Trig and log derivatives test
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
All the trig identities and fundemental limits one would need!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
fundamental sin limit
lim as x approaches 0 of sinx over x (or the inveerse) is 1
Special triangles
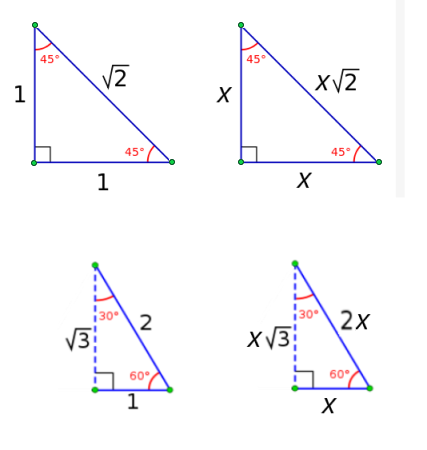
derivative of sinx
=cosx
dy/dx (cosx)
=-sinx
dy/dx (tanx)
=sec²(x)
dy/dx(secx)
=tanxsecx
dy/dx(cotx)
=-csc²x
dy/dx (cscx)
=-cscxcotx
e=
limit as x approaches 0 of (1+x)^1/x or limit as n approaches infinity of (1+1/n)^n
dy/dx (e^x)
=e^x
dy/dx (lnx)
= 1/x
exponential growth or decay function
f(t) = ce^kt where c = initial population, t= time and k = growth/decay factor
pythagorean trig identities
cos²x + sin²x = 1
1 + tan²x = sec²x
1 + cot²x = csc²x
quotient identities
tanx = sinx/cosx
cotx = cosx/sinx
sin (x+y)=
sinxcosy + sinycosx
sin (x-y)=
sinxcosy - sinycosx
cos (x+y)=
cosxcosy - sinxsiny
cos (x-y) =
cosxcosy + sinxsiny
sin2x =
2sinxcosx
cos2x =
cos² x - sin²x
1-2sin²x
2cos²x - 1
sin (pi/2 - x)=
cosx
cos (pi/2 - x)=
sinx
tan (pi/2 - x)
= cotx