Option unit B Geo
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
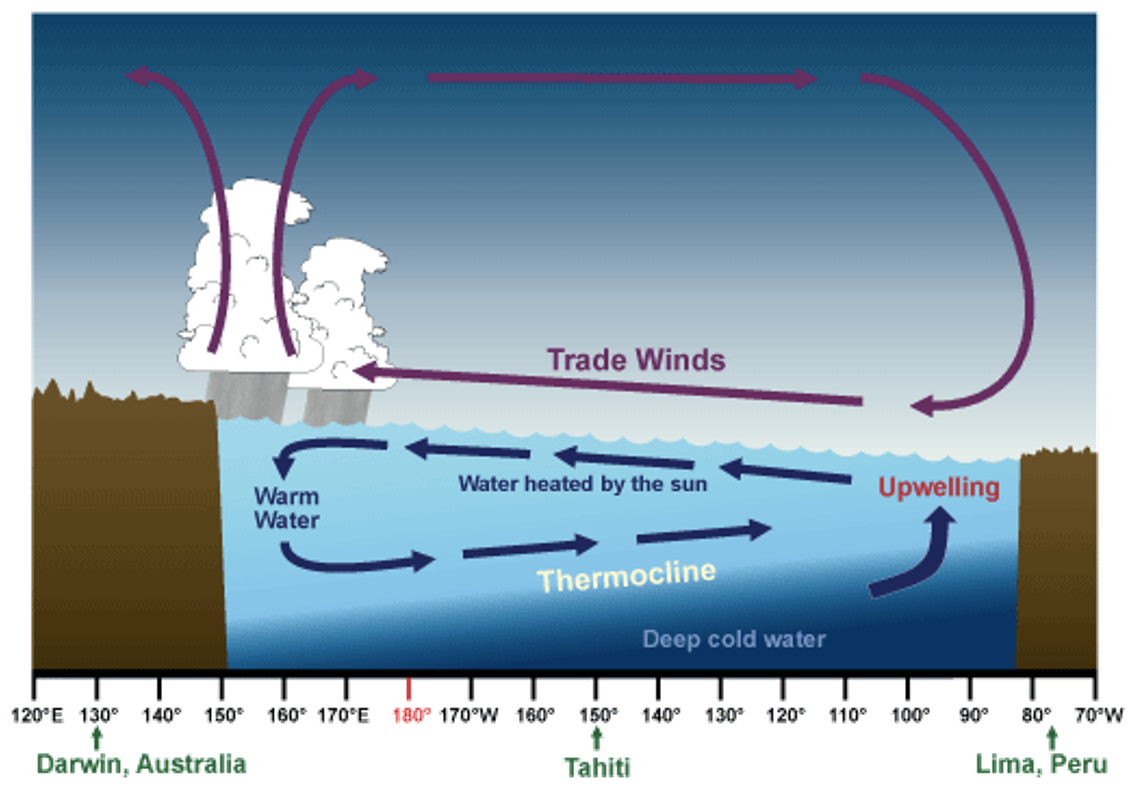
upwelling of cold, nutrient rich water from deeper levels off the northwest coast of South America
sea surface temperature is about 8°C higher in the Western Pacific than the waters off South America
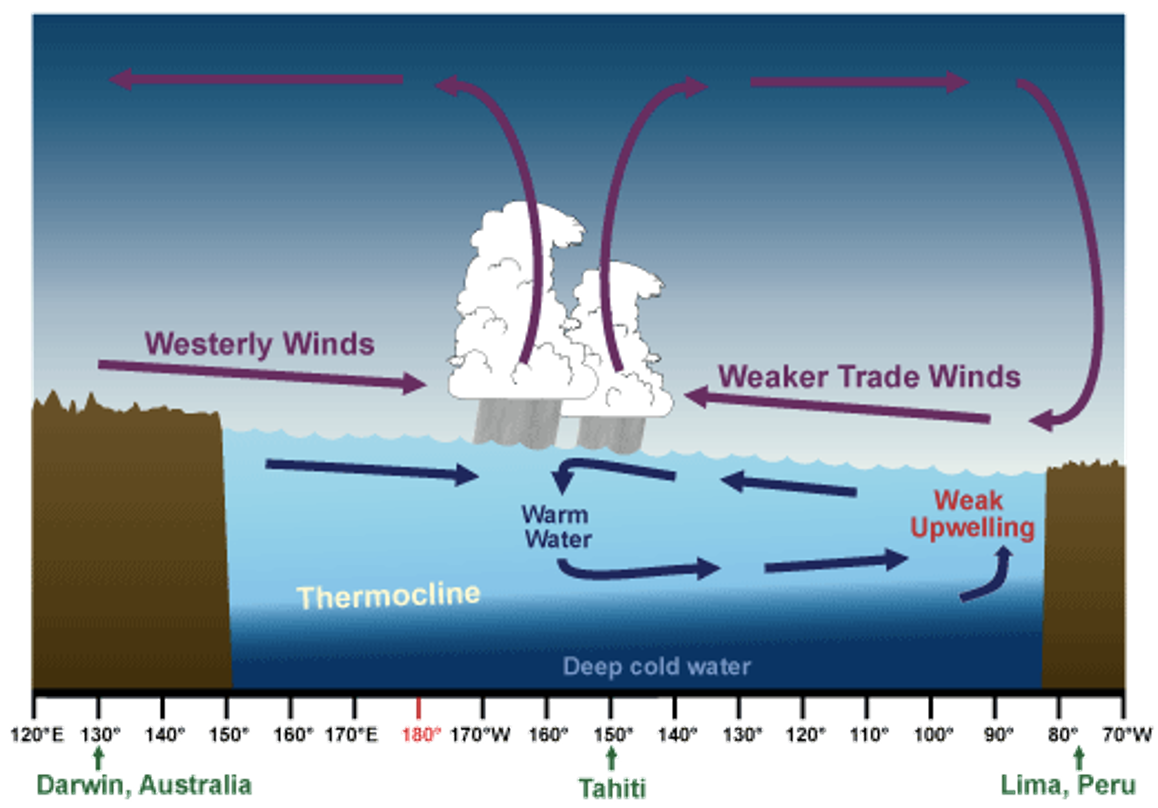
