Lesson 2.5: Costs of Production
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards made from a presentation segment created as a lesson on the costs of production.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
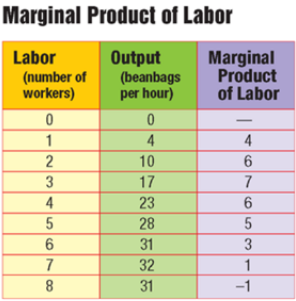
Marginal product of labor
The change in output from hiring one additional unit of labor
How much more of a product can be produced by hiring one more worker

Specialization
The focus of one worker on a specific task for greater efficiency per worker by reducing the time spent switching and performing different tasks
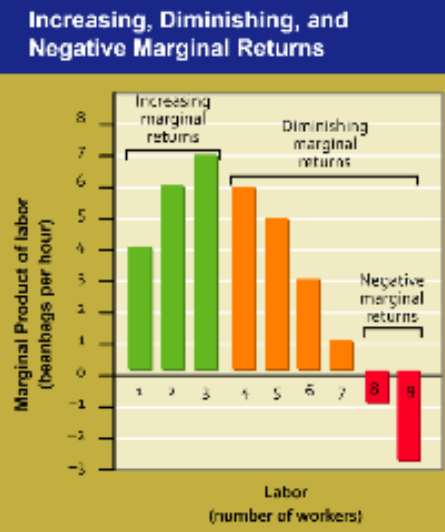
Increasing marginal returns
Level of production in which the marginal product of labor increases as the number of workers increases, thus reaping the benefits of specialization
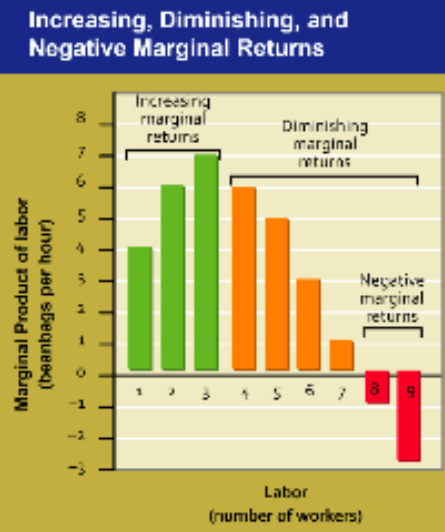
Diminishing marginal returns
Level of production in which the marginal product of labor decreases as the number of workers increase
Insufficient work is being distrubted to effectively specialize the labor needed
This can be limited by fixed capital, where workers may be unable to simultaneously use a machine at one time
Fixed cost
A cost that does not change periodically, no matter how much of a good is produced
Mainly involves production facility, cost of building, and equipment
Examples include rent, machine repairs, and property taxes
Variable cost
A cost that rises or falls depending on how much is produced
Includes raw materials and some labor, electricity, and heating bills
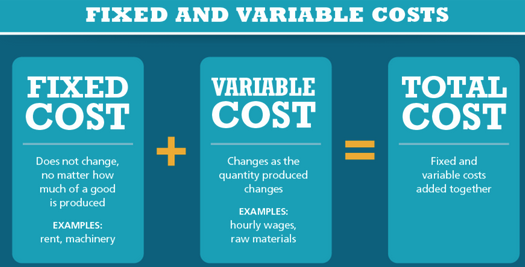
Total cost
The sum of the fixed and variable costs in making a product
Profit maximization
A firm’s primary goal through increasing revenue and reducing operating costs
Highest profitability comes from more revenue and lower costs (a bigger gap)
Total revenue
The total proceeds from the sale of a good
Marginal revenue (market price)
The additional income of selling one more unit of a good or service, typically determined by the market

Marginal cost
The cost of adding one more unit
Efficiency occurs when the price paid at market equals this to produce a good in order to maximize net revenue and resource allocation