Indexing Midterm
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
103 Terms
Index
information retrieval tool
systematic arrangement of entries designed to enable users to locate information in adocument
mind road maps to both known and unknown information
Indexes
points users to specific items on topics of interest
shows users related topics and indicates information trails through vast information stores
Abstract
abbreviated and accuratr representation of the content of the document
Abstract Objective
capture the essential content of the document
Micro-level
concern overselves with specific mechanics of creating an index
Macro-level
put index into larger context of an information retrieval system
Information Retrieval System
stores records in a file
accepts requests for information
searches the file and brings back appropriate information for the user
IR System Purpose
give users the information they need with minimum effort on their part
Web 2.0
foundation for delievering a rich user experience to end users on the web while leveraging the benefits of composite applications, mash up, service-oriented architectures, and ubiquity of the internet
Principles (Mod 1)
store the information our users might need
establish a vocabulary of terms for describing them
assign terms to each specific data item and arrange assigned terms into usable formats to create records
store the records and set up a file of index terms to access the record
user expresses request by using terms from common vocabulary and searching the file and matching requests with stored records
system retrievs and presents the records
Information
patterns imposed in matter and energy
Information is
made up of data organized and interpreted to produce meaning
Wisdom
the process by which we judge between right and wrong
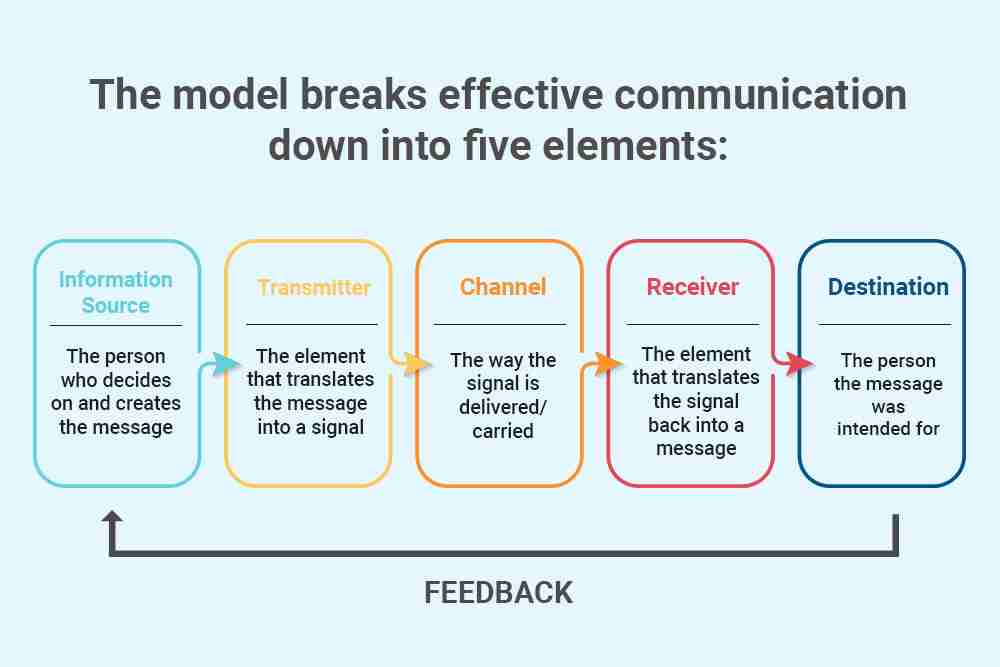
Shannon's Model of Communication
communication source
encoder
channel (noise)
decoder
destination
Three Levels of Communication
physical
semantic (meaning)
effectiveness
Information Science
study of information
Information Organization Life-Cycle
identifying
organizing
managing
preserving
making content accessible
Subject Cataloging
index that uses pre-coordinated terms which are surrogates
The Classic Information Retrieval Model
document
document representation
match
query
information need
restricted language
identify those varieties of a language where the possibilities of novelty and creative variation are minimal, and where all the usage possibilities can be expressed using a very small set of rules
Importance of Linguistics
information is expressed in human language
Selectivity
enables little information to go a long way
perception
process by which living organisms become aware of things and activities around them
Classification
arrangement of similar things into groups or categories
Significance of langauge
organization of knowledge
aboutness of linguistic expressions
representiational componets and their connections
Semantic Relationship
directional links between links
Bibliographic Control
set of processes that effectively organize a body of literature for storage and retrieval
Basic Methods of Bibliographic Control
descriptive cataloging
subject cataloging
classification
indexing
abstracting
Principles of Bibliographic Control
no two documents can be confused with each other
document should be accessible from a variety of view points
descriptive details should follow a uniform format
Ontology
theoty of what exists
Taxonomy
practice of classifying things
Nomenclature
set or system of names or terms used to describe the entries in some domain of knowledge
Terminologies
show more interreationships
Vocabularies
controlled set of language labels or terms conntected to a concept in the domain knowledge
Coding
shorthand for representing concepts
Metadata
structured data bout data
Controlled Vocabulary
artifical language that puts an information specialist between the text and the user
Free-Text Vocabulary
allows any word to represent content
Information Store
random collection of records
Authority List
shows the formal relationships between words and spells out how they are to be used
Thesauri
set of terms structured using a small set of semantic relations to indicate the controlled terms for each concepts ans relationships between the terms/concepts
Broader Term
shows hierarchical relationship upward in classification tree
Narrower Term
goes down in classification tree
Related Term
descriptor that can be used in addition to the basic term
Use
preferred descriptor from a nonusable term
Use For
synonyms or variant forms of preferred descriptor
Scope Note
restrict the usage of a descriptor