•The trade winds decrease in strength when the air pressure patterns in the South Pacific are reversed
Normal flow of water away from South America decreases . This pushes the thermocline deeper and decreases upwelling
The sea surface temperature increases *to greater than normal (~3 degrees)* in the Eastern Pacific
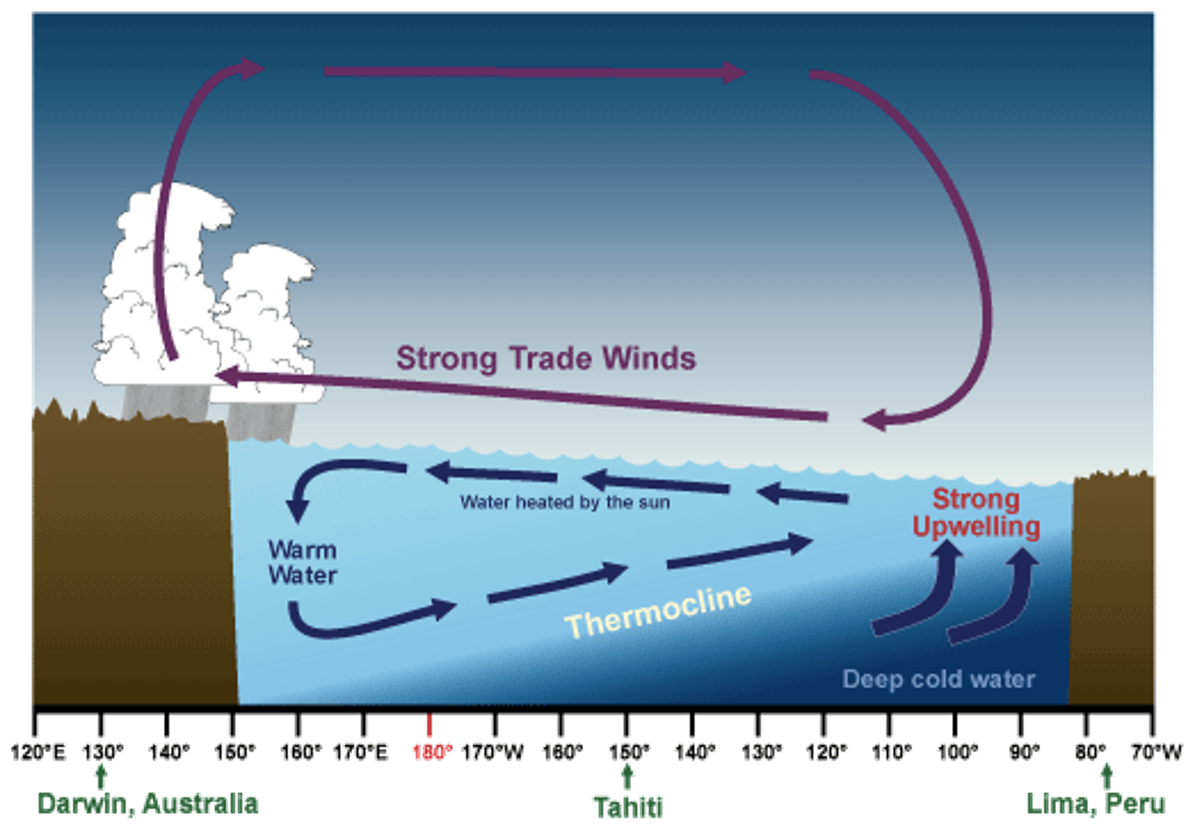
•The trade winds that blow west across the tropical Pacific are stronger than normal
