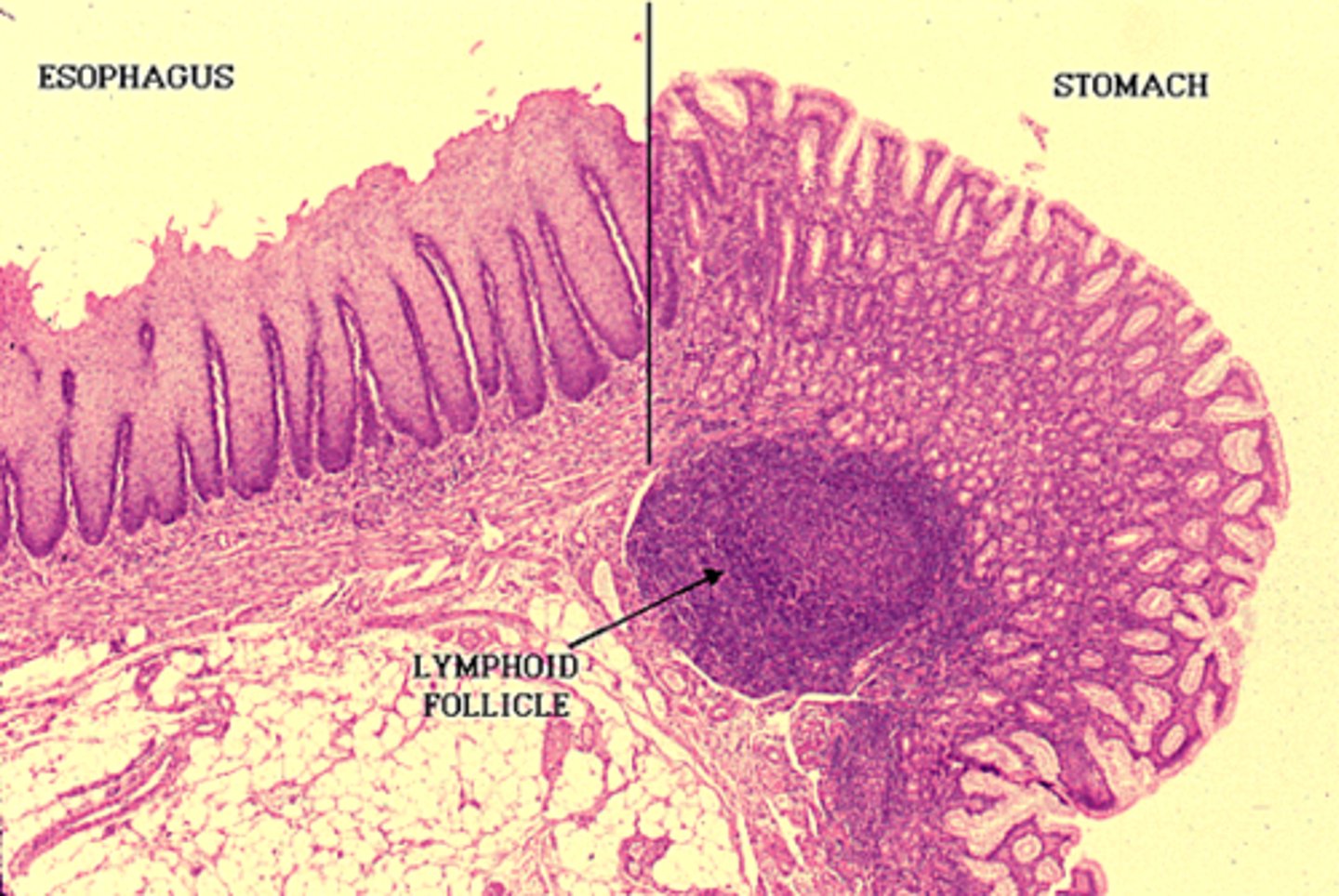
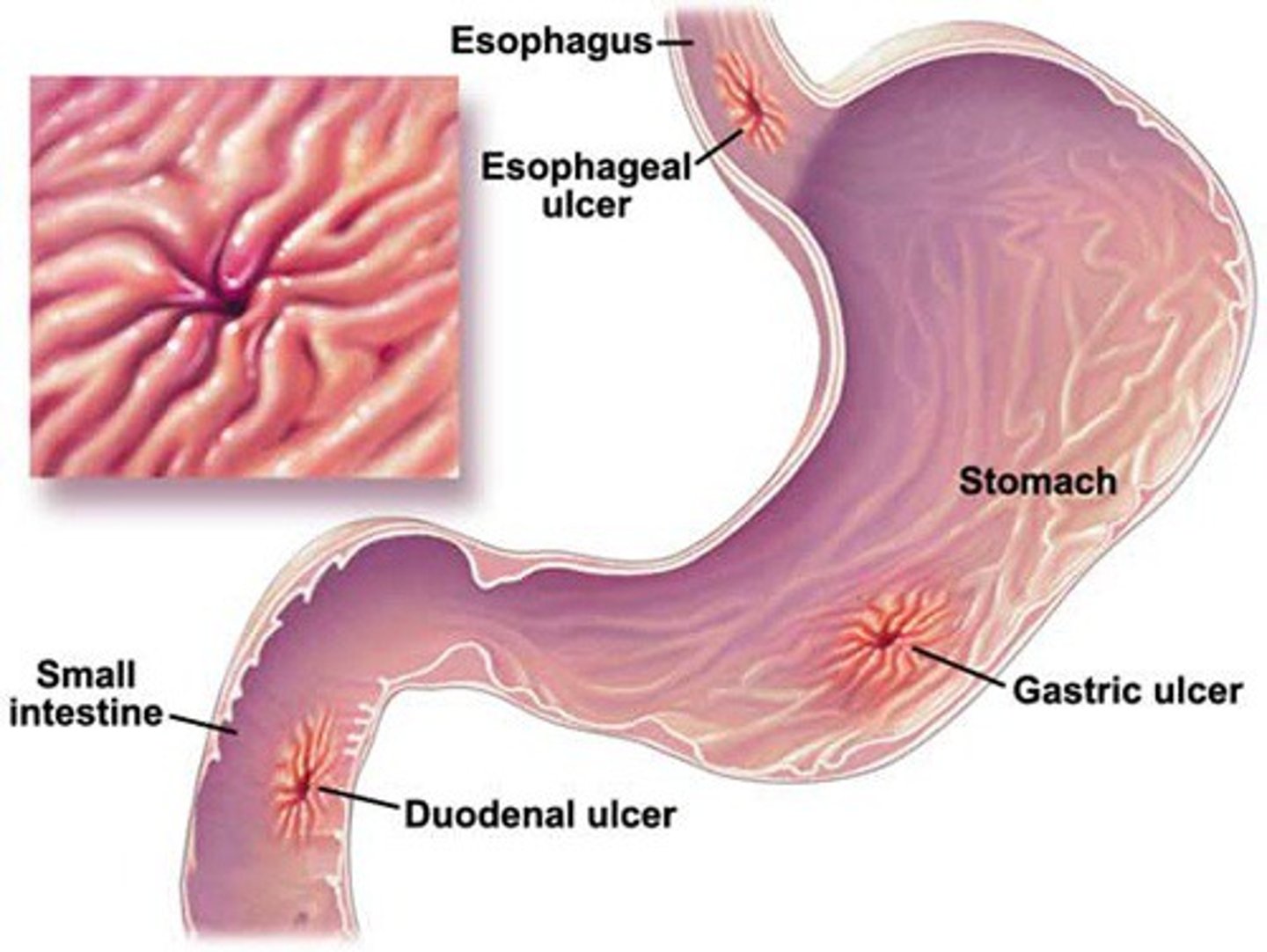
epithelial transition
the gastroesophageal junction is demarcated by a transition from one epithelial type to another epithelial type
• some people are predisposed to esophageal ulceration w/ increased risk of adenocarcinoma if their junction is at the lower one-third of the esophagus instead
duodenal ulceration
usually occur in the superior part of the duodenum
• posterior duodenal ulcers erode either directly onto the gastroduodenal artery or more commonly onto the posterior superior pancreaticoduodenal artery
