Physics 2 - Lesson 10: Rate Laws Part II
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Physics 2 Lesson 10
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Lesson 10: Rate Laws Part II
Lesson 10: Rate Laws Part II
Which of the following are tenets of Collision Theory?
I. Molecules must collide in order to react.
II. Collisions must have the correct orientation.
III. Collisions must have enough energy.
(A) I Only
(B) I and II Only
(C) II and III Only
(D) I, II, and III
(D) I, II, and III
The following are tenets of Collision Theory, which state that in order for a reaction to occur, the:
I. Molecules must collide in order to react.
II. Collisions must have the correct orientation.
III. Collisions must have enough energy.
How does Activation Energy (Ea) relate to these three tenets?
Ea is the amount of energy the molecules must have when they collide in order for a reaction to occur (tenet III).
CRB Some reactions are known as being Irreversible. Explain how Activation Energy would make a reaction Irreversible.
The Activation Energy for the forward reaction is low enough to be achievable in nature, whereas the backwards reaction must have such a high activation energy that this reaction is unlikely to occur.
CRB True or false? Reversible reactions could occur in both the forward and backward direction, and will reach a Static Equilibrium.
False. Reversible reactions could occur in both the forward and backward direction, and will reach a Dynamic Equilibrium.
CRB Fill in the blanks: At equilibrium, the System's Entropy will be at a ____________, and the Gibbs Free Energy of the system is at a ___________.
(A) Maximum, Minimum
(B) Minimum, Maximum
(C) Maximum, Plateau
(D) Plateau, Minimum
(A) Maximum, Minimum
At equilibrium, the System's Entropy will be at a ____________, and the Gibbs Free Energy of the system is at a ___________.
CRB Recall from the Biochemistry II Module that most of the same reactions and enzymes used in Glycolysis can occur in reverse for Gluconeogenesis. Would these reactions and enzymes be considered reversible?
