Lec Exam #2 Review
1/72
Earn XP
Description and Tags
BIO 047
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
The type of cartilage that forms the costal cartilages at the ends of the ribs is
A. fibrocartilage
B. calcified cartilage
C. hyaline cartilage
D. elastic cartilage
C. hyaline cartilage
Which cell is responsible for bone resorption?
A. osteoclast
B) osteocyte
C. osteogenic cells
D. osteoblast
A. osteoclast
The cell responsible for secreting the matrix of bone is the
A. osteocyte
B. chondrocyte
C. osteoblast
D. osteoclast
C. osteoblast
True or false, the ends of a long bone are known as the diaphysis?
False (the ends of a long bone are known as the epiphyses)
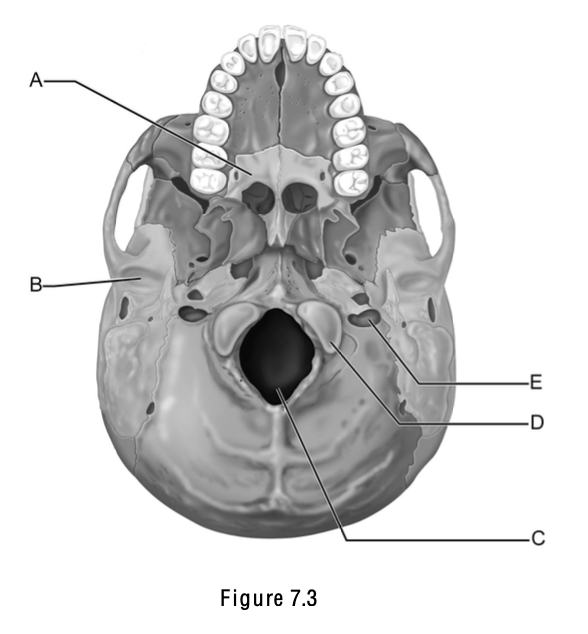
Match the following w/ the correct letter on the skull; A part of the hard palate
A
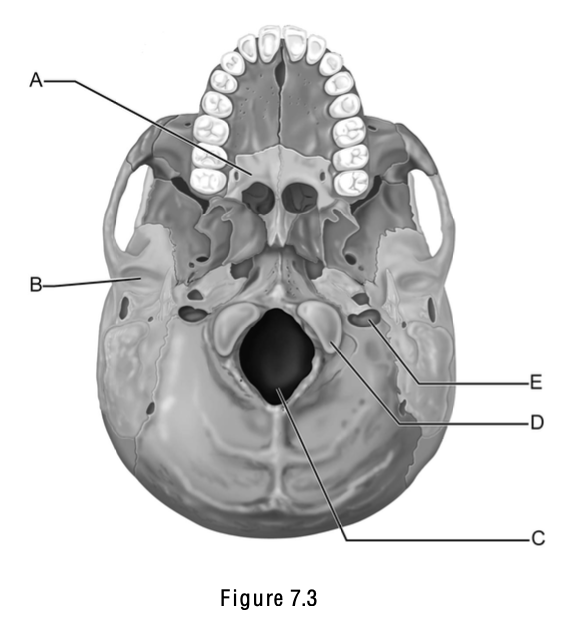
Match the following w/ the correct letter on the skull; Foramen magnum
C
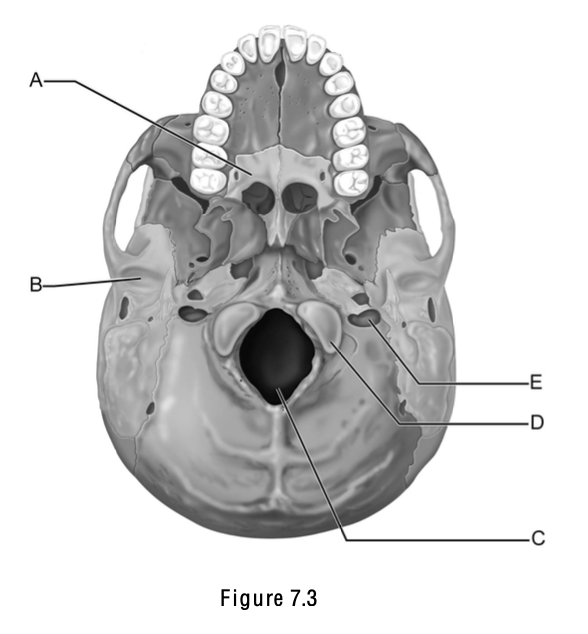
Match the following w/ the correct letter on the skull; Occipital condyle
D
The petrous region is part of this bone.
