physio - vasculature
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
endothelium, elastic tissue, smooth muscle, fibrous connective tissue
the 4 layers of blood vessel structure
endothelium (material of blood vessel)
thin single layer of epithelial cells on basement membrane
elastic tissue (material of blood vesel)
has elastin protein; allows for stretch
smooth muscle (material of blood vessel)
contract or relax to control vessel diameter
fibrous connective tissue (material of blood vessel)
has collagen protein, tensile strength, is durable
elastic arteries
aorta, pulmonary arteries, major aorta branches are examples of ______
elastic arteries
act as “pressure reservoir” - can store and release pressure; stretch when ventricles contract and recoil when ventricles relax
muscular arteries
thick layer of smooth muscle, which allows for vasodilation and vasoconstriction; deliver blood to organs
arterioles
“little arteries” with a smooth muscle layer, precapillary sphincters contract to direct capillary bed flow (_____ are at the top of capillary bed)
capillaries
smallest vessels in body; passage of single red blood cell; they are exchange sites
continuous, fenestrated, sinusoid
3 types of capillaries
continuous (capillary type)
have leaky junctions between endothelial cells; most common in body; paracellular movement
fenestrated (type of capillary)
have large pores/fenestrations; kidney, small intestine
sinusoid (type of capillary)
very large pores; most permeable; proteins and even cells can pass through (bone marrow, spleen, liver)
bulk flow
large number of molecules move in the same direction; passive process; involves pressure differentials
hydrostatic pressure (PH)
pressure exerted by fluid in vessel
colloid osmotic pressure (π)
pressure due to colloidal suspension of molecules in blood
Starling forces
hydrostatic pressure and colloid osmotic pressure
PH > π