• anterior duodenal ulcers erode into the peritoneal cavity, causing peritonitis
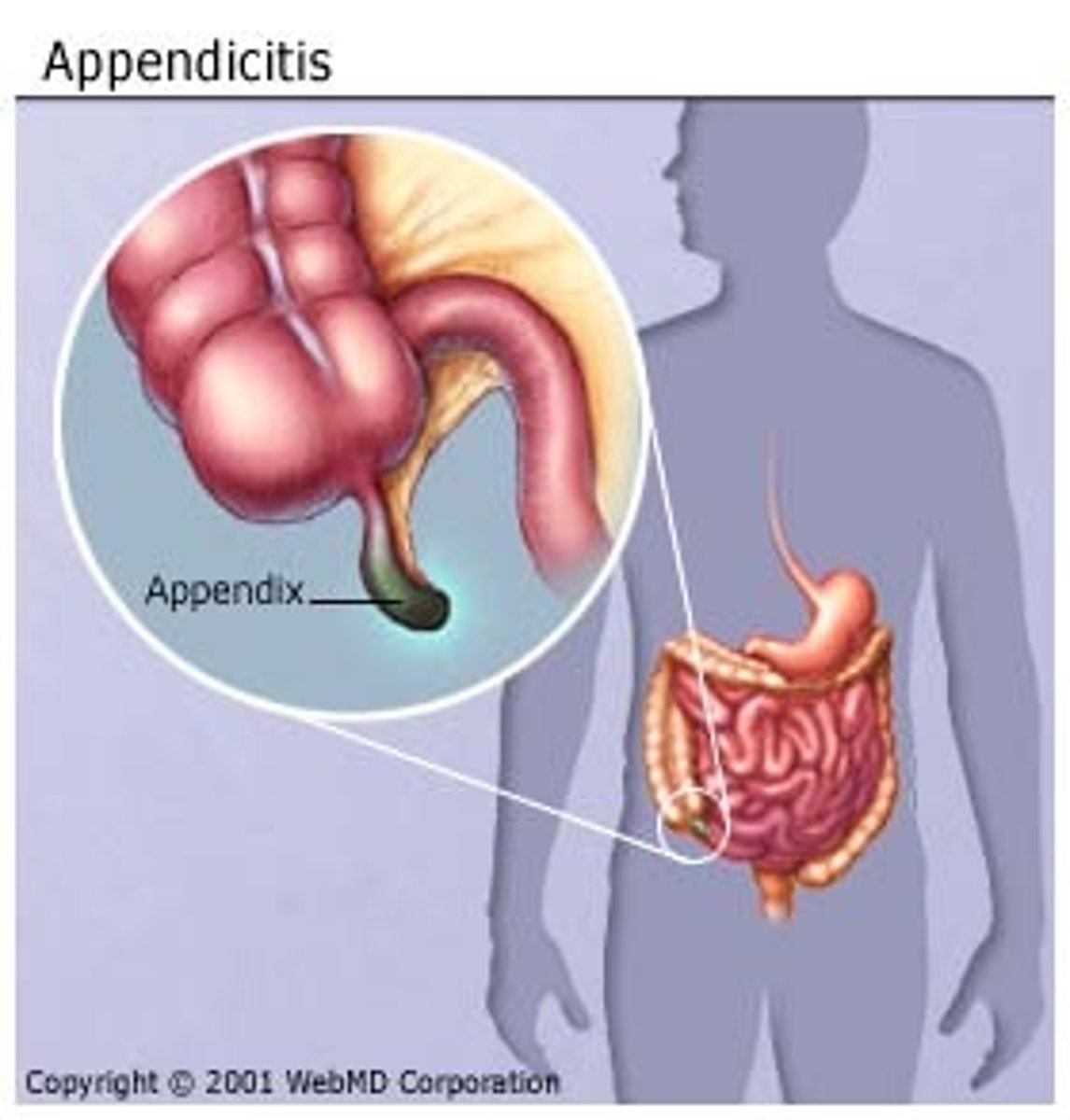
appendicitis
• acute appendicitis is an abdominal emergency
that occurs when the appendix is obstruction ted by either a fecolith or an enlargement of the lymphoid nodules
• bacteria can proliferate and invade the appendix wall, causing pressure necrosis
• localized tenderness in the right groin; begins as a central/periumbilical pain that tends to come and go, and then as the disease progresses, the pain shifts to the lower right groin and is focal.
