NURS 344- exam ii (copy)
1/214
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
215 Terms
rights to medication administration:
Right client
Right medication
Right dose
Right route
Right time
Right documentation
Other rights (assessment, evaluation, refusal, education
Maslow: The five categories are
1. psychological
safety
love and belonging
esteem
self-actualization.
Nurses routinely use Maslow’s hierarchy of needs in prioritizing nursing tasks from the most important to the least important, thereby ensuring they deliver safe and effective care.
keratinocytes—
cells formed in the basal layer of the skin that function to protect the skin from water loss, pathogens, and injury.
Karens protect from injury
Langerhans
cells ingest and package foreign antigens to be presented to lymphocytes, which then trigger an immune response in the epidermis.
Langerhans is like Luis, packages things
maceration
(an irritation of the epidermis caused by moisture)
M for M
dermatitis
a red skin irritation that develops when the skin is exposed to irritants such as feces, urine, stoma effluent, and wound secretions
skin tears
loss of top layer of the skin caused by mechanical forces) and tissue trauma
Lacerations
tears in the skin, which are usually caused by blunt or sharp object
Surgical Incisions:
The incision appears red on days 1 to 4, changes to bright pink on days 5 to 14, and then appears pale pink from day 15 to 1 year after the procedure.
Edema and exudate (fluid consisting of plasma that is secreted by the body during the inflammatory phase of healing) should progressively decrease and resolve by postoperative day 5
The nurse is receiving change of shift report on a group of clients. If you were the nurse in this scenario, which of the following clients would you see first?
a. Nancy Jones, who has an infiltrated IV line and has an IV medication scheduled
b. Justin Foster, who requested pain medication that has not yet been administered
c. Anna Chen, who requested assistance to the bathroom and an AP was notified
d. Lenny Williams, who reports pain in his calf and has localized redness of the area.
d. Lenny Williams, who reports pain in his calf and has localized redness of the area.
A nurse is assisting with mass-casualty triage of clients following a gas explosion. Which of the following clients should the nurse recommend for priority treatment?
a. A client who is unable to walk, has burns on both legs, and reports hurting too much to move
b. A client who has a metal rod penetrating the forearm
c. A client who has a small laceration on his forehead, and is walking around aimlessly
d. A client who has no spontaneous breathing
a. A client who is unable to walk, has burns on both legs, and reports hurting too much to move
Serous
thin, watery wound drainage
Serosanguineous-
Thin, watery wound drainage mixed with blood.
Sanguineous
Bloody wound drainage.
Purulent
Green/yellow wound drainage.
Occipital pressure injuries due to tightly braided hair can lead to scarring, alopecia, and permanent hair loss.
The most frequently seen risk factors are immobility, malnutrition (a condition in which there is a nutritional deficit), reduced perfusion, altered sensation, and decreased level of consciousness
But, the CAUSE OF PRESSURE INJURIES is DECREASED CIRCULATION
Braden: The lower the overall score the client receives, the greater the risk the client has for alterations in skin and tissue integrity.
Tom Braden is low
The skin is intact with a localized area of non-blanchable erythema.
Stage 1 Pressure Injury
Partial-thickness skin loss, with pink or red viable tissue in the wound bed. The tissue is moist, and deeper tissues are not visible.
Stage 2 pressure injuries
there is full-thickness skin loss with visible adipose tissue.
Unndermining and tunneling may also be present.
stage 3 pressure injury
full-thickness tissue loss. The fascia, muscles, tendons, ligaments, cartilage, and/or bone are visible.
Stage 4 pressure injuries
collagenase, papain (papaya extract), and bromelain (pineapple extract), can be applied to wounds to clear dead tissue and debris
The larvae of the green bottle fly and the Australian sheep blowfly secrete an enzyme that liquifies necrotic tissue
Sterile dressings are applied after surgery and are usually kept on the incision site for 24 to 48 hours.
After 48 hours, wounds are managed using clean technique during dressing changes, as the wound is considered to be colonized from the client’s environment.

Gauze bandages are considered open dressings. After being moistened with 0.9% sodium chloride, gauze dressings are used to pack wounds to assist with the debridement process. This type of dressing is called a wet-to-dry dressing. As the gauze dries, it clings to tissue inside the wound.
