Nutrition 202 - Module 7/Metabolic Pathways
1/116
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Taught by Christian Lynch @ Texas A&M
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
117 Terms
What is the relationship between kcals consumed and kcals expended for weight maintenance?
Kcals consumed = kcals expended
What is the relationship between kcals consumed and kcals expended for weight loss?
Kcals consumed < kcals expended
What is the relationship between kcals consumed and kcals expended for weight gain?
Kcals consumed > kcals expended
What are some of the largest sources of added sugar in the diet?
Sugar-sweetened beverages (SSB)
In what 3 ways are calories expended?
Resting energy expenditure (REE)
Physical activity
Thermic effect of food (TEF)
What is total energy expenditure?
The combination of calories burned from REE, physical activity, and TEF
Basal metabolic rate (BMR)
Energy metabolism that occurs after waking up or at least 12 hours after the last meal
What functions make up BMR?
Involuntary life-sustaining functions (e.g. breathing, blood circulation, digestion)
Where are most of our calories burned?
During REE, especially when sleeping
Physical activity
Energy expenditure through voluntary physical effort
Exercise activated thermogenesis
Calories that are burned during moderate to intense activity
Non-exercise activated thermogenesis
Calories that are burned during light activity
Thermic effect of food (TEF)
The process of burning calories as you digest, absorb, transport, store, and metabolize food
What percentage of calories consumed from a meal does your body burn?
10%
What is the thermic effect of protein?
30%
How do you calculate TEF from a meal?
Calories from the meal - 10% of the calories from the feel = calories you actually get after TEF
What is the BMR for women?
665.1 + (9.563 x weight in kg) + (1.85 x height in cm) - (4.676 x age)
What is the BMR for men?
65.1 + (13.75 x weight in kg) + (5.003 x height in cm) - (6.775 x age)
Body mass index (BMI)
A measure of weight relative to height
What is the formula for BMI?
Weight in kg/(height in meters)²
Is BMI a good metric for a population?
Yes
Is BMI a good metric for an individual?
No, it depends
If your BMI is under 18.5, you are __
underweight
If your BMI is between 18.5 and 24.9, you are at __
normal body weight
If your BMI is between 25 and 29.5, you are __
overweight
If your BMI is over 30, you are __
obese
What is the relationship between BMI and mortality?
As BMI increases, your mortality increases. However, there is also an increased risk of mortality with being underweight.
What are some consequences of being obese?
Risk for heart disease, hypertension, type 2 diabetes, stroke, gallbladder disease
What are some consequences of being underweight?
Decreased overall energy, respiratory complications, heart irregularities, infertility, delayed wound healing, weakened immune system, osteoporosis
Osteoporosis
A condition associated with decreased bone mass and bone density
What groups of people are at greater risk of getting osteoporosis?
Older people, women, underweight people, tobacco users, people who aren’t physically active
What hormones drive bone mineral deposition?
Sex hormones
What makes up your total body mass?
Lean tissue mass + fat mass + water
Essential fat
Fat required for normal physiological functions
Where is storage fat located?
In adipose tissue, in tissue under the skin (aka subcutaneous), and around essential organs
Why does body fat usually increase with age?
Less physical activity
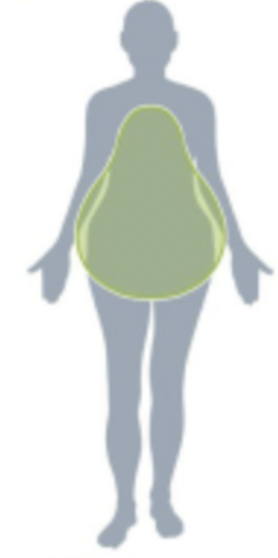
Gynoid pattern
Fat that is located over muscle and under the skin at the hips and thighs
What fat makes up the gynoid pattern?
Subcutaneous fat
What is your body shaped like if you have a gynoid pattern?