• when the appendix first is inflamed, the visceral sensory fibers are stimulated. they enter the spinal cord at the T10 level
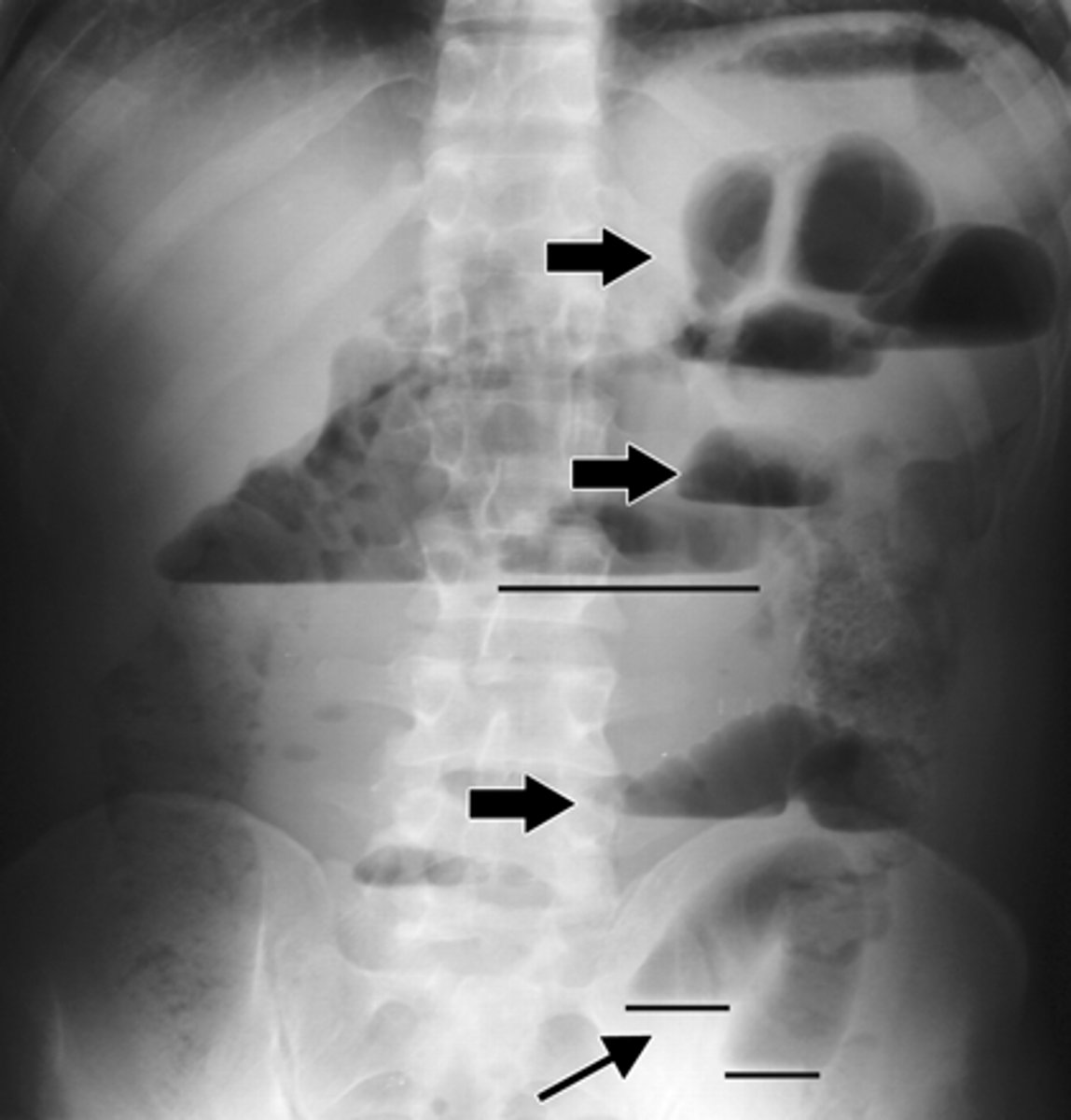
bowel obstruction
can be either mechanical or function
• mechanical obstruction - caused by an intraluminal, mural, or extrinsic mass, which can be secondary to a foreign body, obstructing tumor in the wall, or an extrinsic compression from an adhesion, or an embryological band
• function obstruction - due to an inability of the bowel to peristalse
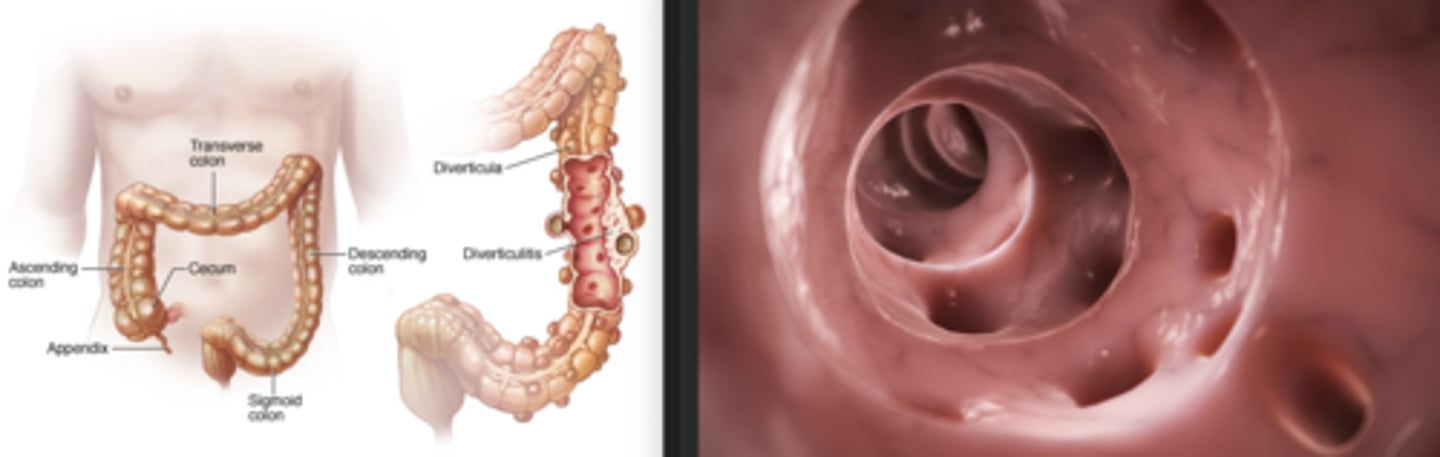
diverticular disease
the development of multiple colonic diverticula, predominately throughout the sigmoid colon, though the entire colon can be affected
• diverticula are small outpouchings
