Criminal Courts Final Exam
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Daubert Standard
established that trial court judges are supposed to act as gatekeepers who have a special obligation to ensure the reliability of scientific evidence
What is the first Daubert Factor?
Empirically testable and capable of replication
What is the second Daubert Factor?
Published and/or subjected to peer review
What is the third Daubert Factor?
Known or potential rate of error is acceptably low
What is the fourth Daubert Factor?
Is logical, avoids bias, and has construct validity
What is the fifth Daubert Factor?
Adheres to recognized research methods, and proper sampling and statistical procedures for data analysis
What is the sixth Daubert Factor?
Generally accepted in the relevant scientific community
Frye Standard
prevents unfounded scientific principles or conclusions based on such principles from being used at trial
Standard of Review
how much deference an appellate court will afford to the decisions of a judge, jury, or administrative agency in an appeal
4 types of evidence
testimonial, real(physical), Demonstrative, and scientific
Procedural law
establishes the methods of enforcing legal obligations
Procedural Law Example
trials
Substantive law
creates legal obligations
Substantive Law Example
criminal law( murder, robbery), civil law( contract and domestic relations )
3 characteristics of common law
Judge made law, precedent, multiple sources of law
Types of multiple sources of law
constitutions, statues, administrative regulations, judge made law
5 standards and burdens of proof
Reasonable Suspicion, Probable Cause, Preponderance of Evidence, Clear and Convincing Evidence, Beyond a Reasonable Doubt
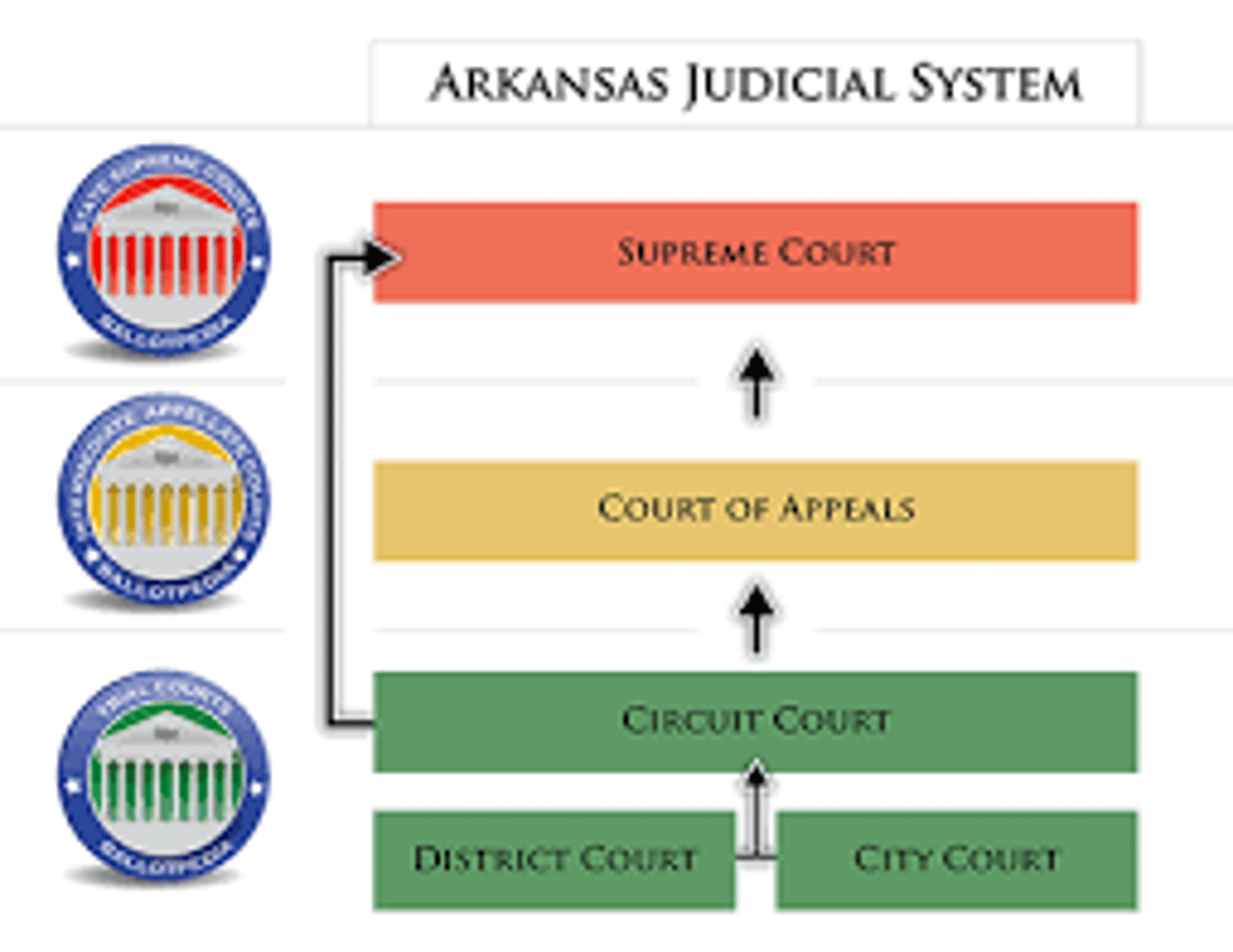
Arkansas State Court Organization
Big 5 Amendments
-4th ( no unreasonable search and seizure)
-5th ( double jeopardy, self incrimination)
-6th ( right to speedy trial, counsel, and jury of peers)
-8th( cruel and unusual punishment/excessive bail)
-14th( due process/equal protection)
12 Steps of Felony Cases
-crime
-arrest
-initial appearance
-charging
- arraignment
-discovery
-pretrial motions
-plea negotiations
-trial
-sentencing
-punishment
-appeal
Whisnant Case facts
- Boyfriend acts as an agent of the government and turns girlfriend in for possessing firearm as a felon
-boyfriend goes through purse and finds stolen checks and credit cards
-Gun in plain view when police get there
-Whisnant won't cooperate
- Whisnant says 4th amendment was violated/ moves to suppress
6 constitutional limits on criminal law
-bills of attainder and Ex Post Facto( no punishment w/o trial & no retroactive laws)
-Statutory clarity: laws must be clear
-speech and religion
-privacy
-Bear Arms: protects gun owners
- Big 5
Whisnant decision
4th amendment was violated
Judge Selection in Arkansas
Nonpartisan election
Trial vs. Appellate Courts
-Trial Courts: Arraign defendant, conduct trials or guilty pleas, and impose sentences
-Ensure proper interpretation of the law( w/o hearing testimony or using juries), decisions made by a panel of judges
Article 3 courts
constitutional courts, establish the federal judiciary
Article 1 courts
Legislative courts, presided over by bankruptcy judges and magistrate judges
4 levels of jurisdiction
-geographical
-subject matter
-personal
-hierarchical
Problem solving courts key elements
-Immediate Interventions
-Non-Adversarial Adjudication
-Hands On Judicial Involvement
-Treatment& Rules/Structure
-Team Approach
Examples of Problem solving courts
drug court, domestic violence court, mental health court
Assembly line of justice
the fast and efficient movement of cases in and out of the court system
Metcalfe article
- informal relationships affect efficiency
