Sports Kinesiology Movement Vocab
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
anatomical position
the upright position of the body with the face directed forward, the arms at the side, and the palms of the hands facing forwards
adduction
moving a part toward the midline of the body
abduction
moving a part away from the midline of the body
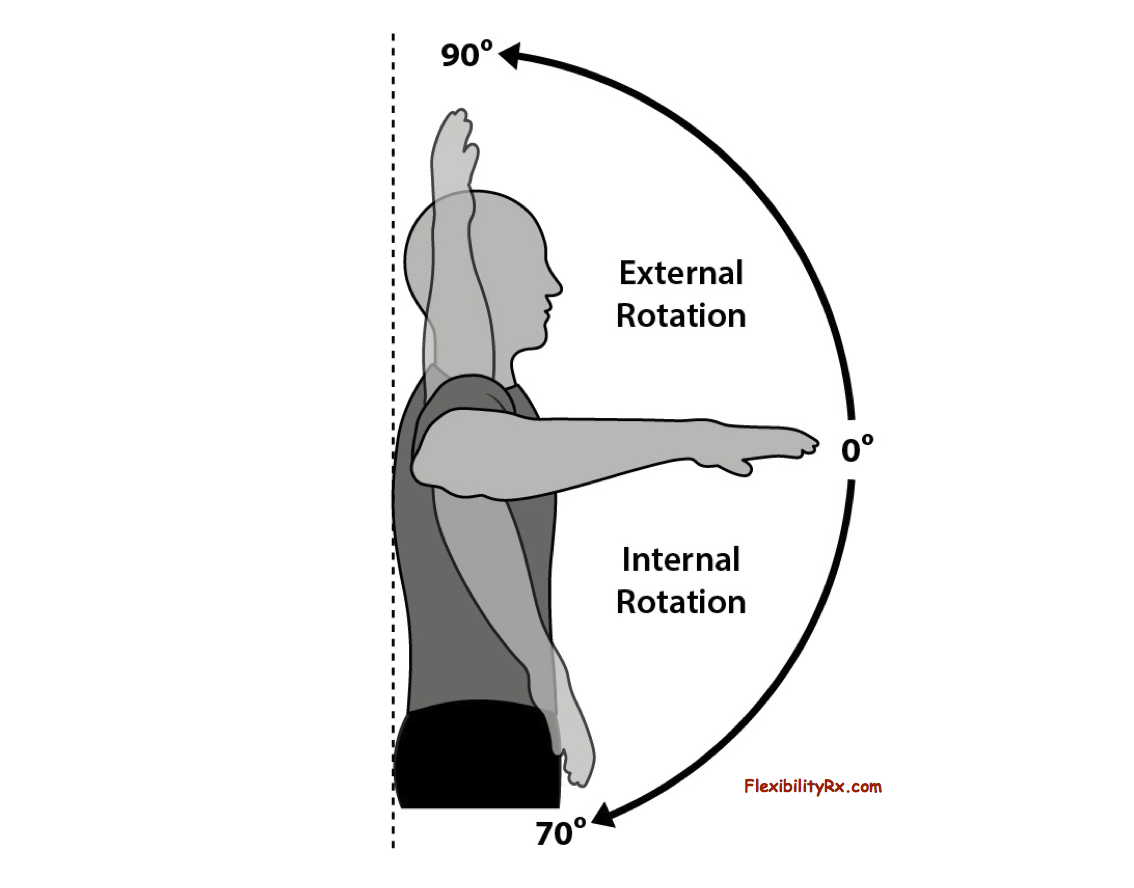
internal rotation
turning a part on a single axis while bringing the anterior surface toward the midline
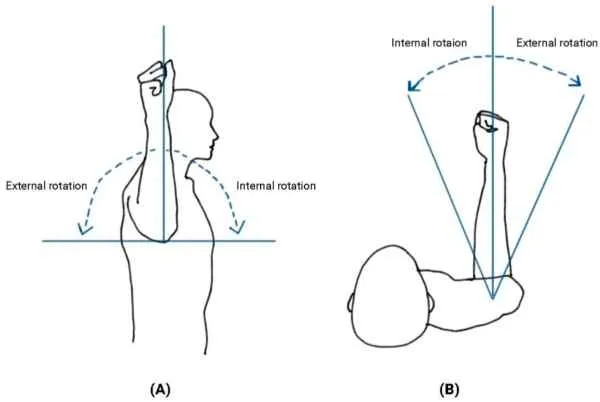
external rotation
turning a part on a single axis while bringing the anterior surface away from the midline
circumduction
following a circular path