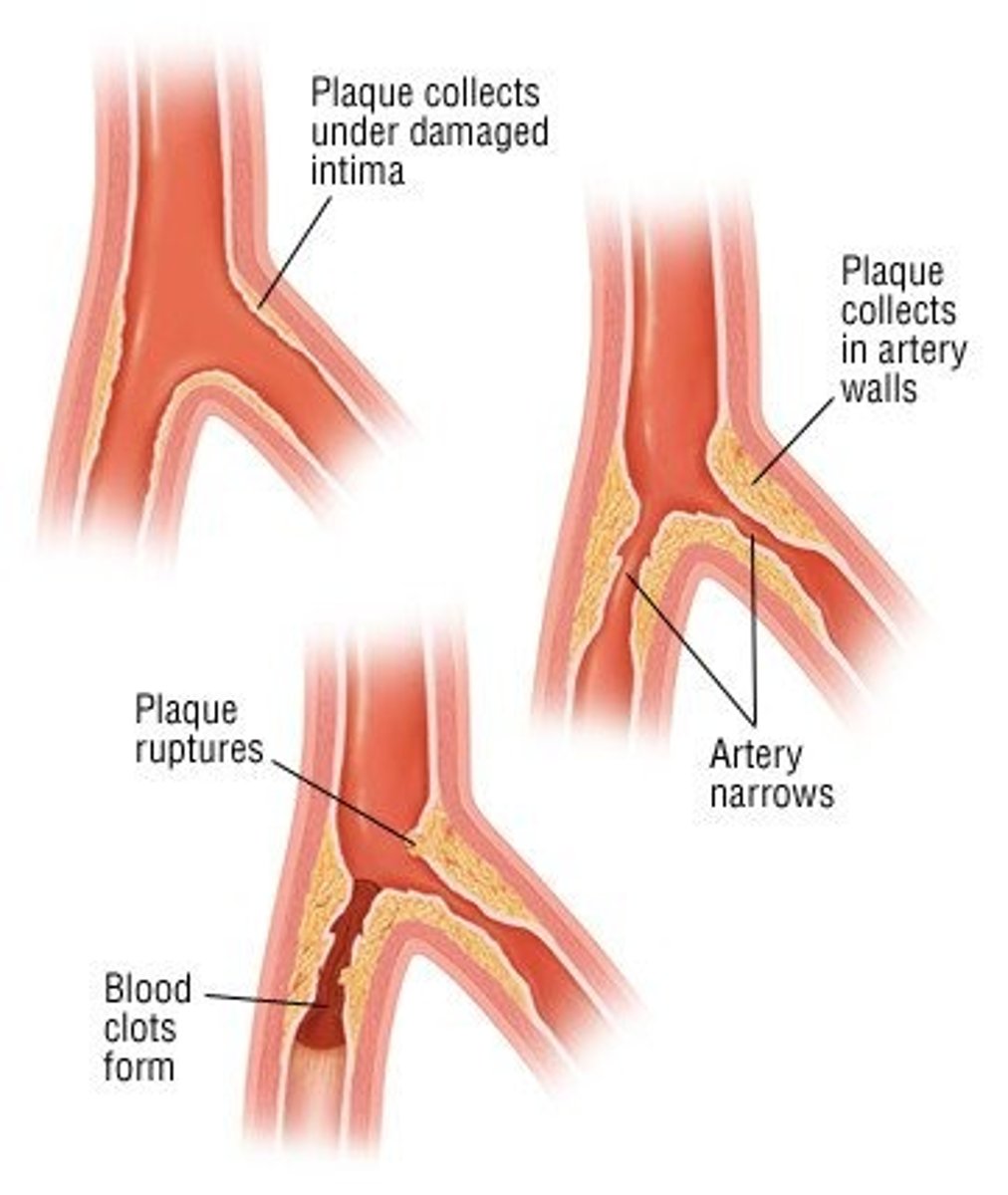
vascular supply of the gastrointestinal system
arteriosclerosis may occur throughout the abdominal aorta and at the openings of the celiac trunk and the superior mesenteric and inferior mesenteric arteries
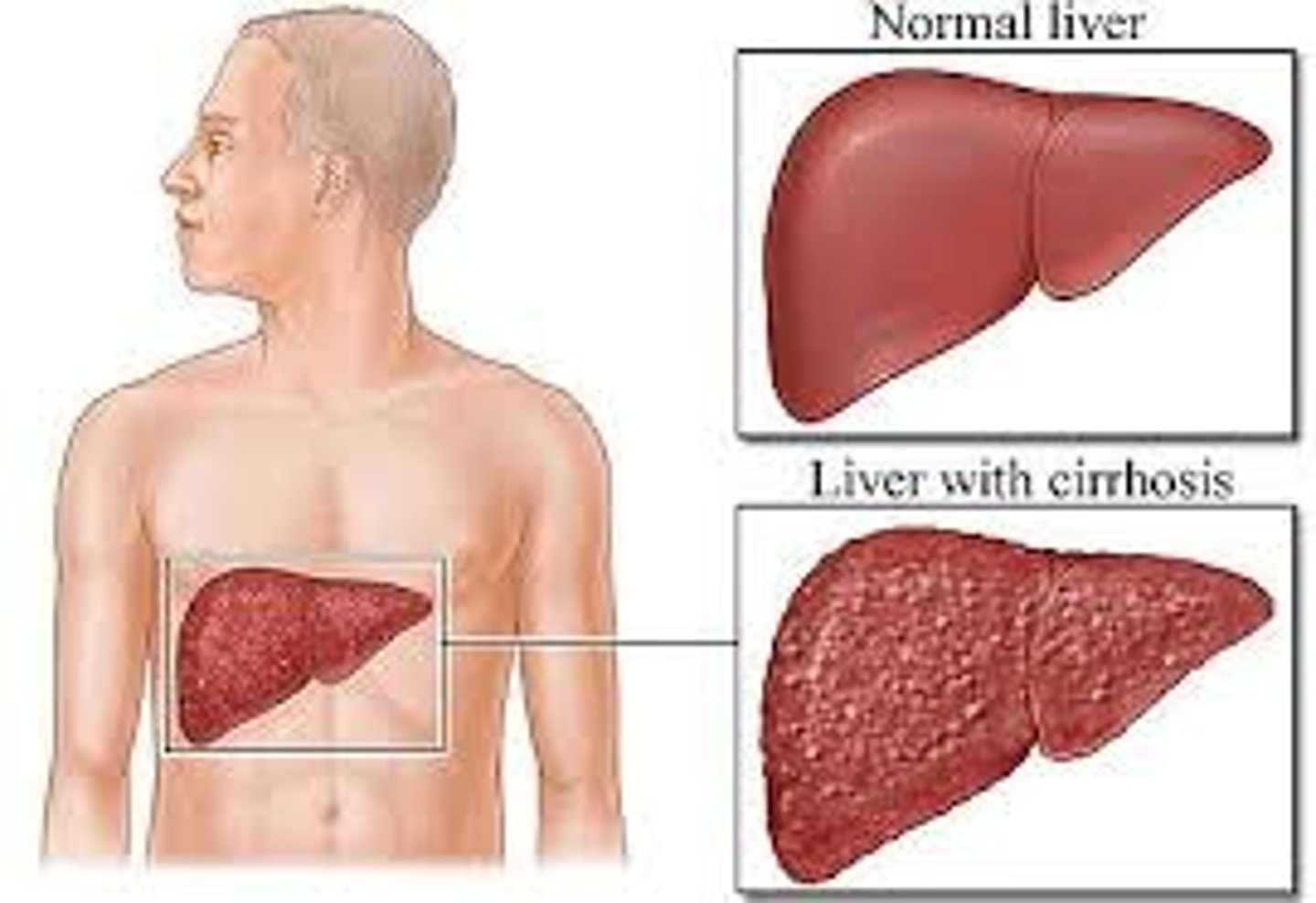
hepatic cirrhosis
cirrhosis is a complex disorder of the liver, diagnosis must be confirmed histologically
if the diagnosis is suspected, a liver biopsy is necessary
• characterized by widespread hepatic fibrosis, which implies liver cell damage
• increase in the serum bilirubin level which manifests as jaundice because the liver cells are unable to break down blood and blood products
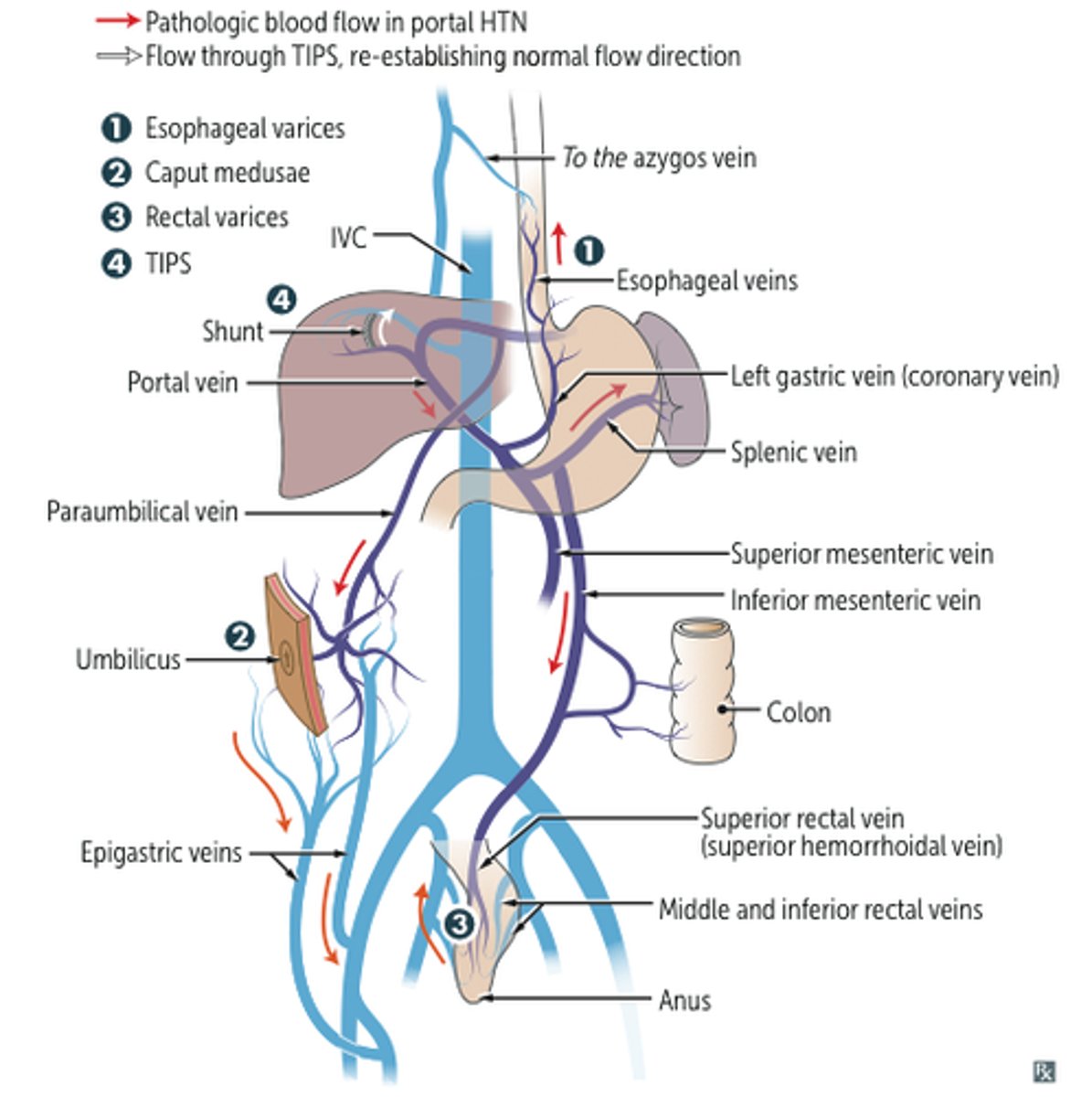
portosystemic anastomosis
