OCR 21st Century Physics
1/142
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
143 Terms
What is wavelength?
The wavelength is the distance between the same points on two adjacent disturbances.
What is frequency?
Frequency is the number of complete waves passing a certain point per second.
State 2 types of transverse waves
Electromagnetic waves and S-waves
State 2 types of longitudinal waves
Sound waves and P-waves
Give the wave speed speed equation
Wave speed (m/s) = frequency (Hz) X wavelength (m)
What is 1KHz?
1000Hz
What is 1MHz?
1,000,000Hz
How is all electromagnetic radiation transmitted through space?
With a very high speed. Travel at the same speed.
What happens when radiation strikes an object?
Some of it may be transmitted, or be reflected, or be absorbed. When radiation is absorbed it ceases to exist as radiation; usually it heats the absorber.
What can exposure to large amounts of ionising radiation cause?
Damage to living cells; smaller amounts can cause changes to cells which makes them grow in an uncontrolled way, causing cancer.
Oxygen is acted on by radiation to produce ozone in the upper atmosphere, what does the ozone absorb?
Ultra violet radiation, and protects living organisms like animals from its harmful effects.
What type of wave has the lowest frequency and the longest wavelength?
Radio waves
Are electromagnetic waves transverse or seismic?
Transverse
What is special about electromagnetic waves?
Electromagnetic waves can travel in a vacuum. It is possible to have electrical and magnetic effects in a vaccum.
What type of light has the lowest frequency of all visible light?
red light
What type of light has the highest frequency of all visible light?
Violet
How are radio waves produced?
By electrical vibrations or oscillations in an aerial.
What type of waves are electromagnetic waves?
Transverse
Recite the Electromagnetic spectrum starting with the wave with the largest wave length
Radio waves; Micro waves; infrared; Visible light; ultra violet; X-rays and Gamma rays