Because the Forward and Backward reaction are both possible for these enzymes and reactions, they would be considered reversible.
CRB When discussing Forwards and Backwards reactions, there are ways to shift the Equilibrium between the 2 reactions. Which of the following principles best fits this criteria and is properly defined?
(A) The Arrhenius Principle claims that many substances that dissolve in water will form ions, and the equilibrium is more likely to favor the reaction that forms less ions if more substances dissolve.
(B) Le Chatelier's Principle claims that if a stress is applied to a system, the system's equilibrium shifts to relieve that stress.
(C) The Arrhenius Principle claims that if a stress is applied to a system, the system's equilibrium shifts to relieve that stress.
(D) Le Chatelier's Principle claims that many substances that dissolve in water will form ions, and the equilibrium is more likely to favor the reaction that forms less ions if more substances dissolve.
(B) Le Chatelier's Principle claims that if a stress is applied to a system, the system's equilibrium shifts to relieve that stress.
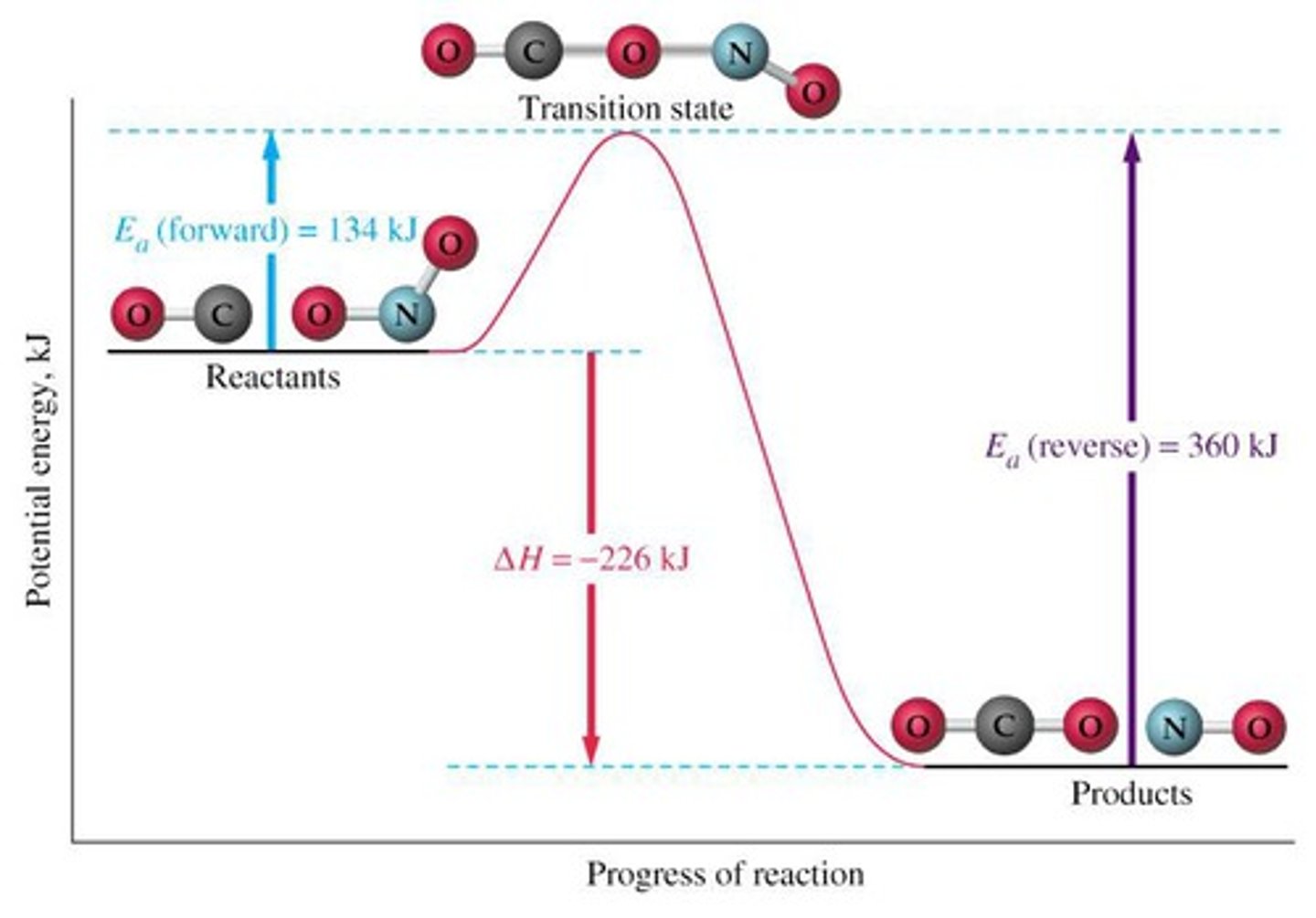
The highest point of an energy diagram is known as the:
I. Activated Complex
II. Transition State
III. Product-Reactant Compound
(A) I Only
(B) I and II Only
(C) II and III Only
(D) I, II, and III
(B) I and II Only
The highest point of an energy diagram is known as the Activated Complex or Transition State.
What is the purpose of the Arrhenius Equation?
The Arrhenius Equation is a mathmatical representation of the three tenets of Collision Theory.
Write out the Arrhenius Equation.
Struggling to keep your MCAT equations straight? Simply conquer the 100 most important equations using Andrew's 100 Most Essential Equations Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-equation-mastery-course/
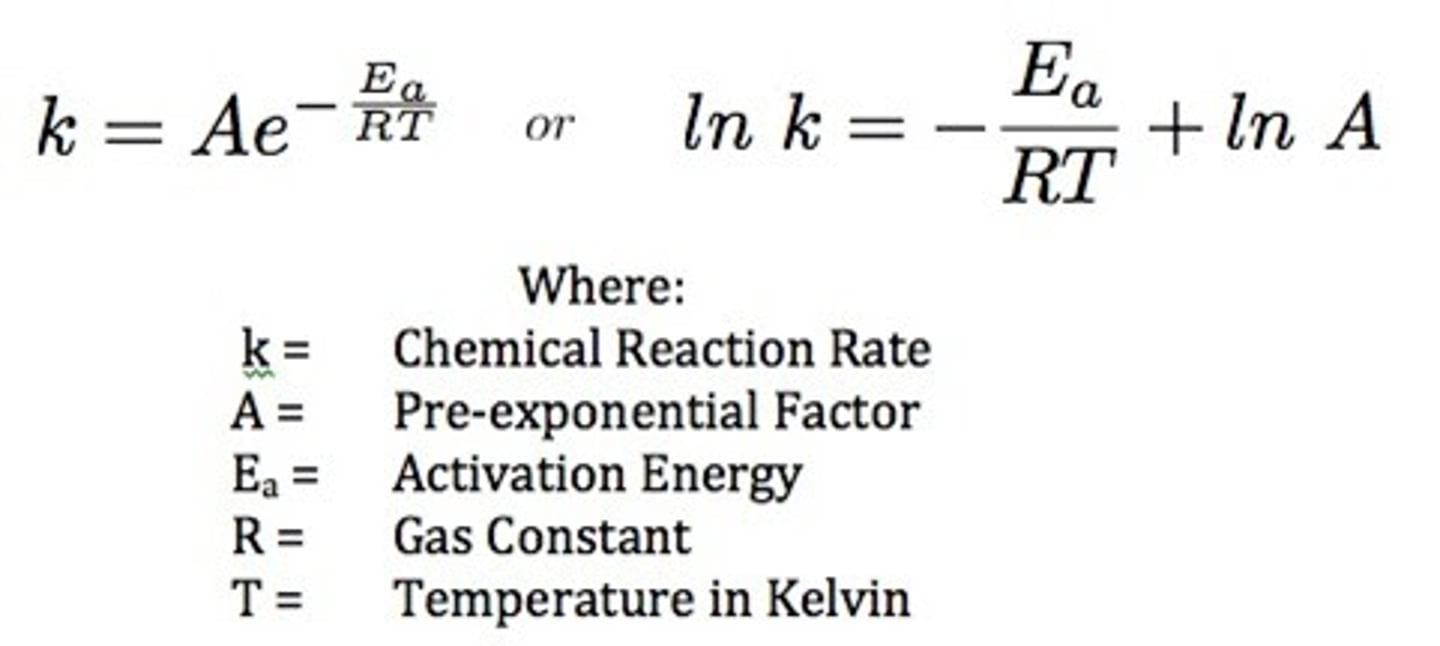
e^(-Ea / RT) is also known as the f. F is equal to 3.74⋅10^-3. What does that tell you?