in patients w/ elevated portal vein pressure (portal hypertension from cirrhosis)
• when the pressure in the portal vein is elevated, venomous enlargement (varies) tends to occur at and around the sites of portosystemic anastomoses
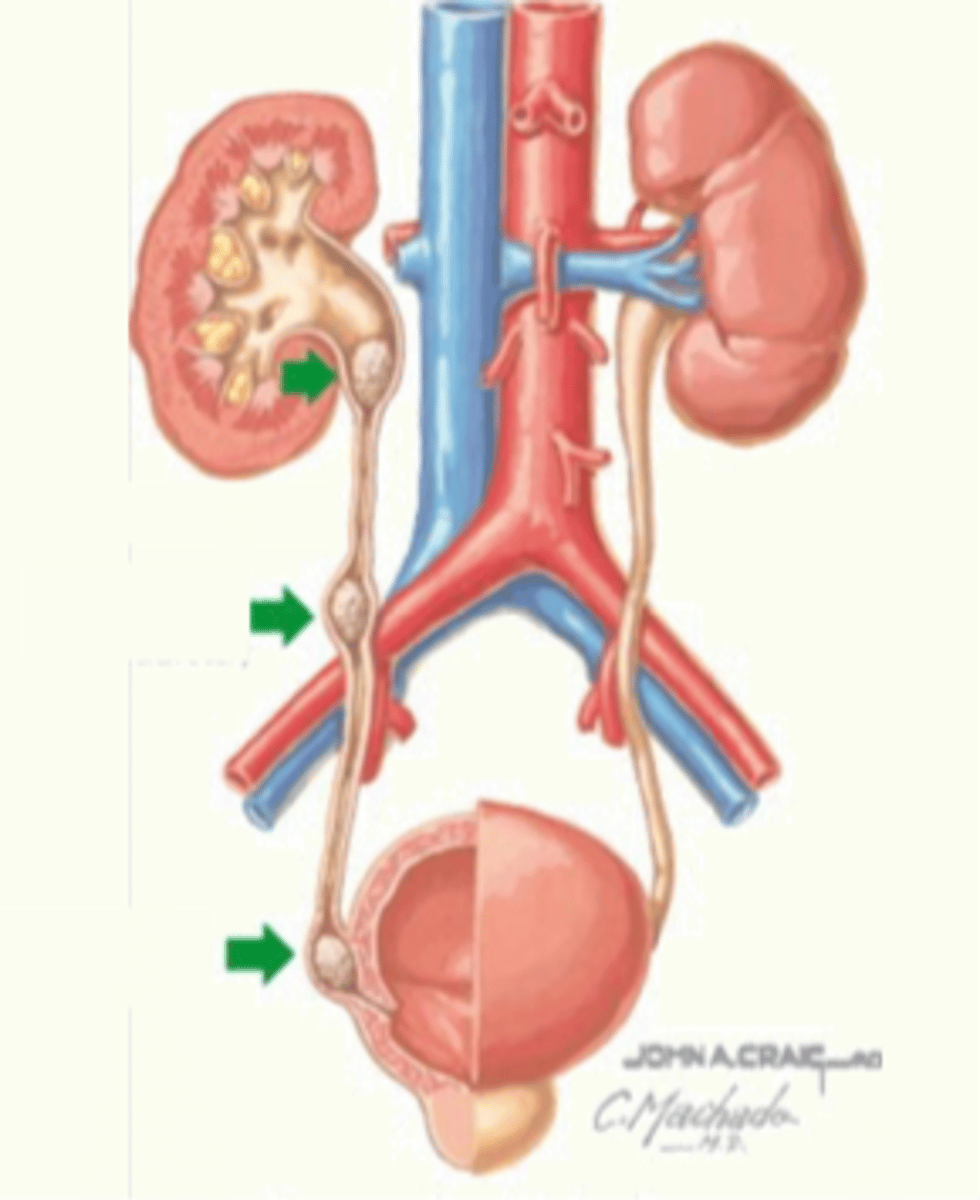
Urinary tract stones
• occur more frequently in men than women, ages between 20-60, usually due to sedentary lifestyles
• stones = polycrystalline aggregates of calcium, phosphate, oxalate, rate, and other soluble salts within an organic matrix
• blood in the urine (hematuria) may be also noted
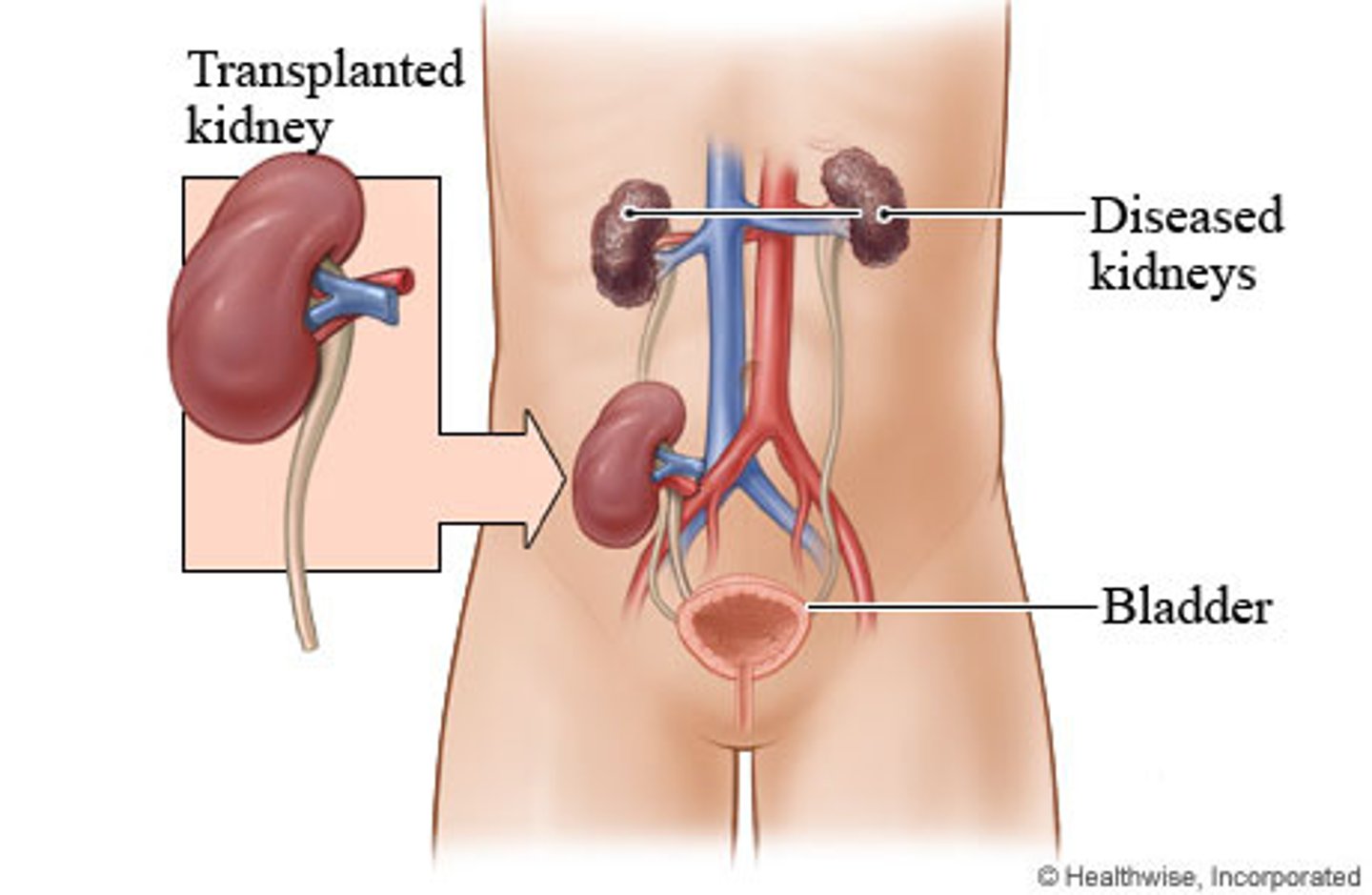
kidney transplant
the major problem with kidney transplants is tissue rejection
• now a common procedure is undertaken in patients with end-stage renal failure
