Chapter 9
1/27
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
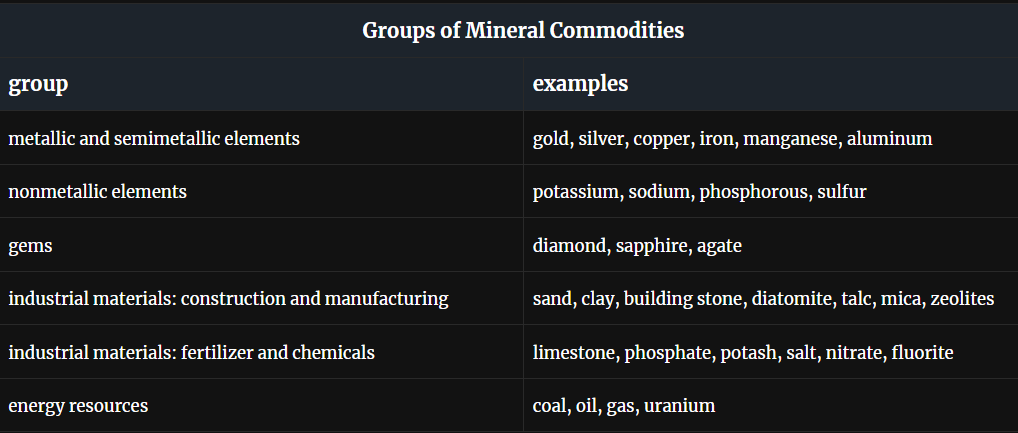
Mineral commodities
mineralogical resources from the earth
Industrial diamonds
Natural diamonds; have little gem quality. Most commonly used as an abrasive or polishing agent. But they are also incorporated into grinding wheels, saw blades, and drill bits used to manufacture products from very hard materials
Most significant advancement in metal use
bronze, an alloy created by melting and combining the metals copper and tin. Iron came afterwards
What allowed people to work with bronze?
after pouring the molten bronze into stone molds and allowing the liquid to cool to a solid, the copper-tin alloy could be formed and shaped using hammers at room temperature
Mineral deposit
place in Earth’s crust where geologic processes have concentrated one or more minerals at greater abundance than in the average crust
Ore deposit
mineral deposit that can be produced to make a profit
Reserve
amount of known ore in a deposit
Ore grade
concentration of a commodity in the ore (“richness”)
Natural abundance for useful minerals
economical concentration factor is the ratio of typical minimum economical ore concentration to average crustal concentration
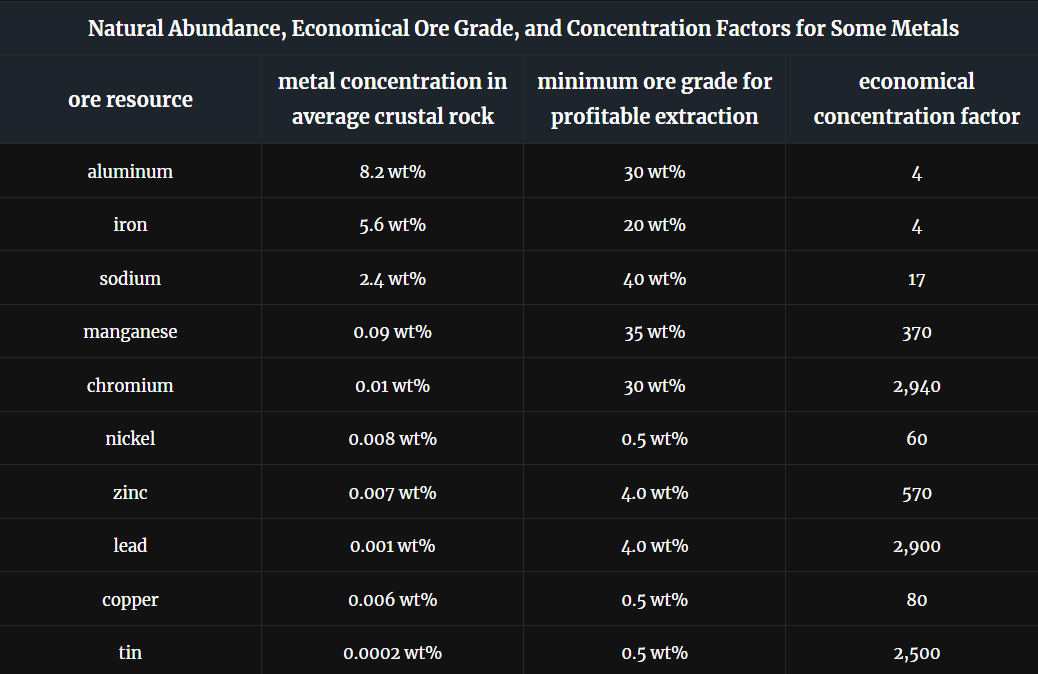
Why is the distribution of ore deposits around the globe uneven?
Because earth’s geology varies and some regions of the world contain most of the supply of certain commodities
Critical (strategic) minerals
important minerals are not produced in the United States, but are needed for many things. We must import these as it would be too expensive to rely on them only in the USA
Most South African ore deposits are associated with
Precambrian greenstone belts (volcanic terranes)
Most economical metal and semimetal deposits are found near
margins of continents, or the former margins of continents, where mountain building and igneous activity have occurred. Still, other types of deposits are found in continental interiors
Ideal ore minerals
Contain 100% ore minerals (that are of interest). Such ores do not exist, but some come close (copper)
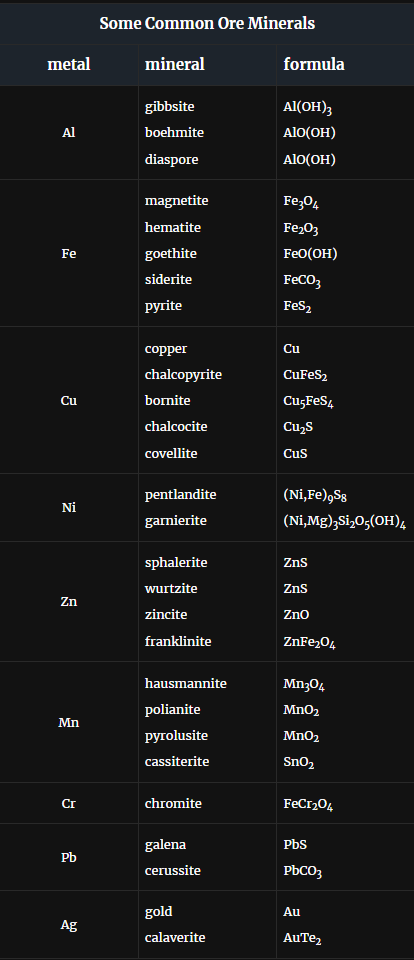
Is processing ore minerals or silicate minerals more cost effective?
Ore minerals are most cost effective. That is why we mine things like copper and Cu-Fe for their mineral content, because elements are relatively easy to extract.
Silicate minerals are not easy to mine because tight bonding makes producing metallic aluminum from silicates uneconomical
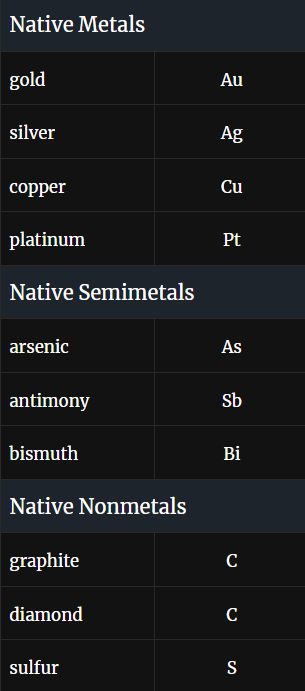
Native elements
First used by early humans. May require no processing before being used in manufacturing, as currency, or for other purposes
Electrum
Compositions containing both gold and silver
Nonmetallic native elements
Graphite, diamond, and sulfur
Sulfides
contain one or several metallic elements and sulfur as the only nonmetallic element. Bonding is variable: generally either covalent, metallic, or a combination of both
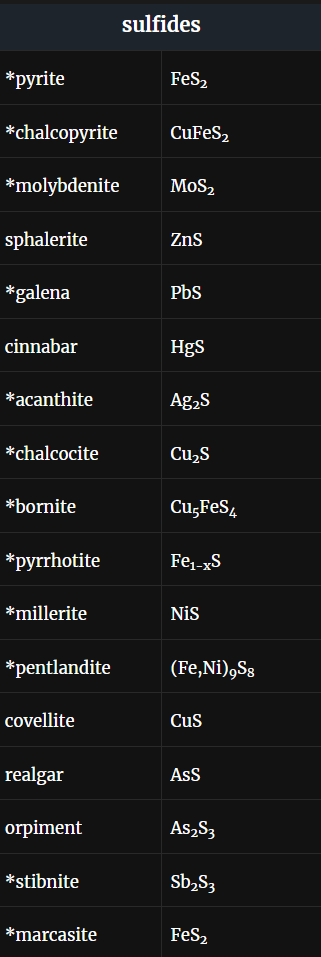
Peacock ore
Forms when the copper mineral bornite, which is unremarkable and hard to identify if unoxidized, commonly oxidizes and tarnishes