How many Types of EM waves are there?
7
What occurs if an EM wave has a high frequency?
The higher the frequency the more energy it absorbs
How are visible light, UV, and X-rays emitted?
They are emitted when electrons drop down energy levels
How are gamma rays emitted?
Changes in the nuclei can cause gamma rays to be emitted this is radioactive decay.
What happens to all EM waves when they are absorbed?
When any type of EM wave is absorbed, it ceases to exist as radiation and instead causes heating (but high-energy UV, X-rays and gamma rays have so much energy that they can cause ionisation)
What do compressions and refractions look like?
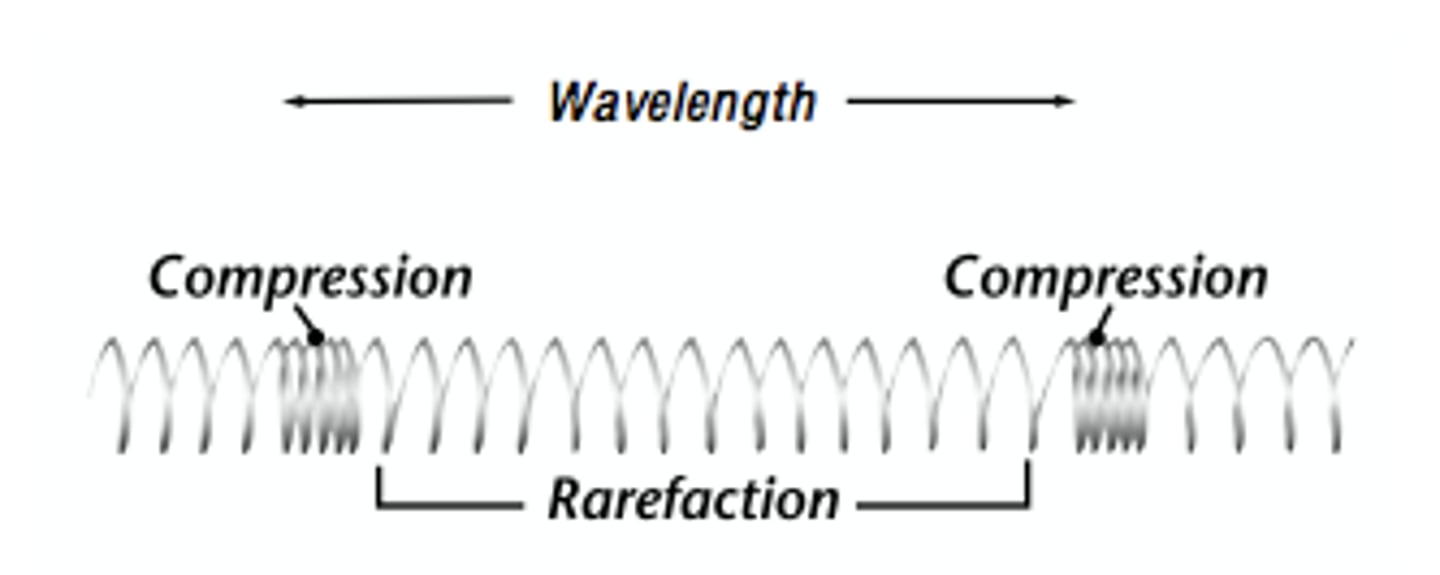
What do waves transfer?
energy
What do waves not transfer?
matter
What are the differences between transverse and longitudinal waves?
In transverse waves the disturbance of the medium is perpendicular (90 degrees) to the direction the wave travels. In longitudinal waves the disturbance of the medium is parallel to the direction the wave travels.
State three things that occur when a wave hits a boundary.
Absorbed. Transmitted. Reflected
State what refraction is
The wavelength of a wave changes as it passes through one medium to another. If the waves pass from one medium to another at an angle to the boundary, they will change direction.
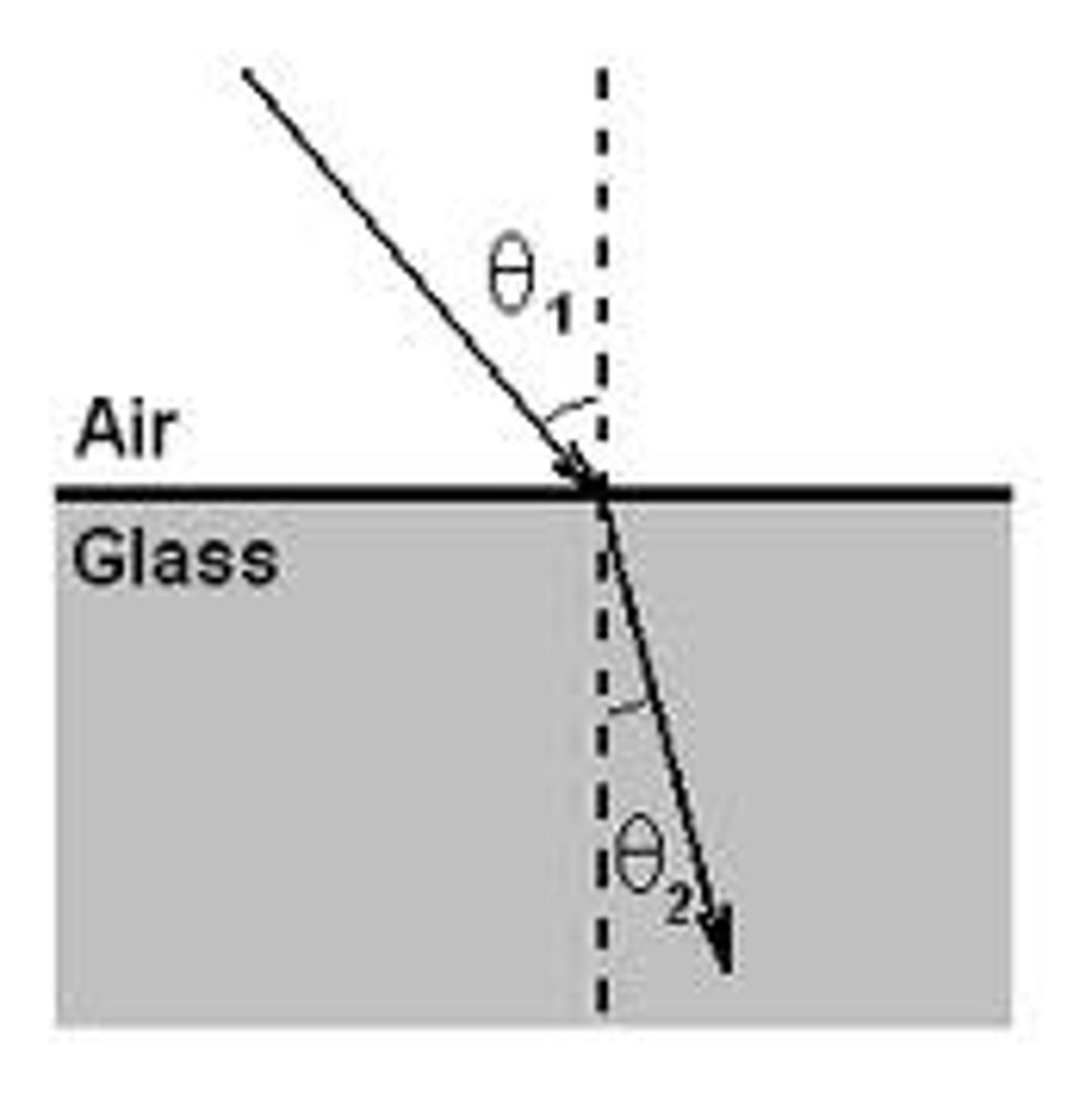
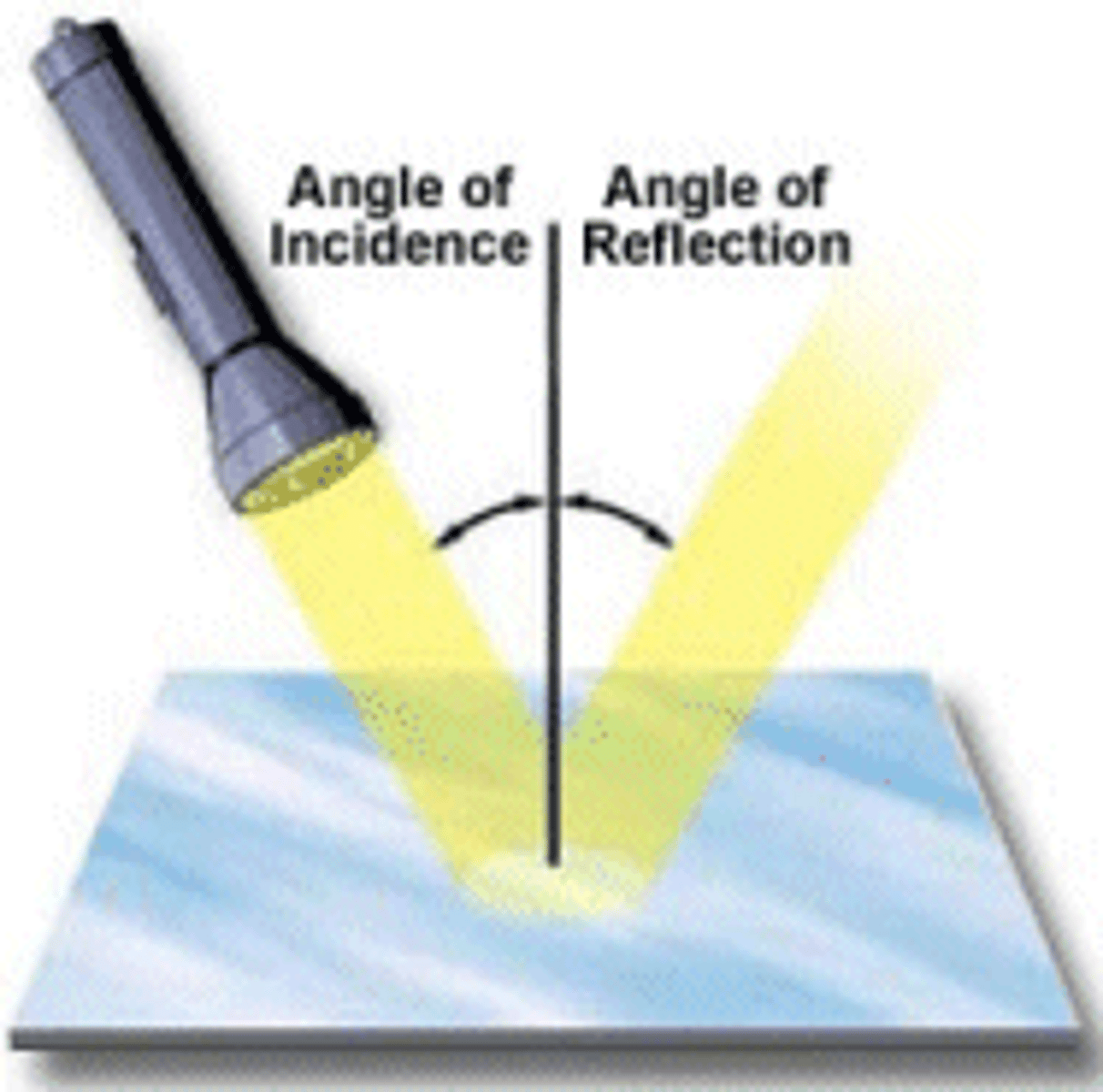
State what reflection is
Reflection is what happens when a wave hits a barrier and bounces off.
What happens to the frequency of a wave when it crosses a boundary?
Nothing. It cannot change.
What is a normal?
A normal is an imaginary line at right angles to the surface at the point the wave hits.
What is a wavefront used to represent?
A wavefront is used to represent a crest or trough of a wave.
What is the amplitude of a wave?
The Amplitude of a wave is the displacement from the rest position to a crest or trough.
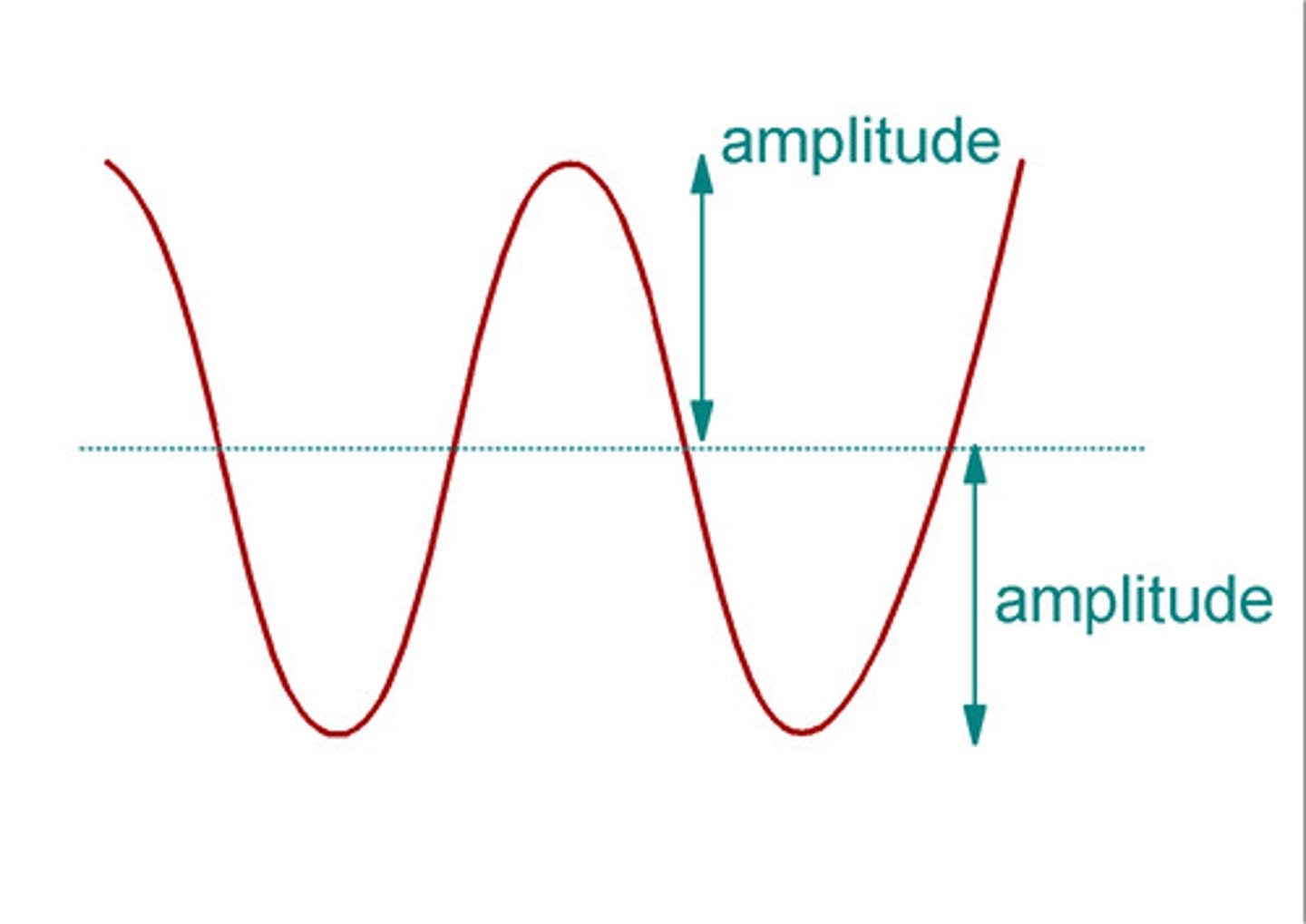
What is the wavelength of a wave?
