MEDS2003 - Metabolism
1/137
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
138 Terms
catabolic pathways
"break down of complex molecules into simpler compounds" releases energy
anabolic pathways
"building complicated molecules from simpler ones": consumes energy
enzyme
"biological catalyst for chemical reactions": speeds up reaction rate & lowers activation energy
ATP
"adenosine triphosphate": cell's main energy source from energy released by spitting off one of three phosphates
ADP
"adenosine diphosphate" compound that remains when a phosphate group is removed from ATP; releasing energy
AMP
"adenosine monophosphate": component of RNA & ATP
phosphorylation
"introducing a phosphate group into an organic molecule" metabolic process
kinase
"enzyme that catalyzes phosphorylation": transfer of phosphate groups from ATP to acceptor molecules
phosphatase
"enzyme that catalyzes dephosphorylation": phosphate groups are removed from a molecule
phosphorylases
"enzyme that catalyzes a phosphorolysis reaction": using phosphate to cleave bigger molecules into smaller ones
synthases
"catalyse condensation reactions": in which no nucleotide triphosphate is required
synthetases
"catalyse condensation reactions" that require a nucleotide triphosphate
dehydrogenases
"catalyst for oxidation-reduction reaction": transfers hydrogen from one compound to another
energy charge
Leads to modulation of anabolic and catabolic flux by ATP, ADP, and AMP
fuel oxidation
"catabolism of biomolecules to maintain ATP homeostasis": exergonic process (releases heat)
NADH
"the reduced form of NAD+": an electron-carrying molecule that functions in cellular respiration
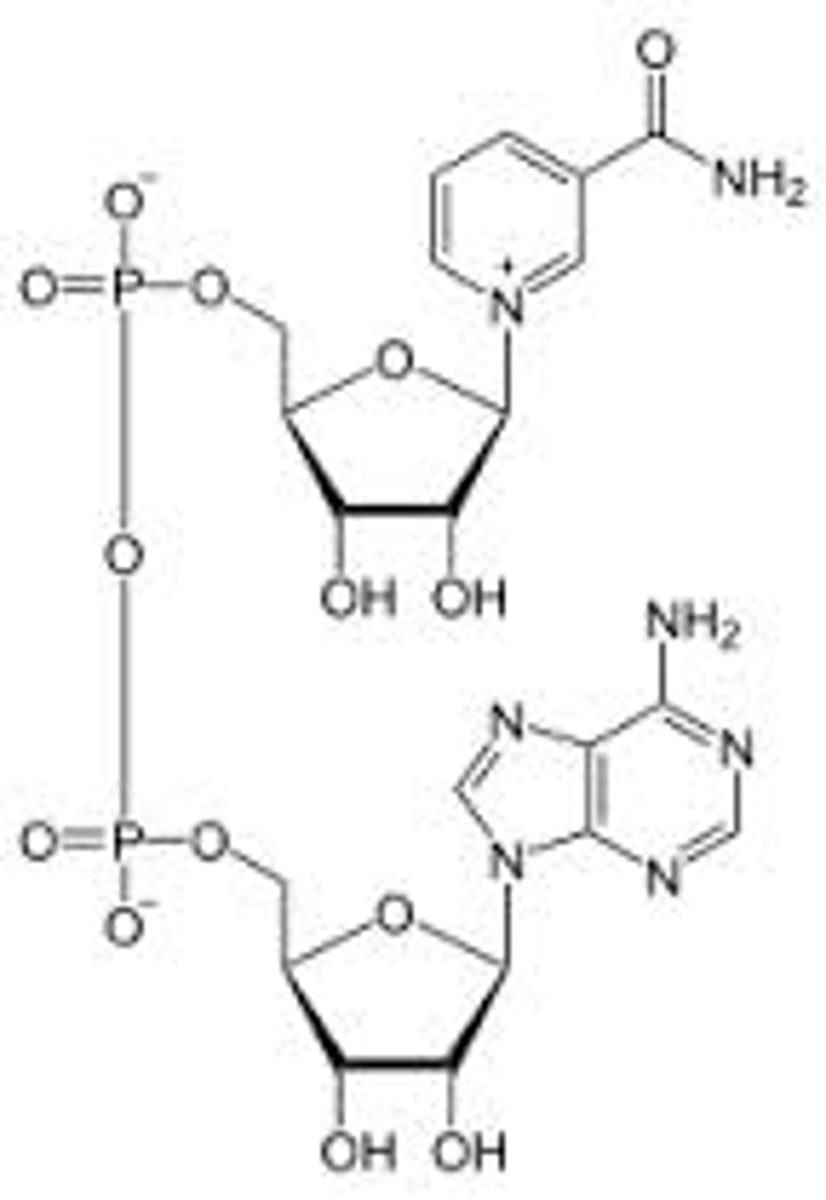
NAD+
electron carrier involved in glycolysis / donates to complex I
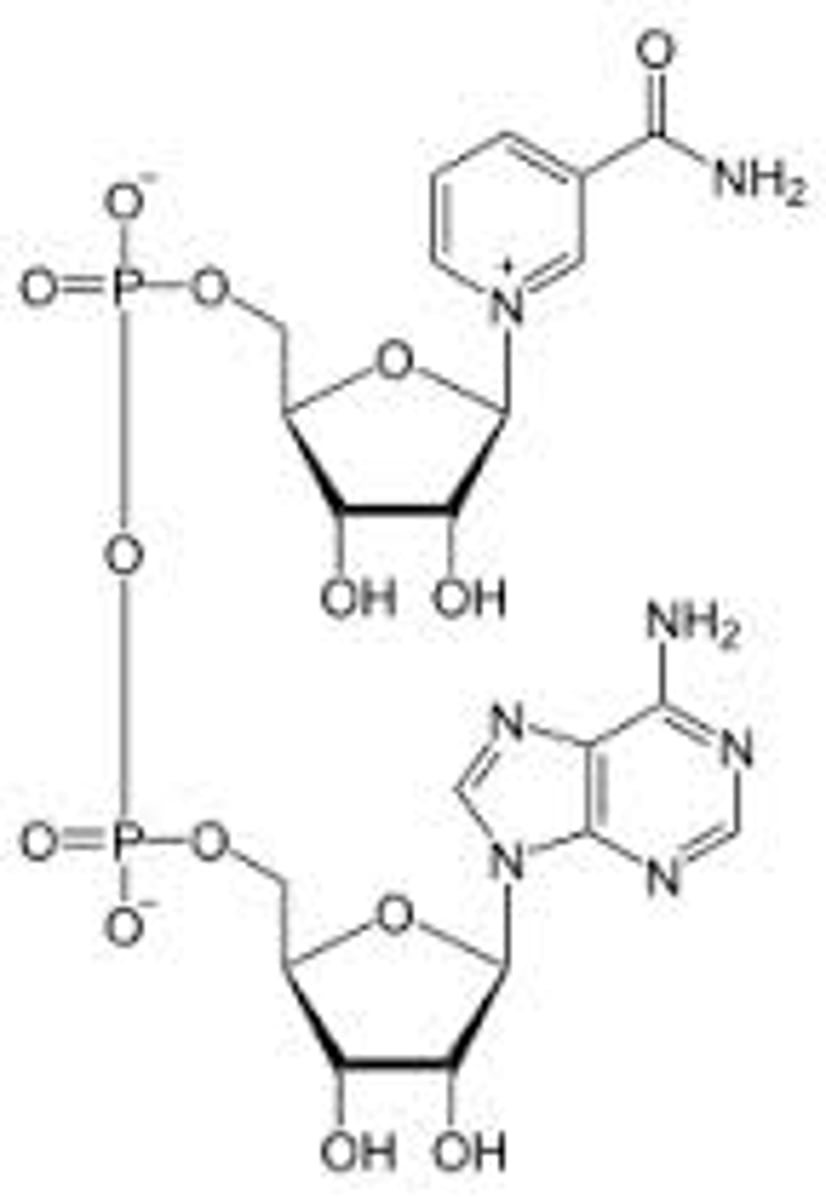
FADH2
molecule that stores energy for harvest by the electron transport chain.
