ITEC 3505 WEEK 1 - 6
1/205
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
206 Terms
Systems Thinking
Taking a holistic view of carrying out projects within the context of the organization.
Three parts of Systems Thinking
Systems philosophy
Systems analysis
Systems management
Systems philosophy
An overall model for thinking about things as systems
Systems analysis
A problem-solving approach
Define the scope of the system to be studied
Divided scope into component parts for identifying and evaluating it’s problems opportunities, constraints, and needs
Systems management
Address business, technological, and organizational issues before making changes to systems
Involve creating, maintaining and modifying a system
Three sphere Model
Organizational
Business
Technology
Organizational Questions
Will the tablet project affect all students, just traditional students, or only certain majors?
How will the project affect students who already have tablets or laptops?
Who will develop special applications or books for the tablets?
Who will train students, faculty and staff?
Business Questions
What will the tablet project cost the college?
What will it cost students?
What will support costs be?
What will the impact be on enrollments?
Technology questions
Should the tablets be based on Apple, Microsoft, Android, or another system?
What applications will be required?
What will the hardware specifications be?
How will the tablets affect various networks and speed?
Will more power cords be required in the classroom?
Organizational project management
Framework in which portfolio, program, and project management are integrated with organizational enablers in order to achieve strategic objectives.
The four frames of organizations
Structural frame
Human resources frame
Political frame
Symbolic frame
Structural frame
Roles and responsibilities, coordination, and control. Organizational charts help describe this frame.
Human resources frame
Providing harmony between needs of the organization and needs of people.
Political frame
Coalitions composed of varied individuals and interest groups. Conflict and power are key issues.
Symbolic frame
Symbols and meanings related to events. Culture, language, traditions, and image are all parts of this frame.
Three basic organizational structures
Functional
Project
Matrix
Functional
managers report to the CEO
Project program managers
report to the CEO
Matrix
middle ground between functional and project structures; personnel often report to two or more bosses; structure can be weak, balanced, or strong matrix
Weak Matrix
The functional manager has more power than the project manager
Balanced Matrix
The project manager and functional manager have the same amount of power
Strong Matrix
The project manager has more power than the functional manager
Organizational culture
is a set of shared assumptions, values and behaviors that characterize the functioning of an organization.
Ten characteristics of organizational culture
Member identity
Group emphasis
People Focus
Unit integration
Control
Risk tolerance
Reward criteria
Conflict tolerance
Means-end orientation
Open systems focus
IT governance
Addresses the authority and control for key It activities in organizations, including IT infrastructure, IT use and project management
Product life cycle
Is a collection of project phases that defines
What work will be performed in each phase
What deliverables will be produced and when
Who is involved in each phase
How management will control and approve work produced in each phase
Deliverable
Is a product or service produced or provided as part of a project
4 phases of a generic life cycle
Concept:
Starting the project
Development:
Organizing and preparing
Implementation:
Carrying out the work
Close-out:
Finishing the project
Early phase
Resources needs are usually lowest
Level uncertainty (risk) is highest
Project stakeholders have the greatest opportunity to influence the project
Middle phases
Certainty of completing a project improves
More resources are needed
Final phase
Ensuring that project requirements were met
Sponsor approves completion
Systems development life cycle (SDLC)
Is a framework for describing the phase of developing information systems
Systems development life cycles projects can follow
Predictive life cycle
Iterative life cycle
Incremental life cycle
Adaptive life cycle
Hybrid life cycle
Predictive life cycle models
Waterfall model
Spiral model
Prototyping model
Rapid Application Development (RAD) model
Waterfall model
Has well-defined, linear stages of systems development and support
Spiral model
Shows that software is developed using an iterative or spiral approach rather than a linear approach
Prototyping model
Used for developing prototypes to clarify user requirements
Rapid Application Development (RAD) model
Used to produce systems quickly without sacrificing quality
Looks like the waterfall model
Management reviews
Also known as phase exits, phase gate reviews, or kill points, should occur after each phase to evaluate the project’s
Progress
Likely success
Continued compatibility with organizational goals
Project context
Has a critical impact on which product development life cycle will be most effective for a particular software development project.
Globalization
The spread of the flow of financial products, goods, technology, information and jobs across national borders and cultures.