-Prosecutor judge familiarity increases guilty pleas
-defense attorney familiarity may slow resolutions
-gender similarity speeds up plea deals especially guilty pleas
Factors of charging decisions
-seriousness of offense
-culpability of defendant
-harm caused
-cooperation
-subject to another jurisdiction
4 types of prosecutorial misconduct
- failure to disclose exculpatory evidence
-introducing false evidence
-using improper arguments
-discriminating in jury selection
Requirements to prove prosecutorial misconduct
-misconduct occurred
-it caused prejudice to the defendant
Elements of Brady Violation
-evidence is favorable to the accused
-evidence was suppressed by the state(willfully or inadvertently)
-prejudice resulted from suppression
Brady v. Maryland Facts
-Maryland state found Brady guilty of first-degree murder
-Brady said he didn't murder anyone he just robbed them
-found out partner confessed to the murder after trial, but prosecution suppressed this
-ruled that prosecutors suppression violated due process
Gideon v. Wainwright Facts
-charged in Florida court for burglary
-demanded a court appointed lawyer and judge said nope
-found guilty, appealed
-SC said that 6th amendment right was violated
-established right to counsel for all criminal defendants
Nelson hearing
-defendant wants to address issues with court appointed counsel
-often related to ineffective assistance of counsel
Faretta Hearings
- defendants want to represent themselves
-judge assesses understanding of legal process, charges, and consequences
- judge may appoint stand by counsel for assistance
Ineffective counsel requirements
-serious errors or deficiencies by counsel
-prejudice: reasonable probability that the trial outcome would have been different
Batson v. Kentucky
Equal Protection Clause of 14th amendment prohibits prosecutors from exercising peremptory challenges in a racially discriminatory manner
Major Sentencing Philosophies
-Retribution: punish wrongdoers
-Incapacitation: remove offenders from community
-Deterrence: prevent the commission of future crimes
-Rehabilitation: restore offender to a constructive place in society
-Restoration:Promte victim healing
Arguments for 6 people jury
- cheaper
-fewer peremptory challenges
-less chance of juror misconduct
Arguments for 12 people jury
- Longer deliberation and better recall of trial testimony
-more likely to produce accurate results
- Larger juries are more likely to be diverse
-more opportunities for people to serve on jury
Arguments for unanimous decision
-jurors evaluate evidence more thoroughly and take more ballots
-protects representativeness (all opinions heard)
Arguments for Majority decision
- decrease in hung juries
-cheaper and more efficient
Innocence is relevant Case facts
- Sweatt came home from work to find that her bf was smoking MJ
-Words were exchanged and he left
-Police came and searched the apartment and found 25 grams
-Said the drugs were hers and was arrested
-Plead guilty to avoid a prison sentence
Innocence is relevant main point
-people plead guilty to avoid extended jail time
-approximately 94% of state cases result in plea bargains, 97% federal
-criminalization of everything is leading to an increase in cases therefore an increase in plea bargains to keep the system running efficently
unprotected speech
-fighting words
-incitement to violent action
-threat
-obscenity
-libel
-hate speech
Defense attorney decisions that can be made
Strategic
-which witness to call
-if, when, and how to cross exam
-which jurors to accept or strike
-what motions to make before and during trial
-trial strategy
decisions defense attorneys can't make
fundamental
-what plea to enter
-jury trial waive
-whether client should testify on their own behalf
-whether to appeal
-objective of the representation