H/e- carriers
in short supply
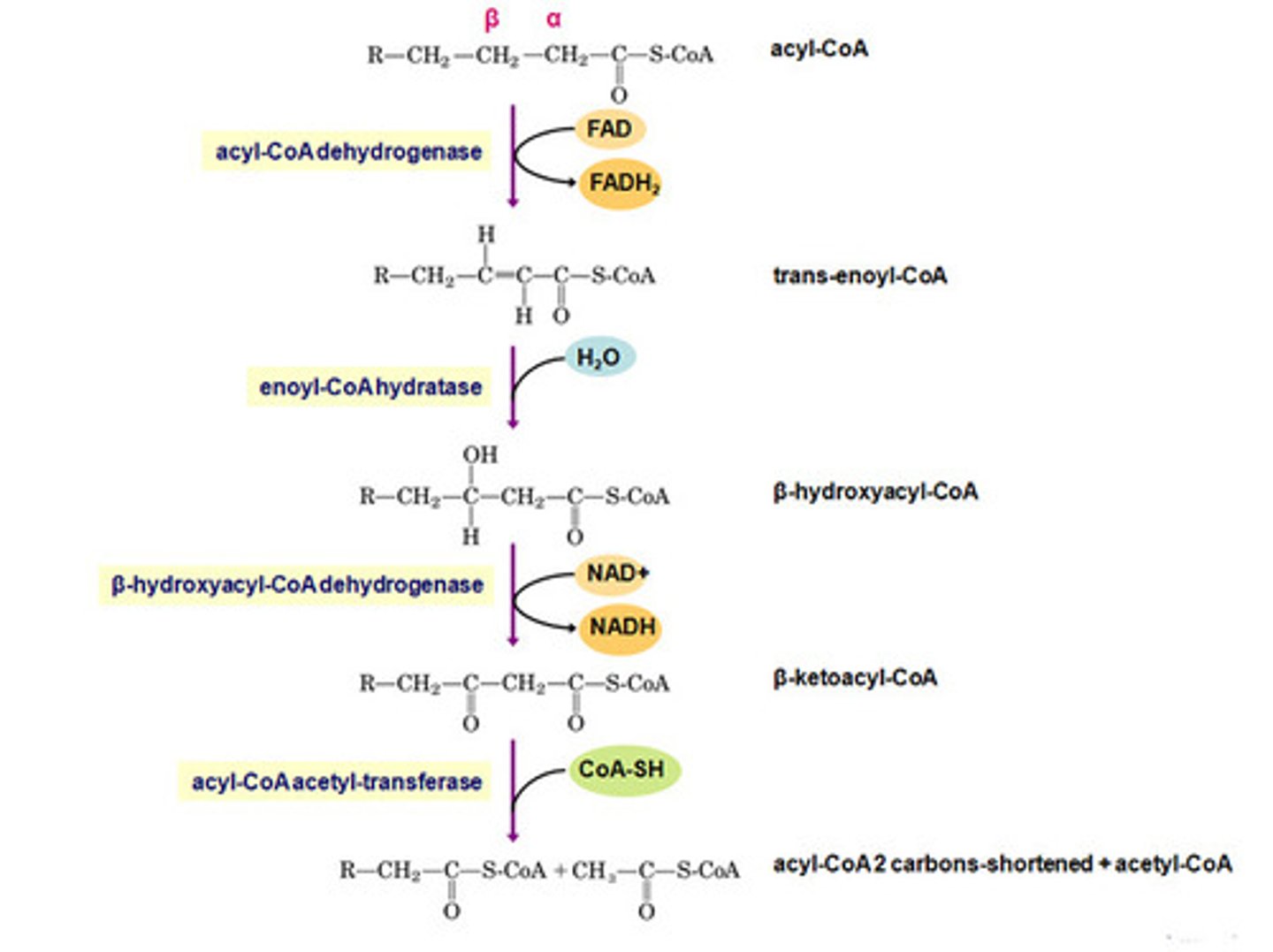
beta oxidation
metabolic sequence that breaks down fatty acids to two-carbon fragments that enter the citric acid cycle as acetyl CoA.
glucose oxidation
"intracellular, enzymatic breakdown of glucose": release of energy to synthesize ATP
muscle contration
"uses ATP": sarcomeres (myosin, actin) in myofibrils allow for contraction and muscle action;
Type 1 muscle fibers
"red & slow-twitch": smaller and slower to produce maximal tension, more resistant to fatigue; good blood supply & many mitochondria
Type 2 muscle fibers
"white & fast-twitch": larger in size, quick to produce maximal tension and fatigue more quickly; poor blood supply, few mitochondria & many contractile filaments
gentle exercise
"most readily available fuel is glucose": minutes later fatty acids take over for glucose recycling to occur
glucose recycling
"fatty acids substitute for glucose as a fuel": preventing glucose from being wastefully oxidized
moderate exercise
"exercise with mixture of fatty acid & glucose oxidation":