A. mandible
B. sphenoid
C. occipital bone
D. temporal
E. ethmoid
D. temporal
This, along with the maxilla, functions in chewing.
A. mandible
B. sphenoid
C. occipital bone
D. temporal
E. ethmoid
A. mandible
This delicate bone forms part of the interior of the nasal cavity.
A. mandible
B. sphenoid
C. occipital bone
D. temporal
E. ethmoid
E. ethmoid
This bone forms the pterygoid processes.
A. mandible
B. sphenoid
C. occipital bone
D. temporal
E. ethmoid
B. sphenoid
This bone has a mastoid process
A. mandible
B. sphenoid
C. occipital bone
D. temporal
E. ethmoid
D. temporal
This bone contains both the cribriform plate & the crista galli
A. mandible
B. sphenoid
C. occipital bone
D. temporal
E. ethmoid
E. ethmoid
True or false, the appendicular skeleton includes the skull, vertebral column, and thoracic cage?
False
True or false, the teeth fit into the alveoli of both the mandible and the maxilla?
True
True or false, the cranium consists of 14 bones?
False (the cranium consists of 8 bones)
The external and internal acoustic meatuses are in the ____ and ____ regions of the temporal bone, respectively.
A. squamous; mastoid
B. mastoid; petrous
C. tympanic; petrous
D. squamous; sphenoid
C. tympanic; petrous
Which bones are divided by the squamous sutures?
A. occipital and parietal
B. frontal and parietal
C. both parietal bones
D. temporal and parietal
D. temporal and parietal
Which of the following is NOT a facial bone?
A. parietal
B. mandibular
C. lacrimal
D. zygomatic
A. parietal
An example of a false rib that is also a floating rib is
A. rib 8
B. rib 11
C. rib 1
D. rib 7
B. rib 11
The manubrium articulates with all of the following except
A. the xiphoid
B. rib 2
C. rib 1
D. the clavicle
B. the xiphoid
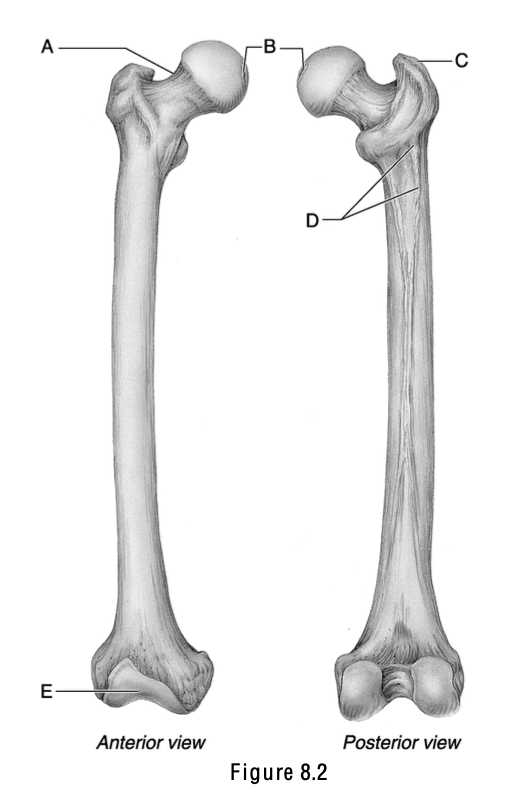
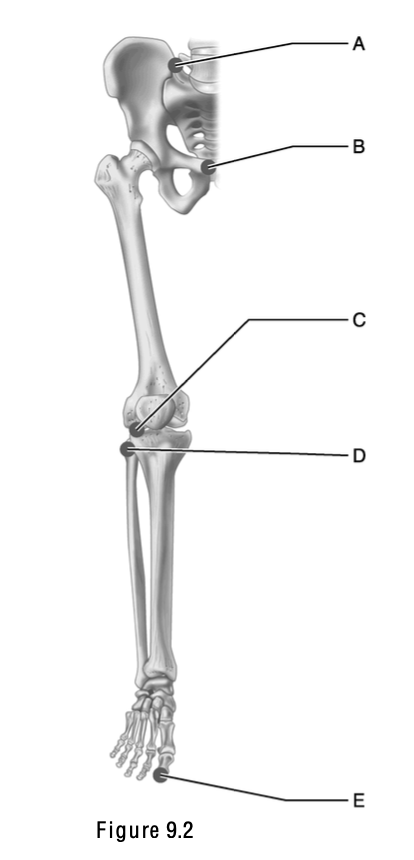
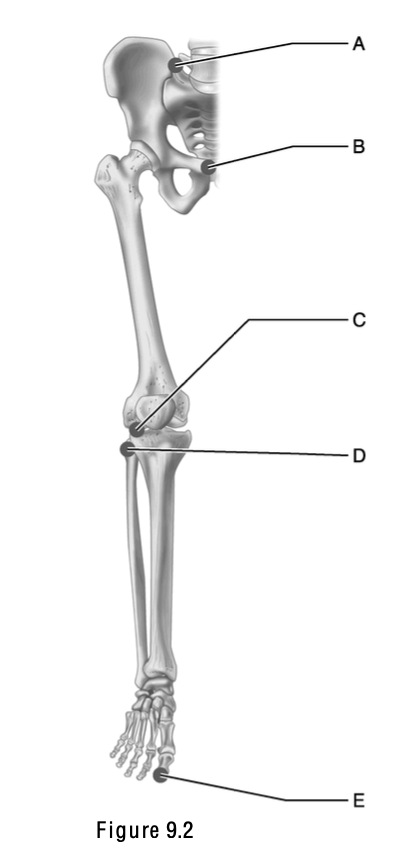
This surface articulates with the patella.
E
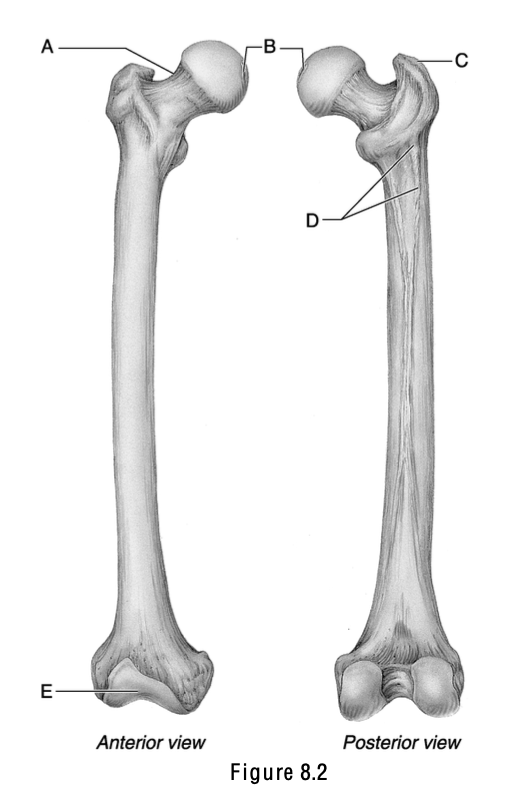
This is the weakest part of the femur.
