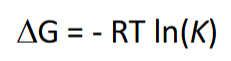K1.1 (revision) & K1.2 (link between kinetics & equilibria)
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms

equation for rate
rate must be the same regardless of whether the concentration of A, B, C or D is followed
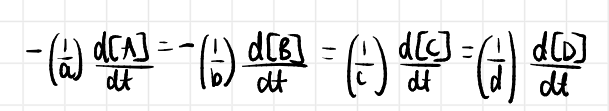
A + A → products
equation for rate

what is molecularity
what does it relate to
what type of property is it
the number of molecules involved in a reaction
relates to an individual reaction step or elementary reaction
it is a microscopic, mechanistic property
what is order
symbol?
what does it relate to
what type of property is it
the measured dependence of rate on concentration
symbol = α
relates to a complete reaction (elementary or complex)
it is macroscopic, measured property
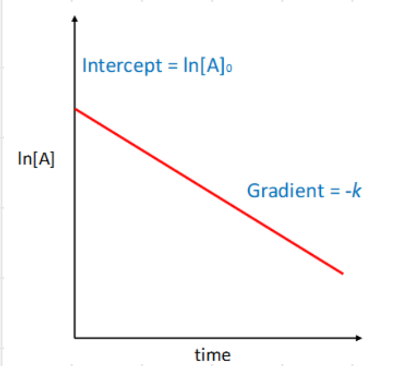
1st order rate law and integrated rate law
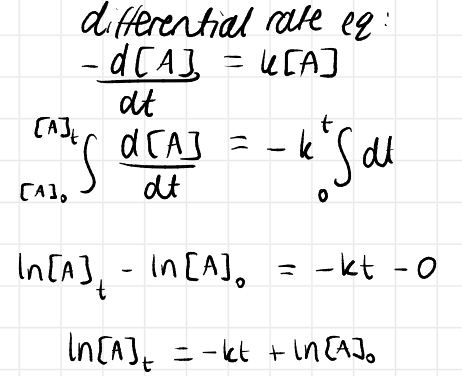
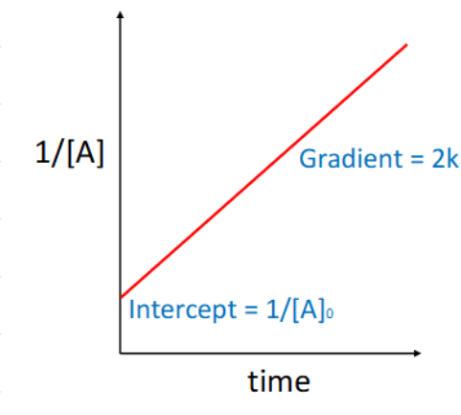
1st order straight line graph
gradient? intercept?