increase rate of fatty acid usage & enzyme catalysing; glucose oxidation occurs, with less glucose recycling
strenuous exercise
"exercise with breakdown of muscle glycogen, fatty acid & glucose oxidation": limited rate of blood glucose oxidation
very strenuous exercise
"exercise with fatty acid, glucose and glycogen oxidation": oxidation of glycogen producing CO2 & lactate
fatty acid oxidation
"beta oxidation": metabolic breakdown of fatty acids to acetyl CoA
coenzyme A
small molecule necessary for cell respiration and fatty-acid metabolism
fatty acyl CoA synthetase
"catalyzes thioester bond between a fatty acid and coenzyme A": degrades fatty acid for energy production to be incorporated into other metabolic pathways.
early glycolysis
energy investment of 2 ATP to break glucose into 2 3-carbon molecules
late glycolysis
energy generation (4 ATP; net gain of 2 ATP, 2 pyruvate & NADH)
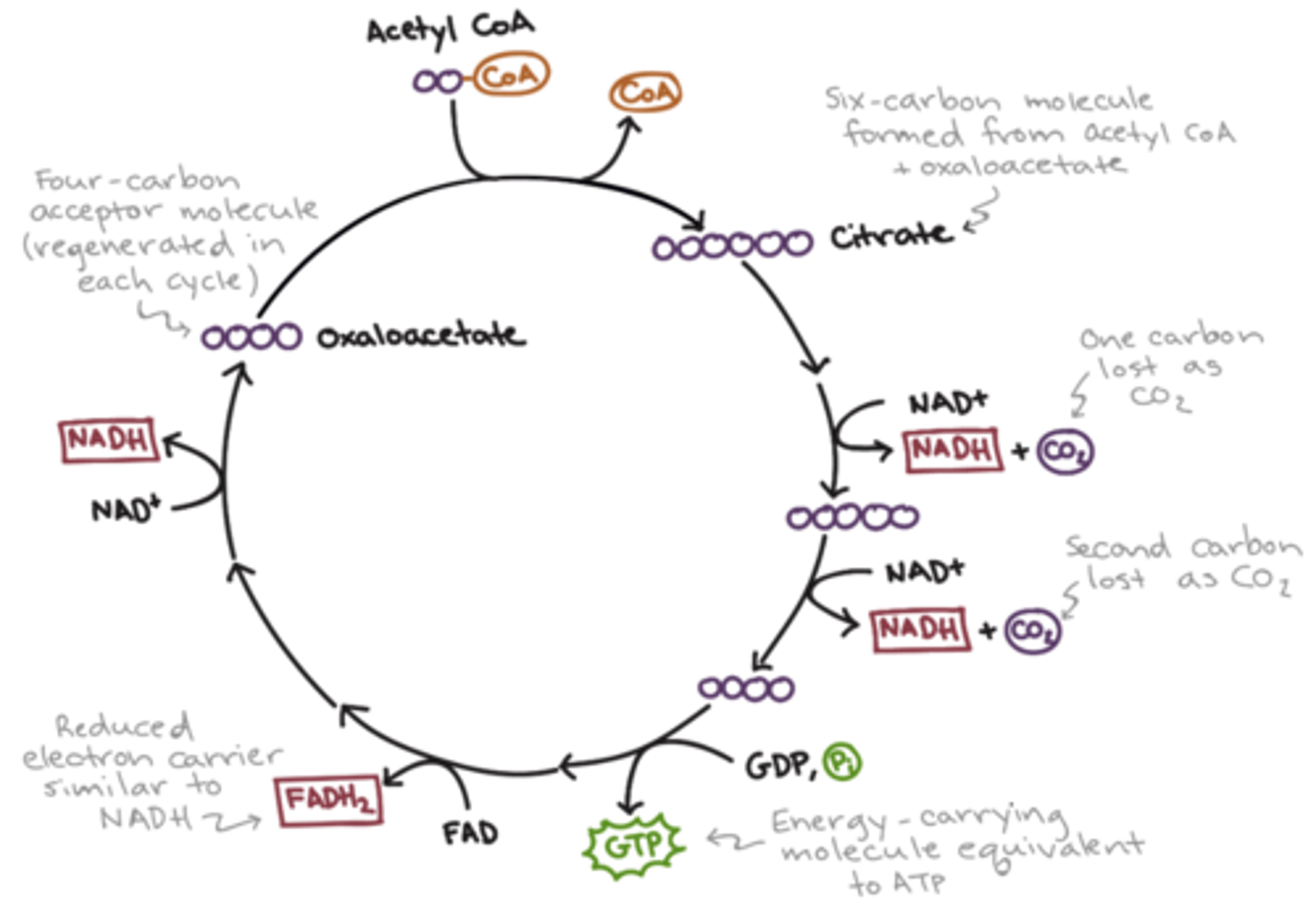
krebs cycle
second stage of cellular respiration, in which pyruvic acid is broken down into carbon dioxide
In:
