bi 114 - lecture 20 (part 2)
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
Is whooping cough an upper or lower respiratory tract infection?
Whooping cough is an upper respiratory tract infection.
you're coughing and you cough up out of your mouth yk.
violent cough is another name for what disease
Whooping cough/Pertussis
Is whooping cough a bacterial or viral disease?
Whooping cough is a bacterial disease
What bacteria causes whooping cough?
Bordetella pertussis
True or false: Bordetella pertussis is a gram negative bacillus bacteria.
True, bordetella pertussis is a gram negative rod
How is whooping cough transmitted?
Whopping cough is acquired by inhalation of aerosolized droplets.
What is the incubation period time for whooping cough?
The incubation period for whooping cough is 7-21 days.
How is whopping cough treated
Usually with antibiotics or the DTap vaccine.
catarrhal stage of whooping cough
stage of whooping cough characterized by fever, sneezing, vomiting, and mild, dry persistent cough (symptoms of upper respiratory tract infection).
Paroxysmal stage of whooping cough
Violent rapidly repeats cough, followed by a struggling deep breath that makes a whooping noise
convalescent stage of whooping cough
Paroxysms gradually disappear during the next 2-3 weeks as patient recovers
Who gets the DTaP vaccine?
It's usually administered to young children, but people of ALL ages can get their own version of it (Tdap is used for people older than 6)
Is bronchitis usually viral or bacterial?
VIRAL but it can be bacterial (even allergen induced)
Is bronchitis an upper or lower respiratory infection?
Bronchitis is a lower respiratory tract infection.
Bronchitis affects the bronchi and that makes me think of the lungs. Lungs are lower. Bronchitis has a deep cough so I think of it coming from deep below. also bronchi are lower.
What is bronchitis
inflammation of the bronchi
symptom of bronchitis
Persistent cough
What causes bronchitis?
There are multiple viral and bacterial etiologies that cause bronchitis.
Is bronchitis acute or chronic?
It can be either acute or chronic. It's acute when the cough persists for more than 5 days
What is used to treat bronchitis?
Azithromycin is the drug of choice (antibiotic) for bronchitis.
Is pneumonia an upper or lower respiratory tract infections?
Pneumonia is a lower respiratory tract infection. Think of an LPN like the nurse. L for lower. P for pneumonia.
Is pneumonia viral or bacterial?
It is usually BACTERIAL. P looks like B
What is pneumonia?
inflammation of the lungs
community acquired pneumonia
a type of pneumonia that results from contagious infection outside of a hospital or clinic
Typical pneumonia is caused by what?
It is caused by S. pneumoniae
Atypical pneumonia is caused by what?
It is caused by ANYTHING OTHER THAN S. PNEUMONIAE like mycoplasma pneumonia, legionella, and chlamydophila.
Which has milder symptoms, typical or atypical pneumonia?
Typical pneumonia usually has milder symptoms.
Is legionellosis an upper or lower respiratory tract infection?
Legionellosis is a lower respiratory tract infection. L for lower.
Is legionellosis bacterial or viral?
Legionellosis is bacterial. It's caused by legionella pneumophila.
What kind of bacteria is legionella pneumophila?
gram negative rods
Legionellosis pneumophila contaminates what sources?
Water sources
How is Legionella transmitted?
aerosal, from environmental water source
Is legionellosis an intracellular or extracellular pathogen?
Legionellosis is an INTRAcellular pathogen that evades phagocytosis.
True or false: mycoplasma pneumoniae causes atypical pneumonia
True. Mycoplasma pneumoniae causes atypical pneumonia.
Mycoplasma
Bacterial genus that LACKS a rigid cell walla and usually exist in filamentous form
True or false: mycoplasma pneumoniae is the smallest known species of bacteria.
TRUE. Mycoplasma pneumoniae is the smallest known species of bacteria.
Symptoms of atypical pneumonia (caused by m. pneymonia) include what?
Headache, malaise, low-grade fever, chills, nonproductive cough
What is the most common cause of hospital acquired pneumonia?