This means that for every 1,000 collisions, 3.74 collisions will result in a successful reaction. The higher the f, the higher the success rate of reactions.
Increasing the Activation Energy will ____________ the frequency of successful collisions. Increasing the Temperature will ____________ the frequency of successful collisions.
(A) Increase, Increase
(B) Increase, Decrease
(C) Decrease, Decrease
(D) Decrease, Increase
(D) Decrease, Increase
Increasing the Activation Energy will decrease the frequency of successful collisions. Increasing the Temperature will increase the frequency of successful collisions.
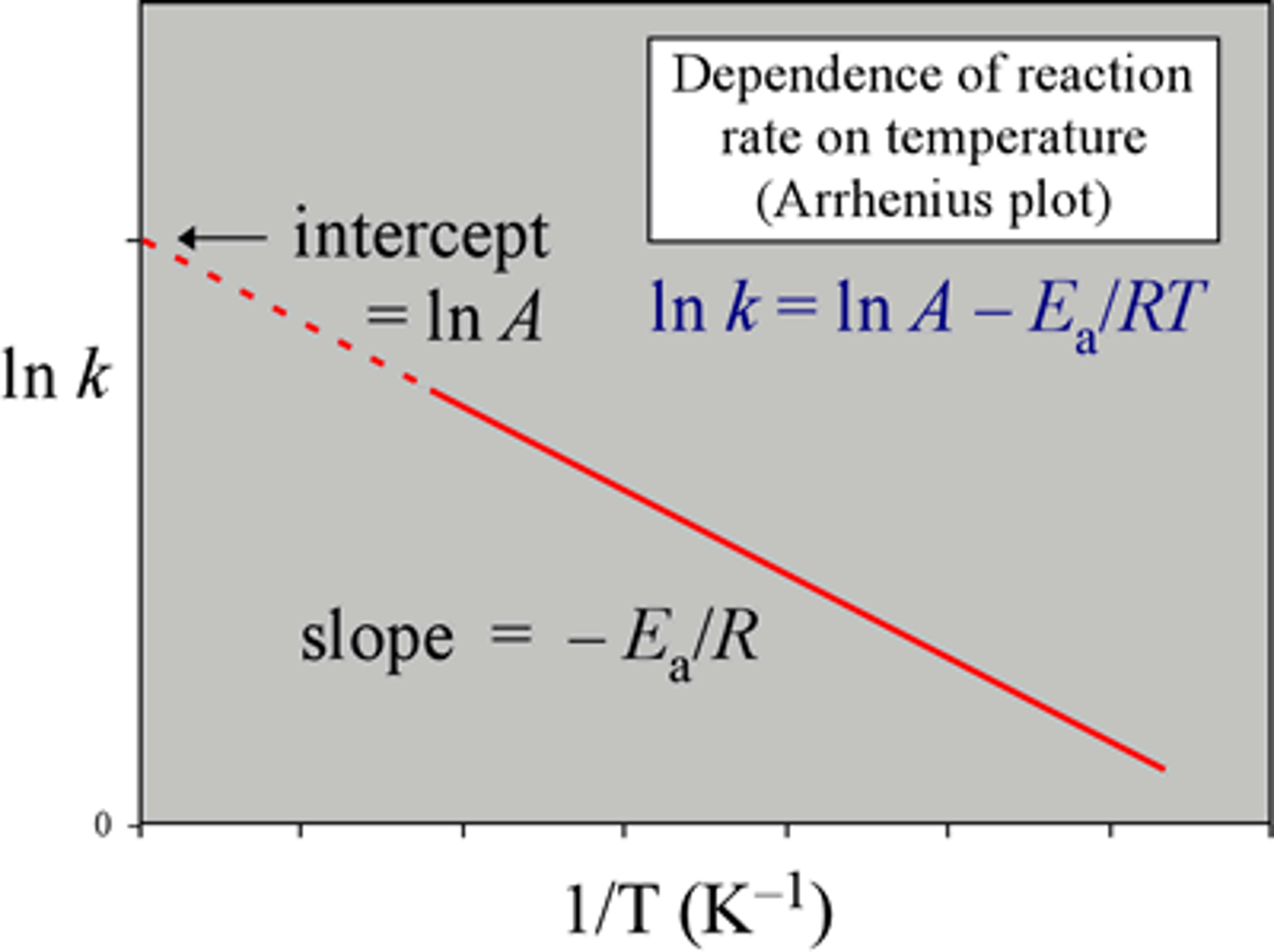
If you were to graph reaction rate data in order to determine the Arrhenius Equation, what would the y-axis be equal to? X-axis? Slope? Y-intercept?