Keywords
raw words that come from the text
Descriptor
terms that have been defined for the use by the thesaurus
Indentifiers
proper nouns
Preferred Terms
words chosen for the thesaurus
Entry Terms
words that allow the user to enter the vocablary structure
General Indexes
provide access to popular, current, and basic information
Specialized Indexes
provide access to specialized information or technical articles
Electronic Indexes
allows search across multiple indexes over different time periods
Document-Oriented Approach
indexing summarizes or represents the content of a document
User-Oriented Approach
indexing reflects the requests for which a document might be relevant
Exhaustivity
ability to identify most of the good stuff out of the document
Specificity
extent to which an index term precisely represent the subject of an document
Precision
ratio of the number of relevant records retrieved to the total number of irrelevant and relevant records retrieved
Recall
ratio of the number of relevant records retrieved to the total number of relevant records
Information Behavior
deals with the complex ways in which users seek and use informatin to satisfy individual information need
Convenience
situational criterion in people's choices and actions during all stages of the information seeking behavior
Alphabetical Index
names and subject entries are in alphabetical order
Author Index
users are guided to titles of documents by way of authors
Book Index
list of words at back of the book giving a page location of the subject or name associated with each word
Chain Index
type of precoordinated index that represents a chain of concepts that make up a subject
Citation Index
list of documents with a sublist wnder each article of subsequently published documents that cite the document
Classified Index
content arranged systematically by classes or subject headings
Coordinate Index
allow terms to be combined or coordinated
Cumulative Index
combination of a set of indexes over time
Database Index
provides a mapping to needed data
Faceted Index
attempts to discover all the individual aspects of a subject and synthesize them in a way that best describes the subject under disscussion
Hypermedia Index
allows users to thread their way to what they want through electronic nodes and links between those nodes
Extract
condensed version of a document created by pulling sentences directly from the document
Annotation
very short and brief content indicator that quickly describes a document
Executive Summary
preview of main points at the head of a report
Informative Abstract
presents the specific data
Critical Abstract
make value judgements or editorical comment on the document
Telegraphic Abstract
uses keywords from the document with very little syntactic integrity
Slanted Abstract
concentrates on selected portion of the document's subject content
Mission-Oriented Abstract
aimed at specific operation with a specific mission
Discipline-Oriented Abstract
aimed at individual subject areas and discipline
Structured Abstract
follows a set form of subheadings and the abstract writer fills in the blanks
Broad Steps
analyze the document
descibe the subject
translate into indexing language
Known-Item Search Task
when an item is known
Exploratory Search Task
when a subject is the object of the query
Subject Analysis
correctly interpret the subjects ina document
ascertain the intent of the author
predict the information need and searching approach of the potential user
Concept
unit of thought, either concrete or abstract, that can be either real or imaginary
Five Factors that Influence Analysis
domain of subject and potential user
major aspects of the text
clarity of the writing
complexity of the subject discussed
bibliographic references
Aboutness
behavioral reaction of a person to a document
what the words say and what the words mean
Perceptional Indexing
indexer recognizes the subject directly from what the text says
Conceptual Indexing
Indexer uses known world knowledge
Domain Analysis
process for analyzing a ayatem to find common and mutually variable parts
Domain-Centered Indexing
user's needs are upfront when indexer analyzes the document and selects the terms
Content-Centered Indexing
indexers uses a number of concrete attributes in the document in the indexing process
Indexing Language
controlled vocabulary or classification system and the rules for its application
Assigned-Term
use some intellectual effort to assign term or descriptors on the basis of subjective interpretation of the concepts
Derived-Term
all descriptors are taken from the text itself
Conventional Indexing
indexer examines the text and searches for indexable concepts