Outsourcing
Is when an organization acquires goods and/or sources from an outside source
Offshoring
is sometimes used to describe outsourcing from another country
Virtual teams
is a group of individual who work across time and space using communication technologies
Agile project management
Is related to the rolling wave planning and scheduling project methodology
Uses iterations (“time boxes”) to develop a workable product that satisfies the customer and other key stakeholders
Stakeholders and customers review progress and re-evaluate priorities to ensure alignment with customer needs and company goals.
Adjustments are made and a different iterative cycle begins that subsumes the work of the previous iterations and adds new capabilities to the evolving product.
Project
Is temporary endeavor undertaken to create a unique product service, or result
Operations
Is work done to sustain the business
Term project
Select an IT project in a field or industry sector that you are interested in or familiar with.
Project managers
are people who work with project sponsors, team, and other people involved in a project to achieve project goals.
Triple constraint
Scope
Time
Cost
Project management
Is the application of knowledge, skills, tools and techniques to project activities to meet project requirements
Project stakeholders
are the people involved in or affected by project activities
Stakeholders include
The project sponsor
Bank and other financial institutions
The project manager
The project team
Support staff
Customers
Users
Suppliers
Opponents to the project
Project management knowledge areas
Knowledge areas that describe the key competencies project managers must develop.
10 Knowledge Areas
Scope
Schedule
Cost
Quality
Resource
Communications
Risk
Procurement
Stakeholder
Project integration management
Project management tools and techniques
Assist project managers and their teams in various aspects of project management
Specific project management tools and techniques
Scope
Project charter, scope statement, and work breakdown structure (WBS)
Time
Gantt charts, network diagrams, critical path analysis, critical chain scheduling.
Cost
Cost estimates and earned value management
Gantt Chart
A standard format for displaying project schedule information by listing project activities and their corresponding start and finish dates in a calendar format
Program
A group of related projects managed in a coordinated manner to obtain benefits and control not available from managing them individually.
Program manager
Provides leadership and direction for the project managers heading the projects within the program
Project portfolio management
Organizations group and manage projects and programs as a portfolio of investments that contribute to the entire enterprise’s success
Portfolio managers
Help organizations make wise investment decisions by helping to select and analyze projects from a strategic perspective
Examples of Project portfolio management
Strategic goals
Are we working on the right projects?
Are we investing in the right areas?
Do we have the right resources to be competitive?
Examples of Project management
Tactical goals
Are we carrying out projects well?
Are projects on time and on budget?
Do project stakeholders know what they should be doing?
Best Practice
An optimal way recognized by industry to achieve a state goal or objective
Organizational project management
Framework in which portfolio, program, and project management are integrated with organizational enablers in order to achieve strategic objectives
Talent triangle
Technical project management skills
Strategic and business management skills
Leadership skills
Leadership styles
Transactional
Servant leader
Transformational
Charismatic
Interactional
Laissez-faire
Project management Office
An organizational group responsible for coordinating the project management function throughout an organization.
Project management institute (PMI)
is an international professional society for project managers founded in 1969
Project management professional (PMP)
A person who has documented sufficient project experience, agreed to follow a code of ethics, and passed the PMP exam.
Ethics
A set of principles that guide our decision making based on personal values of what is “right” and “wrong”
Project management software
There are hundreds of different products to assist in performing project management
Three main categories of tools
Low-end tools: hande single or smaller projects well, cost under $200 per user
Midrange tools: handle multiple projects and users, cost $200-$1000 per user, Microsoft project is still the most popular
High-end tools: Also called enterprise project management software, often licenced on a per-user basis
Five project management process groups
Initiating
Planning
Executing
Monitoring and controlling
Closing
Tailoring
These process groups to meet individual project needs increase the chance of success in managing projects.
Initiating process
Define and authorize a project or project phase
Take place during each phase of a project
Planning process
Devise and maintain a workable scheme to ensure that the project addresses the organization’s needs
Develop a plan to define the work needed for the project, to schedule activities related to that work, to estimate costs for performing the work, and to decide what resources to procure to accomplish the work.
Executing processes
Coordinate people and other resources to carry out the various plans and create the products, servicers, or results of the project or phase
Monitoring and controlling processes
Regularly measure and monitor progress to ensure that the project team meets the project objectives
Closing processes
Formalize acceptance of the project or project phase and ending it efficiently
Administrative activities
Are often involved, in activities such as archiving project files, documenting lessons learned, and receiving formal acceptance of the delivered work.