2 Carbon
Out:
2 Carbon
3 NADH
1 reduced FAD
GTP
GTP
"nucleotide composed of guanine, ribose, and three linked phosphate groups": incorporated into the growing RNA chain during synthesis of RNA and used as a source of energy during synthesis of proteins
DNP
"an uncoupler": facilitates proton transfer across the inner mitochondrial membrane
Thermogenin
"protein that allows movement of protons across mitochondrial membranes": rather than having to generate ATP heat is still released
brown adipose tissue
"masses of specialized fat cells": packed with pigmented mitochondria that produce heat instead of ATP
DNP mechanism
"dissipation of a proton gradient": with a loss of proton as DNP is expelled
UCP-1
"protein produced by brown adipose tissue": forms dissipation channel of H+ down its gradient in mitochondria; generating heat (bypasses ATPase and ATP production)
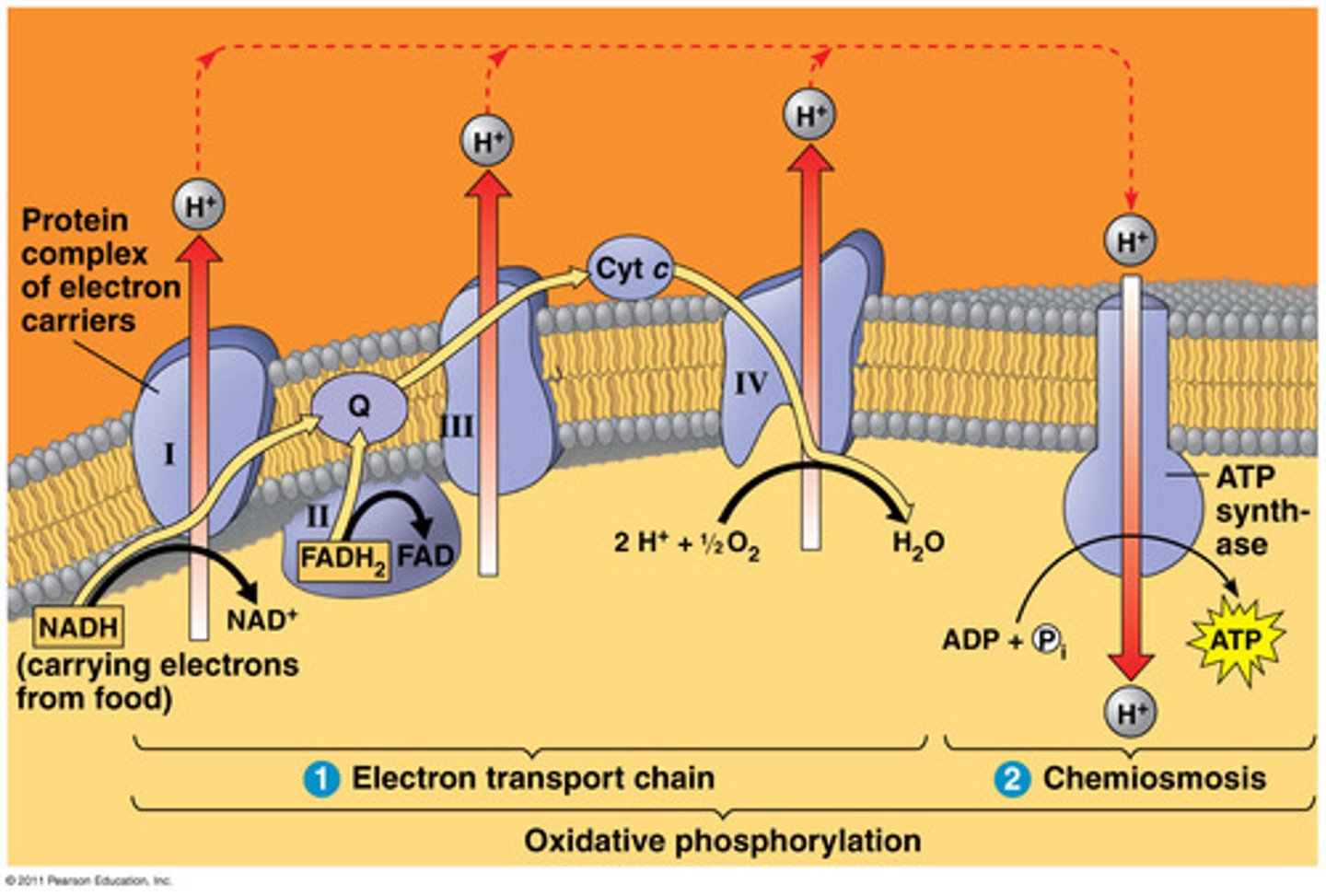
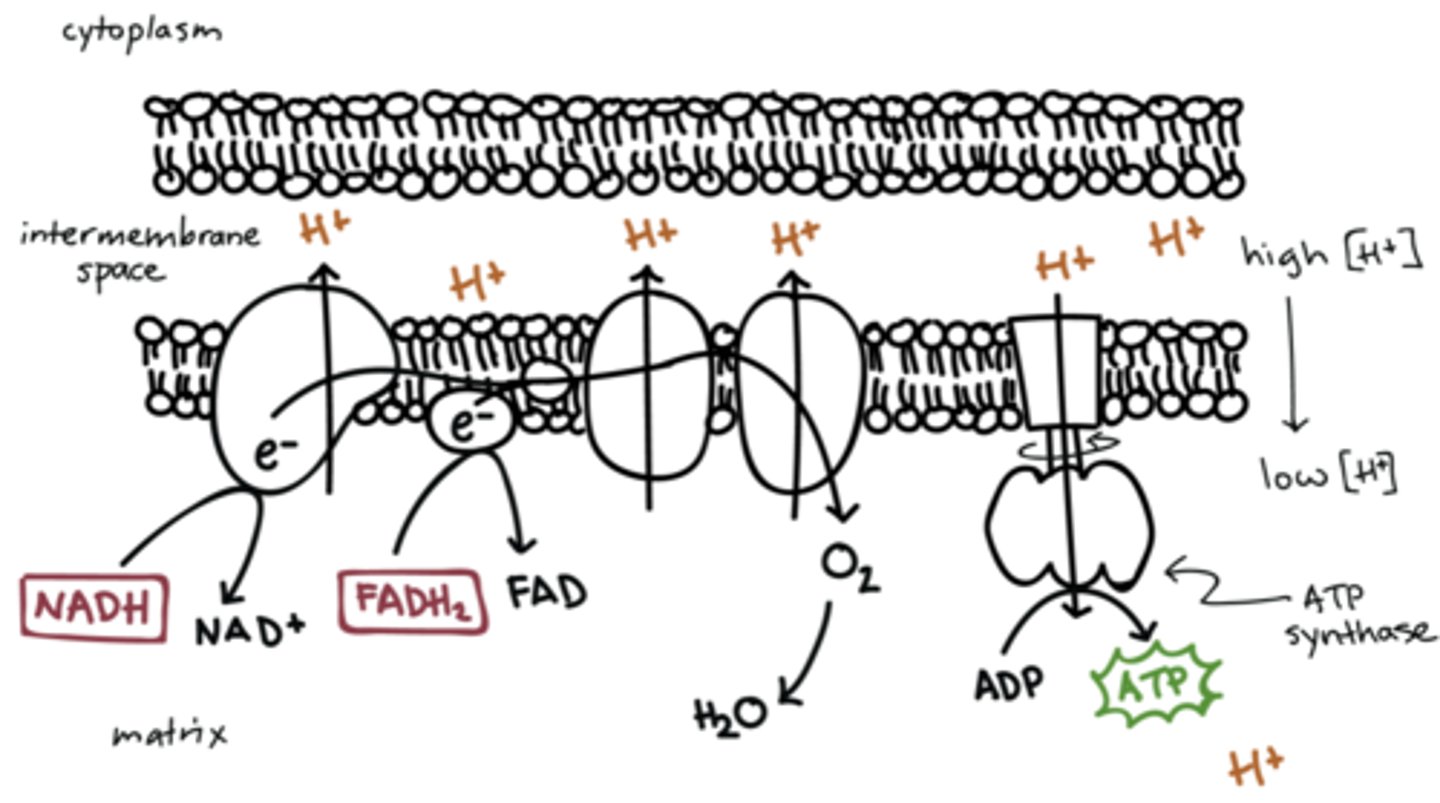
electron transport train (ETC)
"series of proteins": high-energy electrons from the Krebs cycle are used to convert ADP into ATP; 4 complexes in inner mitochondrial membrane