The wavelength is the distance between the same points on two adjacent (neighbouring) disturbances (e.g. from crest to crest or from compression to compression) i.e. one full cycle of the wave
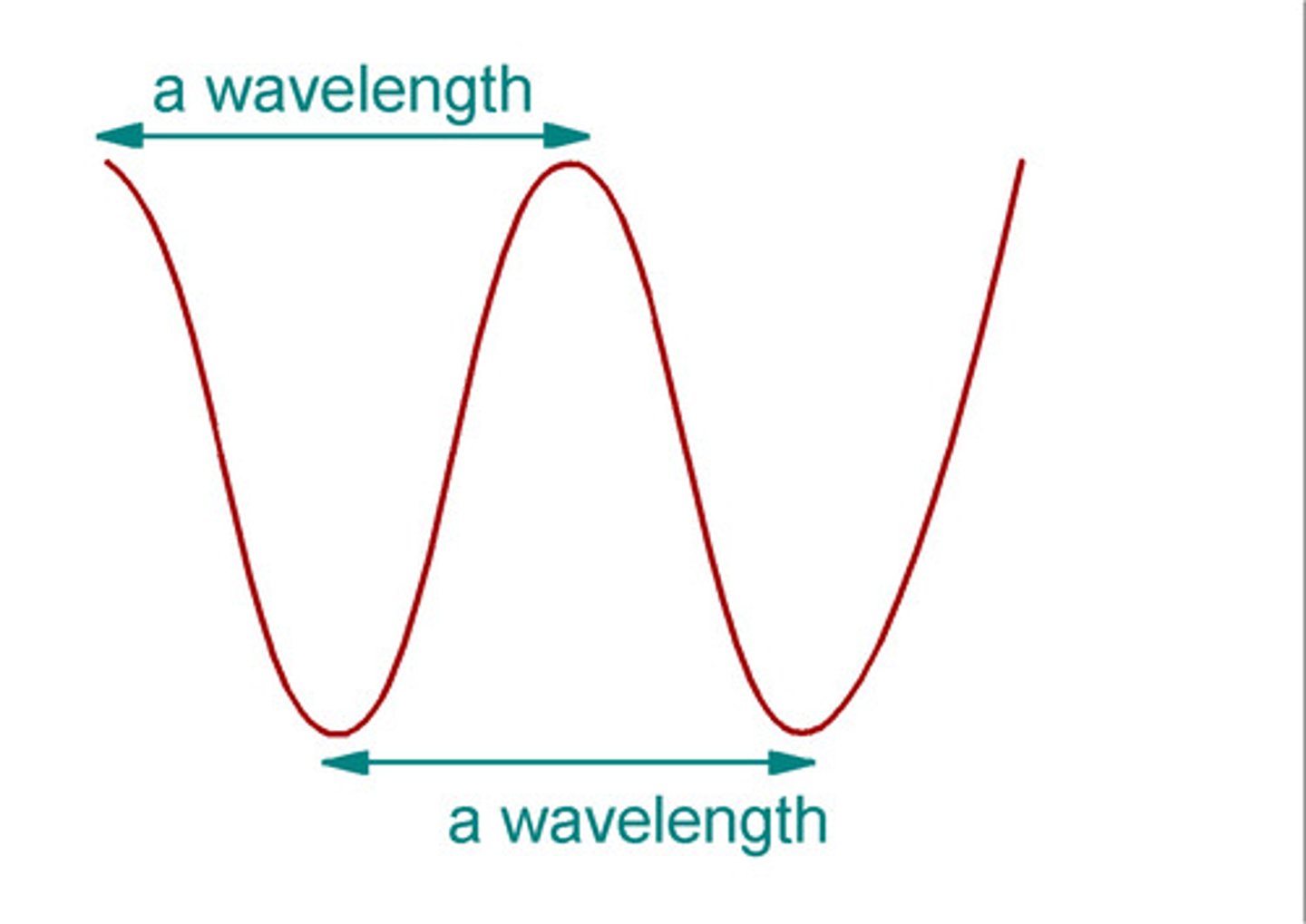
what is the frequency of a wave?
number of waves per second
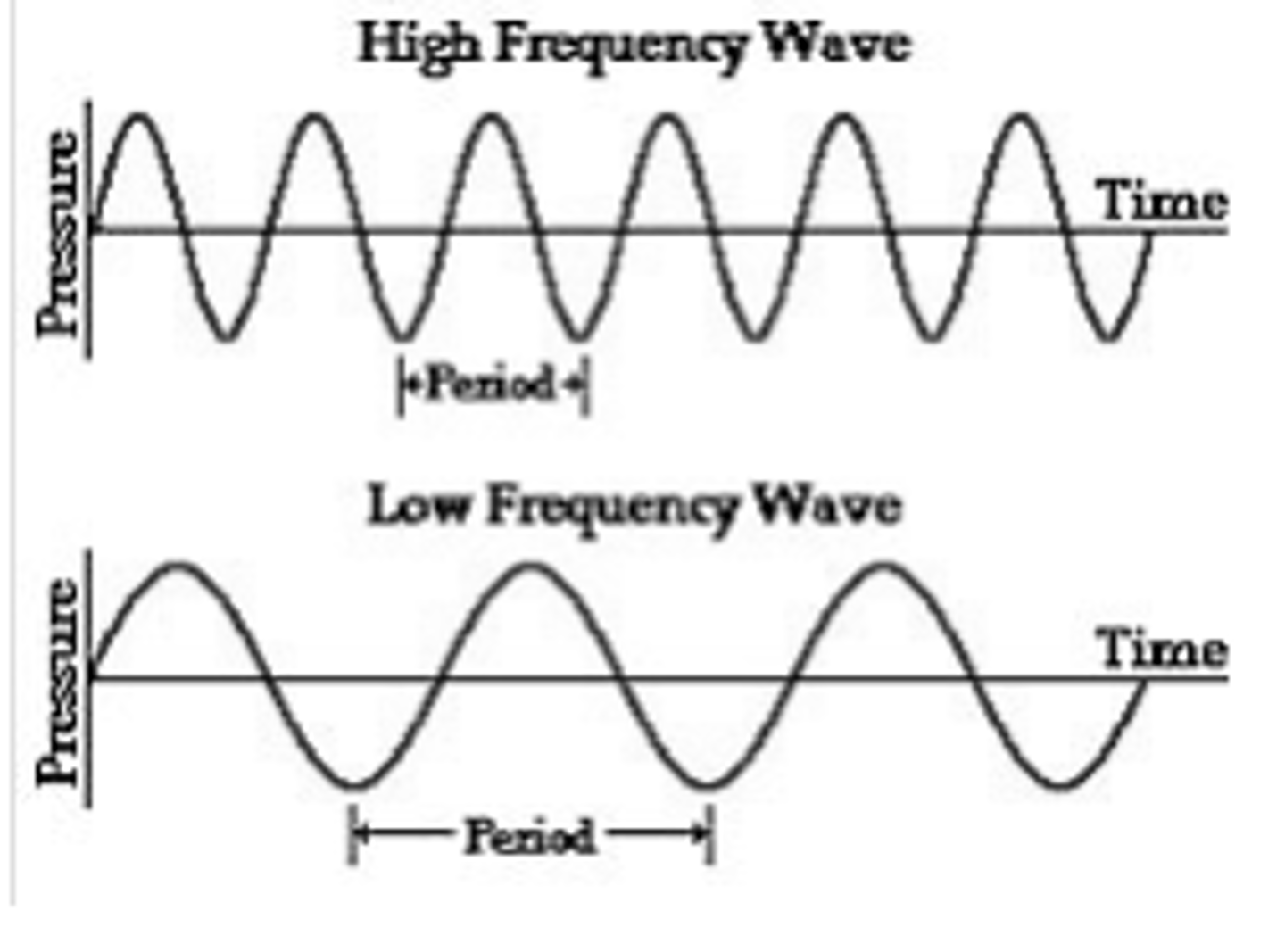
What is the period of a wave?
The period of a wave is the number of seconds it takes for one full cycle to pass a certain point. Period = 1/ Frequency
What is ultrasound?
Ultrasound is sound with frequencies higher than 20,000 Hz.
What happens to both sonar and ultrasound at boundaries?
Some is transmitted and refracted and some is reflected back. Industrial imaging e.g. Finding flaws in materials.
Give two uses of Ultrasound
Medical imaging e.g. pre-natal scanning and Industrial imaging - e.g. Finding flaws in materials
What is echosounding?
A type of sonar used by boats and submarines to find out the distance to the seabed or to locate objects in deepwater.
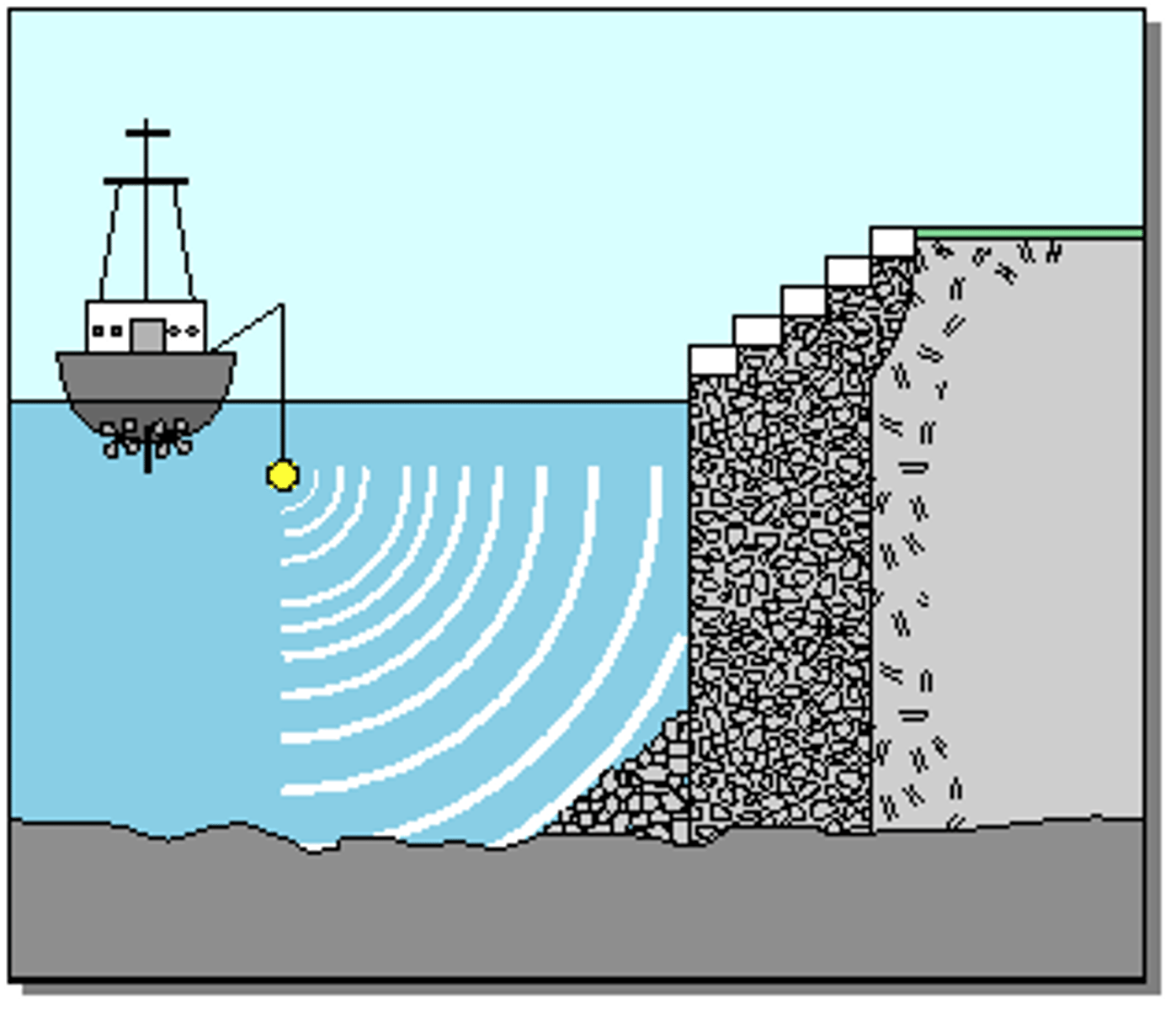
Explain how ultra sound can produce a video image of a foetus
Ultrasound waves can pass through the body, but whenever they reach a boundary between two different media (e.g. Fluid in womb + skin of the foetus) some of the wave is reflected back and detected. The exact timing and distribution of these echoes are processed by a computer to produce a video image of the foetus.