net filtration occurs; net fluid exit
PH < π
net absorption occurs; net fluid entry
lymphatics
excess filtered fluid moves into _______
larger
lymphatic capillary is ______ than blood capillary
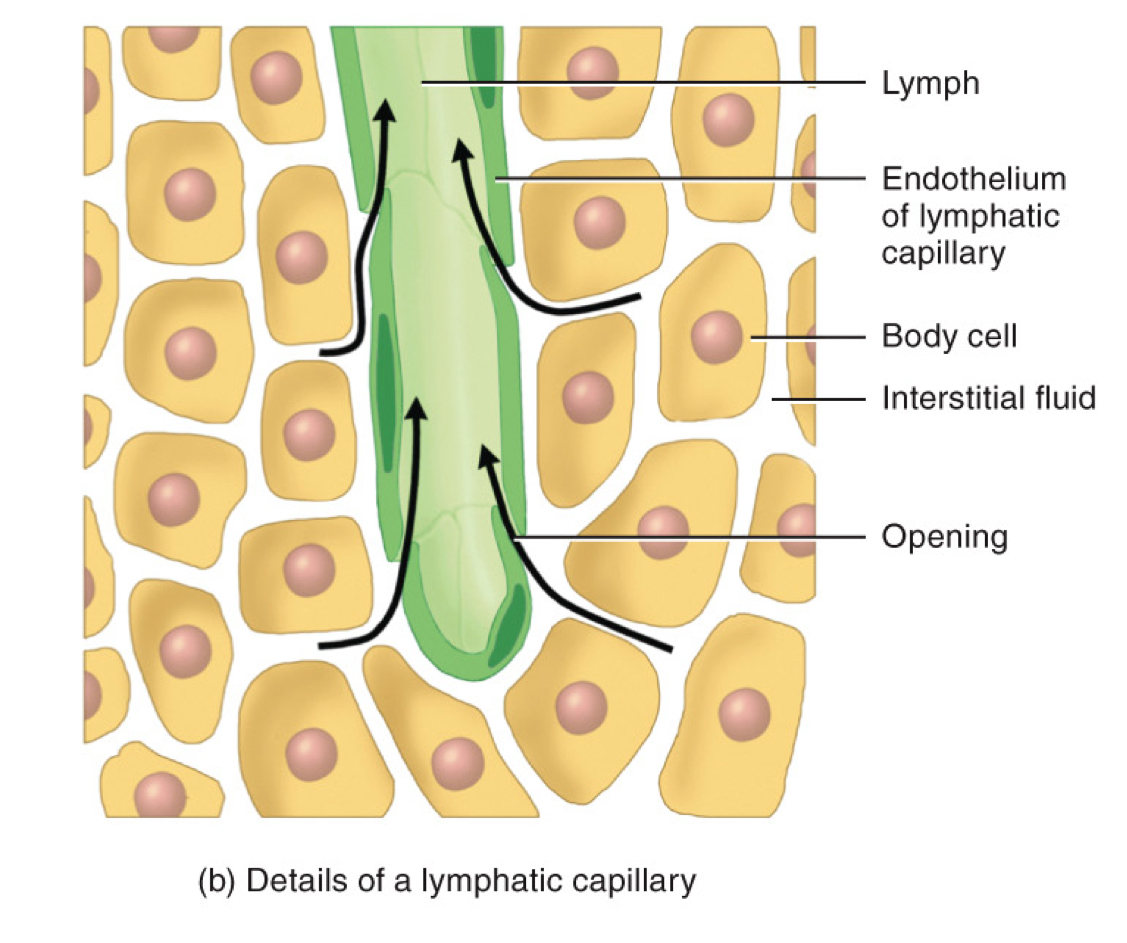
endothelial cells of lymphatic capillary
_____ have overlapping ends which makes them more permeable than blood capillary
bulk flow
capillary exchange occurs via ______
lymphatic vessels
lymphatic capillaries connect to ______
vascular tone
smooth muscle in a state of partial contraction
vasoconstriction
decrease diameter
vasodilation
increase diameter
systolic
highest pressure in arteries during ventricular systole
diastolic
lowest pressure in arteries during ventricular diastolep
pulse
traveling pressure wave
sympathetic innervation
most blood flow control by ________
systemic veins and venules (blood reservoirs)
at any given time, most blood is here
compliance (ability of hollow organ to stretch)
veins have high _______
skeletal muscle pump
muscle contractions compress vessels and promote flow
venous valves (skeletal muscle)
flap-like cusps comprised of endothelium and connective tissue
respiratory pump
pressure changes promote flow (inhale - diaphragm moves down, decrease thoracic pressure and increase abdominal pressure; flow moves toward thoracic cavity)
baroreceptors
Mean arterial pressure is monitored by _______ in aorta and other arteriesB
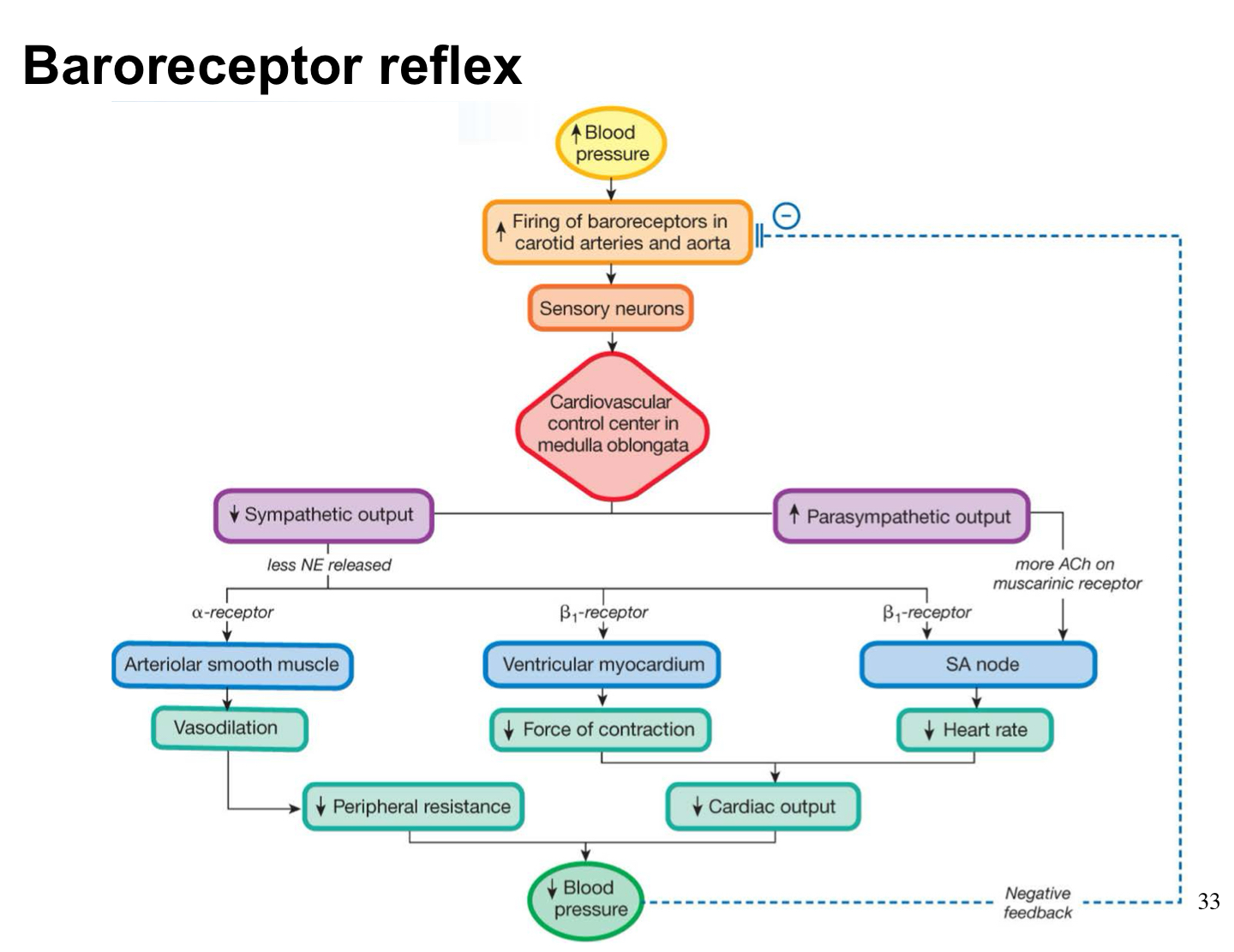
Baroreceptor reflex
know baroreceptor reflex
increased
increase blood pressure leads to _______ firing of baroreceptors in carotid arteries and aorta; lowering sympathetic output (lowering heart rate, force of contraction, etc.) and lowering blood pressure
decreased
decreased blood pressure leads to ________ firing of baroreceptors in carotid arteries and aorta; increasing sympathetic output (increase heart rate, force of contraction, etc.) and increasing blood pressure