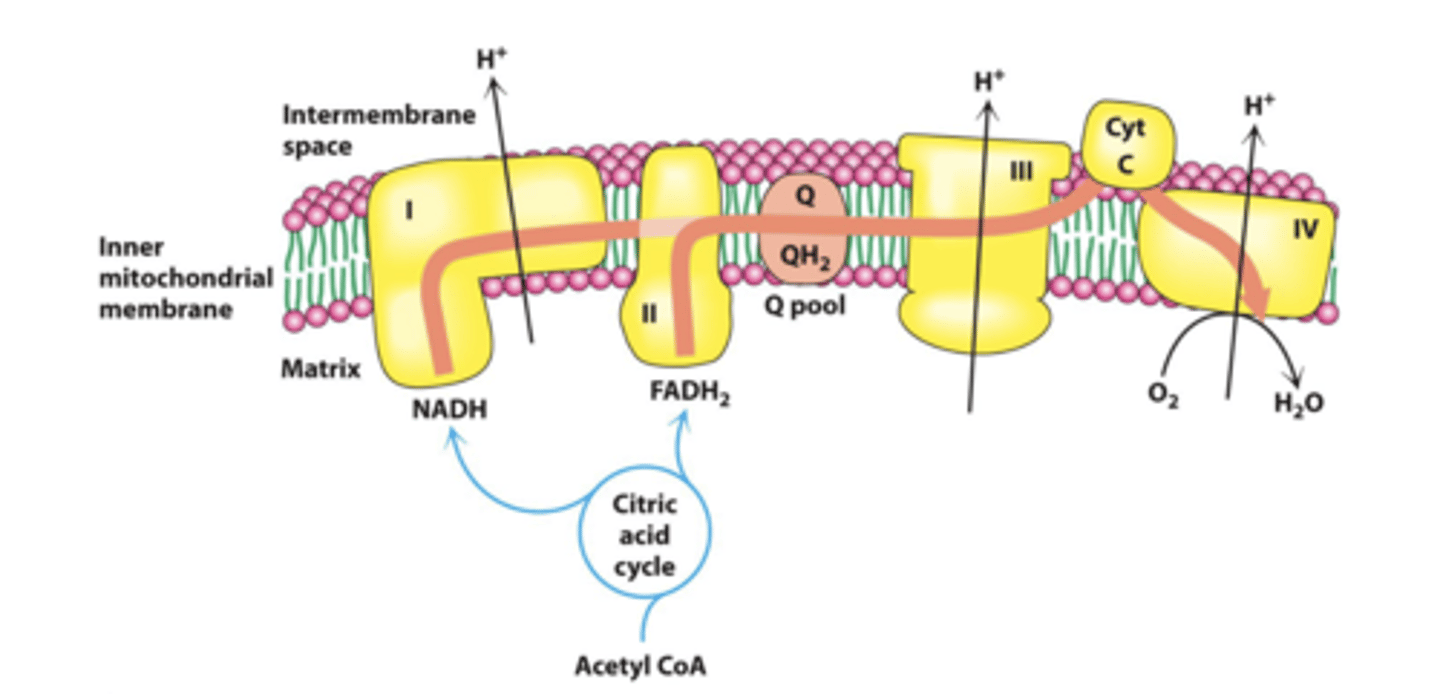
ETC protein arrangement
Proteins are arranged so that:
H + expelling reactions are on the outside
H + consuming reactions are on the matrix side
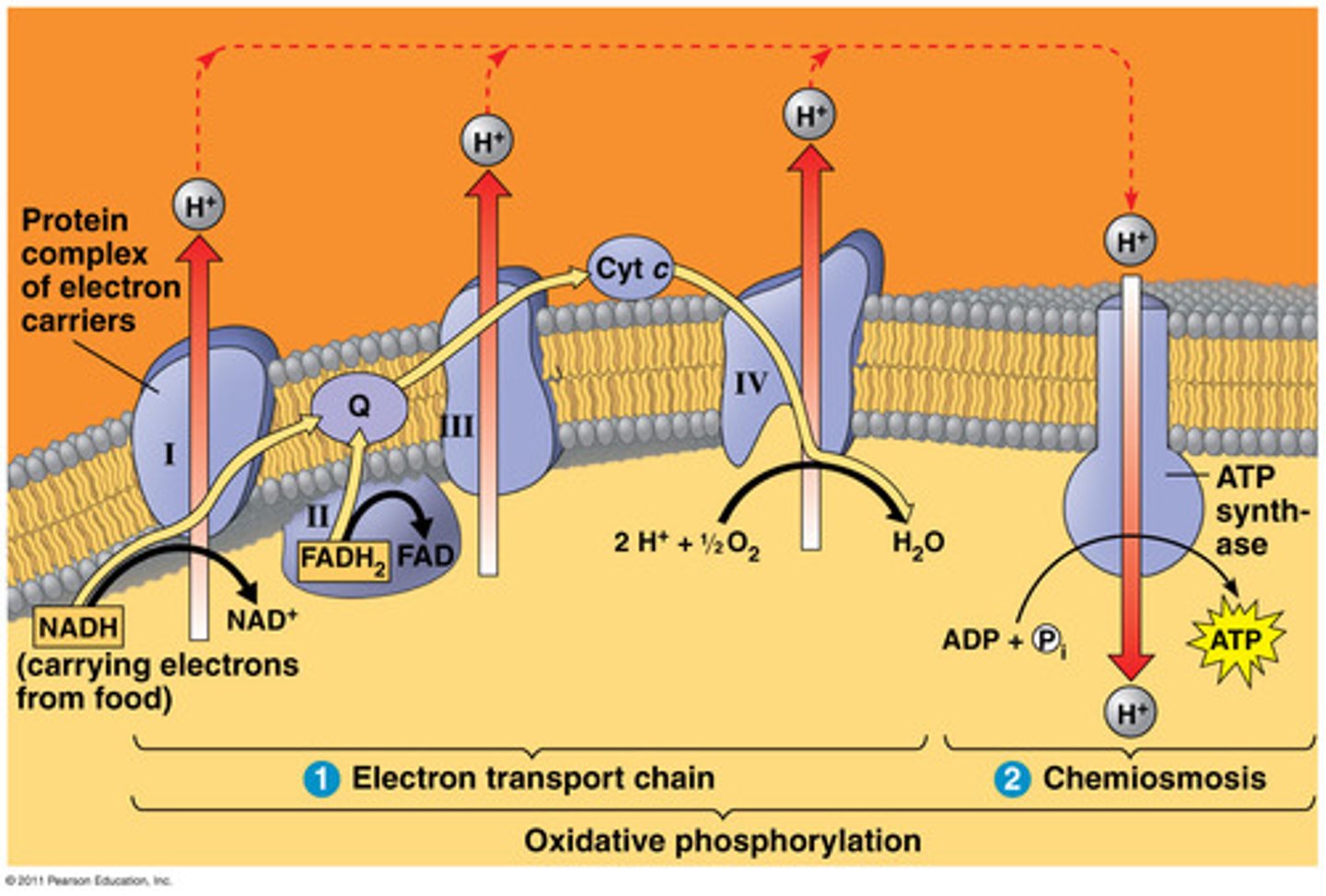
FAD
"proton acceptor & donator": present inside complex 2
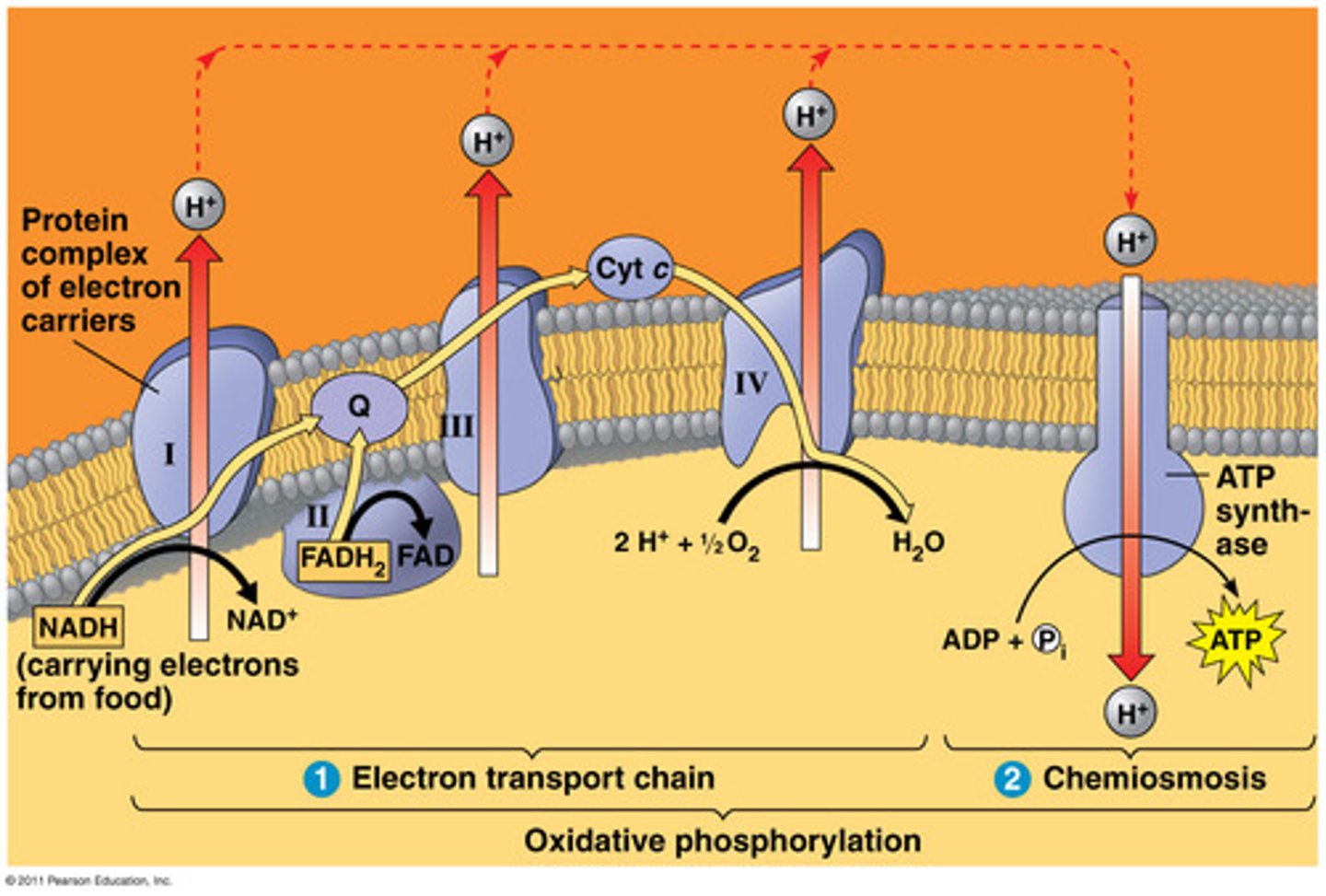
UQ
"soluble electron transporter in the electron transport chain": connects the first/second complex to the third
cytochrome C
"ETC enzyme": transfers electrons from complex III to complex IV
proton pumping
"energy released from high-energy electrons": move protons into inter-membrane space against the concentration gradient in ETC
complex 1
"NADH dehydrogenase": oxidises NADH to NAD+; pumps 4 protons
complex 2
"succinate dehydrogenase": oxidizes FADH2 to FAD+; pumps 0 protons
complex 3
"Q-cytochrome c oxidoreductase": passes electrons from CoQ to Cytochrome C; pumps 4 protons
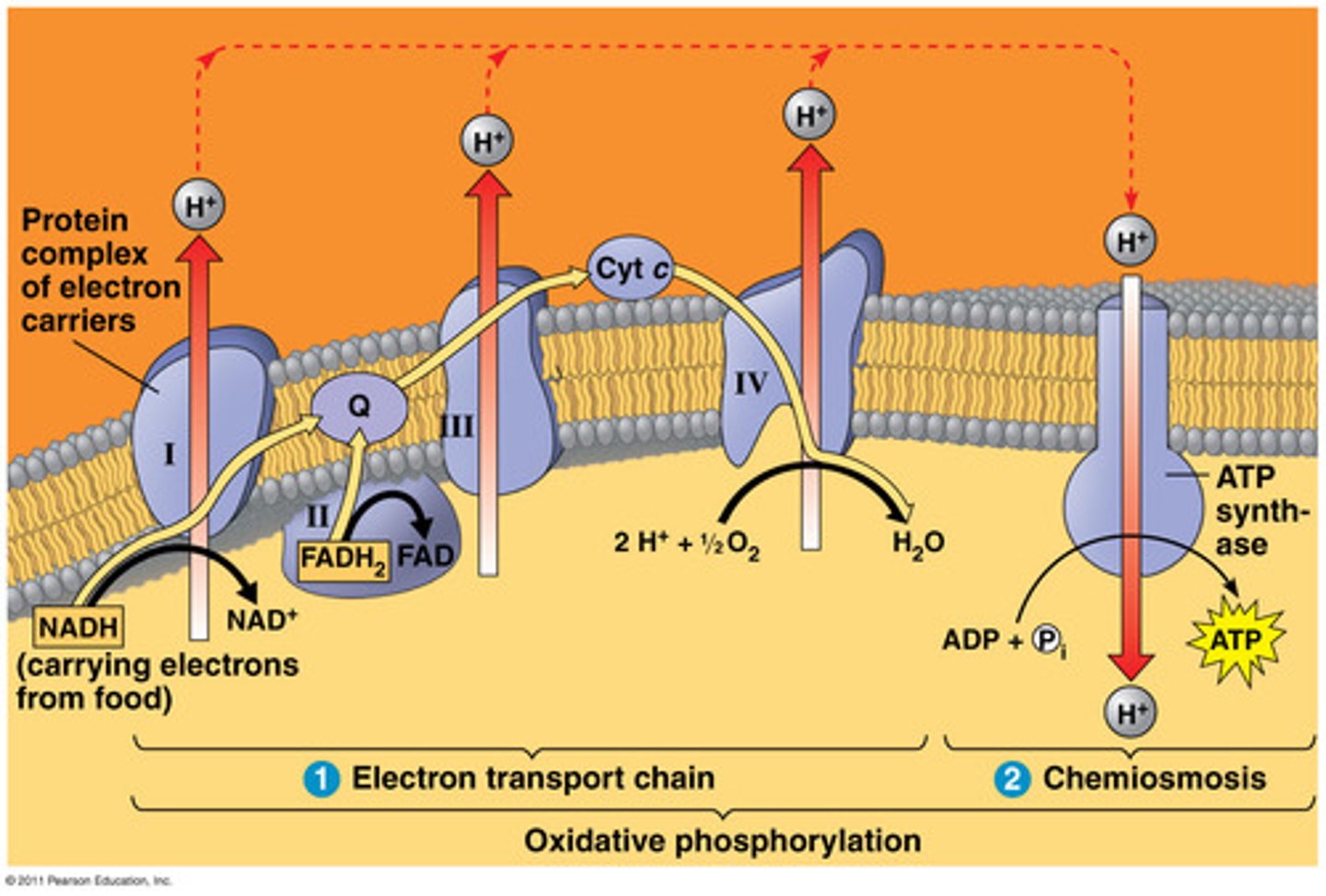
complex 4
"cytochrome c oxidase": 4 electron reduction of O2 to water; pumps 4 protons