What are radiowaves used for?
Communication
What are microwaves used for?
Communication and cooking food
What is infrared used for?
Increase or monitor temperature, Remote controls
What is UV used for?
Fluorescent lamps (emits) visible light, very energy efficient, Tanning
What are X-rays used for?
used to view internal structures such as materials, objects and bodies.
What are gamma rays used for?
Sterilising food and medical equipment
Describe an experiment to measure the speed of sound in air
Use an Oscilloscope: 1) Set up the oscilloscope so the detected waves at each microphone are shown as separate waves.
2) Start with both microphones next to the speaker, then slowly move one way until the two waves are aligned on the display, but have moved exactly one wavelength apart.
3)Measure the distance between the microphones to find one wavelength.
4) You can then use the formula wavespeed = Frequency X Wavelength to find the speed of the sound wave passing through the air - the frequency is whatever you set the signal generator to in the first place
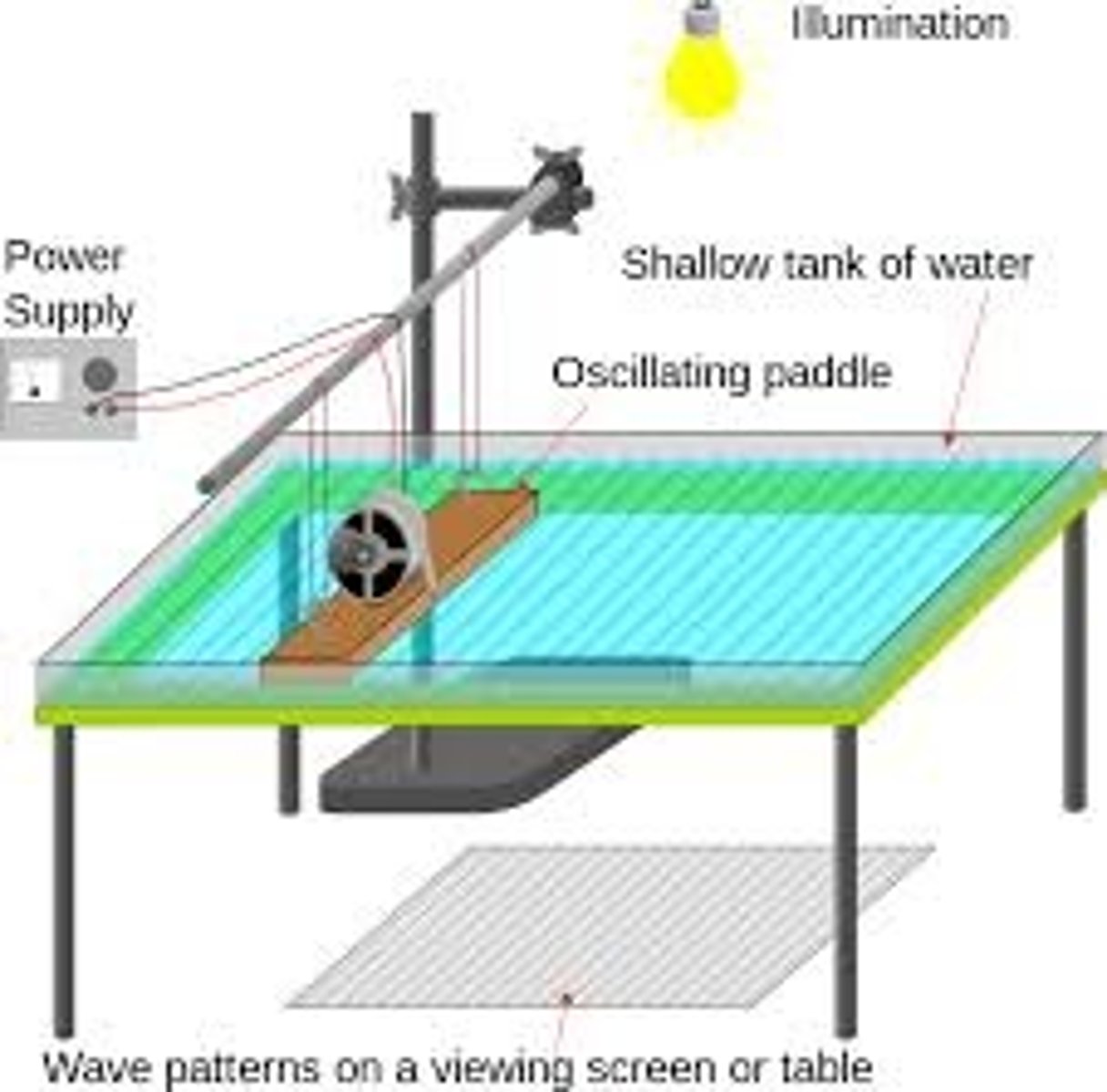
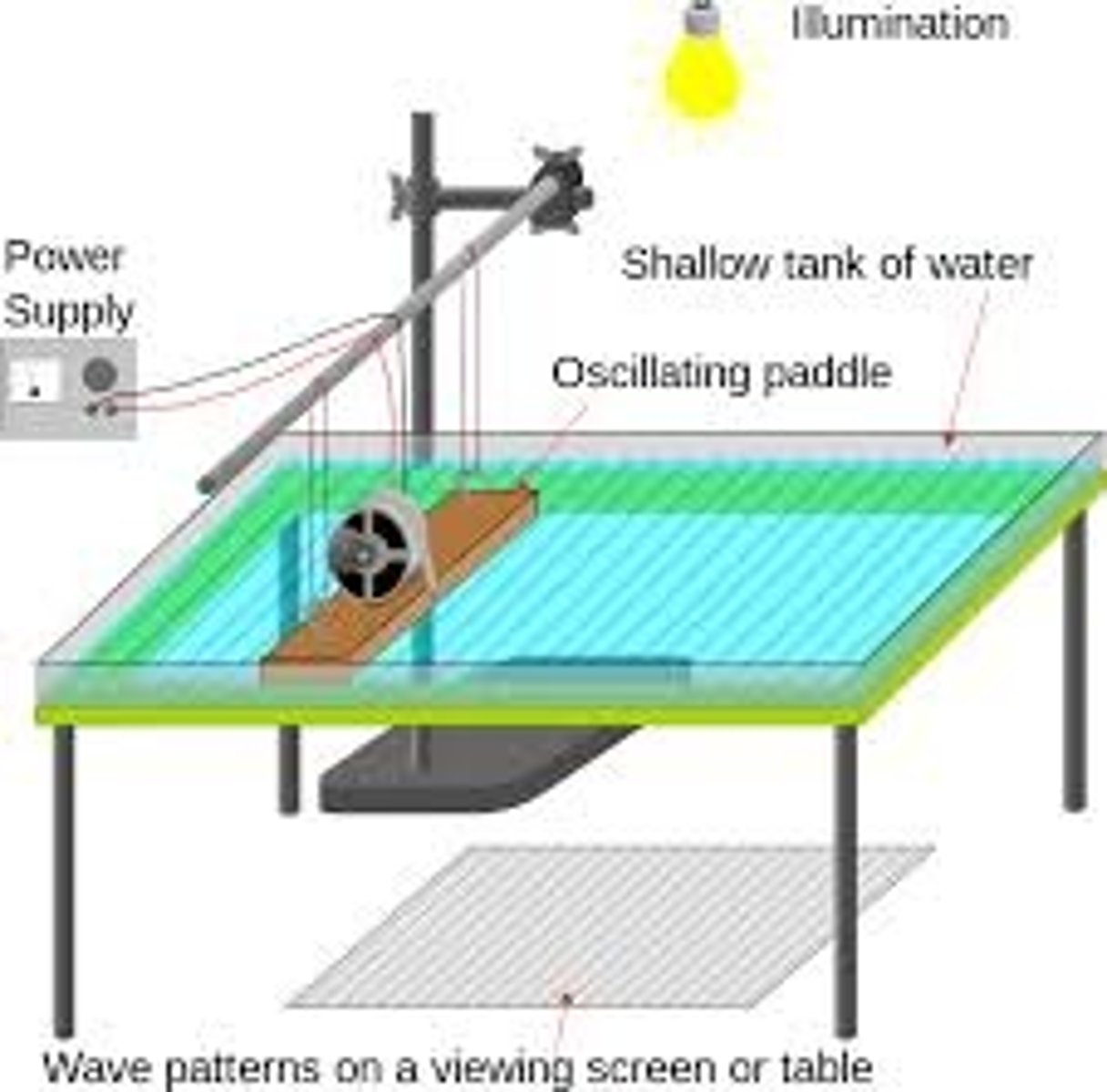
Describe an experiment to measure the wavelength of a water wave
The Ripple tank:
1) Float the cork in the ripple tank. It should bob up and down as the wave passes it.
