Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology (Exam 1 - Chapter 1)
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
Anatomy
The study of internal and external body structures in their physical relationships among’s body parts.
Physicology
The study of how living organisms perform their vital functions.
Gross anatomy or macroscopic anatomy
Anatomy of examing large structures
What are the different types of gross anatomy?
Surface, regional, sectional, systematic, clinical, radiographic, and developmental anatomy
What is surface anatomy? Give an example
the general form of the body’s surface, especially in relation to deeper parts.
What is regional anatomy?
Focuses on the anatomical organization of specific body areas such as the neck, head, or the trunk
What is sectional anatomy?
The study of the relationship of the body’s structure of examining cross sections of tissues.
What is systematic anatomy?
The study of the structure of an organ system. An example would be the looking specifically at the cardiovascular system.
What is clinical anatomy?
Sub specialities in a clinical practices. An example would be pathology.
What is developmental anatomy?
Describes the changes in forms that take place form fertilization until adulthood. An example of this would be embryology.
What is cytology?
The study of the internal structures of individual cells which ate the smallest subunits of life.
What is Histology?
the study of tissues
What are the organization of life that is focused on in anatomy? ( In order)
Cells→Tissue→Organs→ Organ System
What is the special language that is used to learn anatomical and physiological terms?
Medical terminology
How would you describe the body positioning of a body that is in anatomical position?
Body facing the anterior direction , hands are at the sides with the palms facing forward, feet shoulder- width apart and feet facing forward.
What are the major organs of the integumentary system?
Skin, hair, sweat glands, and nails
What are the functions of the integumentary system?
1. Protects against environmental hazards
2. Regulate body temperature
3. Provides sensory information
What are the major organs of the skeletal system?
bones, cartilages, associated ligaments, and bone marrow
What are the functions of the skeletal system?
1. provide support and protection for the other tissues
2. Stores calcium and oven minerals
3. Forms blood cells.
What are the major organs of the nervous system?
Brain, spinal cord, peripheral nerves, and since organs.
What are the functions of the nervous system?
Directs immediate responses to stimuli
Or moderates activities of other organ systems.
Provides and interprets sensory information about external conditions
What are the major organs for the endocrine system?
Pituitary gland, thyroid gland, pancreas, adrenal glands, gonads, and endocrine tissues and other systems
What are the functions for the endocrine system?
1.Directs long term changes in the activities of other organ systems
2.Adjust metabolic activity and energy use by the body
3. Controls many structural and functional changes during development
What are the major organs of the cardiovascular system?
heart, blood, and blood vessels
What are the functions of the cardiovascular system?
1. Distributes blood cells, water, and dissolved materials including nutrients, waste products, oxygen, and carbon dioxide
2. Distributes heat and assist in control of body temperature
What are the major organs for the lymphatic system?
Spleen, Thymus, Lymphatic vessels, lymphatic nodes, and tonsils
What are the functions of the lymphatic system?
1.Defends against infection and disease
2. Returns tissue and fluids to the bloodstream
What are the major functions of the respiratory system?
Nasal cavities, sinuses, larynx, trachea, bronchi, lungs, alveoli
What are the major functions of the respiratory system?
1.Delivers heir to the alveoli (sites in the lungs where gas exchange occurs)
2. Provides oxygen to the bloodstream
3. Remove carbon dioxide from the bloodstream
4. Produces sounds for communication
What are the major organs for the digestive system?
teeth, tongue, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestines, large intestines, liver, gallbladder, and pancreas
What are the functions of the digestive system?
1.Processes and digest food number
2. Absorbs and conserves water number
3. Absorbs nutrients
4. Stores energy
How would you describe the body in supine position?
Body laying faced up
How would you describle a body in prone position?
Body laying faced down (think of face planting)
What are abdominal pelvic quadrants?
Four quadrants that are formed by two perpendicular lines that intersect at the navel also known as the umbilicus
What are the four abdominopelvic quadrants?
Right upper quadrant, left upper quadrant, right, lower quadrant, and left lower quadrant
What does the abdominopelvic regions give insight to?
The relationship among quadrant regions, and internal organs
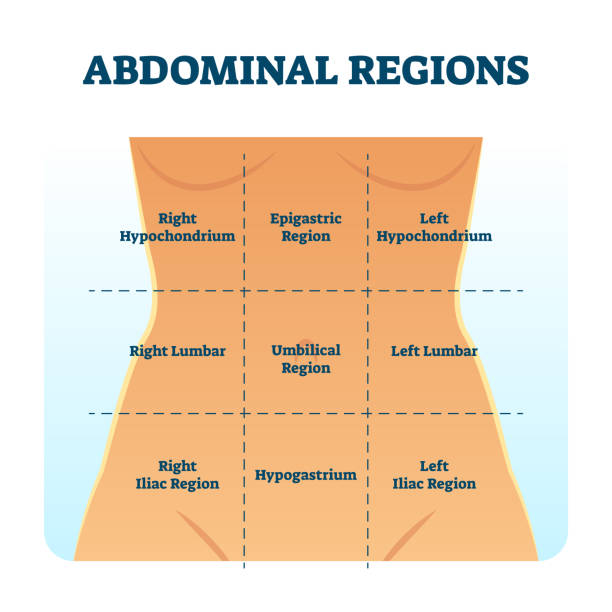
What are the nine abdominal pelvic regions?
