C4 vs. C3 vs. CAM plants
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/12
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
1
New cards
**PEP Carboxylase**
Tetramer of four 110 kDa subunits, found in the cytosol.
HCO3-, PEP are substrates. O2 is not a substrate.
More effective than Rubisco at low inorganic C levels
Light-activated in C4 photosynthesis, and light inactivated in CAM photosynthesis
Has **important non-photosynthetic roles in metabolism and pH regulation** (normally w/HCO3 production)
\
HCO3-, PEP are substrates. O2 is not a substrate.
More effective than Rubisco at low inorganic C levels
Light-activated in C4 photosynthesis, and light inactivated in CAM photosynthesis
Has **important non-photosynthetic roles in metabolism and pH regulation** (normally w/HCO3 production)
\
2
New cards
**Spatial Separation of Fixation Steps in C4 Plants**
Same process for intaking CO2 (via stomates) as C3 plants
The C4 process involves a spatial separation between the two fixation reactions
\
In C4 leaves carbon is initially fixed by the PEP carboxylase reaction in the __cytosol of mesophyll cells__, forming C4 acids
\
The C4 products move to the __bundle sheath__ where they are decarboxylated (likely by malic acid) -→ CO2 is picked up by the C3 pathway (Calvin Cycle) in the bundle sheath cells (which has rubisco enzymes)
\
Why spatial separation between 2 fixation reactions? O2 has large spatial barriers - purposely done to keep O2 away from rubisco → Preventing photorespiration - if does happens, it’s minimal
\
Photorespired CO2 can be trapped by the cytosol of mesophyll before it escapes from the leaf
The C4 process involves a spatial separation between the two fixation reactions
\
In C4 leaves carbon is initially fixed by the PEP carboxylase reaction in the __cytosol of mesophyll cells__, forming C4 acids
\
The C4 products move to the __bundle sheath__ where they are decarboxylated (likely by malic acid) -→ CO2 is picked up by the C3 pathway (Calvin Cycle) in the bundle sheath cells (which has rubisco enzymes)
\
Why spatial separation between 2 fixation reactions? O2 has large spatial barriers - purposely done to keep O2 away from rubisco → Preventing photorespiration - if does happens, it’s minimal
\
Photorespired CO2 can be trapped by the cytosol of mesophyll before it escapes from the leaf
3
New cards
steps of c4 pathway
\

4
New cards
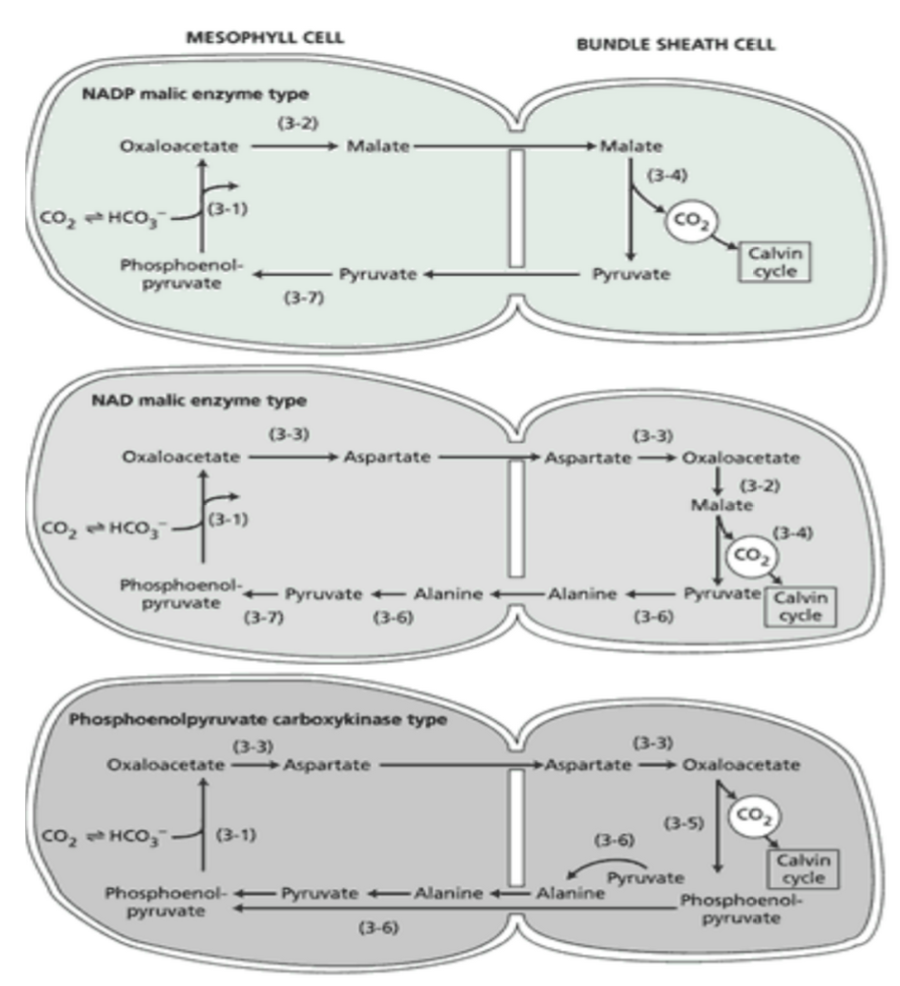
**Variants of the C4 Photosynthetic Carbon Cycle**
they differ in 1, 2,
they differ in 1, 2,
(1) the nature of the four-carbon acid (malate or aspartate) transported into the bundle sheath cell and of the three-carbon molecule (pyruvate or alanine) returned to the mesophyll cell and
\
(2) the nature of the enzyme that catalyzes the decarboxylation step in the bundle sheath cell.