2nd order rate law and integrated rate law
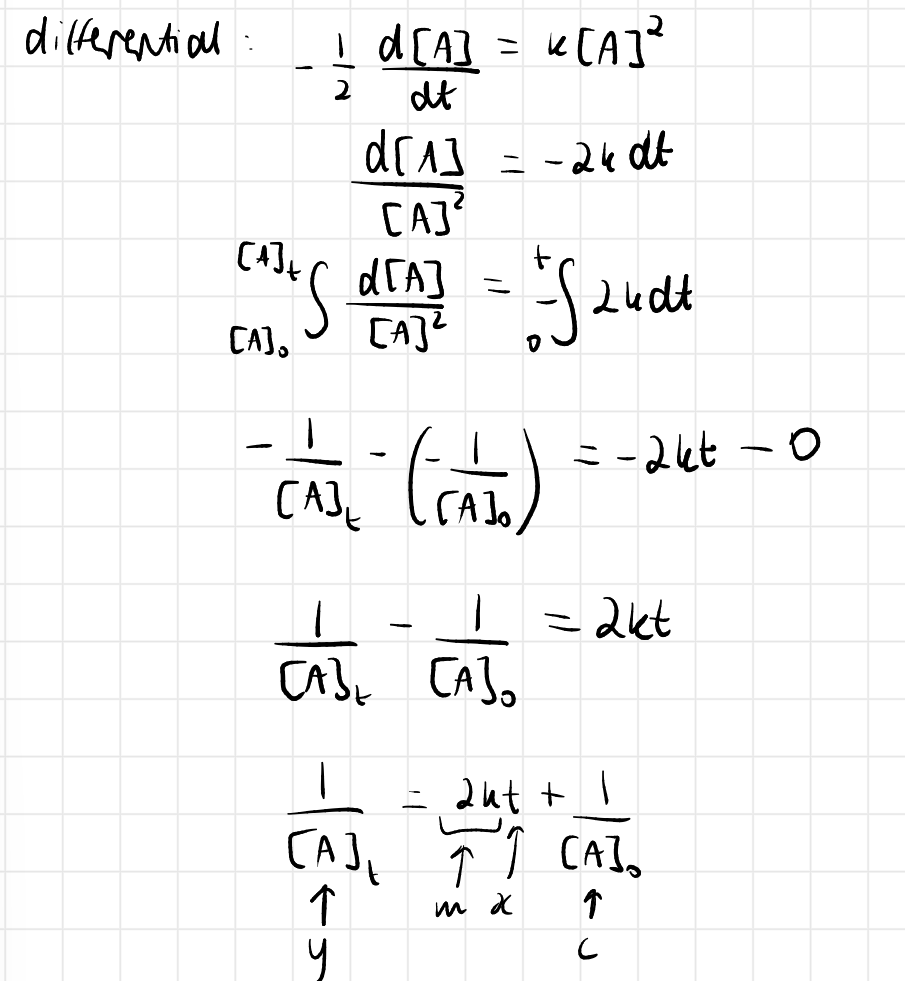
2nd order straight line graph
how to solve rates of reactions for bimolecular reactions such as A+B → products
simplify with the isolation method:
[B] >> [A] → [B] remains constant at [B]0 so can be combined with k
rate equation and integrated rate equation for isolation method

how is k determined from the isolation method
k’ is obtained from the graph of ln[A] vs time
repeat the process at a different [B]0
k’ = k[B]0 so plot k’ vs [B]0
the gradient is k in units of mol-1dm3s-1
![<p>k’ is obtained from the graph of ln[A] vs time</p><p>repeat the process at a different [B]<sub>0</sub></p><p>k’ = k[B]<sub>0 </sub>so plot k’ vs [B]<sub>0</sub></p><p>the gradient is k in units of mol<sup>-1</sup>dm<sup>3</sup>s<sup>-1</sup></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/40ef575c-99af-46c0-ba7c-f03258c700c2.png)
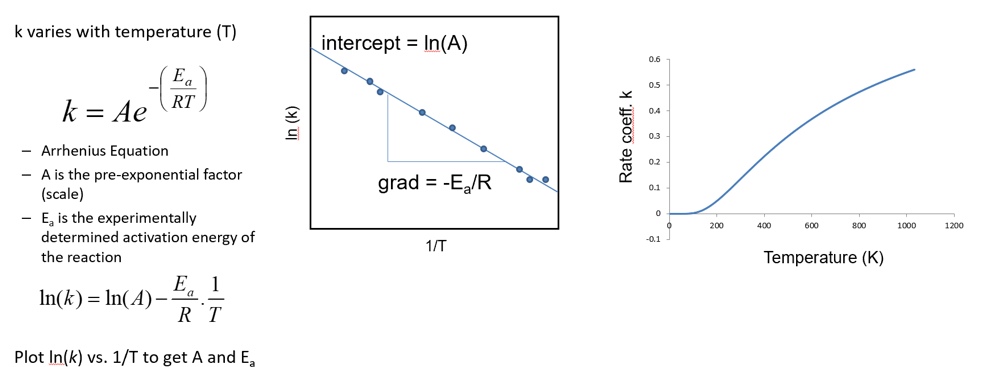
how is the temperature dependence of k described
equations? graphs?