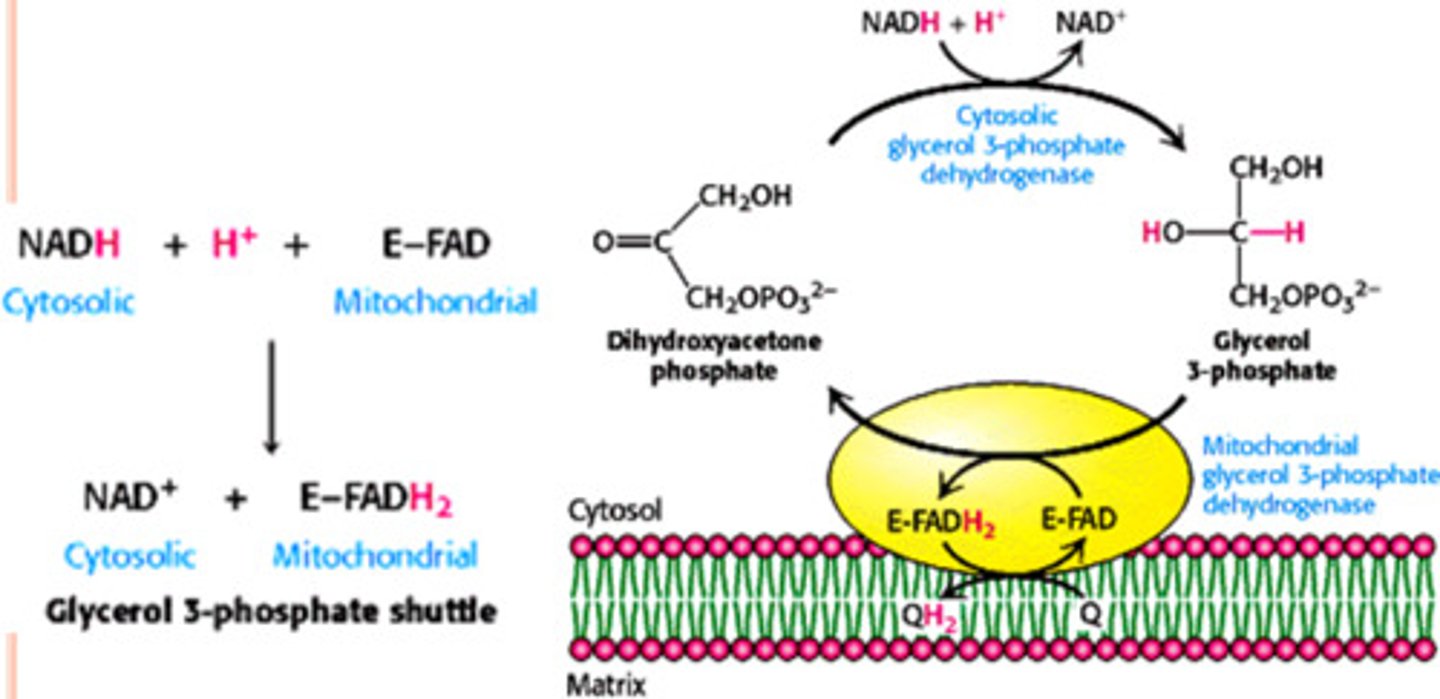
Glycerol 3-Phosphate Shuttle
"forming glycerol 3-phosphate":
electrons are transferred from NADH to dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP);
electrons are then transferred to mitochondrial FAD, forming FADH2
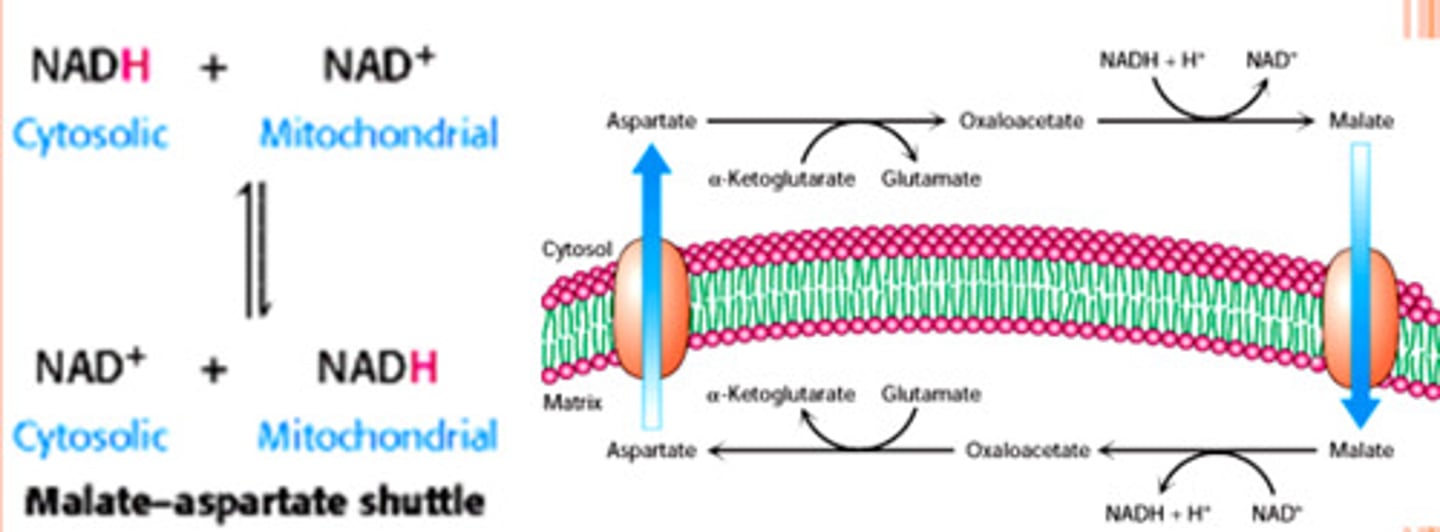
Malate Aspartate Shuttle
"electrons are transferred from NADH to oxaloacetate, forming malate":
malate crosses inner mitochondrial membrane;
transfer electrons to the mitochondrial NAD+, forming NADH
Q cycle
"part of Complex III's function": shuttling electrons between ubiquinol and ubiquinone in the inner mitochondrial membrane
ATP synthase
"large protein that produces ATP": uses energy from H+ ions to bind ADP and a phosphate group together
Glycogenolysis
phosphorylase breaks down glycogen to glucose
G6P
"carbohydrate metabolism": bypasses hexokinase in glucogenesis
Glucose-fatty acid cycle
"relationship between blood glucose and free fatty acids":
When blood glucose levels are high, free-fatty-acid levels are low.