A pear
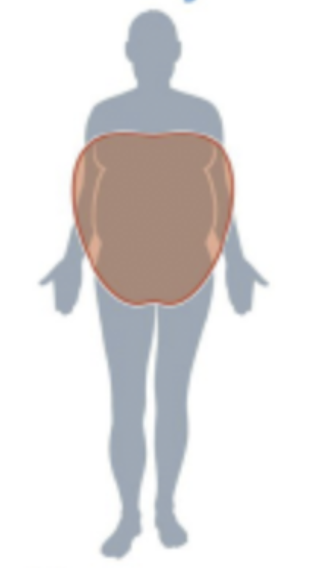
Android pattern
Body fat is stored under the abdominal muscle around the internal organs
What fat makes up the android pattern?
Visceral fat
What is your body shaped like if you have an android pattern?
An apple
What receptors cause fat to be stored in the stomach?
Adrenergic receptors
Obesity is affected by what factors?
Physiological, psychological, lifestyle behaviors, social and economic
What factor mostly affects obesity?
Psychological
Set point theory
The theory that the body is programmed to gravitate toward a certain weight
How does your body ensure that you maintain a stable weight?
Your metabolism may adjust upward or downward to ensure that weight is neither gained nor lost
When a person gains weight in the form of fat, what happens to the number and size of adipocytes?
Both the number and size of adipocytes increase
Hypertrophy
The increase of cells’ size
Hyperplusia
The increase of the number of cells
Atrophy
The decrease of cells’ size
Where are G-cells located?
In the stomach
G-cells function
They secrete gastrin
Gastrin function
It encourages the stomach to contract, which then stimulates parietal cells to secrete HCl
Where are I-cells located?
In the duodenum
I-cells function
They secrete CCK (cholecystokinin)
CCK function
It stimulates the gallbladder to release bile into the small intestine and stimulates the pancreas to release pancreatic amylase, lipase, and protease
Where are S-cells located?
In the duodenum
S-cells function
They secrete secretin
Secretin function
It stimulates the pancreas to secrete alkaline bicarbonate
Where are L-cells located?
In the duodenum
L-cells function
They secrete GLP-1 and peptide YY
GLP-1 function
Increases insulin secretion and delays gastric emptying
Peptide YY
Promotes the feeling of satiety in the brain
Leptin
Hormone released by fat cells to signal to the brain that the body has had enough to eat
Which cells secrete leptin?
Adipocytes
What do increased levels of leptin result in?
Increased energy expenditure and a decrease in food intake
What do decreased levels of leptin result in?
Decreased energy expenditure and an increase in food intake
What 3 hormones are associated with satiety?
GLP-1, peptide YY, and leptin (primary)
What 2 hormones are associated with hunger?
Neuropeptide Y, ghrelin (primary)
Hunger
The physiological need to eat
What can hunger be triggered by?
Low blood sugar and low glycogen
Appetite
The psychological desire to eat
What can appetite be triggered by?
The sight or smell of food
Neuropeptide Y
Neurotransmitter that increases food intake and blood glucose levels, promotes the storage of energy in fat cells
Ghrelin
A hunger-stimulating hormone produced by cells that line the stomach when it is empty
What people are candidates for weight loss surgery?