Arrhenius equation
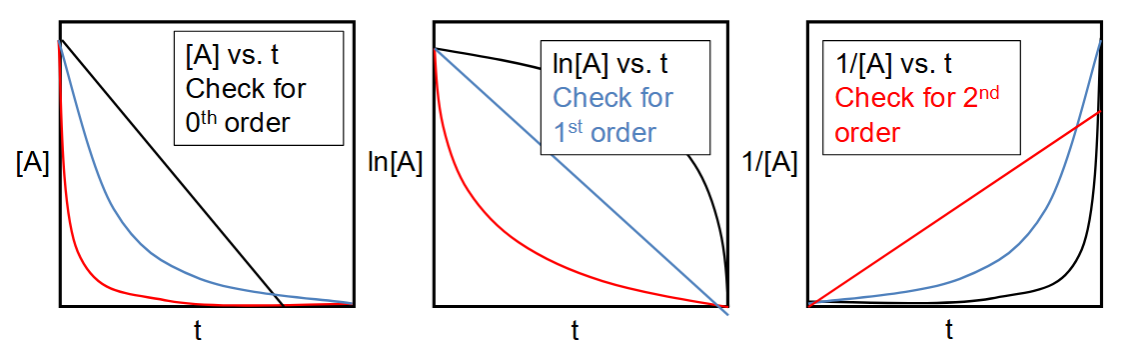
plots of [A], ln[A] & 1/[A] for 0th, 1st and 2nd order reactions
which is used as a check for each order?
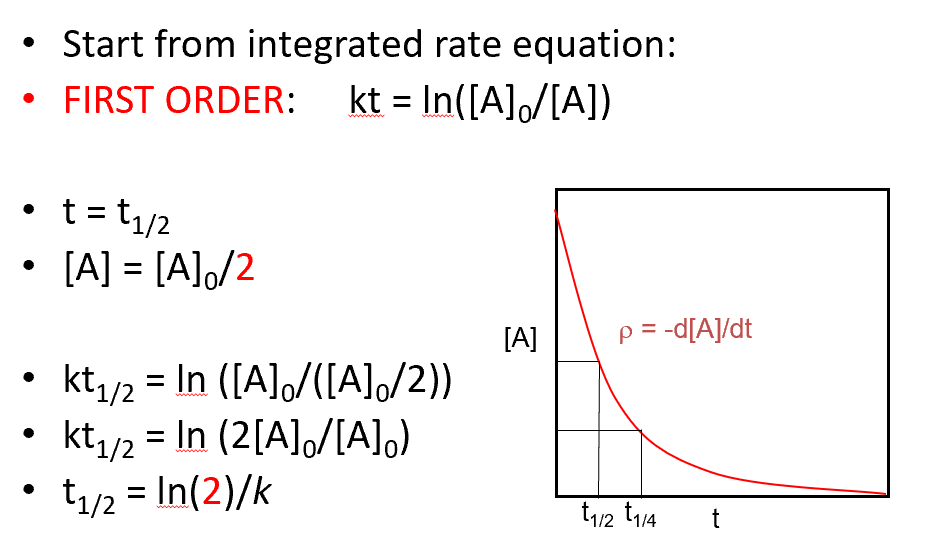
half life for 0th order
[A]0/2k
half life for 1st order
(ln2)/k
half life for 2nd order
1/(2k[A]0)
derivation for 1st order half life
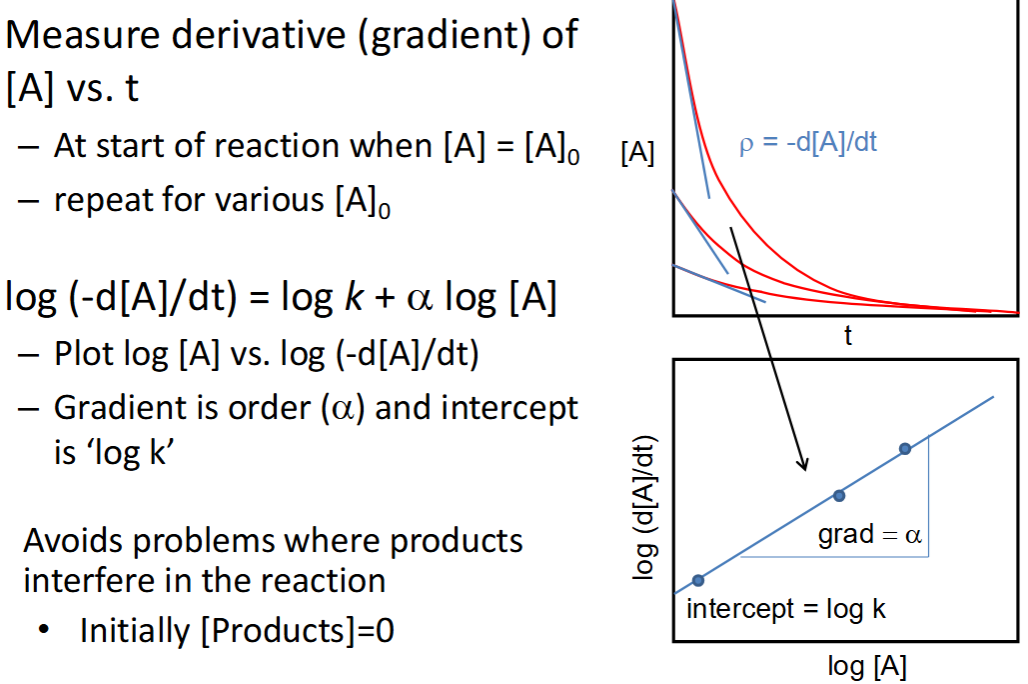
how to determine order and k from one method
graphs? advantage?
initial rates method
possible scenarios for the rate coefficients
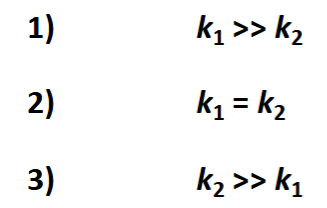
![<p>d[A]/dt, d[B]/dt and d[C]/dt?</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/3d6baa65-a6c5-407c-82fc-0236a1282f77.png)