In the fasting state, when blood glucose levels decline, free-fatty-acid levels increase
cori cycle
cycle of lactate to glucose between the muscle and liver
proteolysis
"breakdown of proteins or peptides into amino acids": action of enzymes --> amino acids used for gluconeogenesis
urea cycle
"preserve nitrogen in the system": takes nitrogen across the rumen wall back to the salivary glands
lipolysis
"release fatty acids": breakdown of fat & lipids by hydrolysis
beta oxidation in liver
"acetyl CoA removed as normal":
Acetyl CoA used in ketogenesis to make ketone bodies
FADH2 and NADH still being made but Acetyl CoA doesnt enter the Krebs cycle
acetoacetate
"1 of 2 Ketone Bodies - fuel to supply energy for cellular activity":
produced in liver from fatty acids during starvation, diabetic ketoacidosis, alcoholism.
glucagon
"raises blood glucose levels": protein hormone secreted by pancreatic endocrine cells; antagonistic hormone to insulin
adenylate kinase
"quick ATP supply": 2 ADP <--> ATP + AMP
ATP:ADP ratio
10 ATP : 1 ATP
rate limiting steps
"slowest step in a pathway": regulates how quickly the pathway can run
flux changing
1. Change gate's intrinsic activity
2. Make more gates open
3. Make/Destroy gates according to need
PFK
"phosphofructokinase": allosteric rate limiting enzyme in glycolysis;
hexokinase
"catalyzes phosphorylation of glucose to glucose-6-phosphate": in the first step of glycolysis; traps glucose & allows it to go back out of cell
PDH
"pyruvate dehydrogenase": part of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex; converts pyruvate into acetyl CoA; inactivated by phosphorylation + activated by phosphatase
futile cycle
"two opposite pathways - simultaneous catabolism & anabolism": run at the same time and use up energy with no useful production, usually generates heat