What is the difference between a unimolecular and bimolecular reaction?
In a unimolecular reaction, one molecule participates in the reaction: A -> products.
In a bimolecular reaction, two molecules participate in the reaction: A + B -> products.
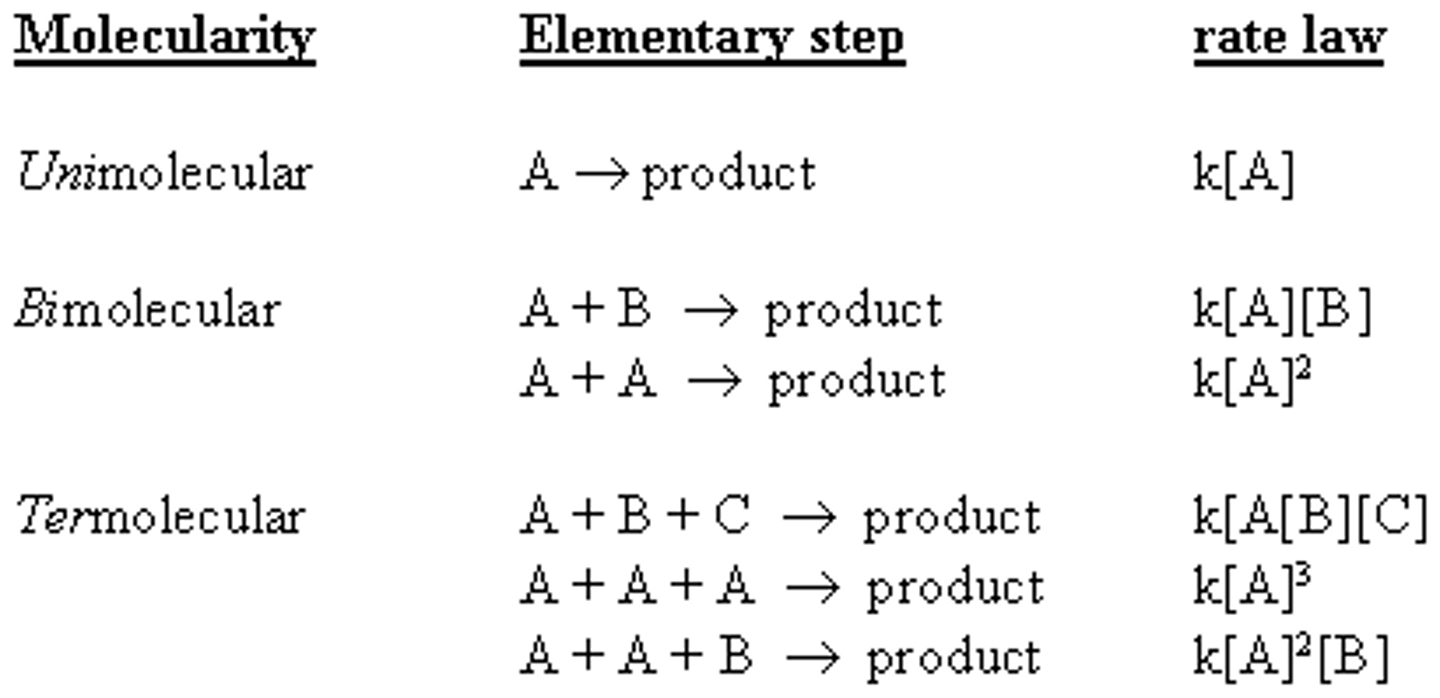
Why are termolecular reactions so rare?
Termolecular reactions are so rare because it is very difficult for 3 molecules to collide at the same time in the proper orientation with the right amount of energy.