Sphalerite
Because of its many different appearances, sphalerite can be hard to identify unless it is brown and resinous

Oxides and hydroxides
most have relatively simple and related formulas. Oxide minerals consist of metal cations bonded to O2-. Hydroxide minerals contain (OH)– anion molecules in place of all or some O2-. Both often have ionic bonding
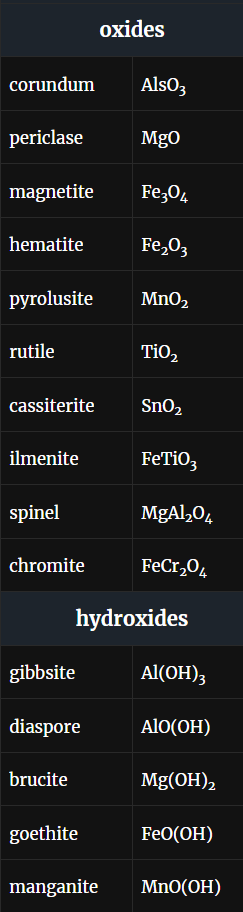
Main difference between oxides and hydroxides
Hydroxides are unstable at high temperature; they exist in low-temperature environments and are commonly products of alteration and weathering. Other oxide minerals – magnetite and ilmenite, for example – are high-temperature minerals generally associated with igneous or metamorphic rocks
Spinel group
Oxides with general formula XY2O4 (spinel and chromite). All have similar atomic arrangements but contain different elements

Gemstone
gems that are minerals. Valuable gems exhibit vibrant color, clarity, brilliance, or play-of-color (diamond)

Fire
a type of play-of-color that appears as changing flashes of different colors when we view a gem from different angles. Common in minerals with dispersion
Dispersion
the ability to separate white light into different colors that pass through the mineral along slightly different paths