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
What kind of bacteria is pseudomonas aeruginosa?
Opportunistic, gram negative pathogen
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a major contributor to pneumonia and mortality in patients with what disease?
Cystic fibrosis
Mantaux test
a diagnostic tool used to detect exposure to the bacteria that cause tuberculosis (TB)
Is tuberculosis an upper or lower respiratory tract infection?
tuberculosis is a lower respiratory tract infection (tuberculosis is lowww it's quite evil)
Is tuberculosis bacterial or viral
Tuberculosis is a bacterial infection
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Bacteria that causes tuberculosis
MDR-TB
Produces rapid onset (fulminant) and fatal disease among patients with HIV. Highly infectious even to healthy people without HIV
How is tuberculosis spread
TB is spread through airborne droplets
Does tuberculosis have an animal reservoir?
yes, cattle sometimes serve as a reservoir for zoonotic TB
How is tuberculosis treated
9-12 months of Isoniazid (long course of antibiotics)
Tubercules
Small hard granulomas form around the site of the tuberculosis infection
Pathogenesis of tuberculosis
Bacteria enter lung, are phagocytized by macrophages, and survive sheltered within modified phagolysosomes.
What do tubercles develop into?
They develop into caseous lesions that have a cheese like consistency and can calcify into hardened Ghon complexes seen on X-rays.
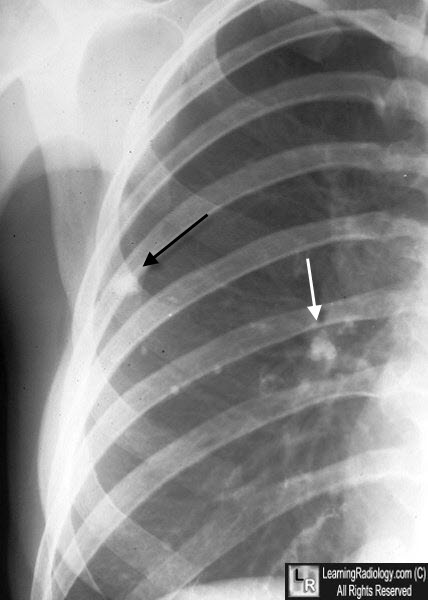
latent tuberculosis
Bacilli contained by immune system. Alive bacteria, but not infectious.
Active tuberculosis
Contagious infection with M. tuberculosis.
Characterized by a productive cough, sputum, fever, night sweats, and weight loss.
Calcified Ghon complex of TB
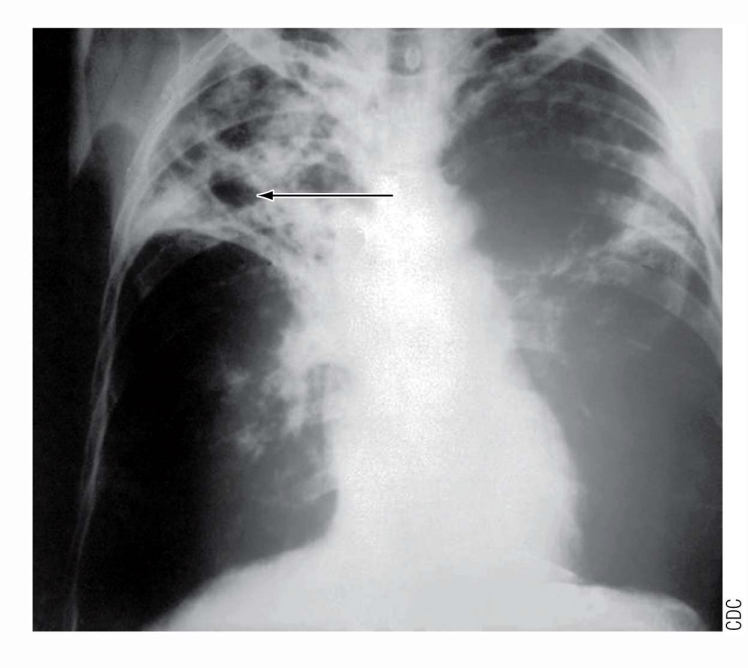
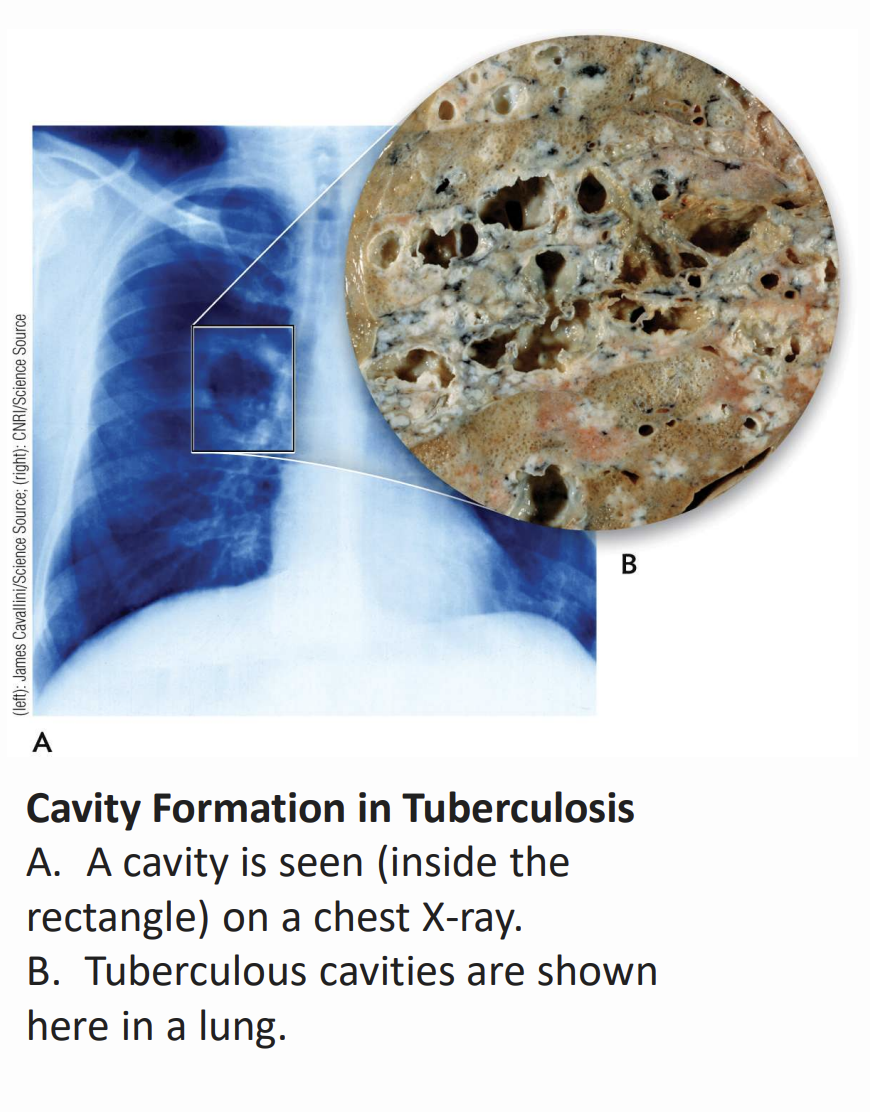
Cavity formation in tuberculosis
Coccidiodomycosis
Fungal respiratory infection. Endemic in the U.S. also known as valley fever.
What causes Coccidioidomycosis?
The fungus Coccidioides immitis.