A
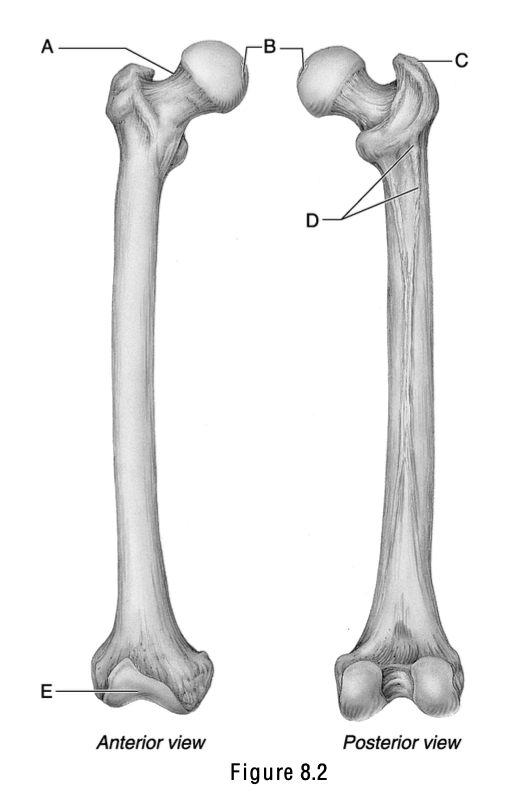
The name of this structure means “a pit at the top” and is the site where a ligament attaches to the acetabulum.
B
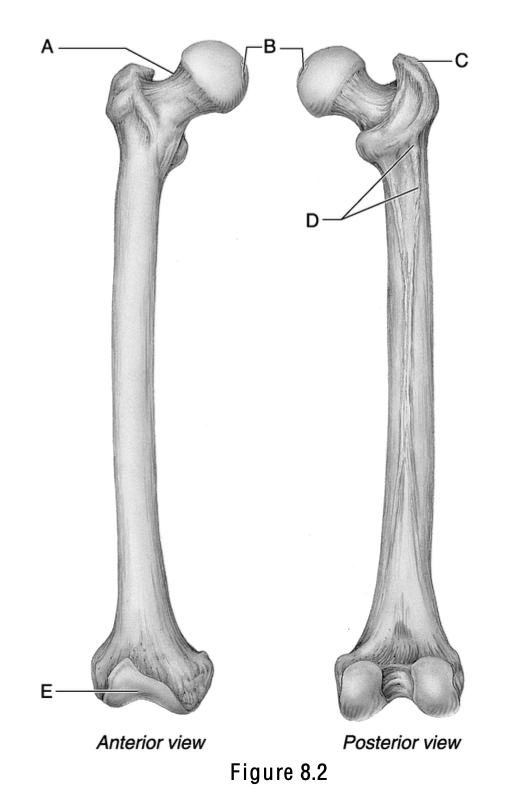
This is the greater trochanter.
C
Match the following; coronoid process
A. radius
B. tibia
C. ulna
D. humerus
D. Humerus
Match the following; trochlear notch
A. radius
B. tibia
C. ulna
D. humerus
C. Ulna
Match the following; styloid process on lateral side
A. radius
B. tibia
C. ulna
D. humerus
A. radius
Match the following; tibial tuberosity
A. radius
B. tibia
C. ulna
D. humerus
B. tibia
True or false, the metacarpus is the palm of the hand?
True
True or false, the thumb had no middle phalanx?
True
True or false, the proximal end of the fibula is the lateral malleolus?
False
All of the bony landmarks contribute to the pelvic inlet (brim) except the
A. arcuate line on the ilia
B. ischial tuberosities
C. sacral promontory
D. pubic crests
B. ischial tuberosities
The bone of the forearm that directly and functionally articulates w/ the carpals is the
A. lunate
B. humerus
C. radius
D. ulna
C. radius
Which of the following statements about the male pelvis is false?
A. the male pubic arch is wider than that of the female
B. the bones are heavier and rougher than in the female
C. the male pelvis is narrow and deep
D. the cavity of the true pelvis is smaller in the female
A. the male pubic arch is wider than that of the female
In anatomical position,
A. the styloid process of the radius is medial to the ulna
B. the ulna is lateral to the radius
C. the head of the radius is medial to the ulna
D. the radius is lateral to the ulna
D. the radius is lateral to the ulna
Which of the following foramina is “closed up” and has very few vessels or nerves passing through?
A. greater sciatic
B. optic
C. suprascapular
D. obturator
D. obturator
Which of the following bones is not part of the appendicular skeleton?