2) When the cork is at the top of a bob , start the stopwatch. Time how long the cork takes to complete 10 bobs.
3) Divide this time by 10 to get the time for 1 bob - the period.
4) Calculate the frequency using the formula frequency = 1/ period
How do soundwaves travel and how are they caused?
Soundwaves are caused by vibrating objects and sound travels as a wave.
Describe the changes in speed in different materials/ states
Generally travels faster in solids than in liquids and faster in liquids than in gases
Does the frequency or wavelength change when the wave passes from one medium into another?
Yes, the wavelength does - it gets longer when it speeds up and shorter when it slows down.
What causes you to hear sound?
When your eardrums vibrate (caused by the waves) - vibrations pass onto ossicles then onto cochlea which turns them into electrical signals that are sent to the brain.
Explain why humans can't hear very low pitched or very high pitched sounds and why old people sometimes are hard of hearing?
The bones in the middle ear (ossicles) only work over a limited frequency range. As you get older the upper limit decreases and sounds may need to be louder for you to hear them. This is due to wear and fear of the cochleat auditory nerve.
Why can't sound travel in space?
Sound can't travel in space because it's mostly a vacuum and there are no particles to move or vibrate
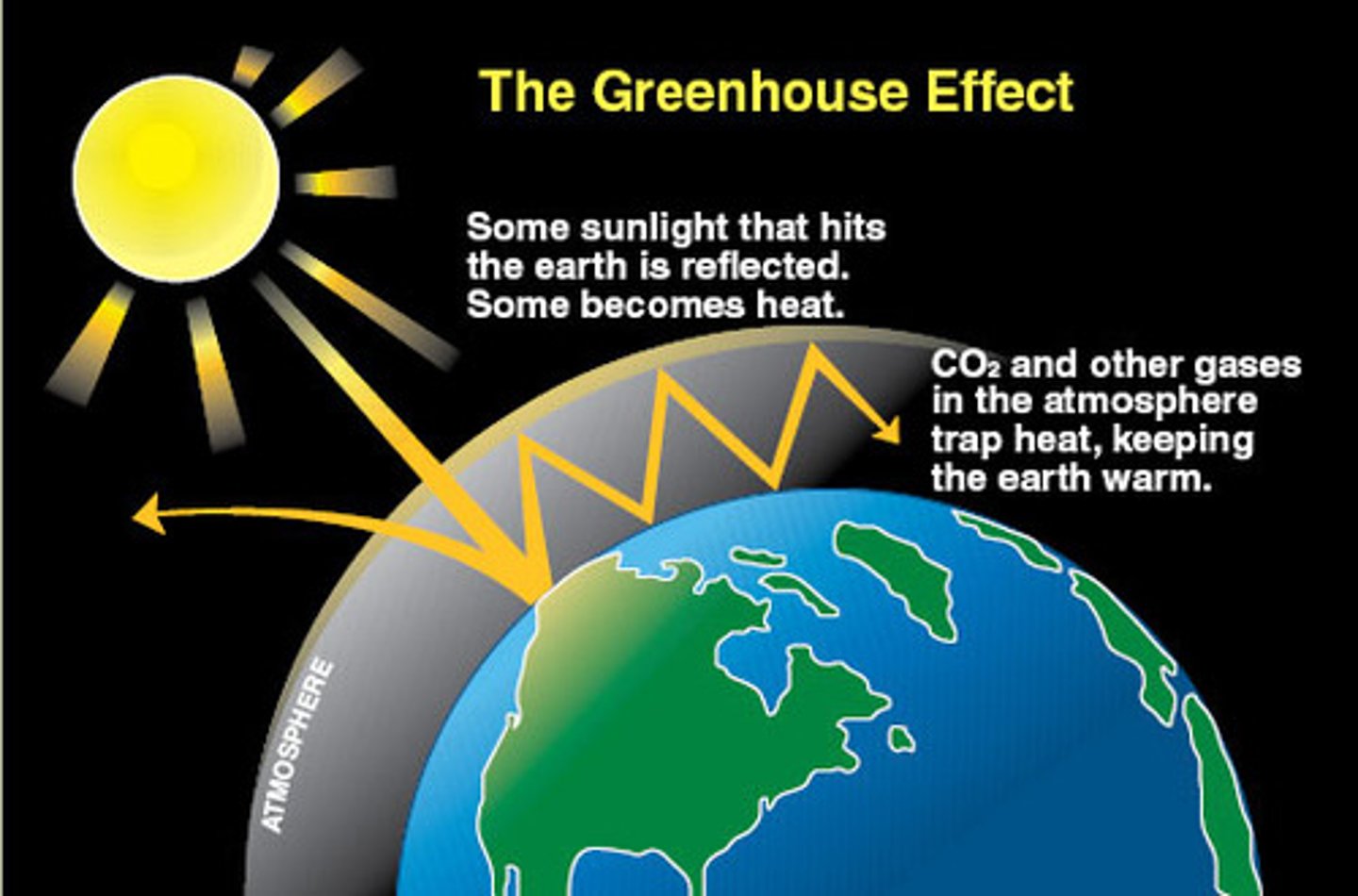
Which gases trap radiation in the Earth's atmosphere?
Carbon dioxide, Methane and water vapour
Describe greenhouse gases in terms of radiation absorbed and emitted
Greenhouse gases absorb lower frequency radiation, so they absorb a large amount of the radiation emitted by the earth (less so much by the sun as frequency tends to be too high). The greenhouse gases then re-emit the radiation in all directions, including back to Earth. The more greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, the more this happens
Give examples of human activity that affect the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere
Deforestation (few trees = Less CO2 being removed). Burning fossil fuels (Carbon in these fuels released as CO2). Agriculture (Methane through digestive processes)
The Earth's temperature varies naturally but the temperature of the Earth's surface has been increasing. Scientists agree that human activity (global warming) is causing the increase but why is it difficult to produce a model for this data?
Climate change is complex. There are many variables. It's difficult to make a model that isn't oversimplified. Although as more accurate data is gathered and refined, they can be used to make better predictions
What is a lens?
A block of transparent material with curved sides. Rays of light are refracted at both surfaces of a lens
Describe a converging (convex) lens and what it does to a parallel-sided beam of light
A converging lens is fatter in the middle than at the edges, A converging lens makes a parallel beam of light converge (coming together) at a point called the focus of the lens.

