Lab 1 Amazing, Wild, Wonderful Water
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
What type of covalent bond is formed between water
polar covalent
emergent properties of water
cohesive, adhesive, expansion when freezing, and versatility as a solvent
Cohesion
linking of like-molecules, often by hydrogen bonds
adhesion
clinging of water to another substance by hydrogen bonds
stomata
minute aperture structures found of leaf skin also known as epidermis. open and close for gases
dependent variable
The outcome factor; the variable that may change in response to manipulations of the independent variable. (the flower's reaction to the water, like dying, or the color it turned into)
independent variable
variable that is manipulated (the substance added to the water)
control group
In an experiment, the group that is not exposed to the treatment ( the carnation in regular water)
surface tension
A measure of how difficult it is to stretch or break the surface of a liquid (cohesion)
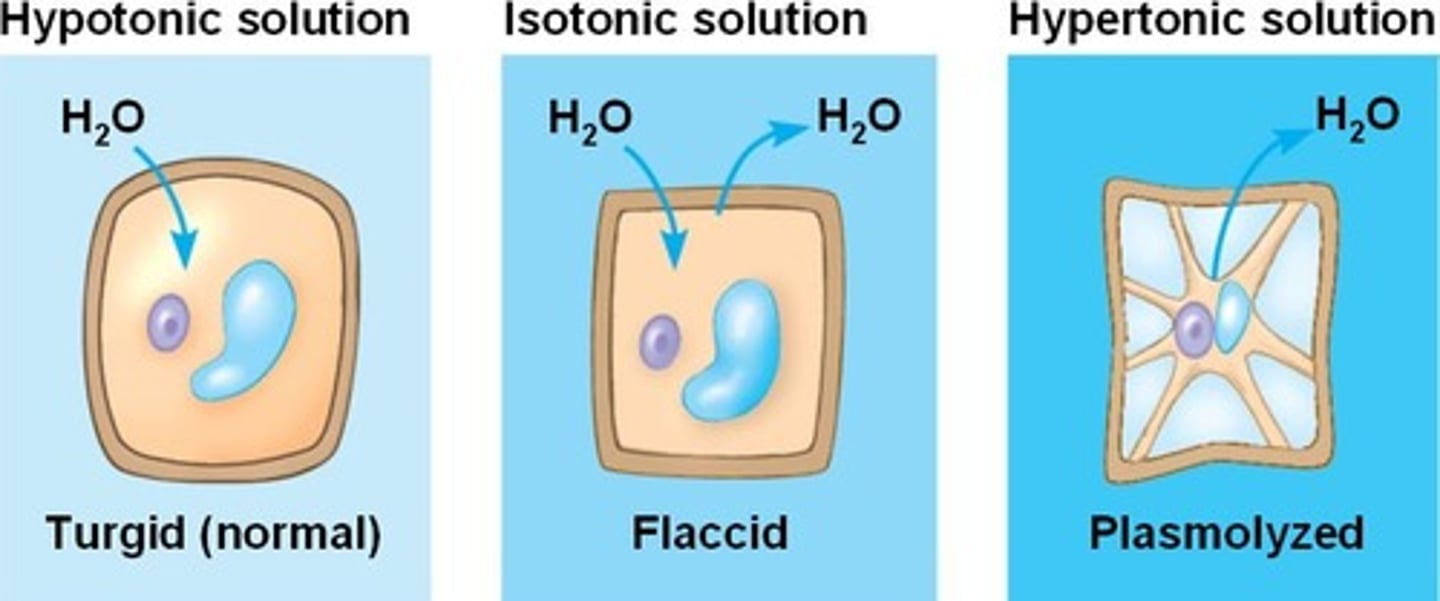
plasmolysis
When a cell loses water when placed in a hypertonic solution. (seen in elodea)
acid
releases H+ ion
base
decreases H+ ion
buffer
regulates pH. Gives an H+ when low and removes H+ when too high
OTC deficiency
excess ammonia
Homeostasis
regulation of body's functions (presence of buffers in the body)