Histoplasmosis
fungal infection of the lungs that causes flu like illness, erythema nodosum, arthritis, and arthralgia. Found in Ohio and Mississippi River valleys
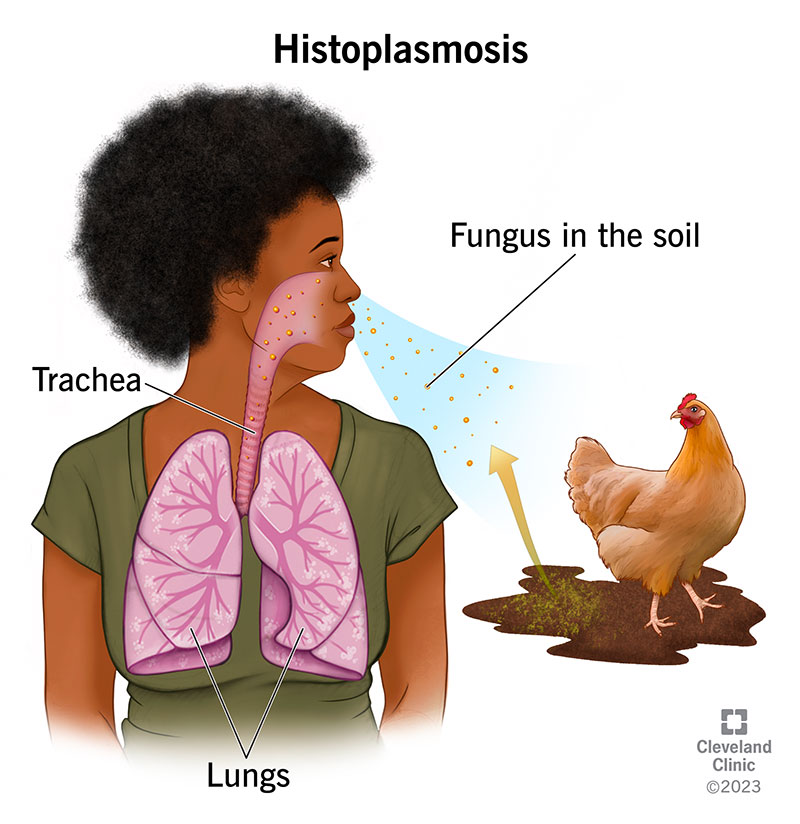
What causes histoplasmosis
The fungus Histoplasma capsulatum
Blastomycosis
Fungal respiratory infection caused by blastomyces dermatitis (dimorphic fungus). Found in Ohio and missispipi river valleys and Eastren U.S.
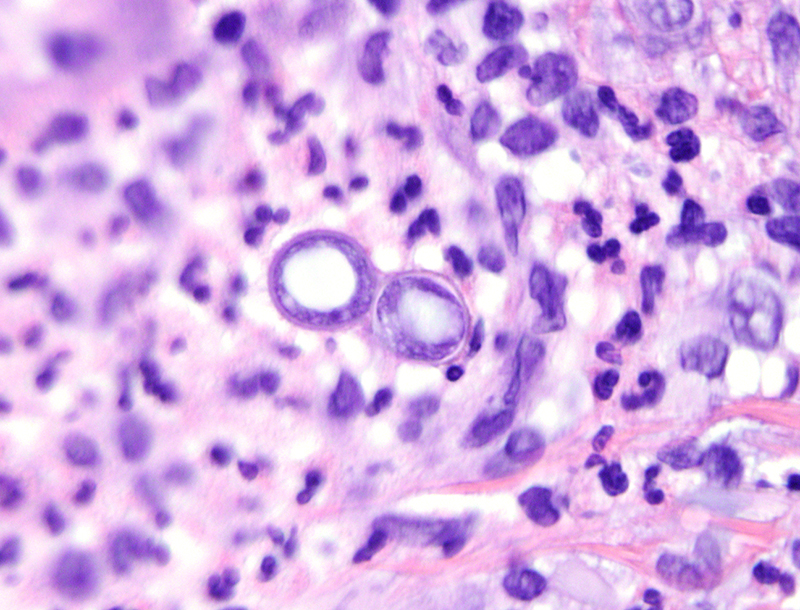
Is Blastomyces dermatitis dimrophic?
Yes, blastomyces is dimorphic.
Cryptococcus
Fungal respiratory infection that can involve skin, lungs, prostrate gland, urinary tract, eyes, bones, and joints
What causes cryptococcosis?
The fungi Cryptococcus neoformans
Meningoencephalitis
The most prevalent clinical form of cryptococcosis in AIDS patients.