• ideal place to situate the transplanted kidney is in the left or the right iliac fossa
IVU (intravenous urogram), ultrasound, computed tomography, nuclear medicine
imaging used for the investigation of the urinary tract
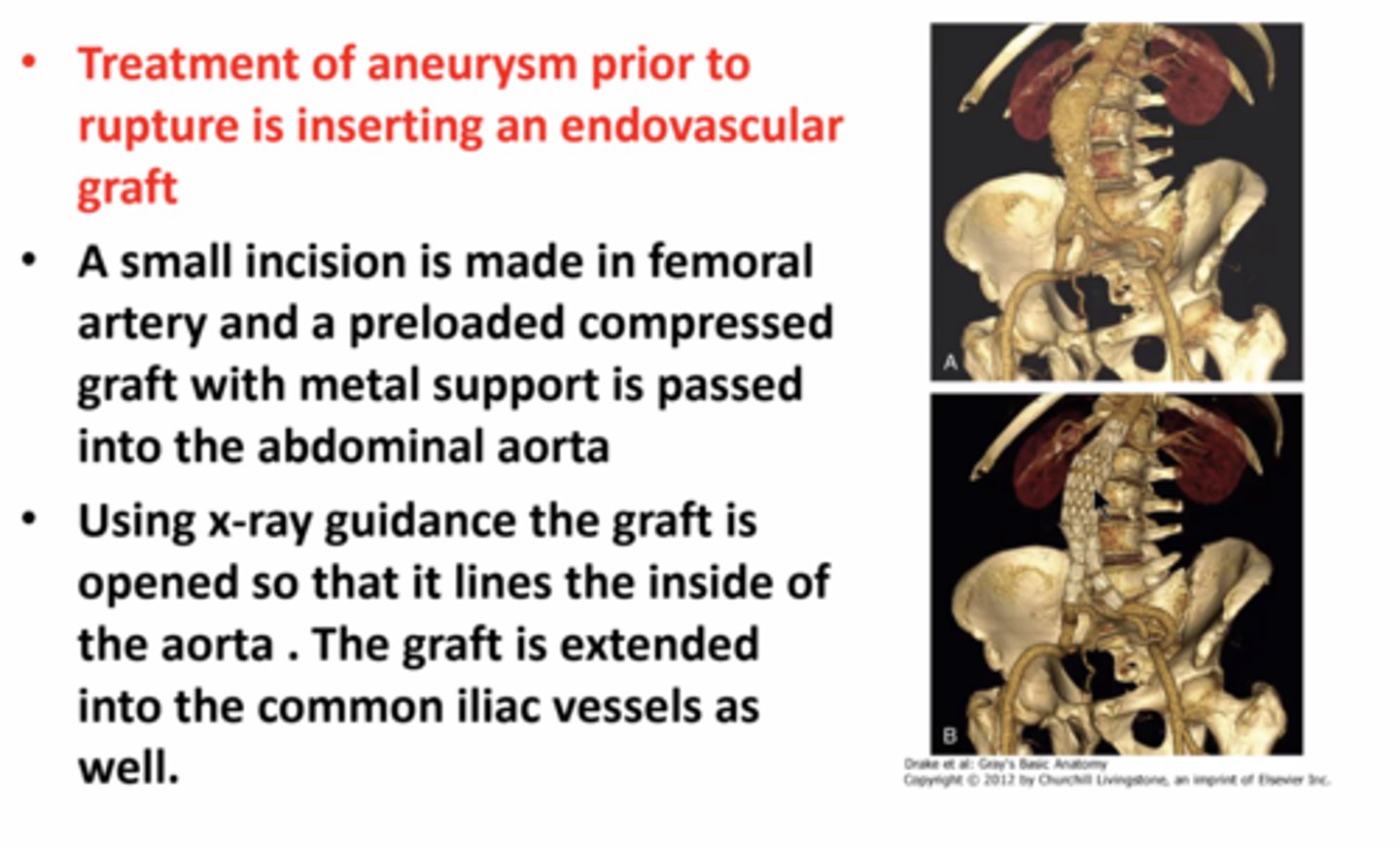
abdominal aortic stent graft
• an abdominal aortic aneurysm is a dilatation of the aorta and generally occurs in the infrarenal region (the region at or below the renal arteries)
treatment prior to rupture of the aorta -
• surgically dissecting the femoral artery below the inguinal ligament; preloaded compressed graft with metal support is passed on a large catheter in the abdominal aorta using the femoral artery. it is fitted inside the aorta and then attachments are made to the graft that extends into the common iliac vessels.
