aviation weather test 3
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
air mass
a large body of air with uniform temp and humidity
arctic(a)
deep cold air mass
polar(p)
shallow cool to cold air mass
tropical(t)
warm to hot air mass
continenal ( c)
dry air mass, develops over land
maritime (m)
moist air mass develops over water
what is cP
cold dry
what is ca
cold dry
what is ct
hot dry
what is mt
warm moist
what is mp
cool moist
warm front
a body of warm mass of air advances and replaces a body of cold air
cold front
cold dense air advances and replaces a body of warm air
sqaull line
showers and thunderstorms
stationary front
fron moving very slowley and battling it out
when two fronts merge its makes an
occuluded front
warm occlusion
the coldest air is ahead of the warm front
all cyclones start as a
stationary front
a wave cyclone is a
low pressure circulation that forms and moves along a front
dry line
low level boundary hundreds of miles long
clouds form due to
water vapor rising
dry adiabatic lapse rate
3c per 1000 ft
saturated adiabatic lapse rate
1c per 1000 ft
rate at which dry air decreases as it rises
dry adiabatic lapse rate
rate at which air cools as it rises(wet air)
saturated adiabatic lapse rate
relative humidity is dependent on
air temp
dew point — as it goes up in the atmosphere
decreases
dew lapse rate
0.5c per 1000 feet
high pressure sinking, compressing and warming leads to
clear skies and less rain
low pressure rising, expanding leads to
clouds and rain
frontal lift
warm air rises over cool air and vises versa which is called overrunning
cumulonimbus and nimbostratus make
rain
cirr
high level above 6000m
alto
mid btwn 2000-6000
the rest of the clouds besides alto and cirr
below 2000m to 0
precipitation
forms of water particles
ingredients for precipitation
water vapor, sufficient lift, growth
the smaller the water droplets
the faster the evaporation
collision coalesce
droplets of different sizes collide and stick together to form larger droplets, once they become to large they fall to the gorund as rain
when the temp and dew point are the same its called
lifting condensation level
both super cooled water droplets and ice crystals are made (occurs in colder clouds and enviorments)
ice crystal process
for — to occur the temp needs to be below frezzing 0c/32f
snow
rain occrs when
all layers of the atmosphere form a cloud base to the surface are above freezing
strong updratfs, large, supercooled liquid water, large cloud sizes
thunderstorm
pilots should anticipate hail with
thunderstorms
amount of energy back scattered by precipitation, also known as
reflectivity
amount of energy turned after striking a target
back scattered energy
radar beams do not travel in straight lines the travel in
bent lines
a narrow band of intense weather
dead zone
relatively continuous
stratiform precipitation
convective(instense) precipitation
echoes tend to form as lines

what cloud is this
startocumulus
draw an wind barb mostly cloudy at 270c 65 knots
do it on paper (look at example)
How do you find LCL
dry adiabatic lapse rate and dew point lapse rate until they match

what cloud is this
altocumulus

what cloud is this
altostratus

what cloud is this
altocumulus

what cloud is this
cirrostratus

what cloud is this
cirrus

what cloud is this
cumulonimbus

what cloud is this
cumulus
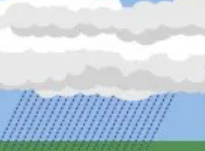
what cloud is that
nimbostratus

what cloud is this
stratus
beam blockage
occurs when radar beam is blocked by terrain
ground clutters
radar echos returns from trees
angels
echos caused by physical phenomenon(bats,birds,insects)