d[A]/dt, d[B]/dt and d[C]/dt?

![<p>how to solve for [B]?</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/c17845a2-a630-4608-8c62-c9479ad16301.png)
how to solve for [B]?
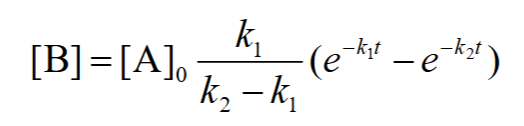
![<p>[C] = ?</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/576061f4-d569-4def-bae4-b2b105a98709.png)
[C] = ?
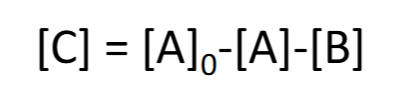
scenario where k1 >> k2
rates of steps + RDS?
graph?
scenario where k1 = k2
rates of steps + RDS?
graph?

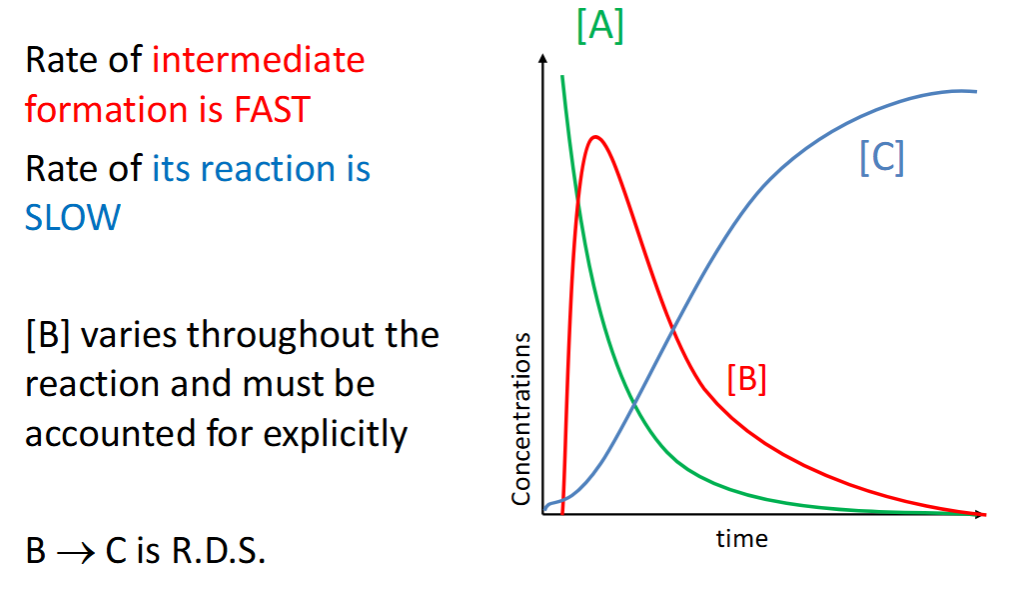
scenario where k2 >> k1
rates of steps + RDS?