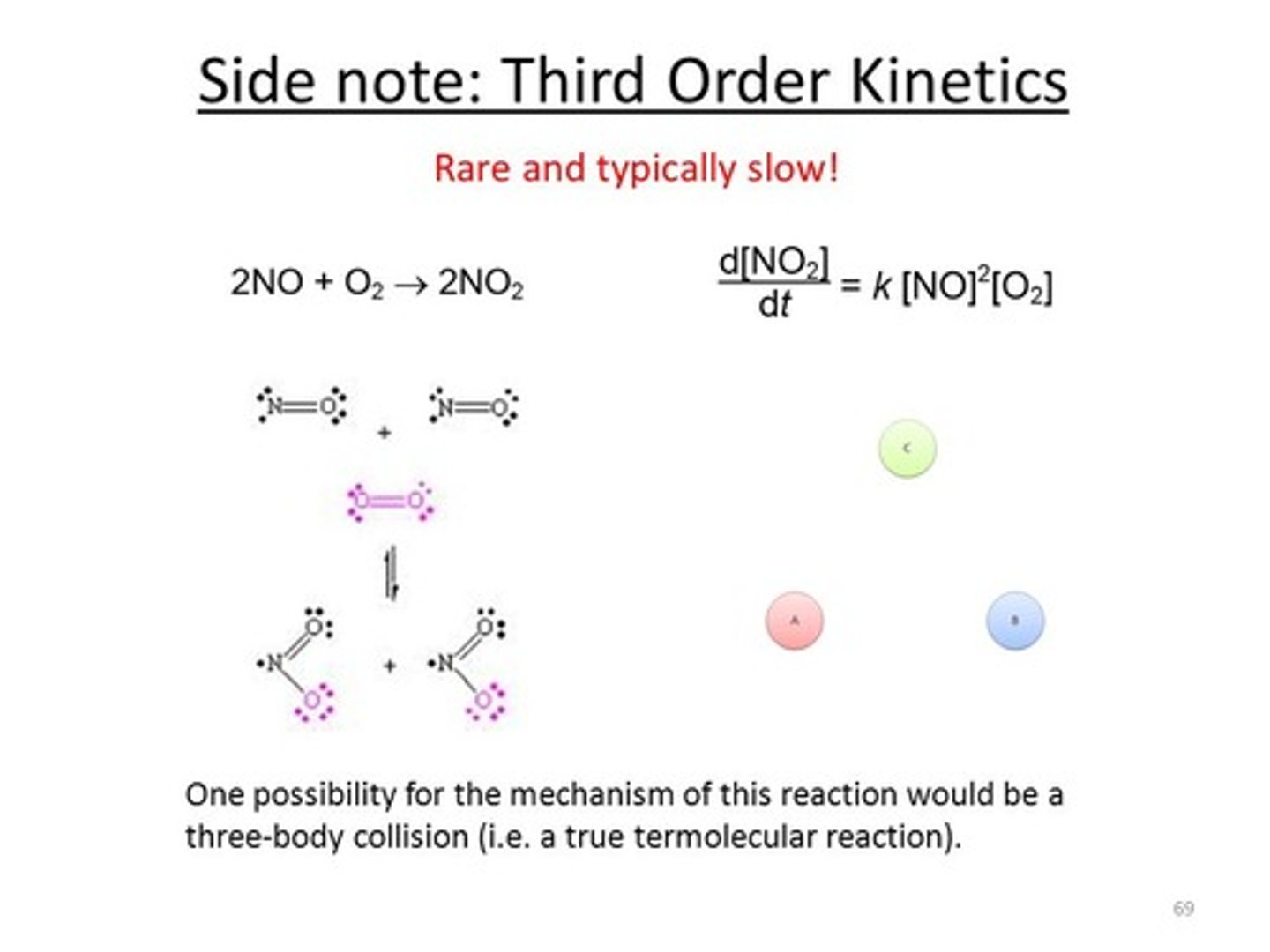
True or False? You can write the rate law for one-step (elementary) reactions simply based on the reaction formula (A + B -> C).
True. You can write the rate law for one-step (elementary) reactions simply based on the reaction formula (A + B -> C). When dealing with multi-step reactions, however, you will need to determine the rate law experimentally.