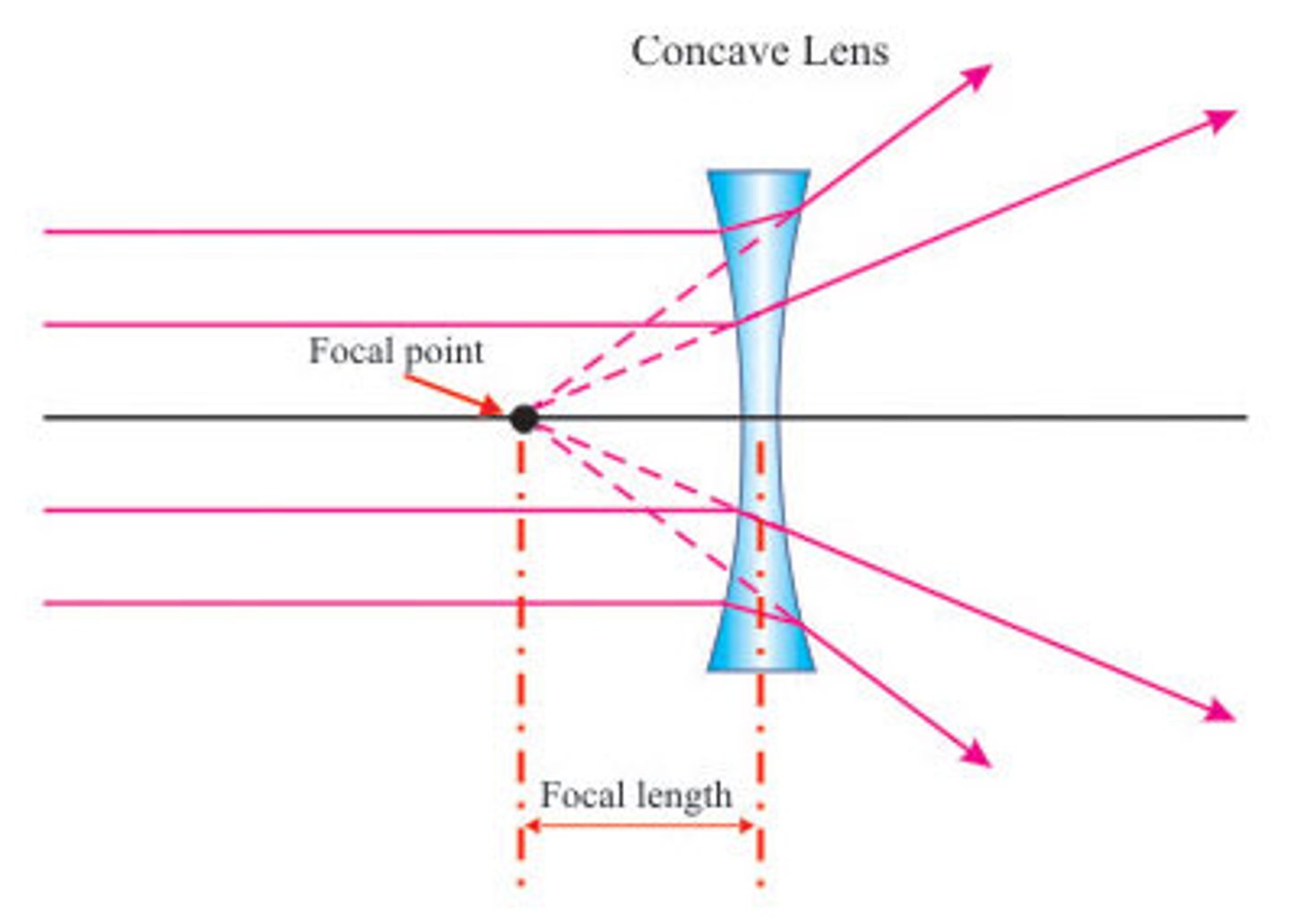
Describe a diverging (concave) lens and what is does to a parallel beam of light
A diverging lens is thinner in the middle than at the edges. A diverging lens makes a parallel beam of light diverge (spread out) so that it appears to come from a point (the focus)
Why does an object look different when you observe it through a lens?
Because the light rays have not taken a straight path to your eye
Give two similarities between convex and concave lenses
Both made up of glass. Light is refracted by both
Give two differences between convex and concave lenses
Converging lenses converge light beams from a source whereas diverging lenses diverge light rays from a source.
Converging lens is thick in the middle whereas concave is thinner in the middle
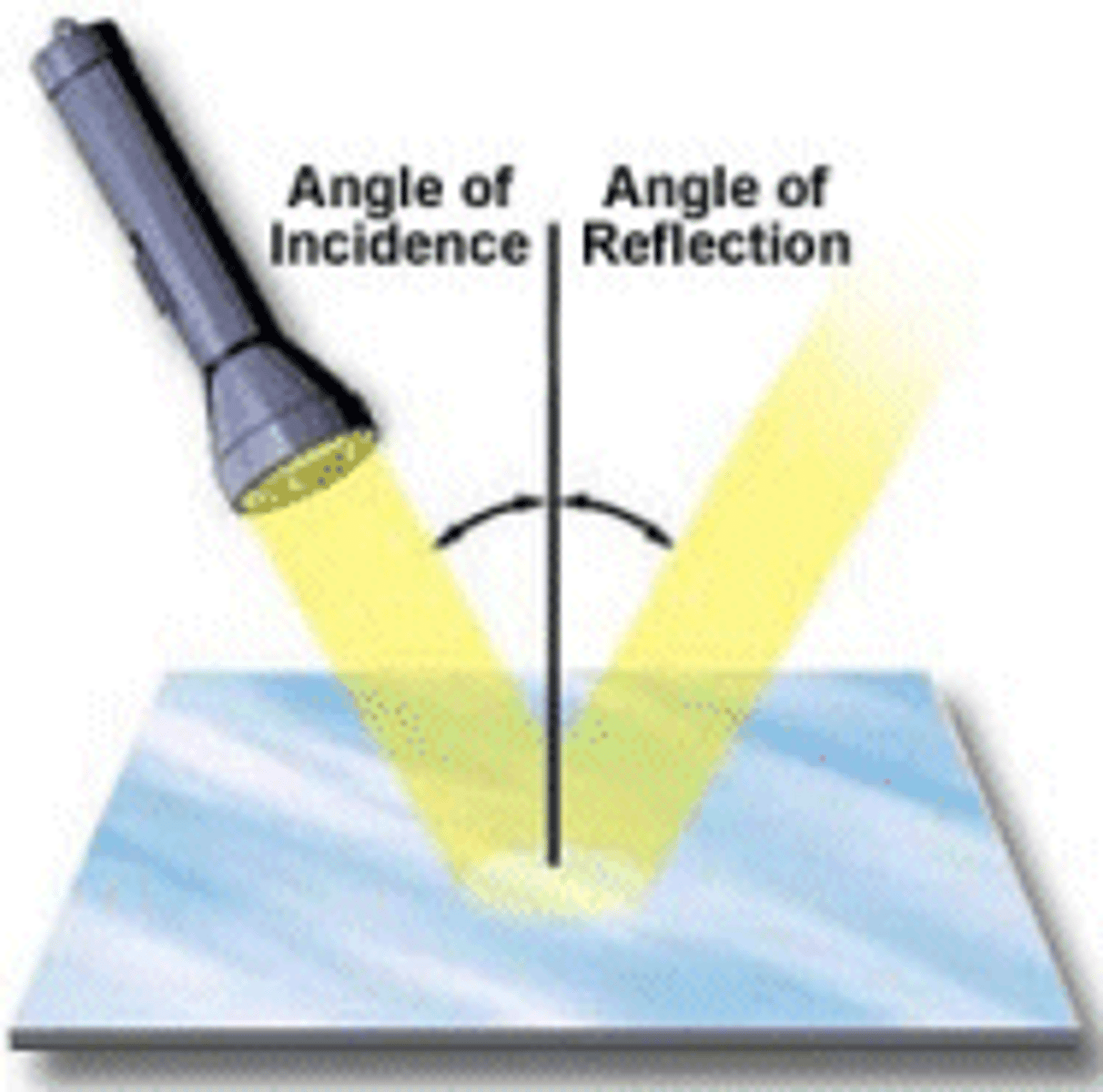
What is the angle of incidence?
the angle which an incident line or ray makes with a perpendicular to the surface at the point of incidence.
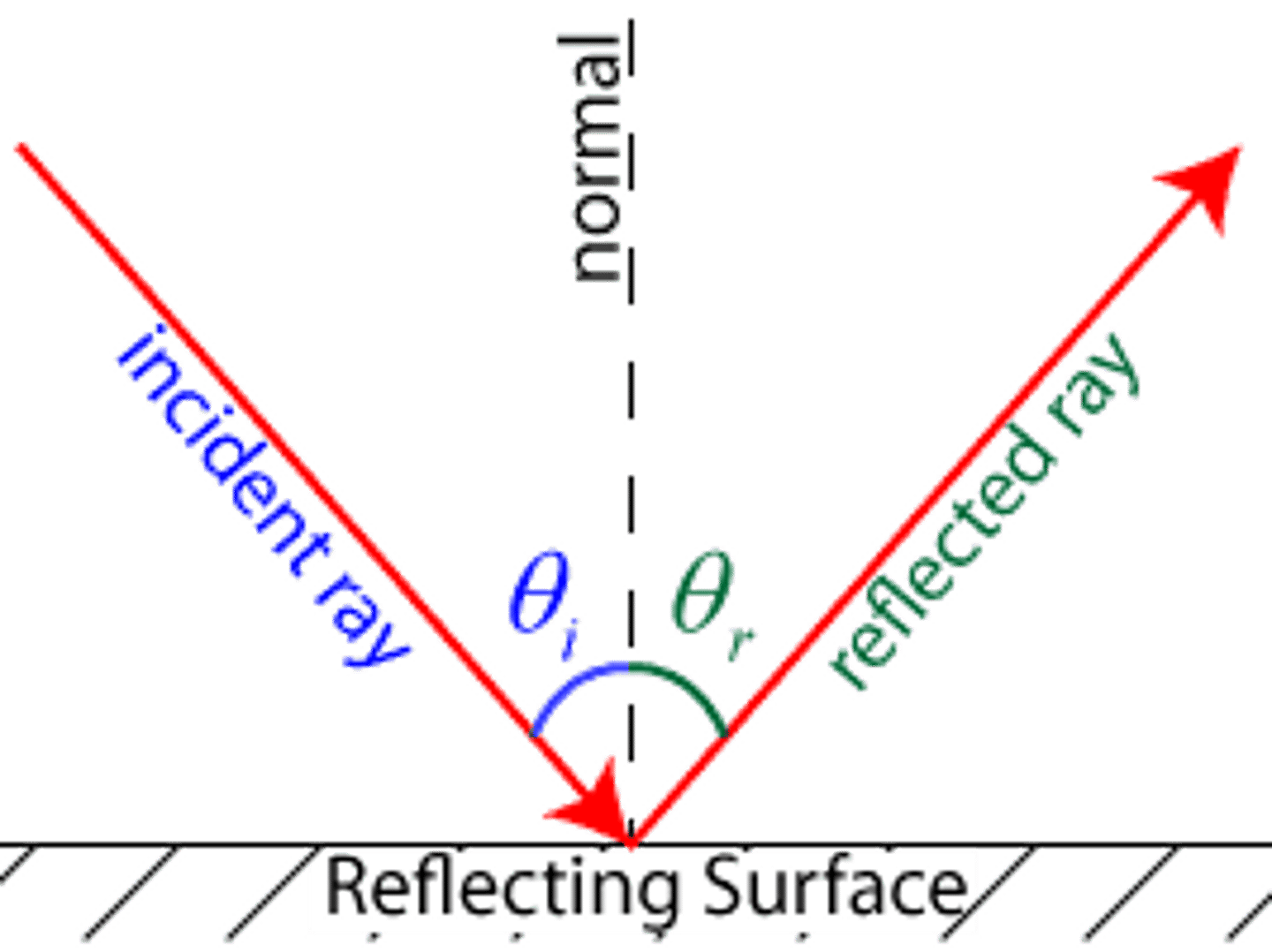
What is the angle of reflection?