Project integration management
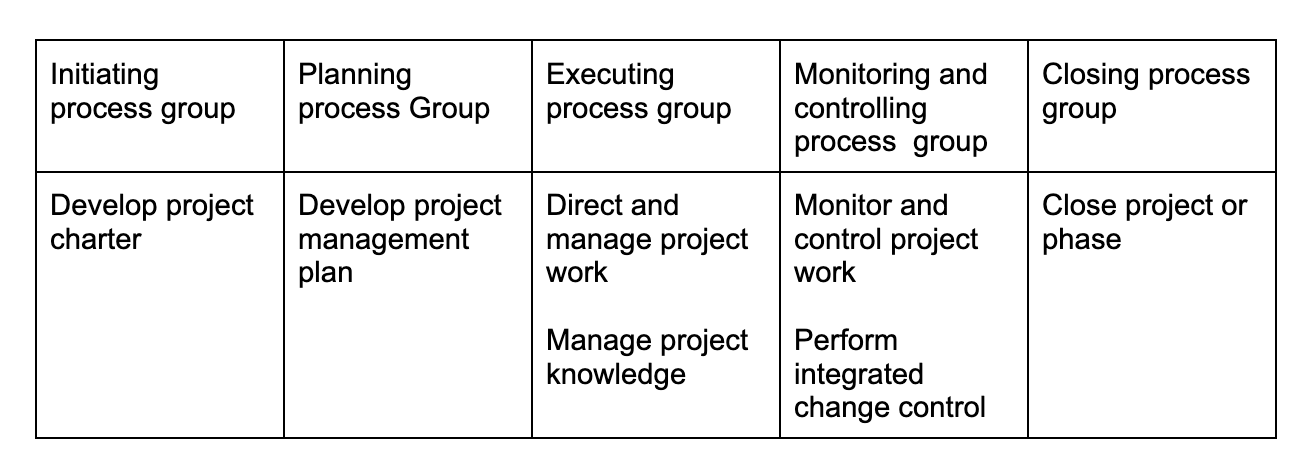
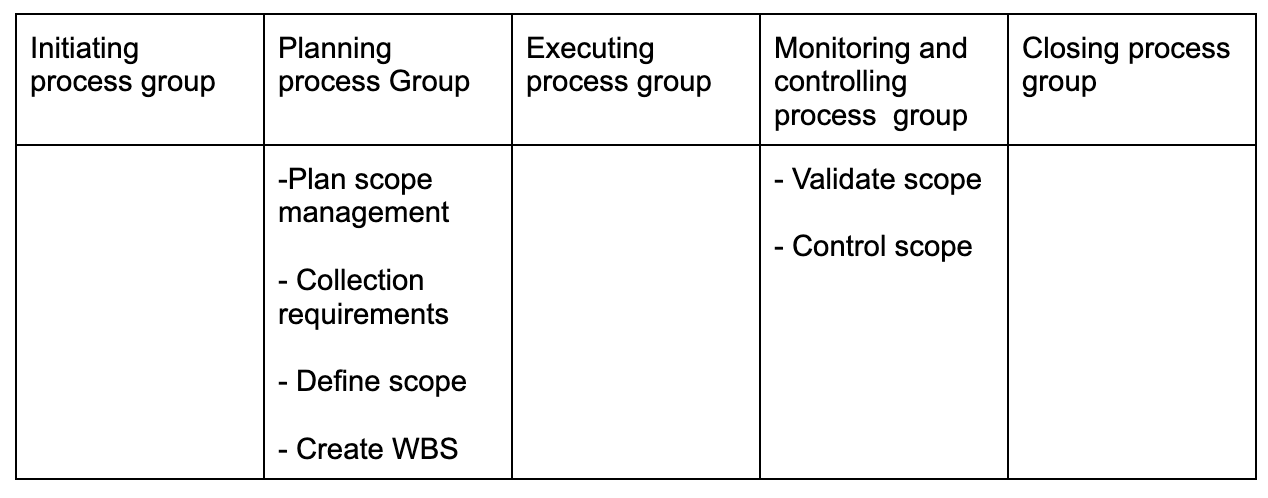
Project Scope Management
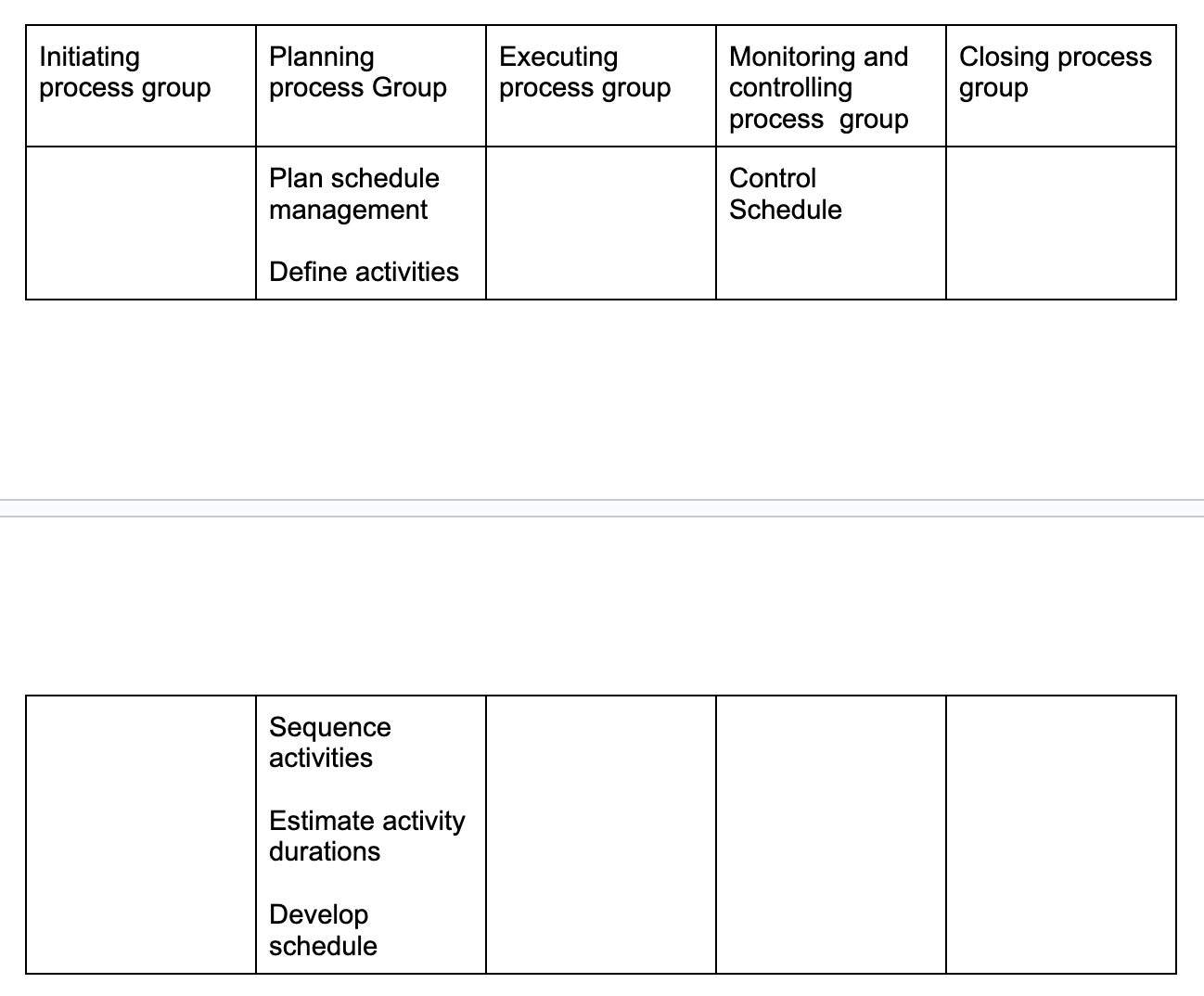
Project schedule management
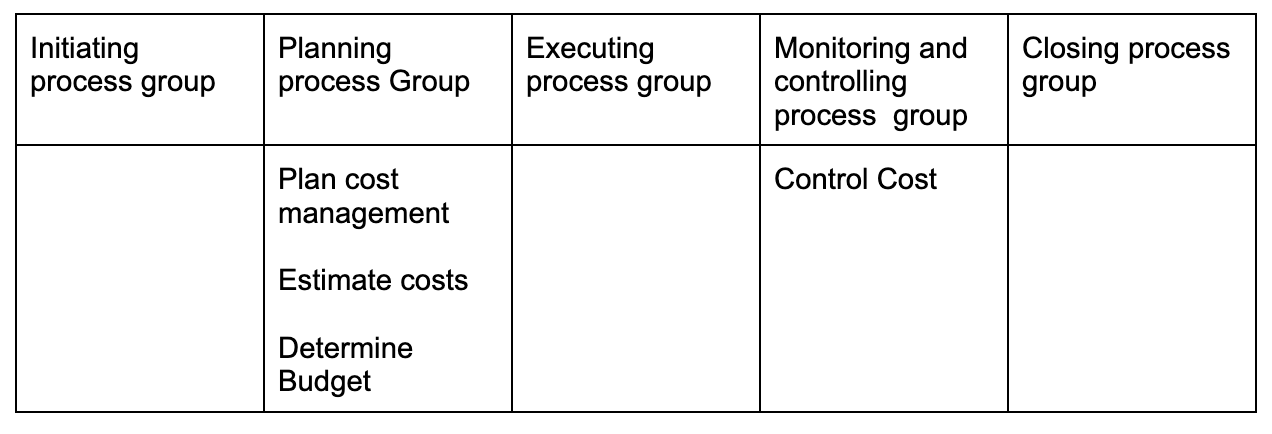
Project cost management
Project quality management
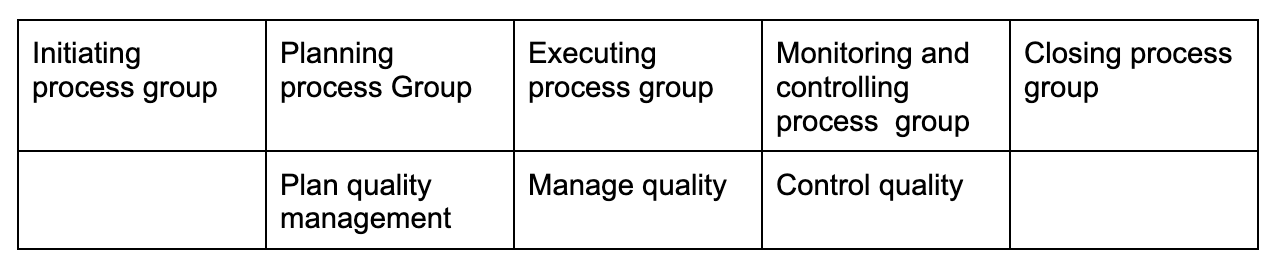
Project resource management
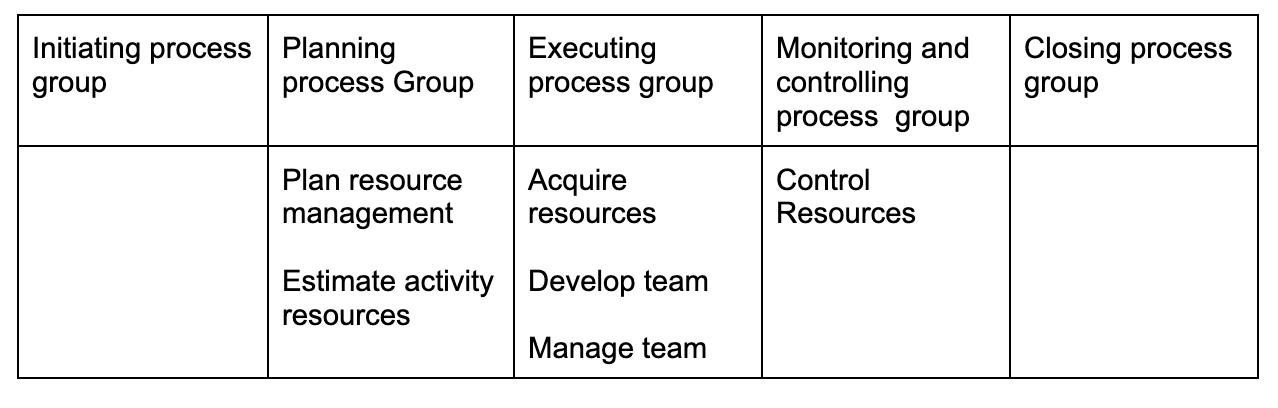
Project communications management