http://d2vlcm61l7u1fs.cloudfront.net/media%2F2a6%2F2a65e4e9-02ba-4730-804f-d9cd73958de9%2FphpJGUFJQ.png
(See the back of the notecard for the answer)
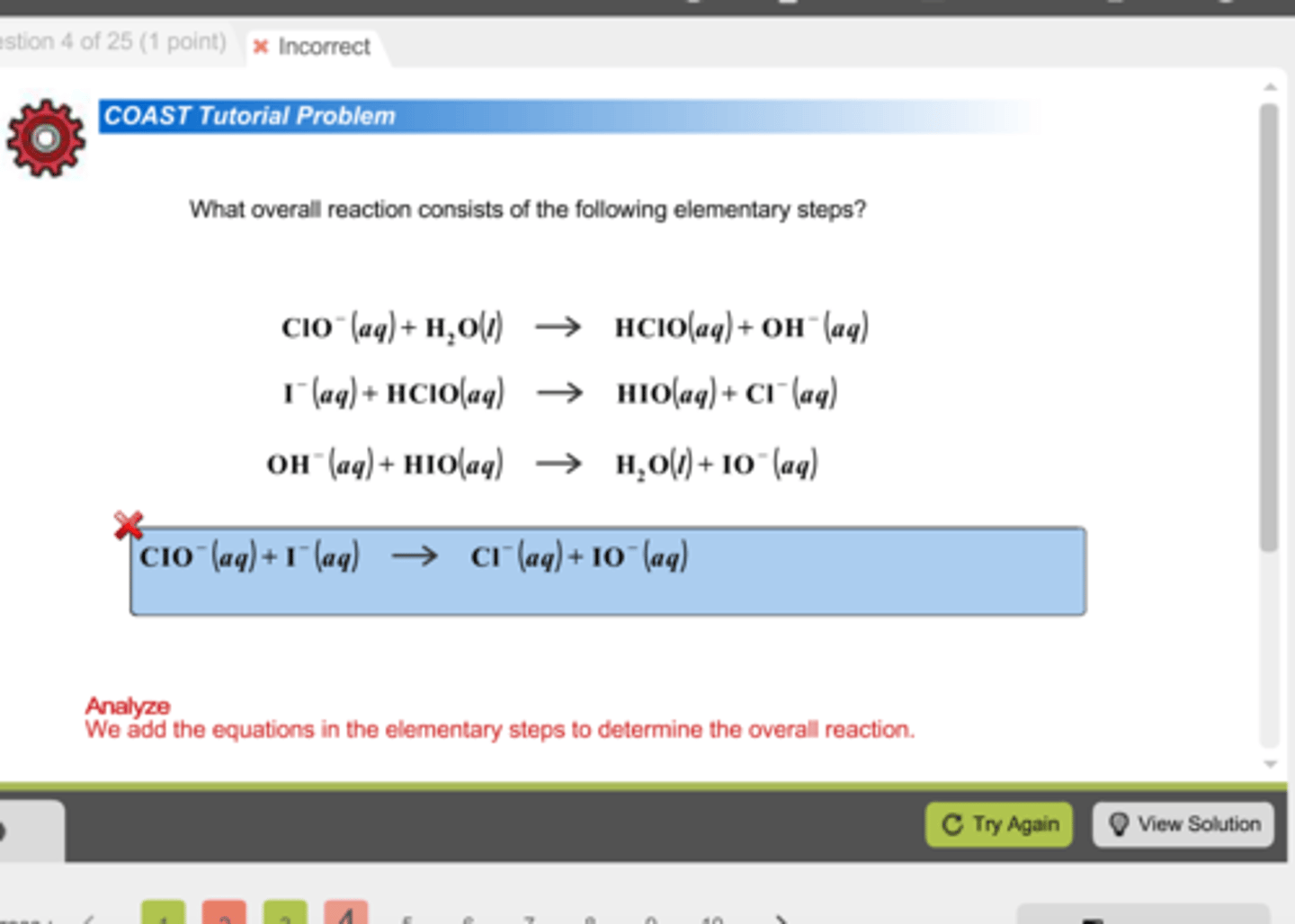
In the previous question (http://d2vlcm61l7u1fs.cloudfront.net/media%2F2a6%2F2a65e4e9-02ba-4730-804f-d9cd73958de9%2FphpJGUFJQ.png), which of the following can be considered an Intermediate?
I. OH-
II. HIO
III. ClO-
(A) I Only
(B) I and II Only
(C) I and III Only
(D) I, II, and III
(B) I and II Only
Both OH- and HIO are intermediates in the reaction because they are produced in one step and used up in another.
True or False? The rate of the overall reaction can be approximated as the rate of the Rate-limiting Step.
True. The rate of the overall reaction can be approximated as the rate of the Rate-limiting Step.
True or False? The rate law for the overall reaction is equal to the rate law of the Rate-limiting Step.
True. The rate law for the overall reaction is equal to the rate law of the Rate-limiting Step.
A catalyst is defined as a substance that increases the rate of a reaction, and:
(A) is used up in a reaction.
(B) is not used up in a reaction.
(C) uses up the other reactants in a reaction.
(D) does not use up the other reactants in a reaction.
(B) is not used up in a reaction.
A catalyst is defined as a substance that increases the rate of a reaction, and is not used up in a reaction.
Consider the following multi-step reaction:
Step 1: H2 + Pd -> 2Pd-H
Step 2: C2H4 + Pd-H -> C2H5-Pd
Step 3: C2H5-Pd + Pd-H -> C2H6 + 2Pd
Which of the following is being used as the catalyst in this reaction?
(A) H2
(B) Pd
(C) C2H4
(D) C2H6
(B) Pd
Pd is not used up in the reaction; thus it must be a catalyst.
Which of the following is affected by a catalyst?
(A) Ea
(B) ∆Erxn
(C) Energy of the Reactants
(D) Energy of the Products
(A) Ea
The Activation Energy is decreased by stabilizing and decreasing the energy of the Transition State.