The downside of this type of dressing is that not only necrotic tissue is removed, but also new, healthy granulation tissue
Semi-open dressings have three layers. The bottom layer comprises a layer of knit gauze that is more closely woven than traditional gauze; it is infused with therapeutic ointments. The middle layer contains padding and absorbent gauze, which is followed by a final layer of adhesive. Semi-open dressings do not control drainage well and place the client at risk for poor wound healing and breakdown of tissue adjacent to the wound.
Self-adhesive transparent dressings are used for covering superficial wounds that have minimal exudate
allow moisture to evaporate while still maintaining a moist wound bed
promote wound healing and decrease the risk of wound infection
when placed over wounds with significant amounts of exudate, leakage can occur, causing skin maceration and injury to the epidermal layer
Hydrocolloids are used for small abrasions, superficial burns, pressure injuries, and postoperative wounds. Like pimple stickers
When placed over wounds, these gel-like dressings occlude the wound, maintain a moist wound bed, have bacteriostatic properties, and stimulate the growth of new granulation tissue. Hydrocolloid dressings are comfortable and produce less maceration.
Disadvantages include their potential to cause contact dermatitis and the foul-smelling, yellow, gelatinous film that develops as bacteria are trapped on the underside of the dressing.
Alginate dressings are recommended for moderate to highly exudative wounds. These dressings provide hemostasis, have high absorptive abilities, and can remain in a wound for several days, so they require less frequent dressing changes.
Used for moderate and highly exudative wounds, hydrofiber dressings provide high absorbency and can stay in the wound for several days. These dressings draw less fluid from the wound edges, resulting in less maceration around the wound compared to alginate dressings.
Foams are used in wounds with mild to moderate exudate, but require more frequent dressing changes as compared to those dressings previously discussed. According to Blagrove, the application of a silicone-foam dressing to the client's sacrum within 24 hr of admission reduces and prevents hospital-acquired pressure injuries (HAPIs). Foam dressings may produce a malodorous discharge.
Polymeric membranes are used in mildly exudative wounds. These dressings stimulate the growth of new epithelium and do not stick to the wound bed, resulting in less trauma to the new granulation tissue.
Hydrogels are available in gel or sheet form. Hydrogels can be used to manage dry wounds for debridement of necrotized tissue and eschar. They work differently than other dressings because they contain water, to provide moisture to or draw moisture away from the wound depending on the needs of the wound. Hydrogels have a soothing or cooling effect and cause little trauma to the wound bed.
Iodine is an antiseptic that cleanses the wound. Honey can be used to manage or prevent wound infection, and decrease the odor of wounds.
Honey has anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties.
Silver is effective on moist wounds with exudate or wounds with infection to attack bacteria.
Clients should be assessed for allergies to iodine or bee stings before using iodine or honey dressings.
During primary closure, a surgeon applies either sutures or staples to the edges of the acute surgical or traumatic wound. Sutures or staples can also be used for delayed primary closures, after the wound has been left open for a period of time.
Healing is also faster with a stapled wound—within 7 to 14 days, after which the staples are removed using a staple remover.
Surgical adhesives save time in terms of placement, and the wound infection rates and cosmetic look of the incisions are comparable to those achieved with other techniques. Skin adhesives form a protective waterproof covering over the wound. Skin adhesives are used for small, minor wounds and wounds that have straight edges. They are suitable for wounds on the face, head, parts of arms, legs, and torso, but are not used over joints.
The skin adhesive is applied in three to four layers, and the edges of the wound should be pressed together for at least 1 min after applying each layer. The skin adhesive glue usually peels off in 5 to 10 days.
Negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT) is used to assist in the healing and closing of large wounds by reducing edema surrounding the wound and increasing granulation tissue formation. In this therapy, a foam dressing is applied over the wound and covered by a semi-porous occlusive dressing, to which suction is applied. Suction during NPWT can be applied constantly or intermittently, depending on the wound and the client’s needs.
A portable wound bulb suction device, or bulb suction drain, is an active, closed system drain that uses negative suction to drain fluid from the wound.
The bulb should be emptied at least every 8 hours or when it is more than half-full.
An active, closed system drain that uses negative suction to drain fluid from the wound; it contains a flexible plastic bulb that is connected to a plastic drainage tube
Advise the client that while showering, water and soap should be allowed to flow gently over the drain site. The skin should be patted dry after the shower, and a new dressing placed around the drain.
Position to prevent pressure injury:
When a client is positioned on their side, tilt their body at an angle between 20° and 30° and support the client with pillows.