A. femur
B. sacrum
C. patella
D. navicular
B. navicular
The auricular surface of the ilium
A. forms the sacroiliac joint
B. attaches gluteal muscles
C. lines the interior of the acetabulum
D. forms the lateral borders of the false pelvis
A. forms the sacroiliac joint
Which of the following bones of the appendicular skeleton is unpaired?
A. clavicle
B. coxal bone
C. humerus
D. none; all appendicular bones are paired
D. none; all appendicular bones are paired
It is easy to forget the anatomical definition of the word leg. The leg extends from the
A. top of the femur to the ankle
B. acetabulum to the metatarsals
C. back (including the pelvis) to the tips of the toes
D. knee to the ankle
D. knee to the ankle
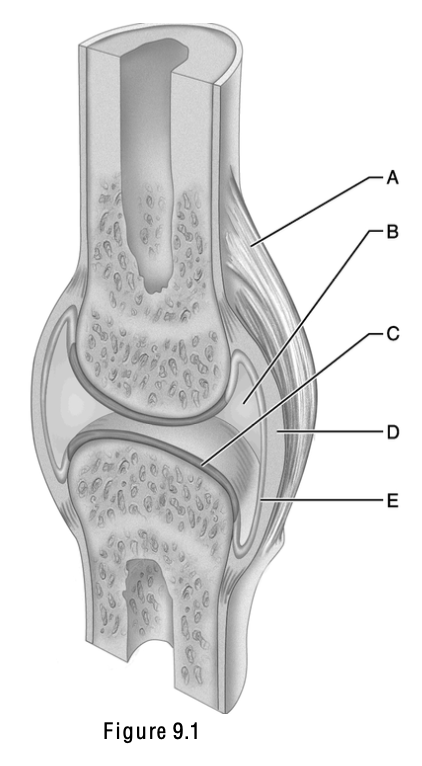
This is a ligament; it connects bone to bone and is external to the joint capsule.
A
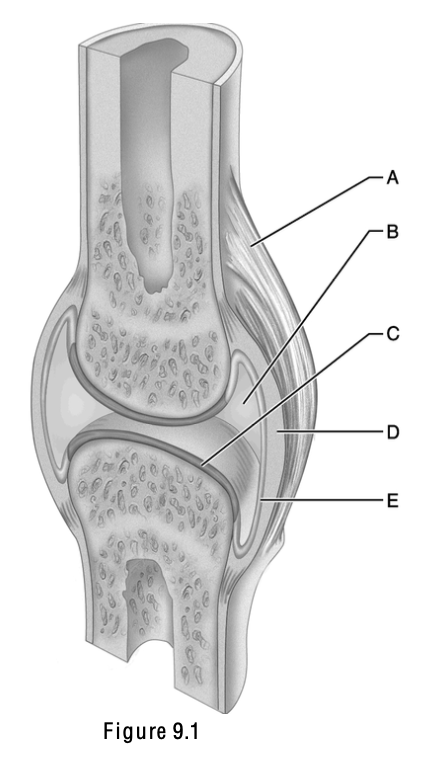
This is composed of hyaline cartilage
C
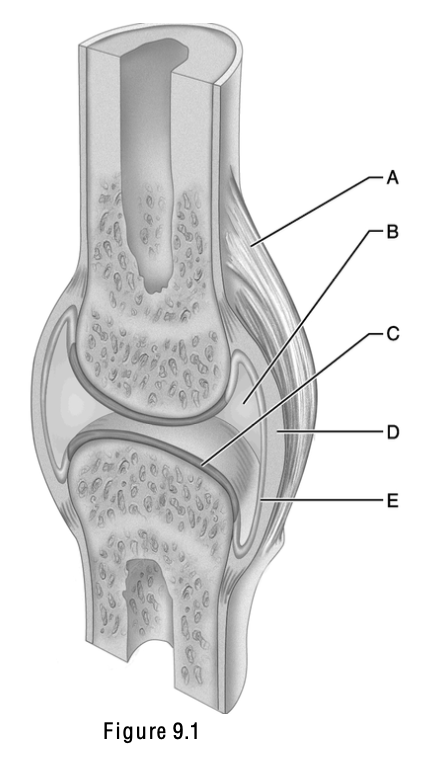
This part of the joint is the most highly vascularized
E
This identifies the interphalangeal joint
E
This is a cartilaginous, amphiarthrotic, symphysis type of joint
B
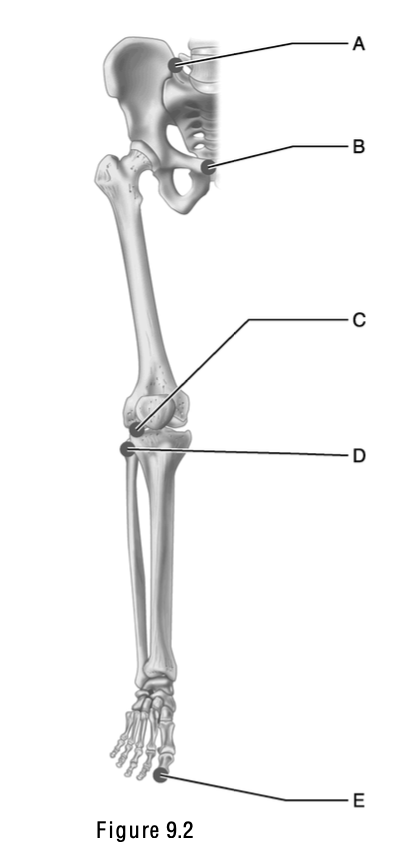
This identifies the proximal articulation between the tibia and fibula, a diarthotic joint.
D
This joint involves the iliofemoral ligament, a pubofemoral ligament, and an ischiofemoral ligament.
Å. elbow joint
B. shoulder joint
C. sternoclavicular joint
D. hip joint
E. ankle joint
D. hip joint
This joint is a hinge joint and primarily involves articulation with the ulna rather than the radius.
Å. elbow joint
B. shoulder joint
C. sternoclavicular joint
D. hip joint