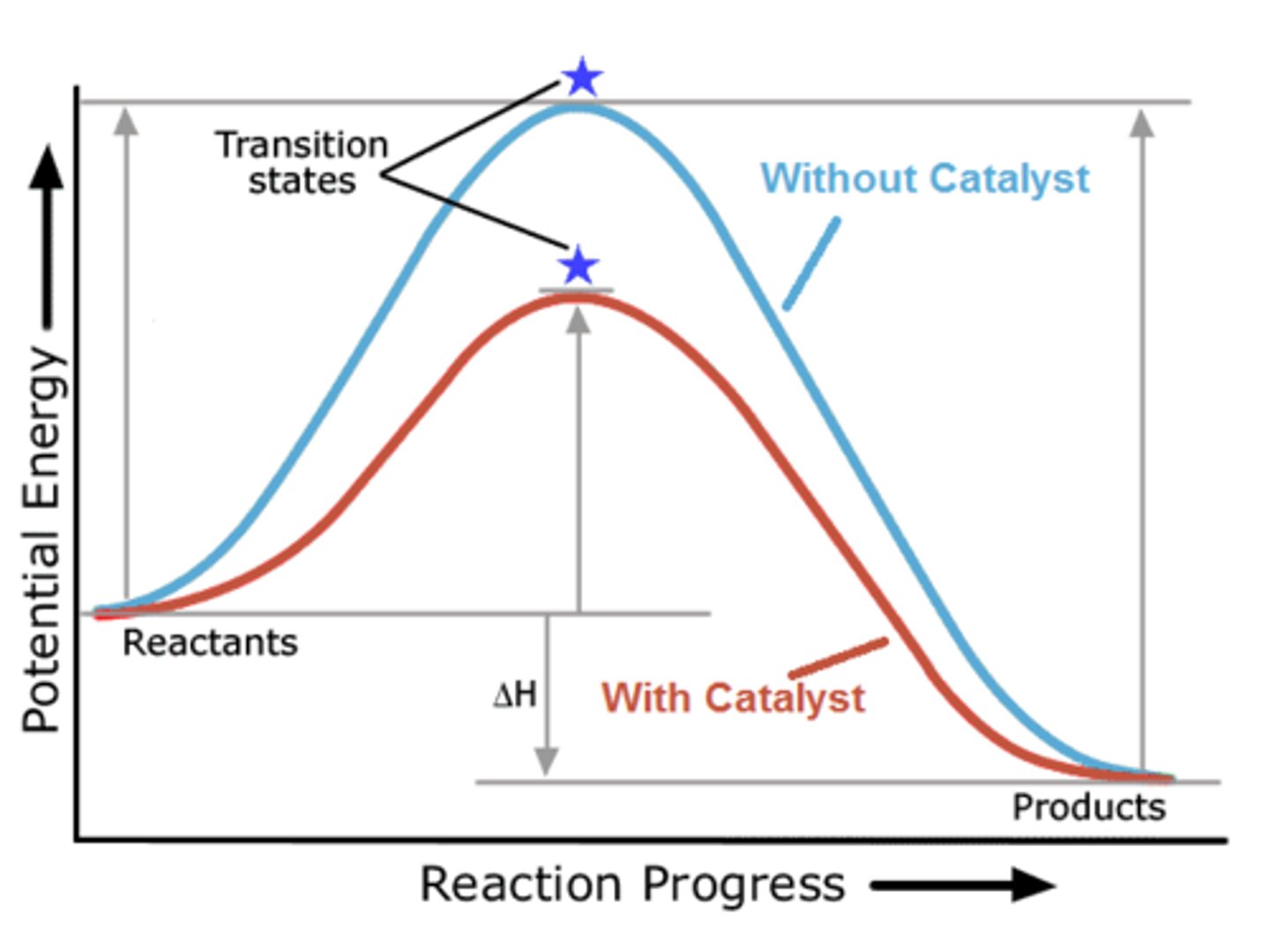
CRB Activation Energy also plays a key factor in determining which of the 2 following types of products are formed?
(A) Stable and Instable
(B) Kinetic and Thermodynamic
(C) Rate-Determining and Rate-Limited
(D) None of the above
(B) Kinetic and Thermodynamic
Activation Energy plays a key role in determining if a reaction is under Kinetic or Thermodynamic Control, and which type of product is formed.
CRB Fill in the blanks: A reaction is under Kinetic Control if the system has ___________ temperatures because of _______________.
(A) High, the Increased Stability of Products.
(B) High, the Lower Activation Energy required
(C) Low, the Increased Stability of Products
(D) Low, the Lower Activation Energy required
(D) Low, the Lower Activation Energy required
A reaction is under Kinetic Control if the system has Low temperatures because of the Lower Activation Energy required.
CRB Fill in the blanks: A reaction is under Thermodynamic Control if the system has ___________ temperatures because of _______________.