graph?
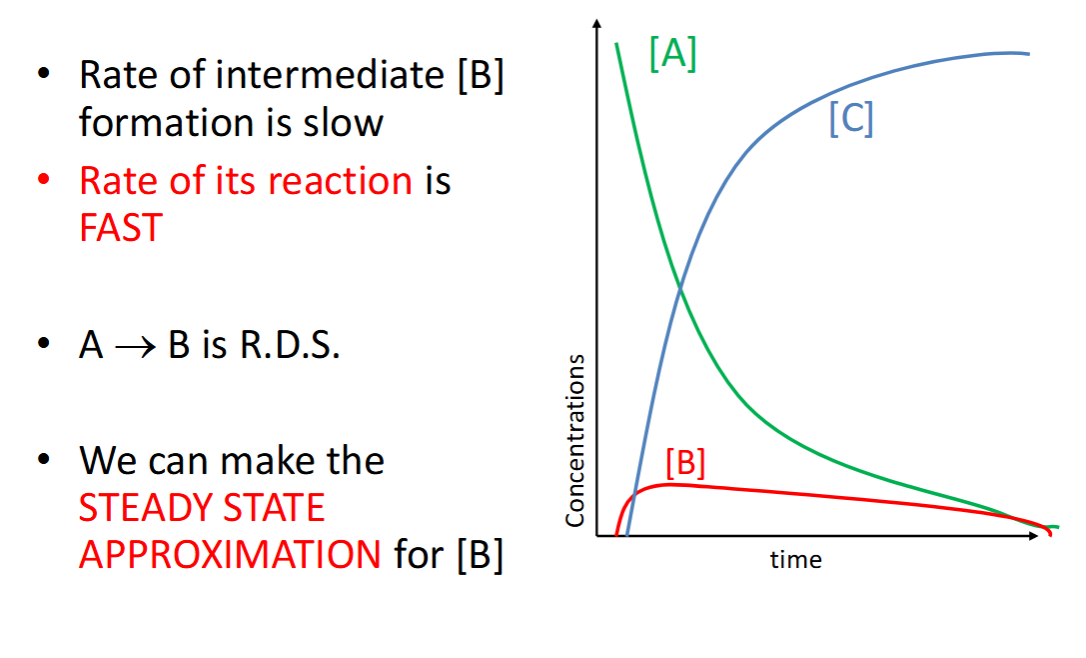
steady state approximation
rate of formation = rate of removal

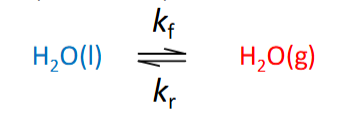
kf & kr equations & relationship
kf[H2O(l)] = kr[H2O(g)]
note rates of forward + reverse reactions are equal but rate coefficients are not the same
![<p>k<sub>f</sub>[H<sub>2</sub>O(l)] = k<sub>r</sub>[H<sub>2</sub>O(g)]</p><p>note rates of forward + reverse reactions are equal but rate coefficients are not the same</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/2ce30500-d3d0-4ed6-9e1e-af48c19a1160.png)
equilibrium constant from rate coefficients
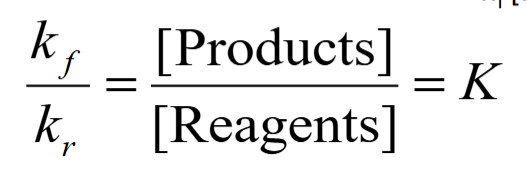
equation for change in Gibbs free energy