The angle between the reflected ray and the normal
What is meant by ionising radiation?
radiation consisting of particles, X-rays, or gamma rays with sufficient energy to cause ionization in the medium through which it passes.
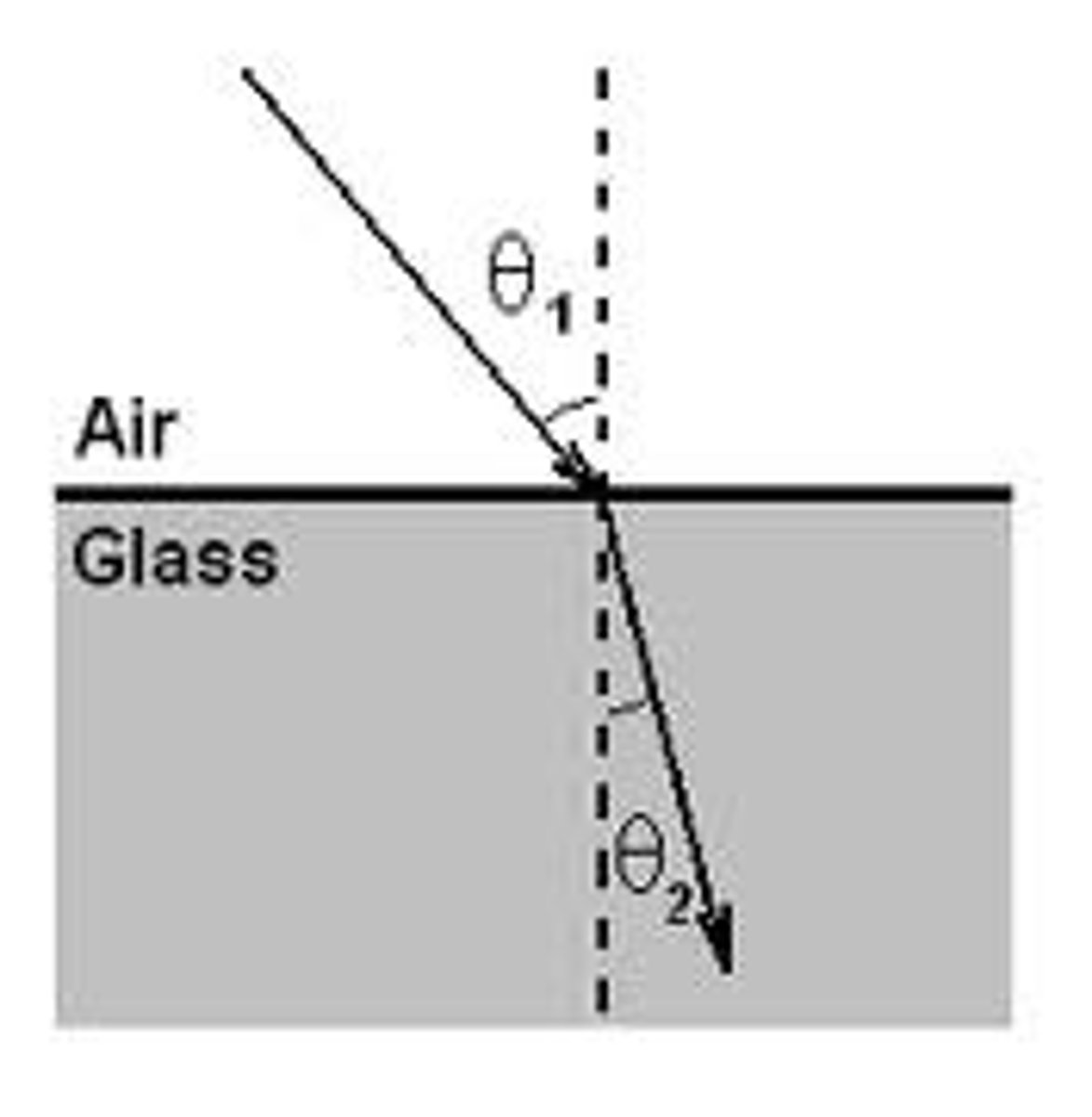
What is the angle of refraction?
The angle that the refracted ray makes with the normal as it leaves the boundary between the media
Are soundwaves in air transverse or longitudinal?
Longitudinal
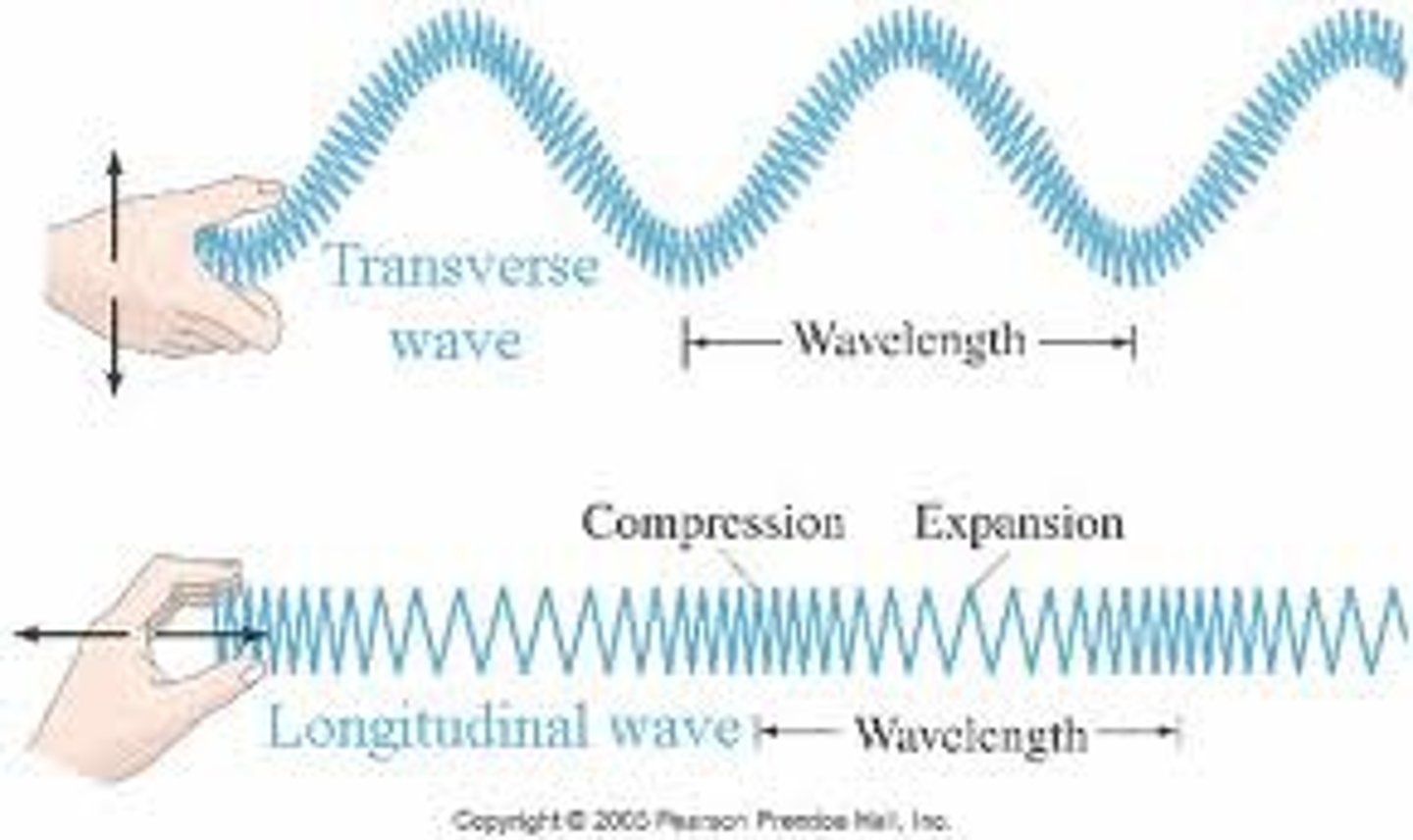
Describe the difference between longitudinal and transverse waves
Transverse waves are where the particles of the medium vibrate at right angles to the direction of travel and Longitudinal waves are waves where the particles vibrate in the same direction of travel.