Correct position of the bed: Clients should be positioned in bed to minimize pressure and shearing forces by keeping the head of the bed lower than 30°
The use of emollients helps promote skin health by moisturizing the skin and decreasing the risk for development of skin tears.
a type of wound healing that occurs in clean lacerations and surgical incisions closed with skin adhesives or sutures. These wounds are the fastest to heal.
Primary healing (also called first intention)
wound healing process that takes place when the wound is left open to heal and granulation tissue forms from the bottom up in the wound bed. The healing process is prolonged, and the wound bed needs to be kept moist for proper healing to occur. The risk of infection in these wounds is much higher, as the wound bed is in direct contact with the environment.
Secondary healing (also called second intention)
comprises a combination of primary and secondary healing, in which the wound is left open for 5 to 10 days before it is closed with sutures. This technique decreases the risk of infection in wounds that were not considered clean at the time the tissue injury occurred.
Delayed primary closure (also called tertiary intention)
The hemostatic or inflammatory phase, which is sometimes separated into two distinct phases, begins the moment injury occurs and lasts 3 to 6 days. Early in this phase, blood vessels constrict, and damaged tissues release proteins that trigger the activation of various clotting factors. These actions work together to stop bleeding at the site of injury. When bleeding is controlled, histamine is released, resulting in vasodilation and increased capillary permeability. These events are important because they increase blood flow to the injury, allowing white blood cells to flood the area and clean the wound.
The proliferative phase begins 3 days after the injury and can last up to 24 days. During this phase, the blood supply to the wound continues to improve. Granulation tissue, composed of predominately fibroblasts and collagen, develops simultaneously with the new blood supply. The presence of collagen strengthens the wound, allowing it to mature and wound closure to begin. As the wound matures and closure begins, re-epithelialization occurs as the keratinocytes around the periphery of the wound begin to move into the center of the wound to cover and fill it.
The remodeling, or maturation, phase is the last phase of wound healing; it begins around day 21 and can last for more than a year. During this time, the collagen formed in the granulation tissues of the wound during the proliferative phase is replaced with a stronger collagen, aiding in wound maturation. Wound closure continues during this phase, as myofibroblasts secrete proteins that produce a contractile force pulling the wound edges together.
Antibiotic therapy is recommended only for wounds that look clinically infected. Clinical manifestations of localized infection include cellulitis, redness around the wound, skin that is warm to touch, exudate, and foul odor.
Indicators that the infection has become systemic—and that the client is at risk of developing sepsis—include fever, chills, nausea, vomiting, hypotension, high blood sugar, increased white blood cell count, and changes in mental status.
The most common causative agent of SSIs is the Staphylococcus aureus bacterium, which is commonly found in the nose and on the skin. Perioperative antiseptic solutions/cloth wipes that contain chlorhexidine gluconate/digluconate (CHG) reduces the colonization of the skin by microorganisms thus reduce the risk of developing SSI.
wound cultures are collected by using a sterile cotton applicator, needle aspiration, or tissue biopsy. To collect a wound culture using a sterile cotton applicator, the nurse should first clean the wound with 0.9% sodium chloride solution.
Dehisence-
This complication generally occurs 7 to 10 days after surgery, and often is preceded by serosanguineous
Cleansing the area helps to loosen any necrotic tissue and exposes the wound bed
If contact with the wound in required, such as needing to manipulate the wound edges, apply a sterile glove on the hand that will make contact with the wound.
Anaerobic culture:
Aspirate 5 to 10 mL of exudate from the wound with the sterile needless syringe.
Remove tbe old dressing:
Lift a corner of the dressing away from the skin with the dominant hand while gently pushing the skin away from the dressing with the nondominant hand.
· Place a layer of sterile gauze dressing over the wound or as prescribed by the provider. Extend at least 1 inch (2.5 cm) past the wound edges. This dressing can be applied with forceps if desired.
Increasing pain can be a sign of a wound infection. The nurse should assess the wound for other signs of infection, such as changes in exudate, erythema, and warmth. Elevated temperature and increased heart rate are other signs of possible infection. Notify the provider regarding changes in the wound.
An antiseptic solution is used to prepare the sterile cotton-tipped applicators to cleanse the site of the sutures or staples before removal.