People whose BMI is > 40 kg/m² and people whose BMI is > 35 kg/m² with health conditions
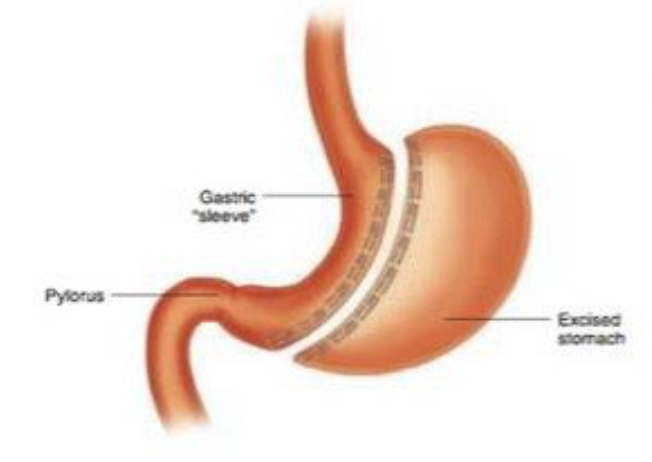
Vertical sleeve gastrectomy
Surgical procedure in which part of the stomach is removed
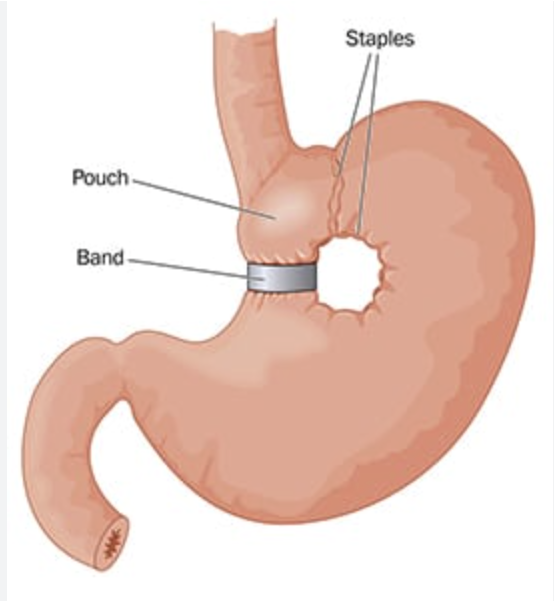
Vertical banded gastroplasty
Surgical procedure in which bonds and staples are used to create a small stomach pouch
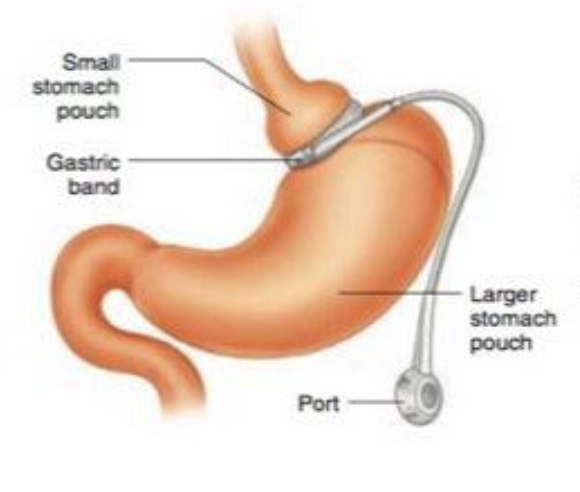
Adjustable gastric band procedure
Adjustable band fits around lower esophageal sphincter
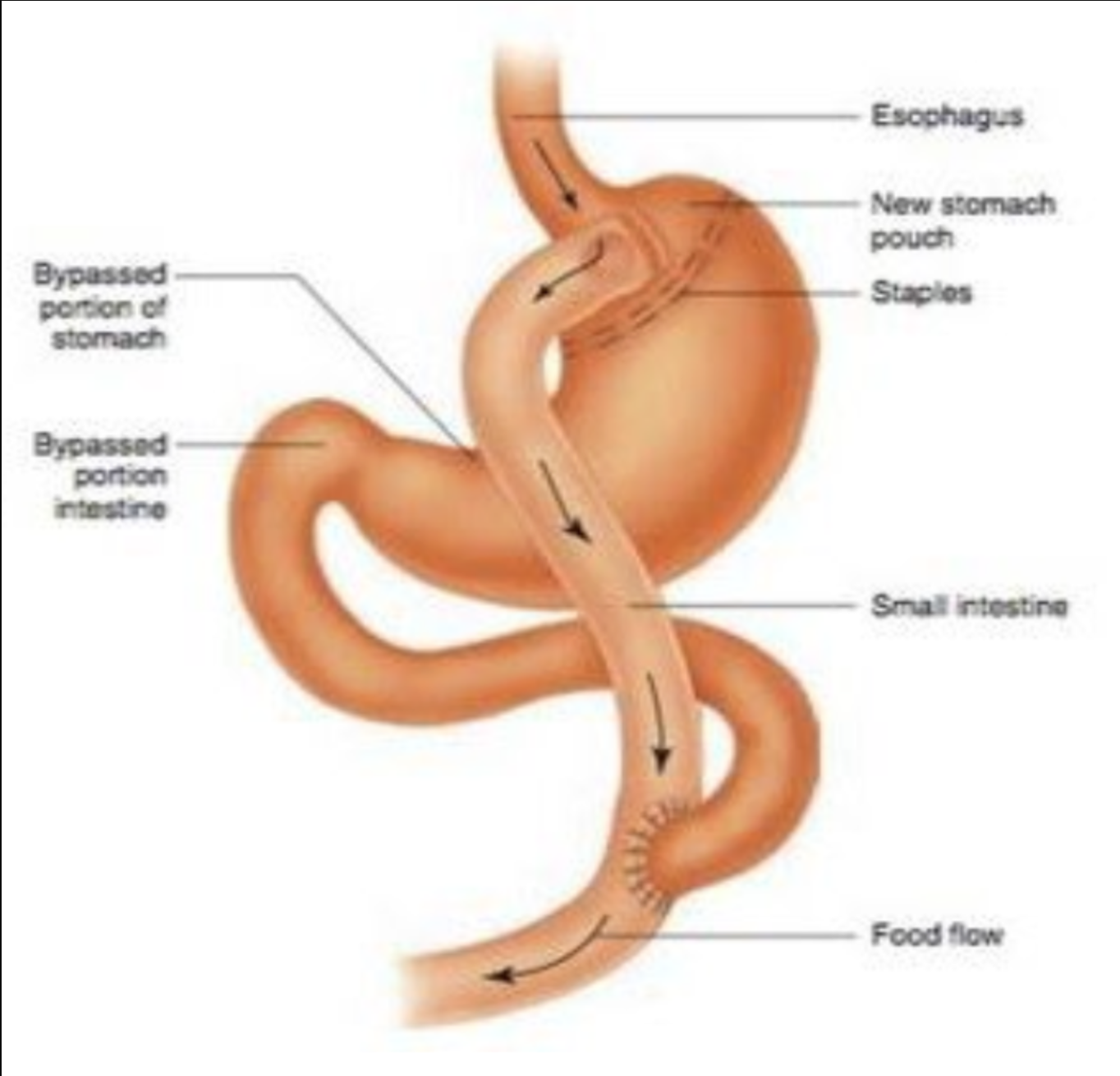
Gastric bypass
Small pouch created from stomach so food can bypass, results in malabsorption of nutrients
Substrate
Anything that can be acted upon by an enzyme
Substrate level phosphorylation
Metabolic process where a phosphate is transferred to a high-energy substrate (in this case, usually an active form of a B vitamin) to ADP, which forms ATP
Oxidative phosphorylation
Metabolic process in which nutrients are oxidized to produce ATP
Oxidative decarboxylation
Produce CO2
Vitamin B1
Thiamin
Active form of vitamin B1
TPP
Vitamin B2
Riboflavin
Active forms of vitamin B2
FADH, FMN
Vitamin B3
Niacin
Active form of vitamin B3
NADH
Where does glycolysis occur?
Cytosol
In what state does glycolysis occur?
A fed state
When does glycolysis occur?
As soon as glucose goes inside a cell
What kind of process is glycolysis?
Anaerobic
What kind of phosphorylation occurs in glycolysis?
Substrate level phosphorylation
What is the starting reactant in glycolysis?
Glucose (C6H12O6)
What is the final product of glycolysis?
2 pyruvate
What enzyme determines the rate of glycolysis?
Phosphofructokinase
What active form of B vitamin is present in glycolysis?
NADH (Vitamin B3)