\
\
The three variants are named after the enzymes that catalyze the decarboxylation reactions.
\
(2) the nature of the enzyme that catalyzes the decarboxylation step in the bundle sheath cell.
\
\
The three variants are named after the enzymes that catalyze the decarboxylation reactions.
5
New cards
**C4 Physiology**
How does its physiology maximize photosynthesis?
How does its physiology maximize photosynthesis?
C4 species often have rapid photosynthesis and growth.
C4 physiology allows it to isolate C3 and C4 processes which minimizes the loss of CO2 from photorespiration.
Almost all CO2 produced is used by the plant/released→ always doing carboxylation reaction, b/c does not need photorespiration
\- Always enough CO2 to caboxylize
\- Water is conserved/ high water use efficiencis
\-- Maximum amount of biomass produced - photosynthesis is optimized
C4 physiology allows it to isolate C3 and C4 processes which minimizes the loss of CO2 from photorespiration.
Almost all CO2 produced is used by the plant/released→ always doing carboxylation reaction, b/c does not need photorespiration
\- Always enough CO2 to caboxylize
\- Water is conserved/ high water use efficiencis
\-- Maximum amount of biomass produced - photosynthesis is optimized
6
New cards
**C4 Physiology**
CO2 compensation points?
CO2 compensation points?
Accordingly, C4 photosynthesis is not inhibited by O2 and their CO2 compensation points are near 0 ppmv.
7
New cards
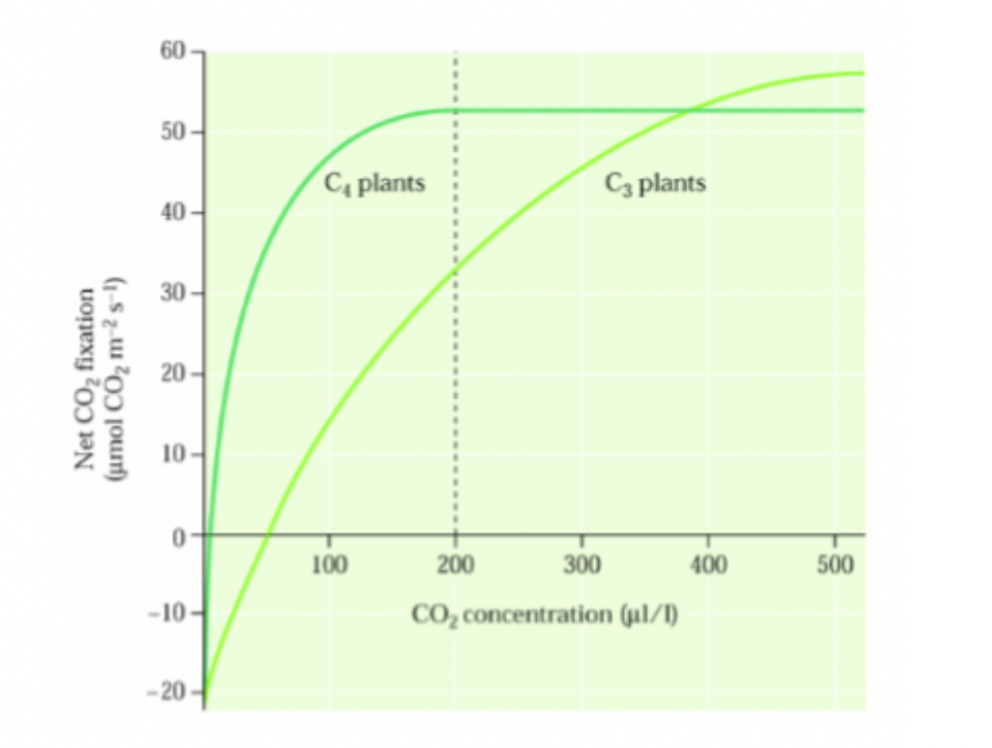
Why do C4 species do better in hot temerpatures than C3 plants?