When there is a lack of surfactant in the lungs, the lung tissue collapses so that there is a loss of volume during expansion; this condition is called atelectasis
Atelectasis can occur in clients for several reasons, but is most commonly observed in the setting of thoracic or abdominal surgery. Atelectasis is often due to the use of general anesthesia or opioids, which lead to slow, unproductive breathing that prevents the exchange of gases.
Ventilation
the flow of air inside or outside of the alveoli.
Lung compliance
is the point to which a lung can expand in response to increased pressure within the alveoli (interalveolar pressure)
Airway resistance
is the pressure or opposition of the tissues in the airway to the flow of air.
tidal volume.
amount of air inspired and expired with each breath
The residual volume
the amount of air remaining in the alveoli after expiration
forced vital capacity
the amount of air that can be expelled from the lungs in 1 second during forced expiration.
vital capacity.
The maximum amount of air that is expelled after maximal inspiration
total lung capacity.
The amount of air remaining in the lung after maximal inspiration is the
What happens to the mitral and tricuspid valve ?
During diastole, the mitral and tricuspid valves permit blood to flow from the atria into the relaxed ventricles. During systole, the mitral and tricuspid valves close and the aortic and pulmonic valves open.
In a healthy resting adult, expected cardiac output ranges from 4 to 6 L/min.
Extreme athletes can have a cardiac output of up to 35 L/min during exercise.
Preload-
The blood remaining in the left ventricle at the end of diastole causing it to stretch.
Afterload-
The amount of resistance or force that occurs when the heart ejects blood from the left ventricle.
Where would one find clubbing?
Where would a barrel chest be found?
Clubbing: COPD, cystic fibrosis, or lung cancer.
,A barrel chest is often observed in clients with COPD.
To assess for jugular vein distention (JVD), the client should be reclined to30° to 45° with the head turned slightly away from the examiner. Using a ruler, the jugular vein should be measured from the sternal notch to the highest point of pulsation. A measurement of greater than 1.5 inches indicates abnormal distention and indicates increased central venous pressure, which could be indicative of a cardiopulmonary condition
Crackles
caused by fluid filling the air sacs; they sound like popping and crackling. Clients with pneumonia or an infection may have crackles.
Infected and Fluidy Rice Krispies- a sac of rice krispies
Wheezing
a whistling or a musical noise that is heard on exhalation. It is caused by constricted airways. Wheezing may be heard in clients with asthma and COPD.
Rhonchi
sound like rattling and are caused by obstruction of the airway. Rhonchi may be auscultated in clients with asthma and COPD.
The rattle is obstructing justice.
Stridor
sounds much like wheezing but is caused constriction in the upper airways and is heard on inhalation. Stridor is a medical emergency. It can be caused by an inflammation of the epiglottis (epiglottitis) or by croup, a viral infection
Hypoxemia
Low amount of oxygen in the blood.
Hypoxia
- below the expected level of oxygen in body tissue
Manifestations of hypoxemia and hypoxia include confusion, irritability, restlessness, dyspnea, tachypnea, tachycardia or bradycardia, restlessness, confusion, and cyanosis.
Hyperventilation is an increase in the rate and depth of breathing.
increased amount of carbon dioxide is exhaled, leading to lower than expected levels of carbon dioxide in the blood. These low levels of carbon dioxide can cause the client’s arterial pH to increase and alkalosis to develop. Alkalosis may cause weakness, dizziness, headache, anxiety, increased heart rate, and difficulty breathing. The client may also experience numbness and tingling in the fingers.
hyperventilation include:
Anxiety attacks
Infections such as pneumonia
Lung disease such as COPD and asthma
Diabetic ketoacidosis
Brain injury
Manifestations of left-sided heart failure include
hypoxia, crackles in the lungs, and shortness of breath.
Treatment for angina pectoris
includes rest, nitroglycerin, aspirin, or drugs to prevent the formation of clots.