E. ankle joint
A. elbow joint
This joint involves the acetabulum.
Å. elbow joint
B. shoulder joint
C. sternoclavicular joint
D. hip joint
E. ankle joint
D. hip joint
This joint involves the glenohumeral ligaments.
Å. elbow joint
B. shoulder joint
C. sternoclavicular joint
D. hip joint
E. ankle joint
B. shoulder joint
True or false, amphiarthroses are more movable than diarthroses?
False
True or false, one type of cartilage, fibrocartilage, characterizes most cartilaginous joints?
False, hyaline cartilage does
What structures are most important in keeping the knee from moving medially to laterally?
A. the oblique popliteal ligaments
B. the collateral ligaments
C. the menisci
D. the patellar ligament
B. the collateral ligaments
An example of a synarthrotic fibrous joint is the
A. pubic symphysis
B. intervertebral discs
C. interosseous membrane between the radius and ulna
D. sagittal suture
D. sagittal suture
What movement occurs when one moves the foot from the anatomical position to point toes laterally, but with the foot flat on the floor?
A. plantar flexion
B. lateral rotation
C. inversion
D. eversion
B. lateral rotation
True or false, of the surrounding connective tissues of the muscle, the endomysium is the most superficial?
False
True or false, the repeating segments seen in a skeletal muscle fiber are the T tubules?
False
In muscle cells, which of the following structures stores the calcium ions that trigger contraction?
A. T tubules
B. the myofibrils
C. the terminal cisterns
D. the internal surface of the plasma membrane
C. the terminal cisterns
Which region of the sarcomere does not change in length during contraction?