(A) High, the Increased Stability of Products.
(B) High, the Lower Activation Energy required
(C) Low, the Increased Stability of Products
(D) Low, the Lower Activation Energy required
(A) High, the Increased Stability of Products.
A reaction is under Thermodynamic Control if the system has High temperatures because of the Increased Stability of Products.
A reaction will be _________ when ∆G is positive. A reaction will be _________ when ∆G is negative.
(A) spontaneous, spontaneous
(B) spontaneous, non-spontaneous
(C) non-spontaneous, non-spontaneous
(D) non-spontaneous, spontaneous
(D) non-spontaneous, spontaneous
A reaction will be non-spontaneous when ∆G is positive. A reaction will be spontaneous when ∆G is negative.
What equation can be used to calculate ∆G based on Q?
∆G = ∆G° + RTlnQ
∆G = Gibb's Free Energy
∆G° = Standard Gibb's Free Energy
R = Gas Constant (8.314J/molK)
T = Temperature (298 K at standard conditions)
Q = Reaction Quotient
Struggling to keep your MCAT equations straight? Simply conquer the 100 most important equations using Andrew's 100 Most Essential Equations Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-equation-mastery-course/
Write the Keq expression for the following unbalanced reaction: O2 + N2H2 -> NO2 + H2
First, balance the reaction as follows:
2O2 + N2H2 -> 2NO2 + H2
Then write the Keq expression as follows:
Keq = [NO2]^2[H2] / ([O2]^2[N2H2])
CRB Recall that the Reaction Quotient Q can also be related to Keq. If Q < Keq, then in which direction do you expect the reaction to occur?
(A) Forward
(B) Backward
(C) Both Forward and Backward Equally
(D) I will review Reaction Quotients and return to this question!
(A) Forward
If Q < Keq, then the forward reaction hasn't reached equilibrium yet and will continue to occur.
CRB The Law of Mass Action dictates how the Equilibrium Constant Keq is written (Products over Reactants). Which of the following would NOT be included in an Equilibrium Constant according to the Law of Mass Action?
I. Ethanol and Water if they form a mixed solvent.
II. Pure Solids, like undissolved Silver
III. Pure Liquids, like an unmixed solvent.
(A) II only
(B) I and II only
(C) II and III only
(D) I, II and III
(C) II and III only
Pure Solids and Liquids are said to have an activity of 1, meaning that they do not have to be considered when calculating the Equilibrium Constants.
For the previous question, assume the following:
O2 = 2.4 atm
N2H2 = 4.3 atm
NO2 = 5.6 atm
H2 = 1.3 atm
What is the value of ∆G (in kJ/mol) for this reaction assuming a temperature of 32.4° C and a standard gibb's free energy of -23.5 kJ/mol.
(A) -12.869 kJ/mol
(B) -12869 kJ/mol
(C) -22.234 kJ/mol
(D) -22,234 kJ/mol
(C) -22.234 kJ/mol
Q = [NO2]^2[H2] / ([O2]^2[N2H2])
Q = (5.6)^2(1.3)/ (2.4)^2(4.3)
Q = approx. 2 (actual: 1.65)
∆G = ∆G° + RTlnQ
∆G = -23.5⋅10^3 + (8.314)(305.4)(ln1.6)
∆G = -23.5⋅10^3 + approx. 1000 (actual: 1265)
∆G = -22,234 J/mol
∆G = -22.234 kJ/mol
Need help with MCAT math? Become an MCAT math wizard using Andrew's High-speed Math Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-high-speed-math-mastery-course/
What equation is used to calculate ∆G° based on the Equillibrium Constant?
∆G° = -RTlnK
∆G° = Standard Gibb's Free Energy
R = Gas Constant (8.314J/molK)
T = Temperature (298 K at standard conditions)
K = Equilibrium Constant
Struggling to keep your MCAT equations straight? Simply conquer the 100 most important equations using Andrew's 100 Most Essential Equations Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-equation-mastery-course/
Calculate the Equilibrium Constant for a reaction in which ∆G°= -44.7 kJ/mol and the Temperature is at 25° C.
(A) 69,026.427
(B) 690,264.27
(C) 6,902,642.7
(D) 69,026,427
(D) 69,026,427
∆G° = -RTlnK
-44.7⋅10^3 = -(8.314)(298)(lnK)
-4.47⋅10^4 / (approx. -2.5⋅10^3 (actual: -2.477⋅10^3)) = lnK
lnK = approx. 20 (actual: 18.05)
K = e^18.05
K = approx. 70,000,000 (69,026,427)
Need help with MCAT math? Become an MCAT math wizard using Andrew's High-speed Math Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-high-speed-math-mastery-course/
When K = 1, what is the value of ∆G°? What about when K > 1? K < 1?
∆G° = 0 when K = 1.
∆G° > 0 when K < 1.
∆G° < 0 when K > 1.