The signal generator is turned on for 50s. During this time, 400 complete cycles of the wave pass point X. Calculate the frequency of the wave
8hz
A child throws a stone into a pond. The stone creates ripples when it hits the water, which spreads across the pond. The ripples pass a leaf floating on the pond. State whether the leaf will be carried to the edge of the pond
Waves cannot transfer matter only energy, the ripples do not move the leaf or water therefore the leaf will not be carried by the waves.
The ripples have a wavelength of 15mm. Given that the frequency = 1.4 x 10^-2 kHz calculate their speed in m/s
15/ 1000 = 0.015m 1.4 X 10^-2x 1000 = 14Hz
14X0.015 = 0.21 m/s
0.21m/s
A vibrating violin string produces a sound wave. A violinist is practising in a village hall. Her teacher sits at the back. State the medium the sound waves travel through to reach the teacher?
Air
The violinist plays a note with a frequency of 2.49 kHz. The sound waves travel at speed of 340 m/s. Calculate the wavelength of the sound waves. Give your answer to 2 s.f
2.49 Khz X 1000 = 2490 Khz
340/ 2490 = 0.1365...
0.14
Harry wants to measure the frequency of ripples. He floats a cork in the ripple tank and measures the time it takes for the cork to oscillate 30 times. He repeats his test 5 times. he does not adjust the variable power supply between tests. State two other factors that should remain the same between repeats
The position of the cork in the experiment
Depth of the dipper (thing creating the ripples) in the water
When a wave is reflected it
bounces back off the material
When a wave is absorbed it
transfers all its energy to the material
When a wave is transmitted it
passes through the material
When a wave passes through a boundary between materials, it can change direction. Name this effect?
Refraction
A light ray hits a glass block and passes through it without changing direction. Give the angle to the surface at which the light ray hits the glass block
90 degrees
What instrument do you use to measure a potential difference?
A voltmeter
What is the Equation for potential difference
Potential difference = current x resistance
What does an ammeter measure?
measures current
A volmeter must be connected in...
parallel
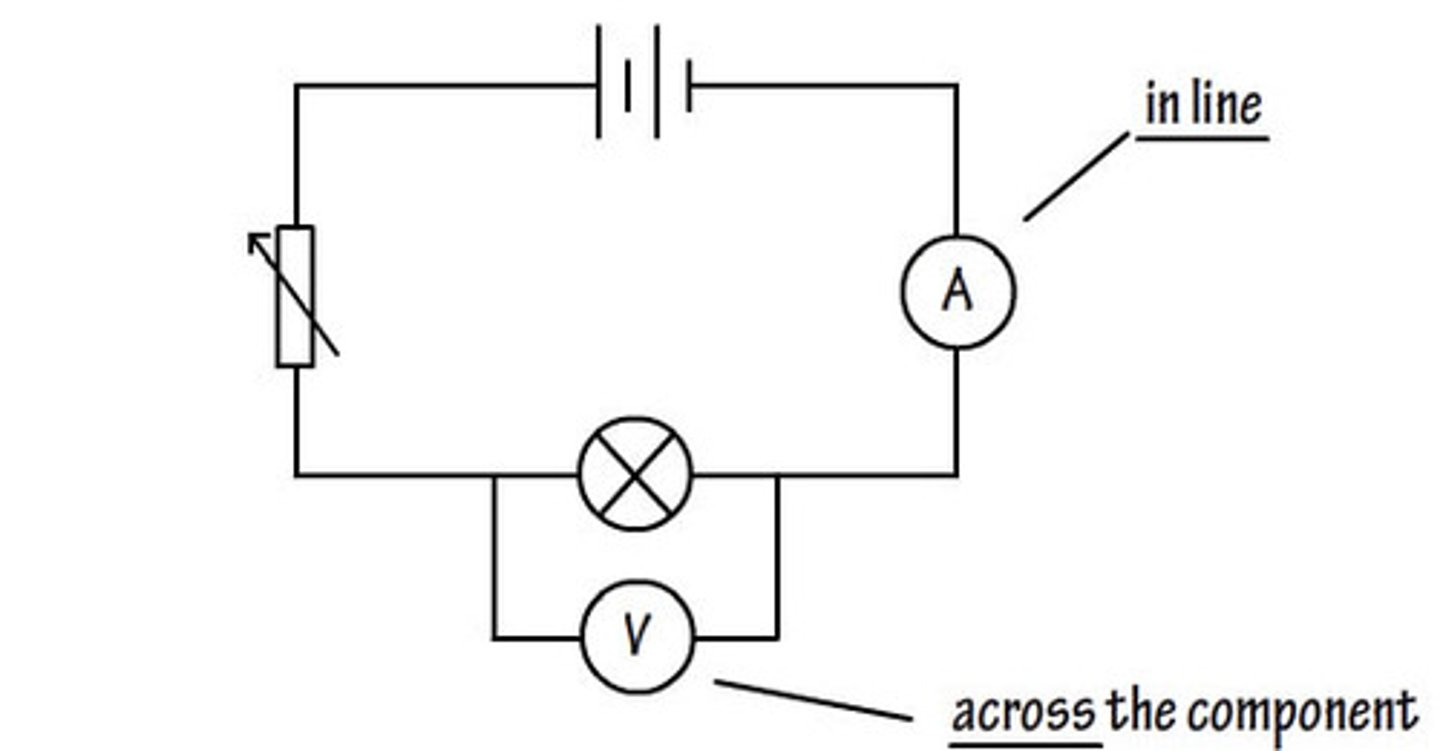
An ammeter must be connect in....
series
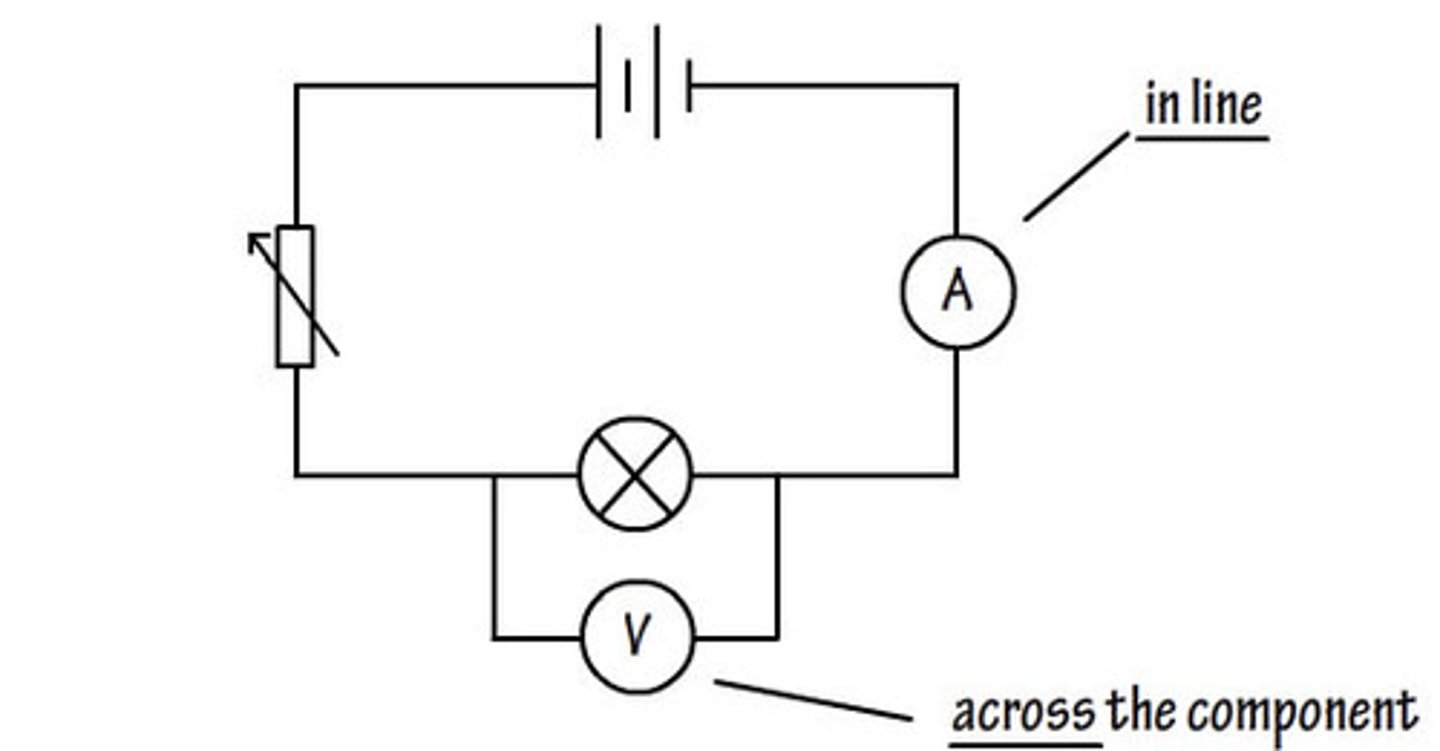
what is potential difference measured in?
Volts (V) using a voltmeter
Energy =
Power x time
Power = (pd)
current x potential difference
What two things affects the size of a current?
Resistance and Potential difference
What is the unit of resistance?
Ohm (Ω)
An electric current will increase when:
Potential difference increases and Resistance decreases
What is the equation for resistance? (Ohm's Law)
Resistance = Potential difference / current
How do you measure resistance?
you measure the potential difference across the component and the charge
What would you use to measure potential difference across a component?
A voltmeter
What is an ohmic conductor?
A conductor that obeys Ohm's law
In an Ohmic conductor, the resistance...
remains constant