flexion
bending a part (decreasing the angle)
extension
extending a part (increasing the angle)
hyperextension
going beyond anatomical position (past extension)
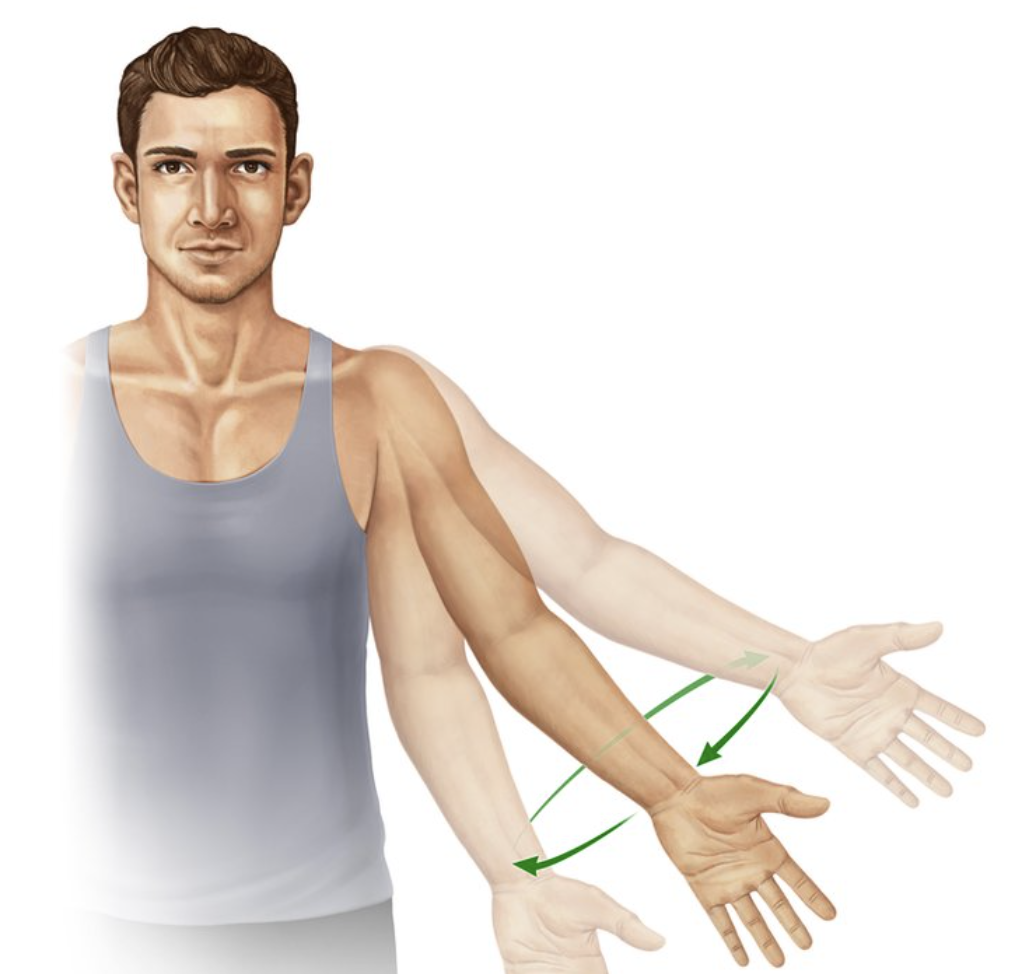
supination
turning the hand anteriorly (toward the front) (movement occurs at the wrist joint)
pronation
turning that hand posteriorly (toward the back) (movement occurs at the wrist joint)
dorsiflexion
bringing the toes toward the shin
plantar flexion
pointing the toes downward
retraction
moving a body part on the transverse plane backward
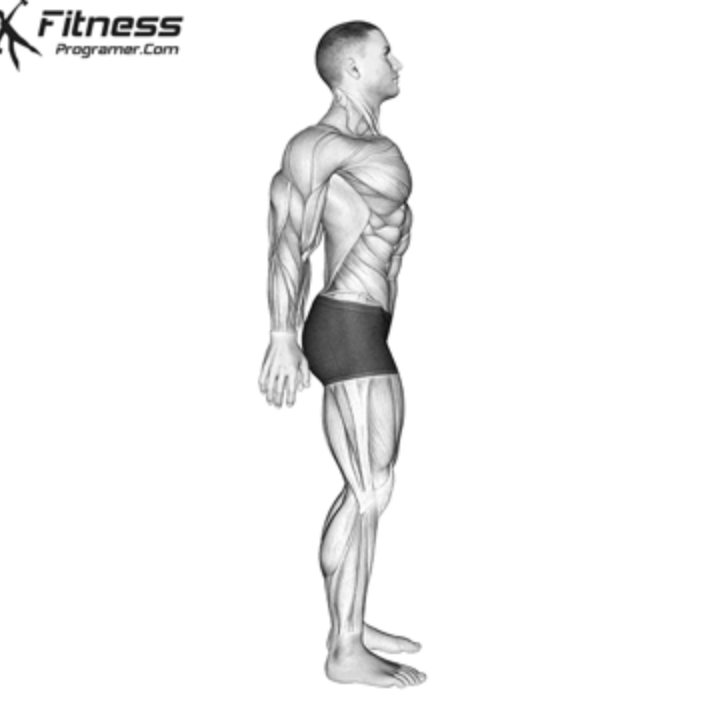

protraction
moving a body part on the transverse plane forward
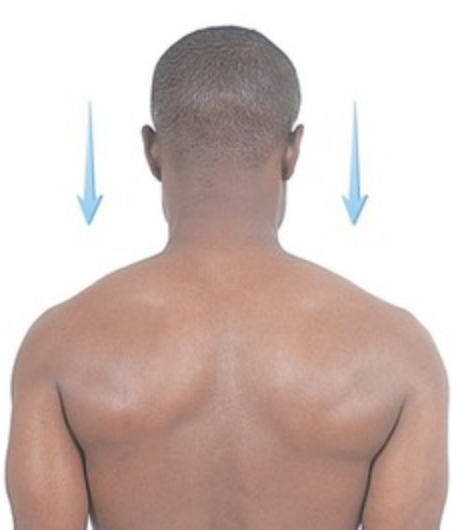