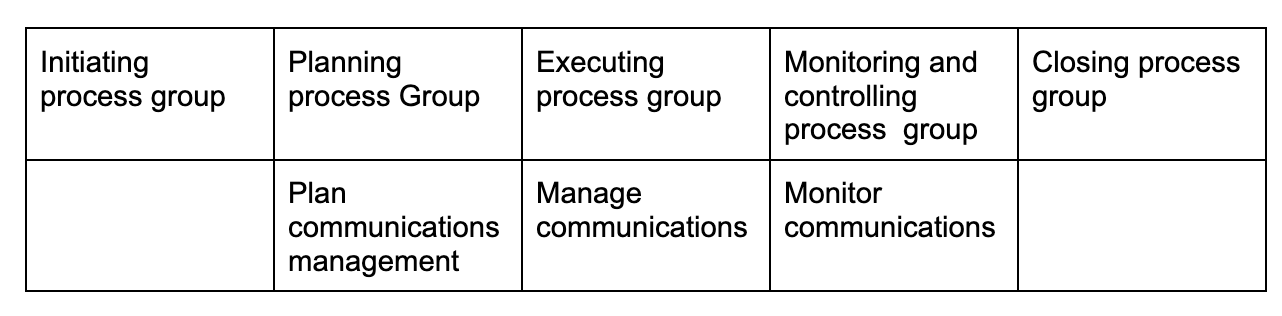
Project risk management
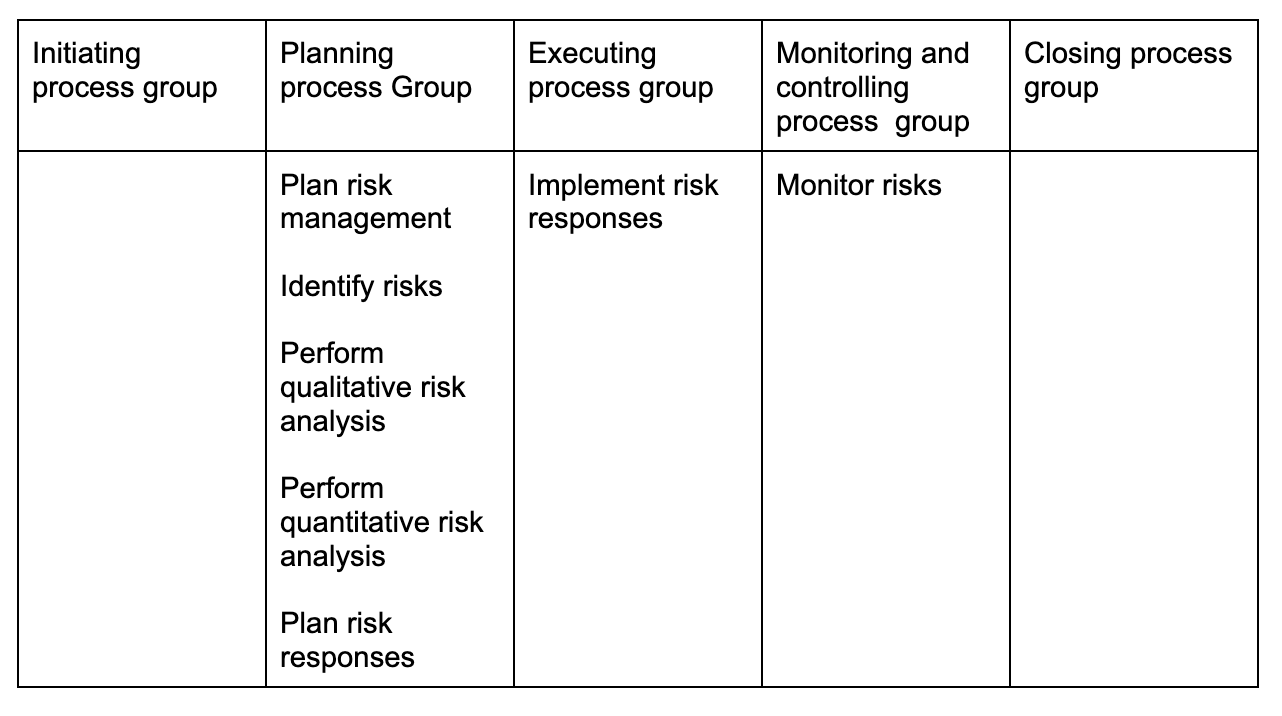
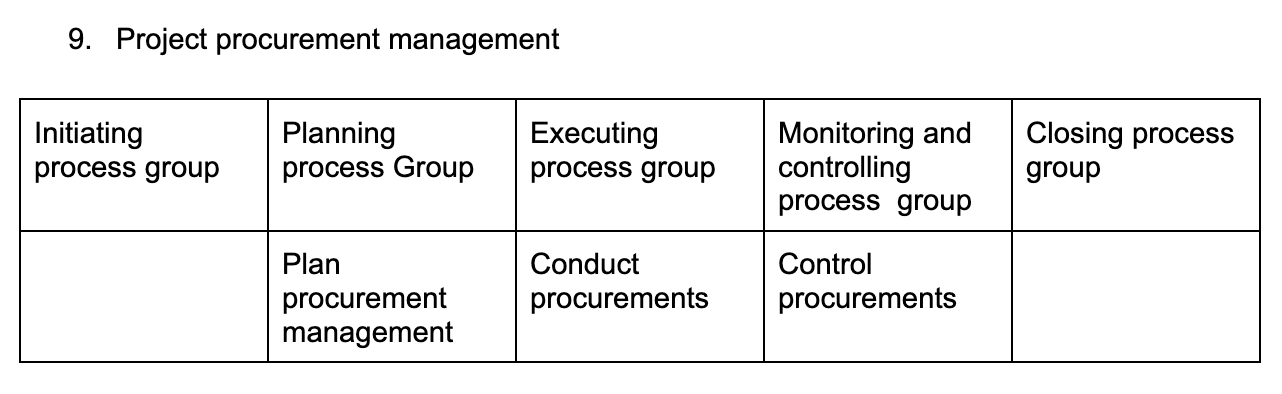
Project procurement management
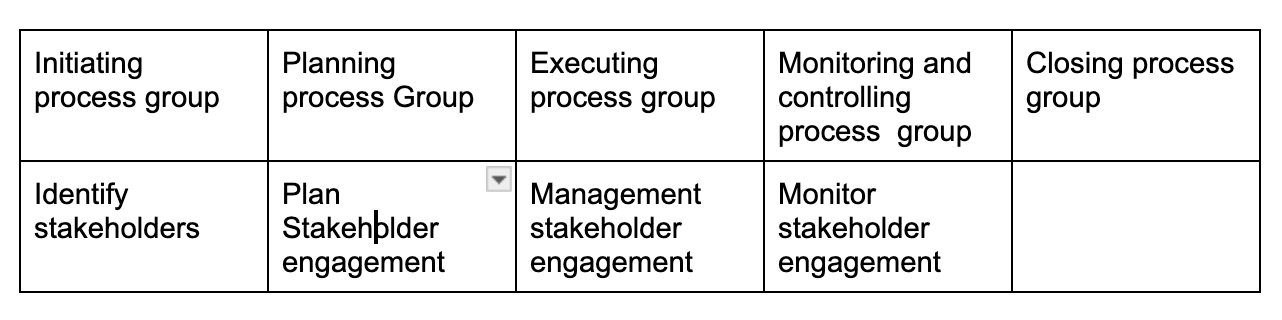
Project stakeholder Management
Methodology
Describes how things should be done
Project management methodologies
PRojects IN Controlled Environments (PRINCE2)
Agile
Rational Unified process (RUP)
Six sigma
Standard
Describes what should be done
PRojects IN Controlled Environments (PRINCE2)
Released in 1996 as a generic project management methodology by the united kingdom office of government commerce (OGC)
8 PRINCE2 Process Groups
Starting up a project
Planning
Initiating a project
Directing a project
Controlling a stage
Managing product delivery
Managing stage boundaries
Closing a project
Rational Unified Process (RUP)
An interactive software development process created by IBM
Focus on team productivity
Enable all team members to deliver software best practices to the organization
Provide a software engineering process particularly suited to creating and maintaining component-based software system solutions
Several other projects management methodologies are used specifically for software development projects
Joint Application Development (JAD)
Rapid Application Development (RAD)
Six Sigma
a set of management techniques intended to improve business processes by greatly reducing the probability that an error or defect will occur.
DMAIC is used to improve an existing business process
Define, Measure, analyze, improve, and control
DMADV is used to create new product or process designs to achieve predictable, defect-free performance
Define, measure, analyze, design, and verify