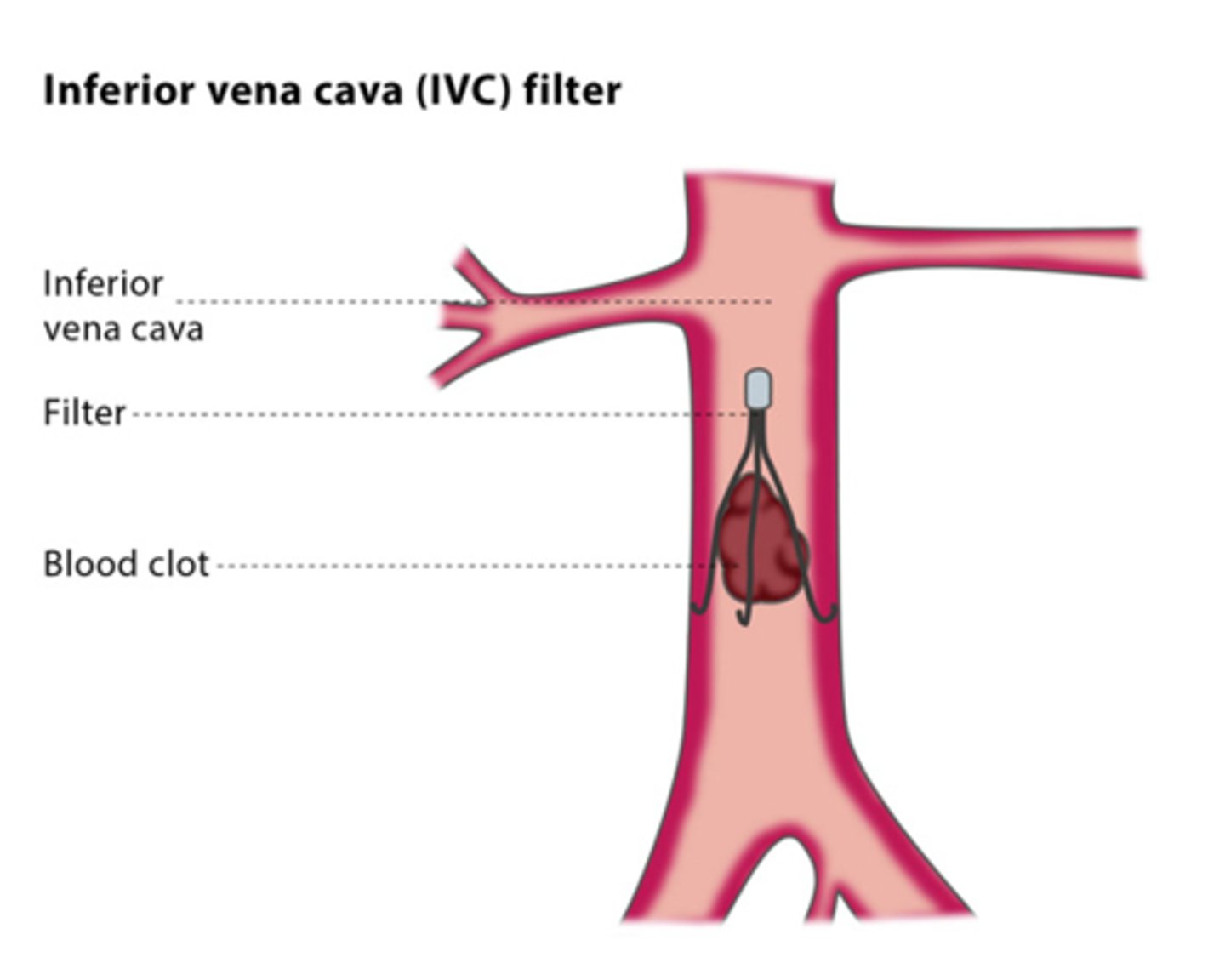
inferior vena cava filter
deep vein thrombosis is a potentially fatal condition where a clot (thrombus) is formed in the deep venous system of the legs and the veins of the pelvis
predispositions: hospitalization, surgery, oral contraceptives, smoking, air travel, clotting abnormalities (e.g., protein S and protein C deficiencies)
• inferior vena cava filter is placed to trap any large clots and removed after the risk period has ended if it is not possible to treat pt with prophylactic treatment
psoas muscle abscess
• in certain types of infections, the intervertebral disc is affected (e.g., tuberculosis and salmonella disci tis)