depression
moving a body part on the frontal plane downward
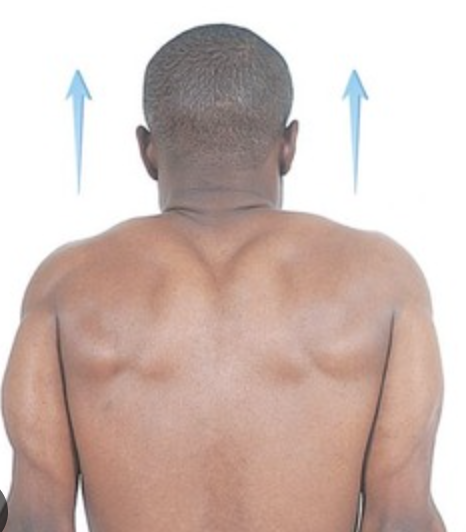
elevation
moving a body part on the transverse plane upward
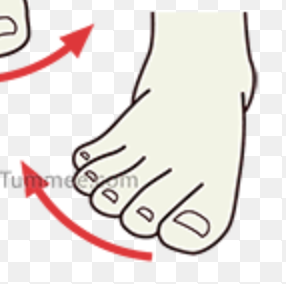
eversion
turning the sole of the foot outward
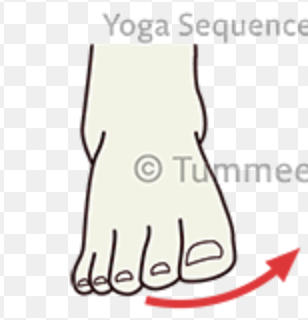
inversion
turning the sole of the foot inward
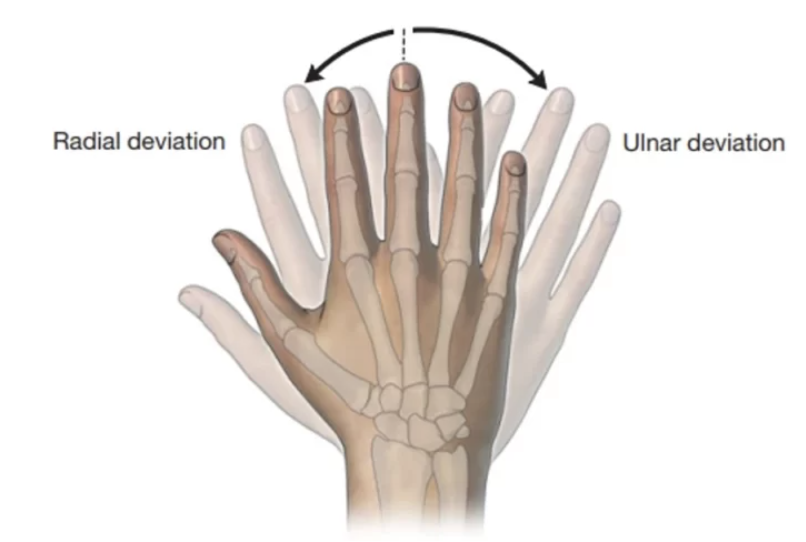
radial deviation
bending the wrist toward the radius
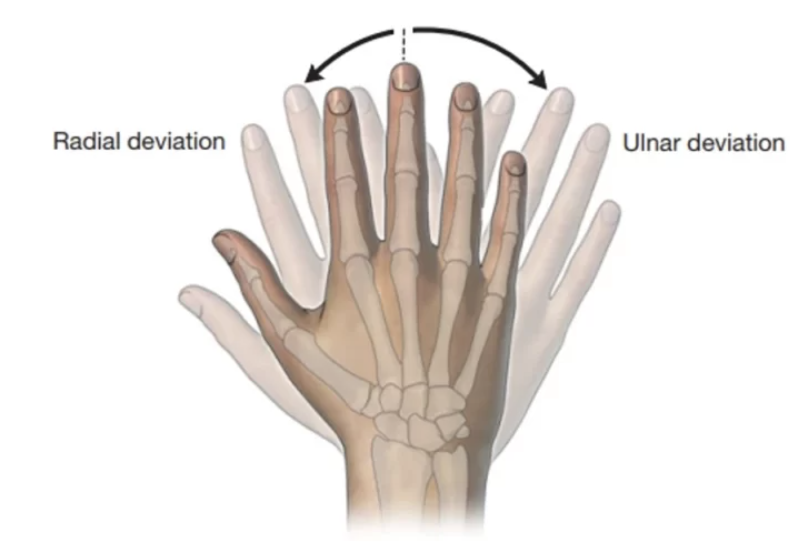
ulnar deviation
bending the wrist toward the radius
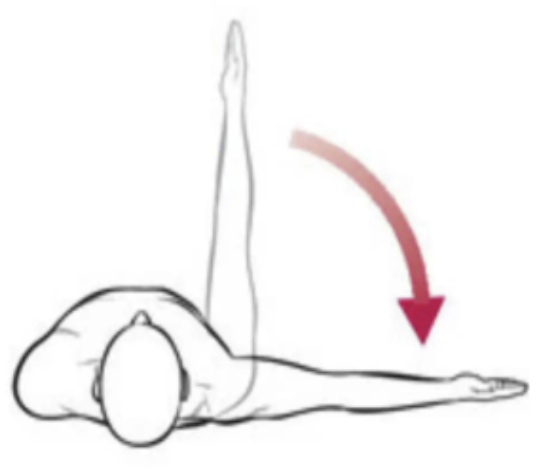
horizontal abduction
movement of the arm horizontally away from the body
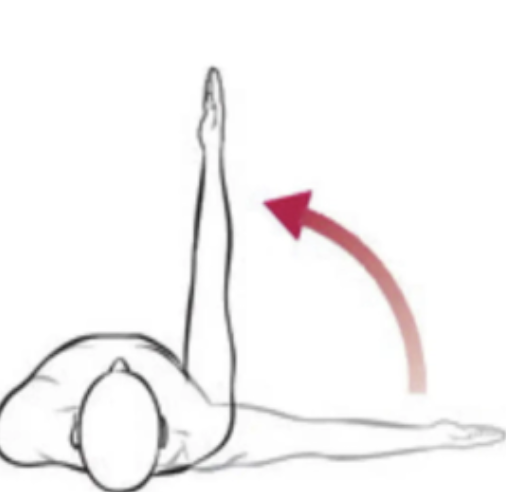