C4 species have high optimum temperatures for photosynthesis, sometimes exceeding 40 C.
C3 don’t have storage compartments to store CO2. C3 plants don’t do very well in these environments b/c will lose water vapour when stomates open which can result in increased photorespiration.
\
C4 stores CO2 as malic acid → doesn’t need to open stomates so often. The high affinity of PEP carboxylase allows C4 species to maintain rapid photosynthesis when stomates are partly closed.
C3 don’t have storage compartments to store CO2. C3 plants don’t do very well in these environments b/c will lose water vapour when stomates open which can result in increased photorespiration.
\
C4 stores CO2 as malic acid → doesn’t need to open stomates so often. The high affinity of PEP carboxylase allows C4 species to maintain rapid photosynthesis when stomates are partly closed.
8
New cards
C4 species are ecologically distinctive from C3 – temperature and moisture are the two strongest factors.
C4 taxa tend to have centres of distribution in warm, sometimes arid, regions.
C4 species successfully grow in conditions of intense light, high soil salt content, warm climate, and often experience drought conditions.
\*\*more efficient in using water! → C4 don’t need to open stomata as often to collect CO2 from external
\
\
Example:) High soil content areas --- Water is pulled from soils
In high salt environments, if C3 plants are constantly trying to get more water vapour from the soils, they will be constantly intaking salts.
As opposed to C4 plants, conserving water → not as much salt intake.
C4 species successfully grow in conditions of intense light, high soil salt content, warm climate, and often experience drought conditions.
\*\*more efficient in using water! → C4 don’t need to open stomata as often to collect CO2 from external
\
\
Example:) High soil content areas --- Water is pulled from soils
In high salt environments, if C3 plants are constantly trying to get more water vapour from the soils, they will be constantly intaking salts.
As opposed to C4 plants, conserving water → not as much salt intake.
9
New cards
**Photosynthesis in CAM plants**
These plants, known as **CAM plants for crassulacean acid metabolism (CAM)**, open stomata during the night and close them during the day.
Why? Temperatures are typically lower at night and humidity is higher - less chance of losing water vapor
\
\
During the night, these plants fix CO2 into a variety of organic acids in mesophyll cells.
\-→ CO2 assimilation is proportional to water gain/loss
During the day, the light reactions supply ATP and NADPH to the Calvin cycle and CO2 is released from the organic acids.
\-→ Low CO2 assimilation due to low water evaporation
Why? Temperatures are typically lower at night and humidity is higher - less chance of losing water vapor
\
\
During the night, these plants fix CO2 into a variety of organic acids in mesophyll cells.
\-→ CO2 assimilation is proportional to water gain/loss
During the day, the light reactions supply ATP and NADPH to the Calvin cycle and CO2 is released from the organic acids.
\-→ Low CO2 assimilation due to low water evaporation
10
New cards
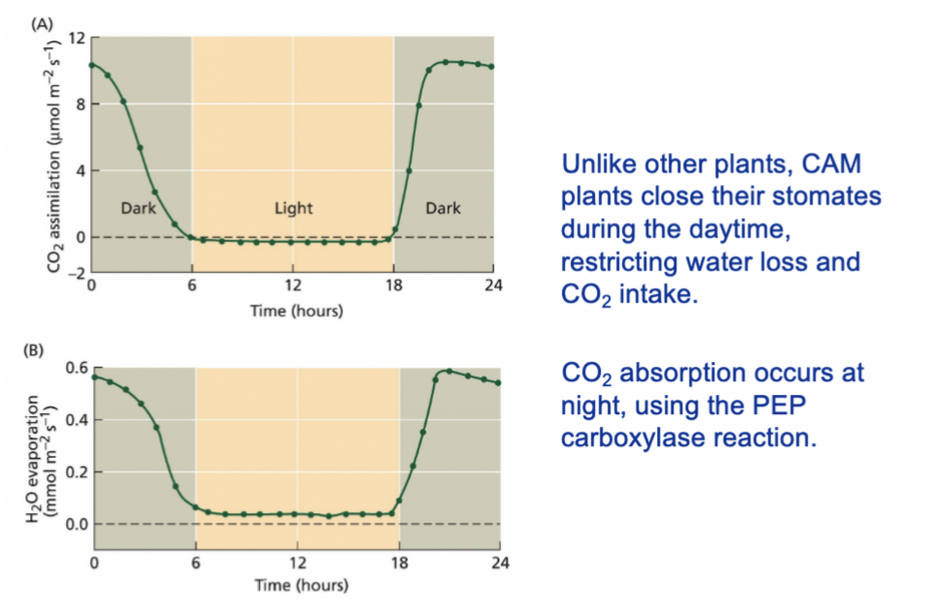
**CAM Plants Absorb CO2 at Night**
During the night, when the stomata are open, CO2 is taken in by the plant and converted into oxaloacetate by the enzyme PEP carboxylase. Oxaloacetate is then converted into malate by the enzyme malate synthase. The malate is then stored in the vacuoles of plant cells until it is needed the next day.