Nasal Cannula
Oxygen is inspired when the client inhales. Oxygen via nasal cannula can be delivered at low concentrations of 1 to 6 L/min
Disadvantage: dermatitis and nasal irritation can occur/ headaches and dry mucous membranes can occur if the flow greater than 4L/min
Simple Face Mask
Can deliver oxygen at a medium concentration
Simple: 5-10L/min
Contraindicated: clients with carbon dioxide retention
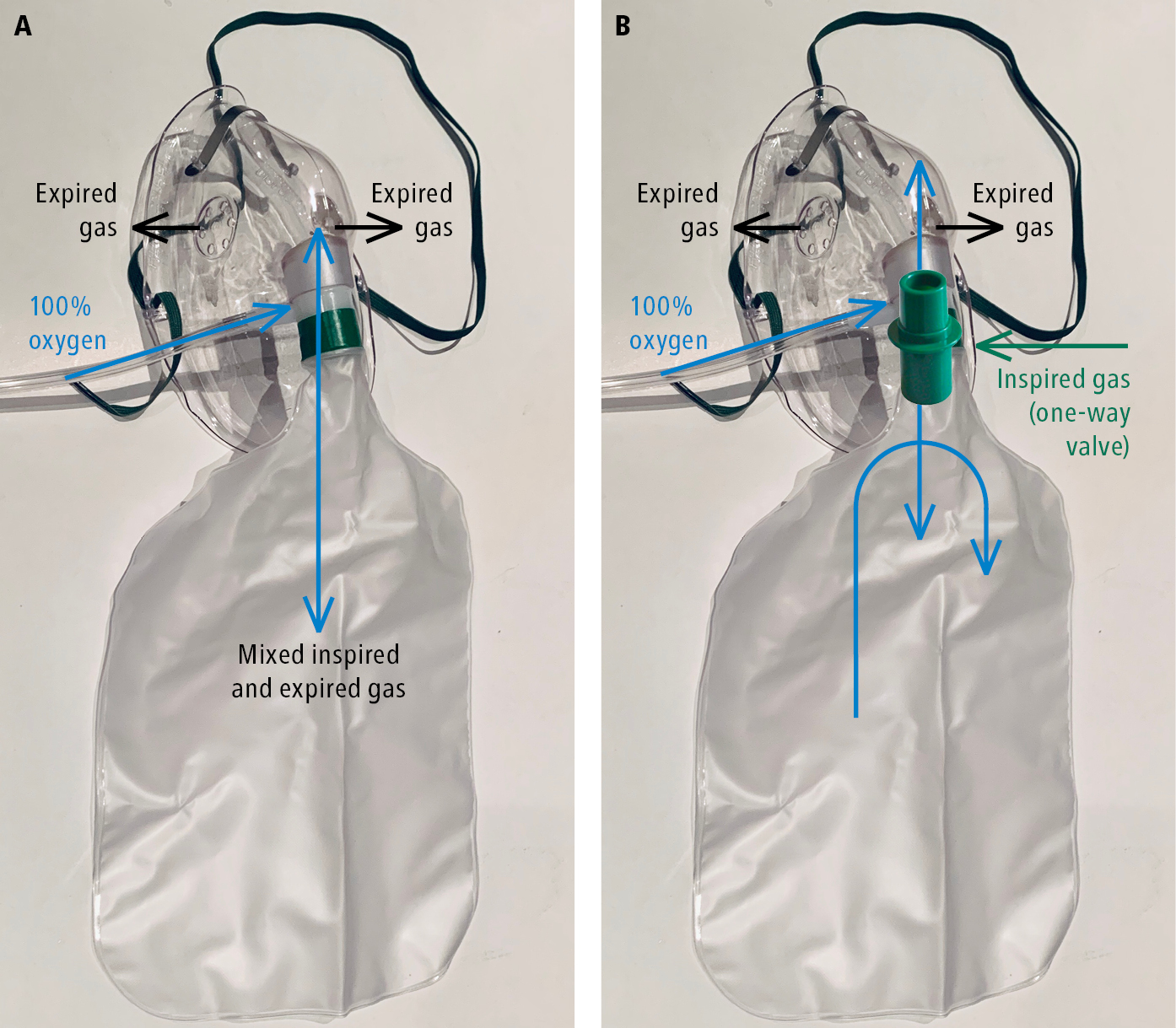
Partial
With this device, oxygen is delivered at a higher flow rate (10 to 15 L/min) and at a higher concentration (60% to 90%) compared to the simple face mask.
On inspiration, the client’s air is drawn into the holes of the mask and oxygen by the inflated bag.
On exhalation, gases are sent to the reservoir or out through the holes in the mask, and oxygen is drawn in from the inflated bag. When the client inhales again, oxygen and carbon dioxide are mixed.