• as the infection progresses, it spreads anterolaterally and passes into the posts muscle sheath
• the infection spreads inferiorly in the sheath and may appear below the inguinal ligament as a mass
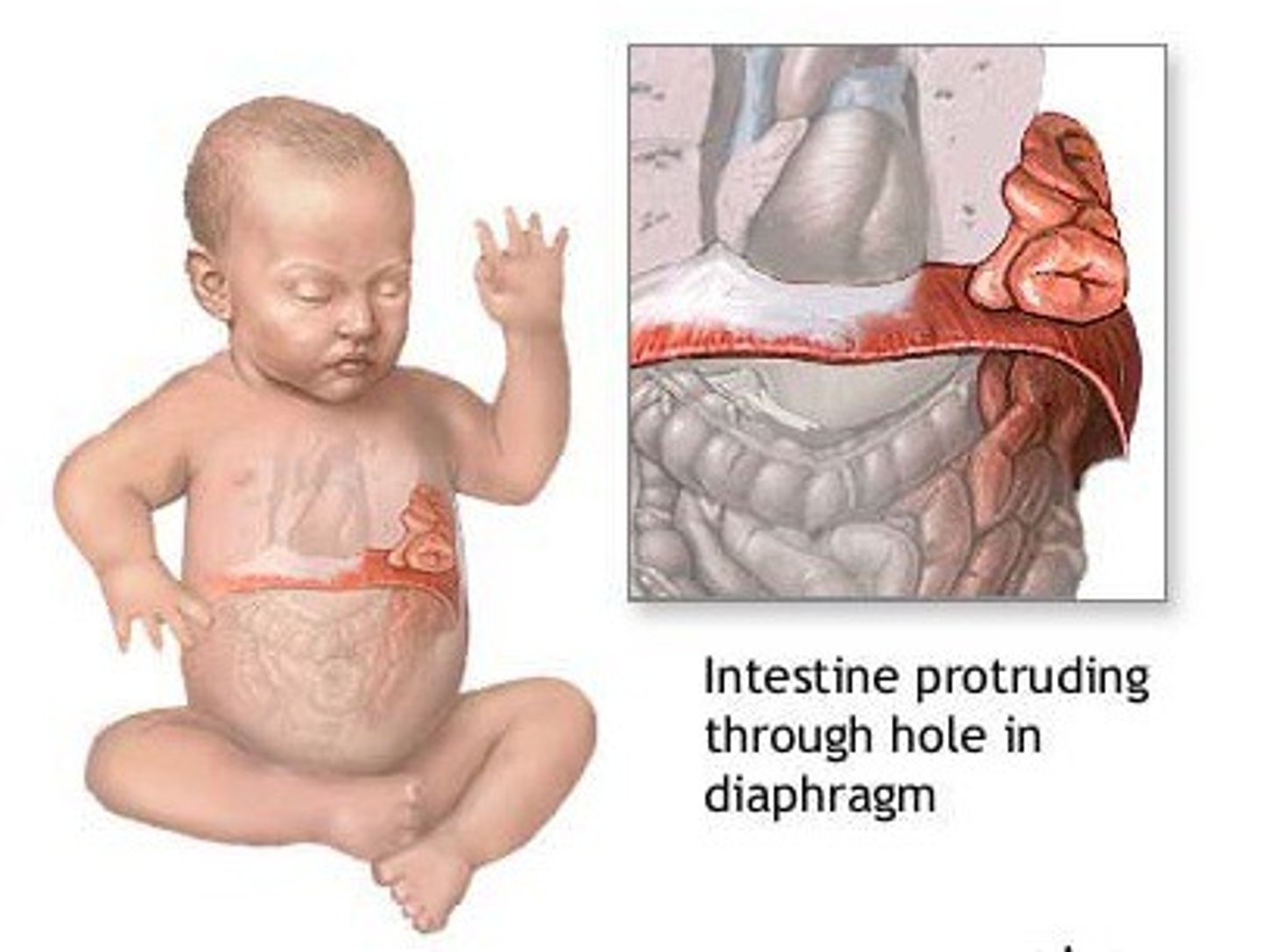
diaphragmatic hernias
embryological fusion of the various components of the diaphragm may fail, and hernias may occur through the failed points of fusion
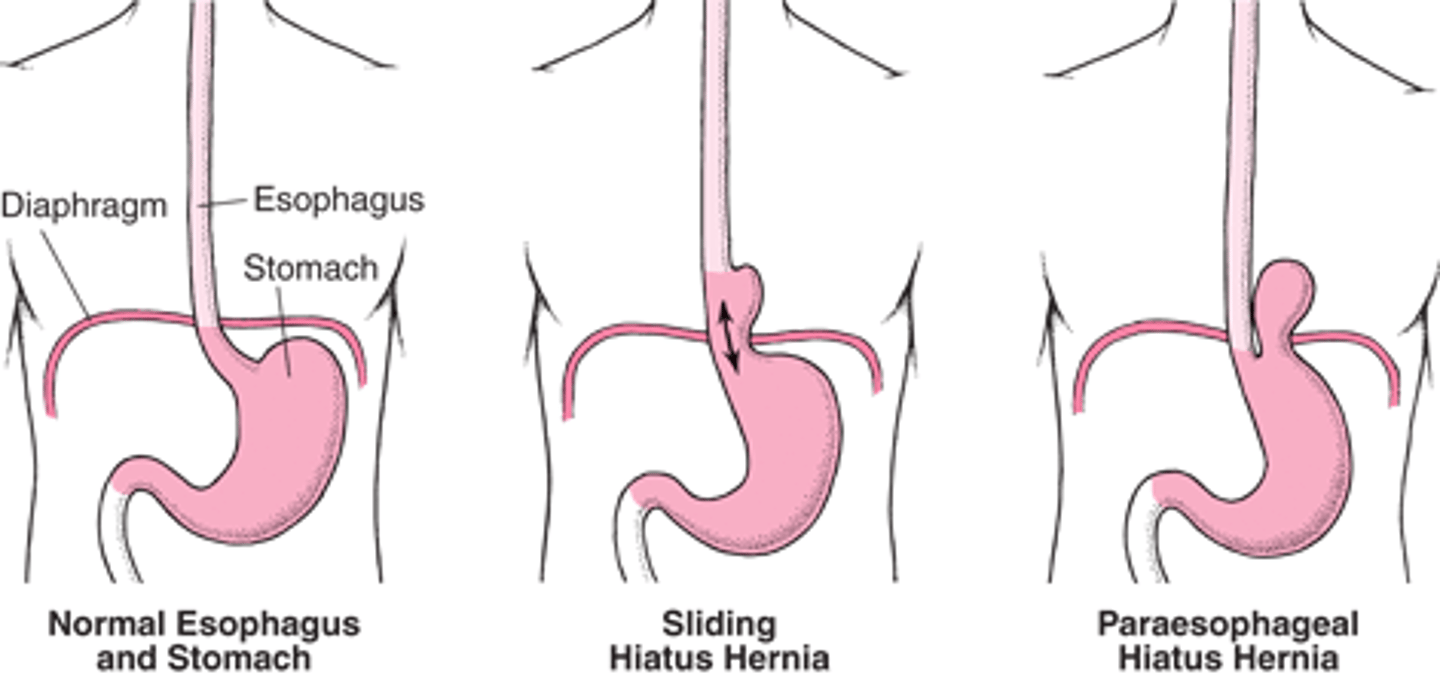
hiatal hernia
at the level of the esophageal hiatus, the diaphragm may be lax, allowing the funds of the stomach to herniate into the posterior mediastinum
• typically causes symptoms of acid reflux
• ulceration may occur and may produce bleeding and anemia