Lecture 4&5: Urine Concentration Analysis & Constant Rate Infusion
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
What are the two ways drugs can be eliminated by?
Excretion (Urine)
Metabolism (Liver)
True or false: Some drugs can be eliminated completely unchanged in the urine (they can be excreted w/o being metabolized by liver)
True
What does the renal excretion rate constant ku represent?
The proportionality constant relates the rate of elimination into the urine and the amount of drug in the body.
Renal clearance (CLR) is the proportionality constant relating the __________ and the _________.
rate of urinary drug excretion, plasma concentration
Formula for fraction of drug excreted unchanged in urine (fe)
fe = rate of excretion/rate of elimination = CLR/CL = ku/ke
True or false: For fe, a value of 0 = drug is completely excreted unchanged in urine and 1 = no renal function
False.
0 = no renal function
1 = drug completely excreted unchanged in urine
Why is urine collected during the period of 5 half-lives?
it takes 5 half lives for ~97% of drug to be eliminated from body
based on one-compartment theory
What is needed to plot in the rate of excretion method?
rate of drug excreted in each time interval vs midpoint of time interval
What is needed to plot for the amount remaining to be excreted method (ARE)?
Amount remaining to be excreted vs Time
For Rate of Excretion Method,
__ = y-intercept/dose
ku (urinary excretion rate constant)
For Amount Remaining to be Excreted Method (ARE),
__ = y-intercept/dose
fe
How to calculate renal clearance?
Total amount excreted/AUC (0 to inf)
A constant rate infusion is a direct method by which the drug is administered systemically at a ______ or _____ rate.
constant, zero-order
True or false: We do not assume a one-compartment model for IV (constant rate infusion)
False. We do assume like for IV bolus.
Which is not a reason why we give a drug through infusion?
a. makes drug faster and work more effectively
b. maintenance of constant plasma concentration
c. convenience, given with IV fluids
d. given when bolus gives unacceptable toxicity
e. easier to regulate blood levels
a.
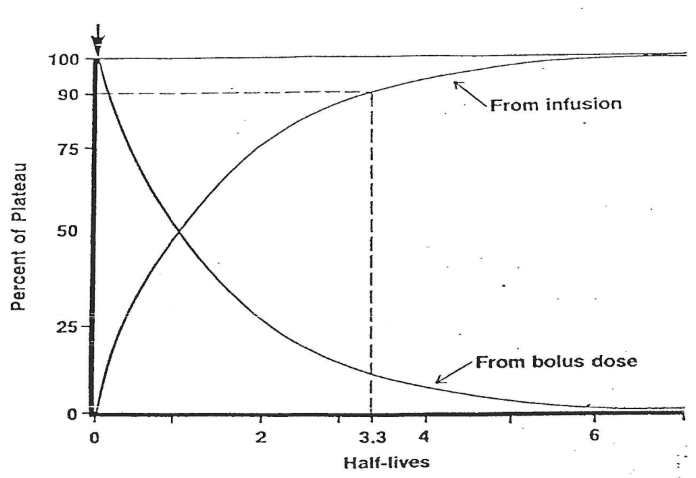
What does the horizontal line represent on the graph?
bolus dose + infusion
Equation for Cinf (concentration of infusion)
Cinf = Cpss (1-e-kt)
Cinf (concentration of infusion)
Cpss (concentration of plasama in steady state)
Equation for IV bolus injection
Cp = C0 * e-kt
What is steady state?
when rate of drug in (R0) = rate of drug out (Cpss * CL)
point in time when change in drug concentration/amount =0)
on infusion graph —> plateau
Abss = R0/k (amount in body at steady state)
Cpss = R0/CL
What factors govern the amount of drug in the body at steady state (Abss)?
a. CL (clearance)
b. Ro (Infusion rate)
c. t1/2 (half-life)
d. k (elimination rate constant)
b, d
What factors govern the concentration at steady state (Cpss)?
a. CL (clearance)
b. Ro (Infusion rate)
c. t1/2 (half-life)
d. k (elimination rate constant)
a, b
True or false: All drugs infused at the same R0 and having the same k reach the same Cpss.
False. They reach the same Abss
True or false: All drugs infused at the same R0 and having the same CL reach the same Cpss.
True
Only drugs for which CL and Vd are the same will both _____ and _____ be the same when infused at the same _____.
Cpss and Abss, R0
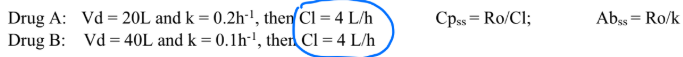
If Drugs A and B are infused at the same R0, what value will be the same?
a. Abss
b. Cpss
c. both a and b
b
What is true about the Time to Steady State?
a. Time to steady state depends only on half-life
b. Time to steady state can be reached faster by increasing the infusion rate (R0)
c. The shorter the half-life the sooner we reach steady state
d. Increasing the dose can help reach steady state faster
a, c
True or false: The time to go from one plateau concentration to another depends only on the half-life of the drug
True
Why might we change the infusion rate (R0)?
increasing rate to elicit a response
decreasing rate because of toxicity
True or false: Post infusion behaves like a bolus dose (C0 = Cend inf) and drug concentration decreases by one half every half-life
True
What is the purpose of a bolus loading dose?
administered in addition to the constant rate infusion when the plateau concentration (steady state) should be reached immediately
used when drugs with long half-lives (may not reach plateau for hours/days)
Loading Dose Equation
DL = Cpss desired * Vd