A. I band
B. Z disk to Z disk
C. H zone
D. A band
D. A band
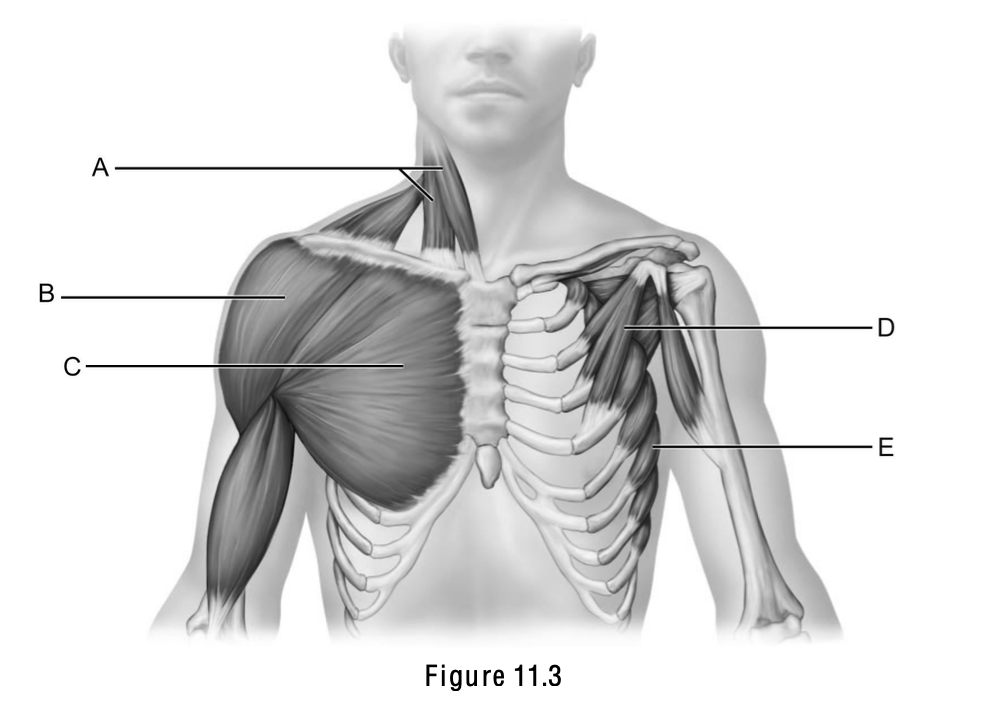
Sternocleidomastoid is letter ____.
A
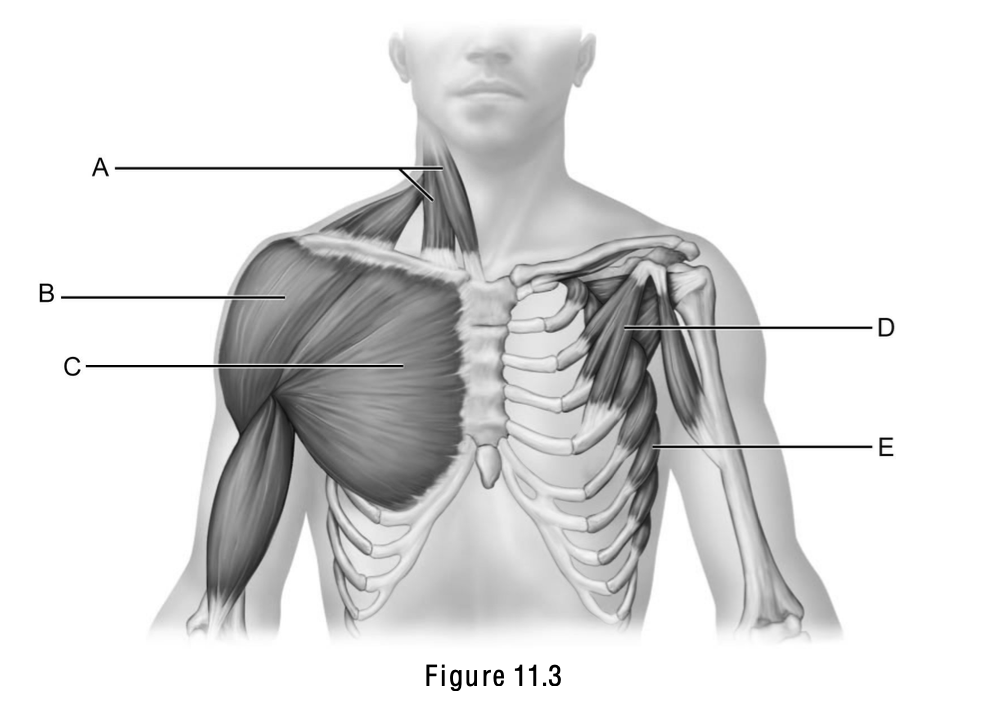
Pectoralis major is letter ___.