Increased upwelling off South America and hence the *lower than normal* sea surface temperatures
The prevailing rain pattern also shifts farther west than normal
* limestone
* clay
* marl
* basalt
* schist
* gneiss
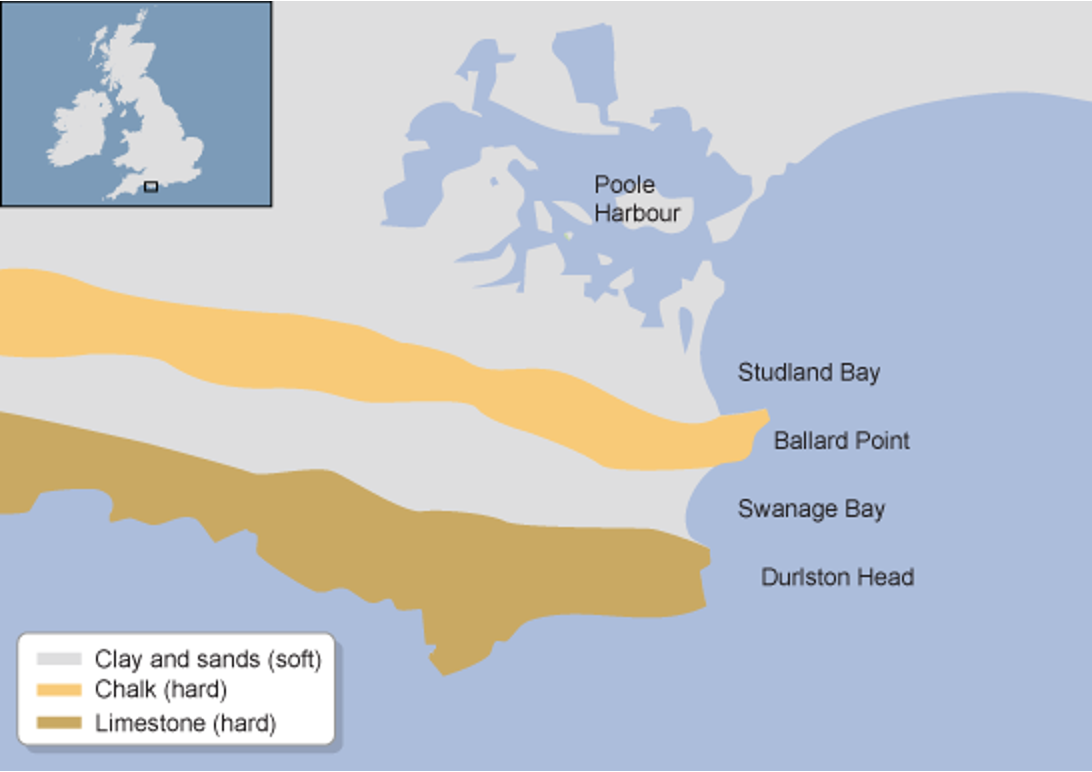
the bands of differing rock types run **parallel** to the coast.
The outer hard provides a protective barrier to erosion of the softer rocks further inland.