The enzyme PEP carboxylase is made from starch stored in the chloroplast through a series of reactions
The enzyme PEP carboxylase is made from starch stored in the chloroplast through a series of reactions
11
New cards
CAM plants fix CO2 during the day
During the day, when the stomata are closed, the stored malic acid in the vacuole is transported into the chloroplasts as malate where it is converted into pyruvate by the NADP+ malic enzyme. The pyruvate is stored as starch in the chloroplast. The malate is also changed back into CO2 to be fixed through the Calvin cycle.
12
New cards
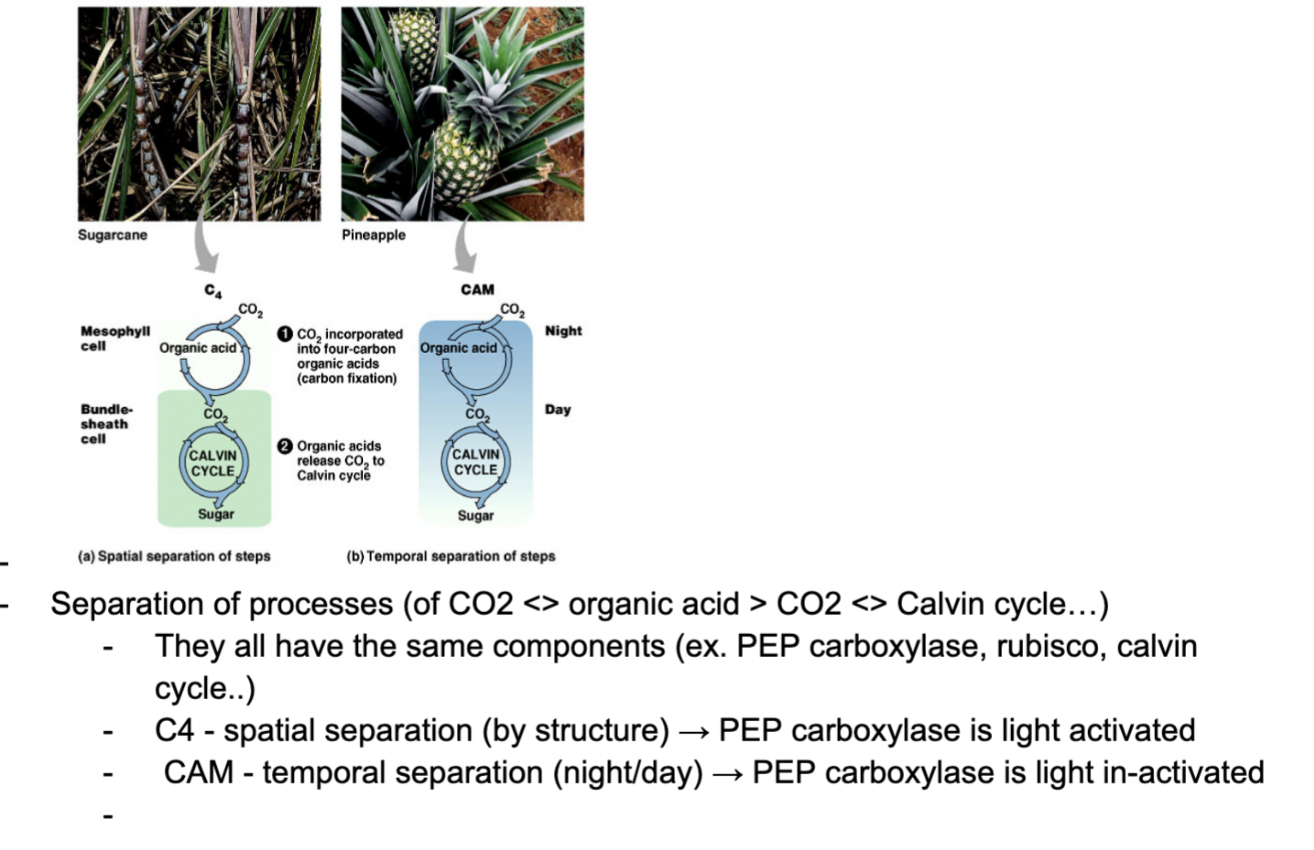
**Summary: CO2 concentrating mechanisms in C4 and CAM species**
13
New cards
C3 vs C4 vs CAM
Overall, C4, C3, and CAM are three different pathways that plants can use for photosynthesis. C4 and CAM plants are typically found in dry or desert environments, where water is limited, and they are more efficient and better able to tolerate environmental stresses than C3 plants.