C
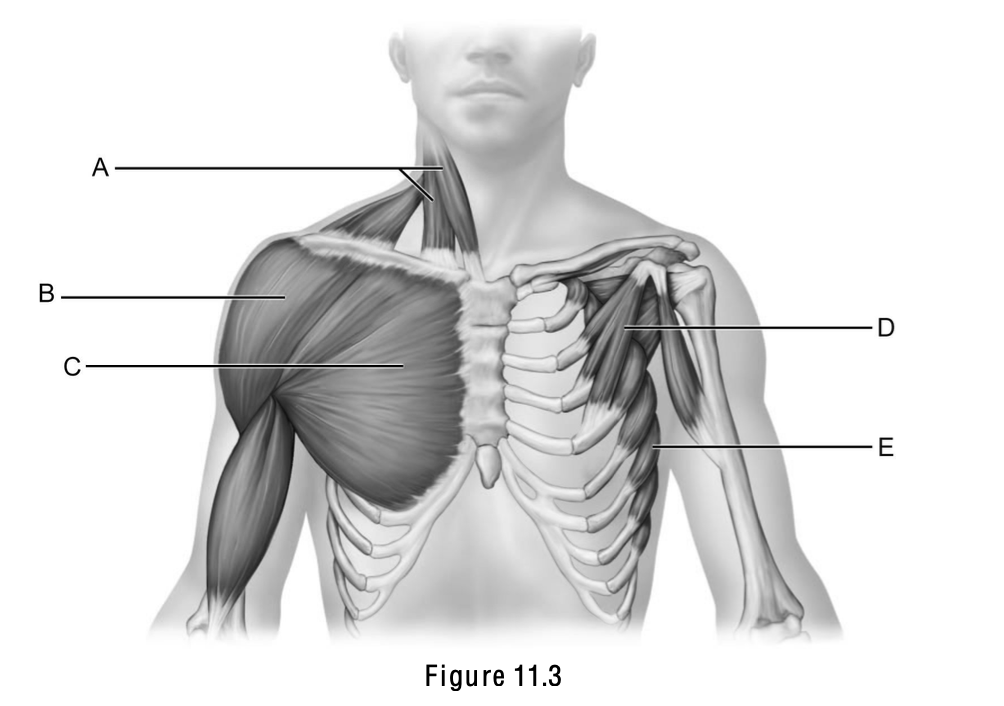
Serratus anterior is letter ___.
E
True or false, interestingly, some synergists may act by canceling out some of the actions of a prime mover?
True
True or false, the iliacus and psoas major are prime movers in thigh extension?
False, they are prime movers for thigh flexion.
True or false, the four muscles of the quadriceps femoris are biceps femoris, vastus laterals, vastus medialis, and vastus intermedius?
False, it is the rectus femoris that forms the quadriceps femoris along w/ the other vastus muscles.
An important function of the soleus muscle is to
A. extend the leg at the knee
B. plantar flex the foot
C. Evert the foot
D. invert the foot
B. plantar flex the foot
A prime mover for knee extension is
A. sartorius
B. rectus femoris
C. biceps femoris
D. semimembranosus
B. rectus femoris
Which muscle inserts on the lesser tubercle of the humerus?
A. deltoid
B. supraspinatus
C. subscapularis
D. biceps brachii
C. subscapularis
A prime mover for flexing the forearm at the elbow is the
A. brachioradialis
B. brachialis
C. triceps brachii
D. deltoid
B. brachialis
The extensor muscles of the upper limb lie almost exclusively in the ____ region of that limb.
A. anterior
B. lateral
C. medial
D. posterior
D. posterior
The muscle that originates on the anterior superior iliac spine is the
A. rectus femoris
B. psoas major
C. sartorius
D. pectinous
C. sartorius
A muscle that originates along most of the shaft of the femur is the
A. iliopsoas
B. semitendinosus
C. vastus intermedius
D. adductor Magnus
C. vastus intermedius