Right hypochondriac region, epigastric region, left hypochondriac region, right lumbar region, umbilical region, left lumbar region, right inguinal region, hypogastric (pubic region), and left inguinal region.
What is the anterior view or ventral of the body referring to?
The frontal plane of the body
What is the posterior or dorsal view refer to?
The back of the body
What is the proximal direction referring to?
toward the point of attachment of a limb to the trunk
What is the later direction referring to?
away from the midline
What the medial direction referring?
toward of the midline
What direction is distal referring to?
away from the point of attachment of limb to the trunk.
What is cranial or cephalic?
toward the head
What is caudal?
towards the tail
What is superficial referring to?
At, near, or relatively close to the body surface
What is deep referring?
toward the inferior of body; farther from the surface
What is frontal (coronal) plane?
vertical plane that divides the body and organs into anterior and posterior portions
What is the sagittal plane?
vertical plane that divides the body from left to right portions
What is the midsagittal plane?
vertical plane divided the body in equal left and right parts
What are the parasagittal planes?
vertical planes divide the body in unequal left and right parts
What is a transverse plane?
horizontal plane that divides the body from superior to inferior
What three major regions in established by the body wall?
thoracic, abdominal, and pelvic
What are pleural cavities?
found in the thoracic cavity surround in the lungs
What is the pleura?
a serous membrane lining the pleural cavity that reduces friction as the lungs expand
What is the viscera pleura?
serous membrane in the pleural cavity that cover the outer surfaces of the lungs
What is parietal pleura?
Covers the mediastinal surface and the inner body wall.
What is the pericardium cavity?
found in the thoracic cavity surrounding the heart
What is the mediastinum?
found in the thoracic cavity a large tissue mass
What does the mediastinum contain?
the pericardial cavity
What is the pericardial cavity
a small chamber that surrounds the heart.
What is the peritoneal cavity?
surrounding the abdominal organs and extends in the pelvic cavity
What is the abdominal cavity?
extends from the diaphragm to the level of the superior margins of the pelvis
What is retroperitoneal?
Organs that are said to be behind the abdominal cavity such as the kidneys and pancreas.
What is the diaphragm?
flat muscular sheet that separates the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavity.
What is the pelvic cavity?
inferior to the abdominal cavity
What is the function of body cavities?
(1) protects the organs from impact and shook
(2) prevents significant change in shape and size
What i is intraperitoneal? (“infra”-below)
Refers to organs that extend toward the bottom of the pelvic cavity which includes the uterus and urinary bladder.
What is homeostasis?
Psychological processes that establishes a relatively stable internal environment
What is homeostatic regulation?
the adjustment of a psychological system to preserve homeostasis
What are the two mechanisms of homeostatic regulation?
Autoregulation and extrinsic regulation
What is auto regulation?
a process that occurs when a cell, tissue, organ, or organ system adjust in response to some environmental change. For example, when the oxygen level decreases in a tissue, the cells release chemicals that widen, or delete, blood vessels. This dilation increases the blood flow and provides more oxygen to the region.
What is extrinsic regulation?
A process that results from the activities of the nervous system or endocrine system. These organ systems detect an environmental change and send an electrical signal (nervous system) or chemical messenger (endocrine system) to control or adjust the activities of another or many other systems simultaneously. For example, during exercise, the nervous system issues commands that increase heart rate so that the blood circulates faster. The nervous system also causes blood flow to be reduced to less active organs, such as the digestive tract. The oxygen in circulating blood is then available to the active muscles, which need it most
According to homeostatic regulation what is a receptor?
A sensor that is sensitive to a particular stimulus for environmental change.
According to the homeostatic regulation what is a control center?
receives and processes the information supplied by the receptor and sends out commands.
According to the homeostatic regulation, what is an effector?
a cell or organ that responds to the commands of the control center and whose activity either opposes or enhances stimulus.
What is negative feedback?
a way of counteracting a change, is the control of body temperature, a process called thermoregulation
What is positive feedback?
an initial stimulus produces a response that amplifies or enhances the original change in condition, rather than opposing it.
What is positive feedback loop?
an escalating cycle