Not to be used with humdification
Risk of atelectasis and oxygen therapy
Nonrebreather
valves going into the reservoir bag and holes in the mask
Nurses should ensure that the reservoir bag, which supplies the inhaled oxygen, does not completely collapse with exhalation.
oxygen can be delivered at a high flow (10 to 15 L/min)
not breathing in carbon dioxide. Nonrebreather masks are not recommended for clients with COPD or respiratory failure for long-term use due to a risk of oxygen toxicity
Not to be used with humdification
Risk of atelectasis and oxygen therapy
Venturi Mask
With this device, oxygen may be delivered at flow rates in the range of 4 to 15 L/min
Most Precise
Aerosol Mask
aerosol mask is used to administer nebulized solutions—that is, medications that are changed from a liquid form into a mist, which the client inhales
They include corticosteroids, which decrease inflammation in the lungs, and bronchodilators, which open the airways
CPAP keeps the alveoli open and improves the amount of oxygen in the client’s blood. It is used as a treatment for obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). clients with cardiopulmonary diseases such as stroke, hypertension, and CAD.
A bilevel positive airway pressure (BiPAP)
With this device, air moves through a tube into a mask that fits over the client’s nose.
BiPAP may also be required for clients who have disorders that cause muscle weakness that inhibits breathing. Thus, clients with COPD, heart failure, and sleep apnea may benefit using a BIPAP machine,
Acute toxicity affects the central nervous system (CNS). CNS manifestations may appear as twitching of the hand muscles; prolonged exposure can lead to nausea, generalized convulsions, dysphoria, and tinnitus (ringing in the ears). Aggravating factors include stress, cold, and increased carbon dioxide in the blood.
With chronic oxygen toxicity, manifestations affecting the pulmonary system include atelectasis, coughing, dyspnea, pleuritic chest pain, and heaviness substernally (Cooper et al., 2020). However, once oxygen is discontinued, symptoms lessen within 4 hours.
Prevention of oxygen toxicity includes avoiding stress, cold, or fatigue
The sputum sample needs be collected at the right time, preferably in the morning before eating or drinking, or when the client is able to produce a sample.
To collect the sample, the nurse should instruct the client to take several deep breaths to loosen the secretions and force a deep cough to move mucus from the lower respiratory tract. The client should then cough 1 to 2 teaspoons of mucus into a sterile specimen cup.
For clients with thick secretions or difficulty producing specimens, nurses may perform chest physiotherapy to promote sputum collection.
Chest physiotherapy (CPT) consists of percussion of the chest, vibration, and postural drainage.
CPT enhances the clearance of secretions from the lungs through the use of external mechanical maneuvers.
This intervention is beneficial for clients who have COPD, cystic fibrosis, or pneumonia, and for other clients who are unable to expectorate thick, copious secretions.
The result of this therapy is expansion of the alveoli within the lungs, decreased risk of infection, and strengthening of the respiratory muscles.
PT sessions usually last between 20 and 30 minutes, and are performed up to four times a day
client should be positioned supine first, then prone with the left side up at 45°, then prone with the right side up at 45°, and finally back to supine.
To perform percussion, the caregiver’s hand should be cupped, with the fingers and thumb together, and the caregiver should use a clapping motion to the back.
ercussion is not done over the ribs, the sides of the chest, or the lower back. The breastbone, lower back, and spine should be avoided to prevent damage to the internal organs
When CPT is performed properly, a hollow sound is heard.
Indication of The purse-lipped breathing technique
PEC
For clients who have chronic lung diseases such as pulmonary fibrosis, emphysema, COPD (PEC)
Who would benefit from flutter valve?
• The client makes a tight seal around the mouthpiece and inhales air with a deep breath. The desired breathing pattern is to exhale at twice the rate of how the client typically breathes.
• The client exhales for at least 3 to 4 seconds during use of the flutter valve. Breaths should be repeated at least 10 times.
Clients who have cystic fibrosis, chronic bronchitis, or cardiopulmonary diseases can benefit from use of the flutter valve.
Huffing is similar to exhaling onto a mirror or steaming up a window. A cycle of four to five huffs should be performed to clear the airways.
An endotracheal tube (ETT) is an artificial airway inserted through the mouth past the vocal cords into the trachea. It keeps the airway open, protects it against aspiration, and ensures oxygenation and ventilation
Complications associated with using an ETT include bleeding, infection, perforation of the oropharynx, hoarseness (vocal cord injury), damage to teeth/lips, or esophageal placement.