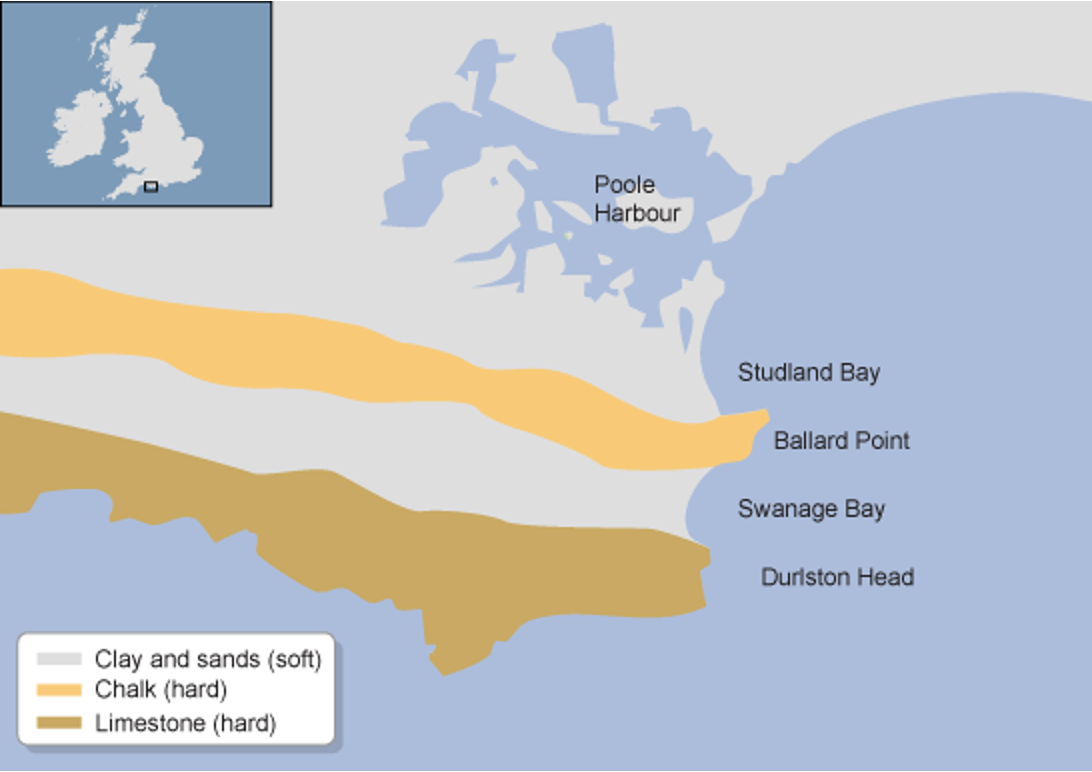
differing rock type run perpendicular to the coast.
The differing resistance to erosion leads to the formation of headlands and bays.
Weathering breaks down and loosens the surface minerals of rock so they can be transported away by agents of erosion
A natural feature of the earth's surface
hurricanes/tropical cyclones
low pressure systems that bring heavy rainfall, strong winds and high waves, and cause other hazards such as floods and mudslides
only forms in warm waters near the equator
warm air rises causing an area of lower air pressure below
hurricanes/tropical cyclones formation
air from surrounding areas with higher air pressure pushes in to the low pressure area
that “new” air becomes warm and moist and rises too
as the warm air continues to rise the surrounding air swirls in to take its place
as the warmed, moist air rises and cools off, the water in the air forms clouds. the whole system of clouds and wind spins and grows, fed by the ocean’s heat and water evaporating from the surface
impacts of hurricanes
hurricane classification using the saffir-simpson scale
tropical cyclones usually weaken when they hit land, because they are no longer being “fed” by the energy from the warm ocean waters. However they often more far inland dumping many inches of rain and causing lots of wind damage before they die out completely
hurricane prediction
hurricane forecasts traditionally focused on predicting a storm’s track and intensity.
hazard mitigation
urban planning laws
emergency planning
relief operations
evacuation measures
oceanic carbon cycle
biological processes such as photosynthesis turns carbon dioxide into organic material
gradually organic carbon settles into the deep ocean
the upper ocean therefore has a lower concentration of carbon than the deep ocean
if carbon on the ocean floor was lifted to the surface (as in a thermohaline circulation) the ocean could become a source of CO2 rather than a sink
ocean acidification
poses a threat to shell forming organisms like corals and calcifying plankton, because in a more acidic ocean these creatures will not be able to create their shells and grow
lithology
the type of rock that makes up the coastal materials
geological structure
the disposition and nature of the materials in the coast