lateral flexion
bending side to side on the frontal plane
horizontal adduction
movement of the arms horizontally toward the body
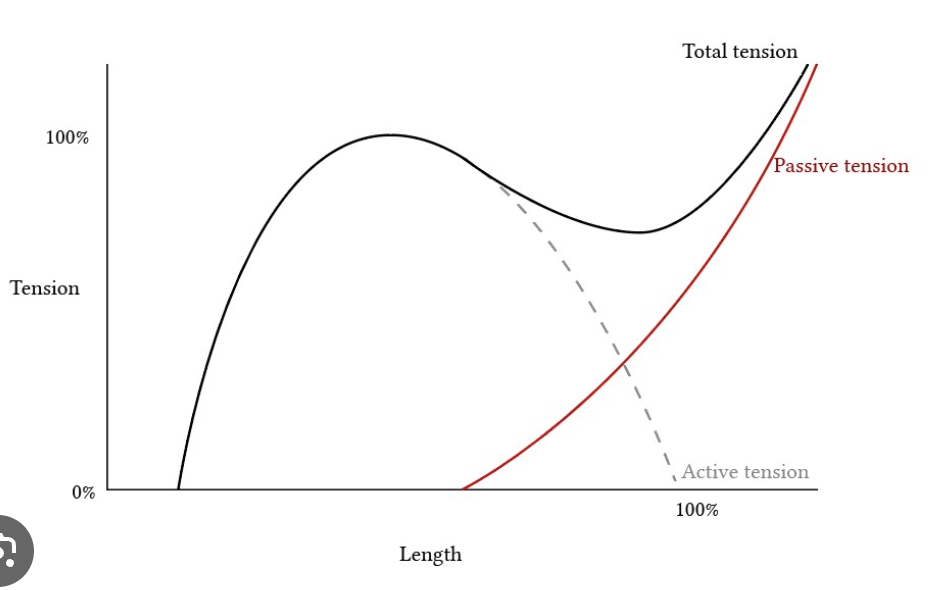
Tension vs. Length graph (for muscles)
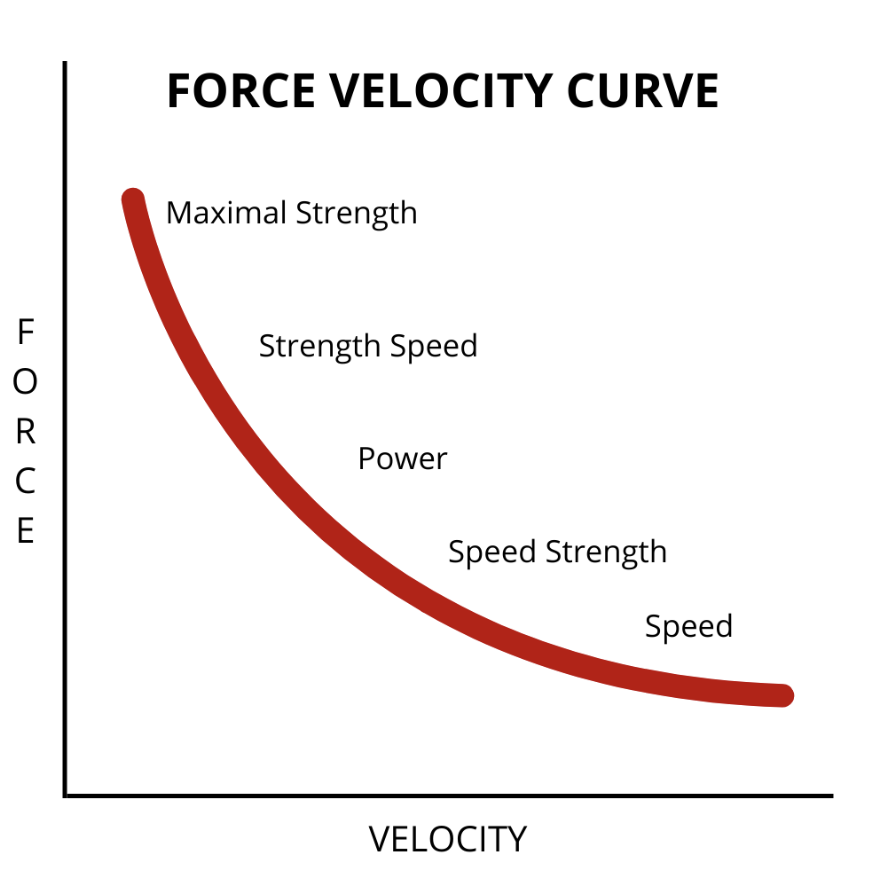
Force vs. Velocity
NASM’s OPT model (5 levels)
stability, muscular endurance, hypertrophy, strength, power
medial
relative to the midline of the body
lateral
relatively further away from the midline or toward the outside of the body
contralateral
positioned on the opposite side of the body
ipsilateral
positioned on the same side of the body
anterior
positioned on or toward the front of the body
posterior
positioned on or toward the back of the body
proximal
positioned nearest to the center of the body or other identified reference point
distal
positioned farthest from the center of the body or other identified reference point
inferior
positioned below an identified reference point
superior
positioned above an identified reference point
transverse plane
upper and lower halves
sagittal plane
left and right
frontal plane
front and back
ROM
range of motion
concentric
(+) bending movement
isometric
staying in bent position
eccentric
(-) going back to anatomical position
closed kinetic-chain
hands or feet stay on the ground
open kinetic-chain
body stays grounded
muscle balance
muscles staying in equilibrium when moving