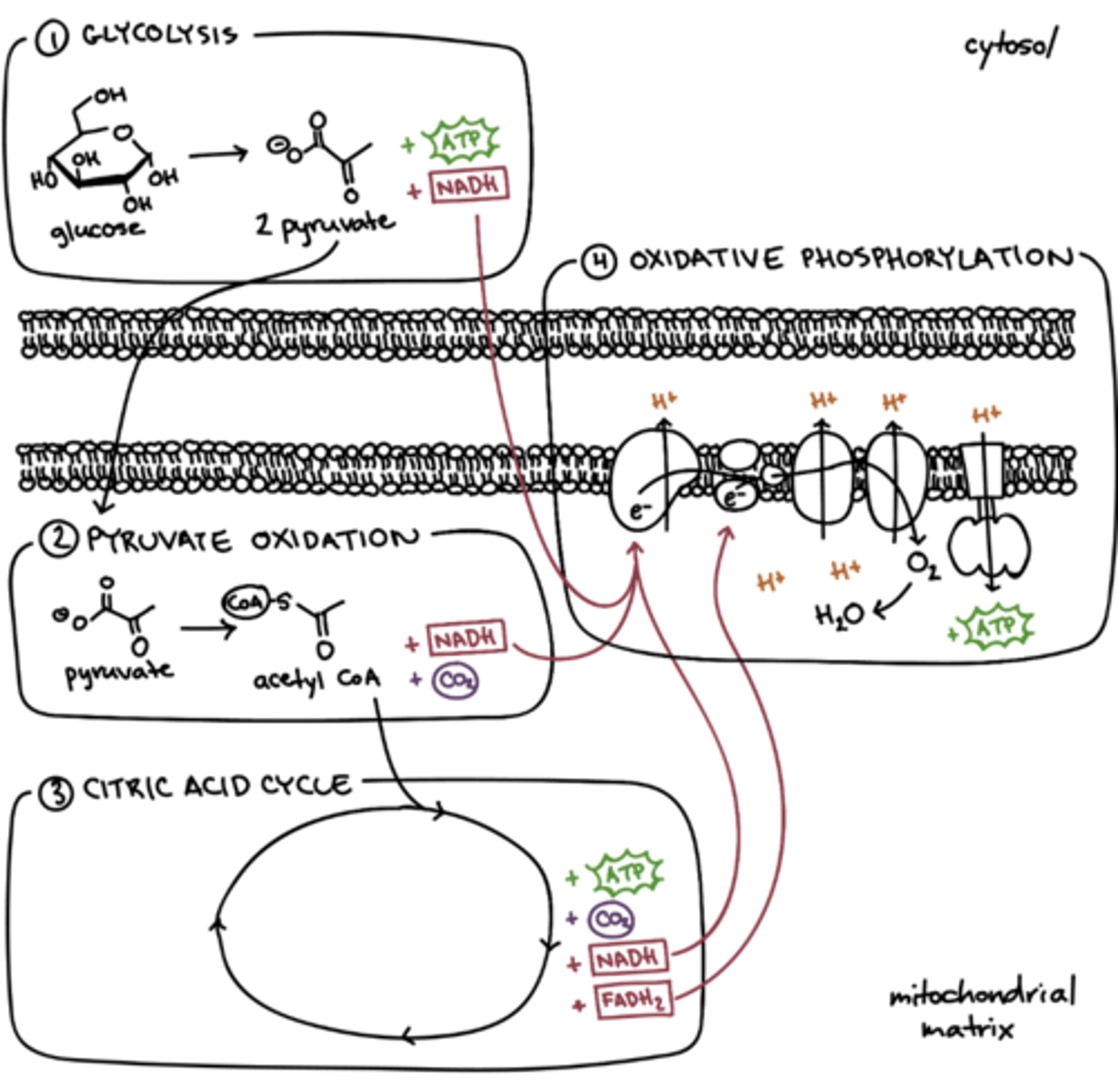
glycolysis
"1st stage of cellular respiration": breaks down glucose into 2 pyruvate, ATP & NADH
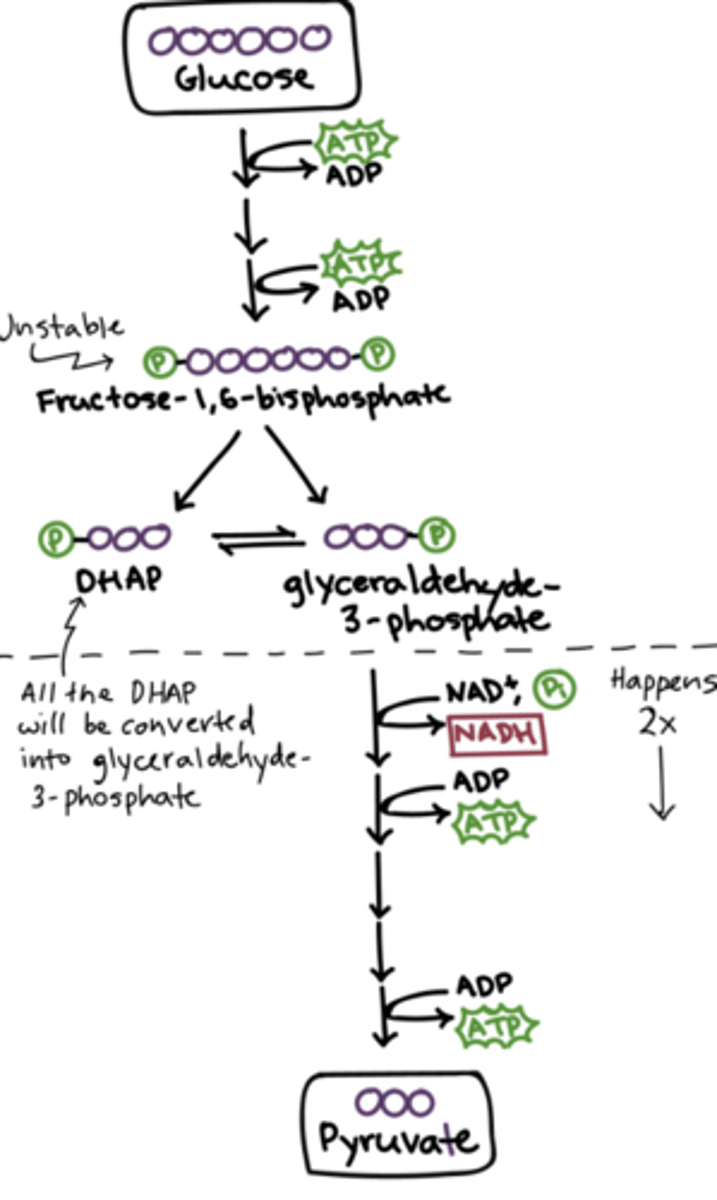
glucose
"toxic in excess":
necessary organic compound with a backbone of 6 carbon atoms
pyruvate
organic compound with a backbone of three carbon atoms
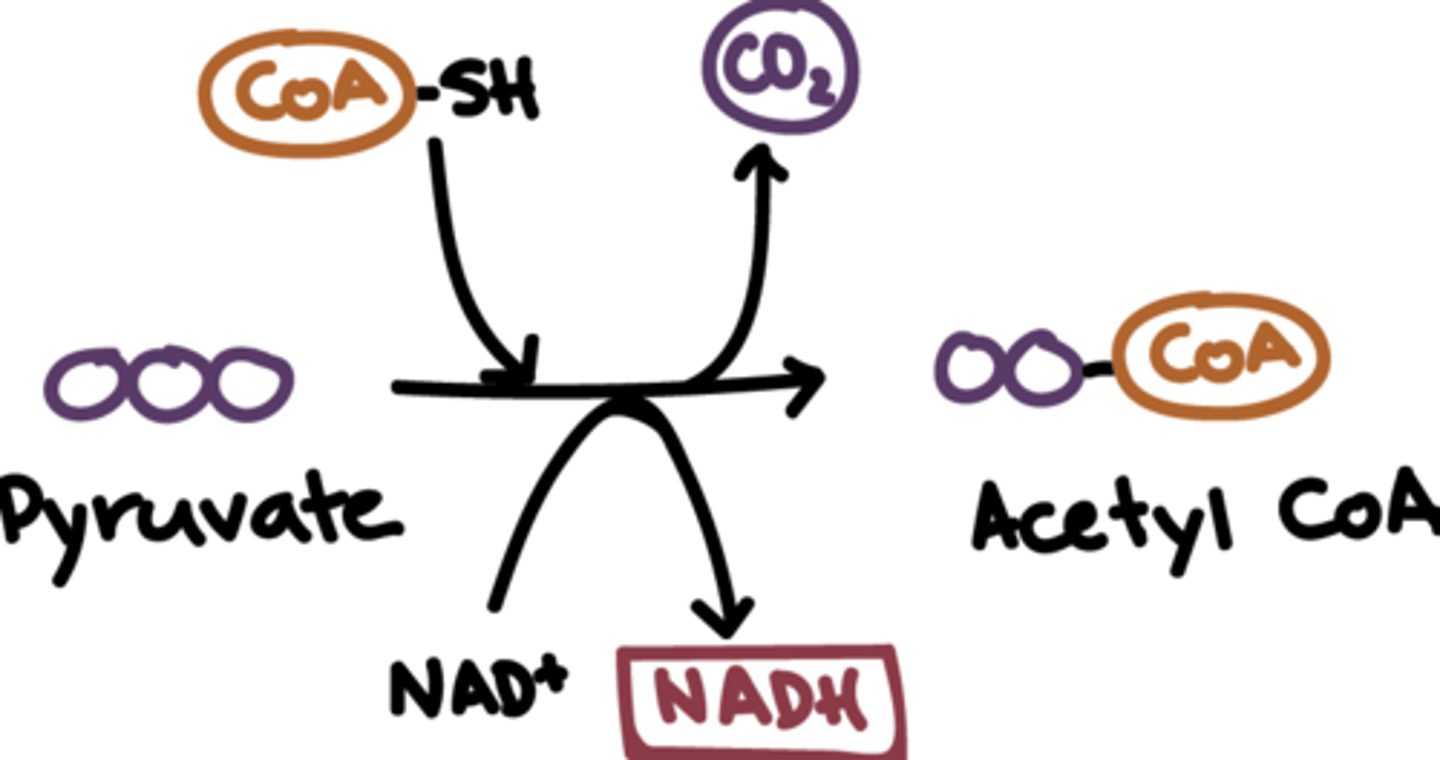
pyruvate oxidation
"2nd stage of cellular respiration": conversion of pyruvate to acetyl CoA and CO2 that occurs in the mitochondrial matrix in the presence of O2 (aerobic)
citric acid cycle
"3rd stage of cellular respiration": completes the breakdown of glucose to carbon dioxide by oxidizing a pyruvate derivative
oxidative phosphorylation
"4th stage of cellular respiration": production of ATP using energy derived from the redox reactions of the ETC
cellular respiration
"releases energy by breaking down glucose": in the presence of oxygen
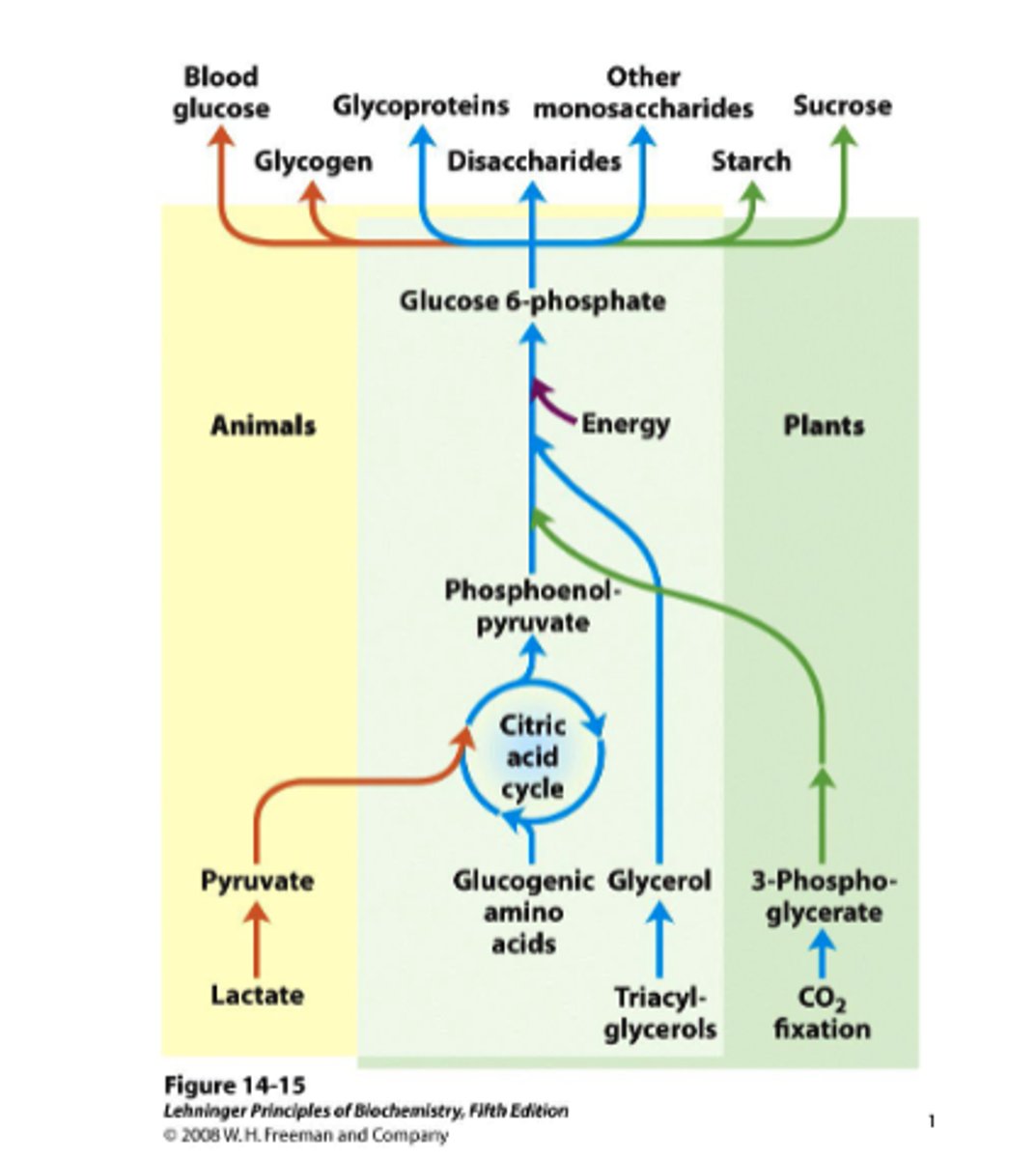
Gluconeogenesis
"glucose formation": during early stages of starvation from noncarbohydrate sources (glycerol)
F6P --> F16BP
PFK-2 --> F26BP
PKa catalysis phosphorylation of PFK-2
F6P
"fructose-6-phosphate": inhibits glucokinase
F16BP
"fructose-1,6-bisphosphate": activates pyruvate kinase
PFK-2
"Phosphofructokinase-2": generates F2,6-BP which activates PFK-1, allows glycolysis to continue in the presence of ATP.
F26BP
"Fructose-2,6-bisphosphate":
Inhibits gluconeogenesis
positively modulates PFK-1 and ups glycolysis
Anaplerosis
replenishing TCA cycle intermediates that have been extracted for biosynthesis
glycation
"binding a protein molecule to a glucose molecule": forms damaged, nonfunctioning structures
post-prandial glucose disposal
"quick disposal of glucose after a meal": via insulin secretion & liver absorption
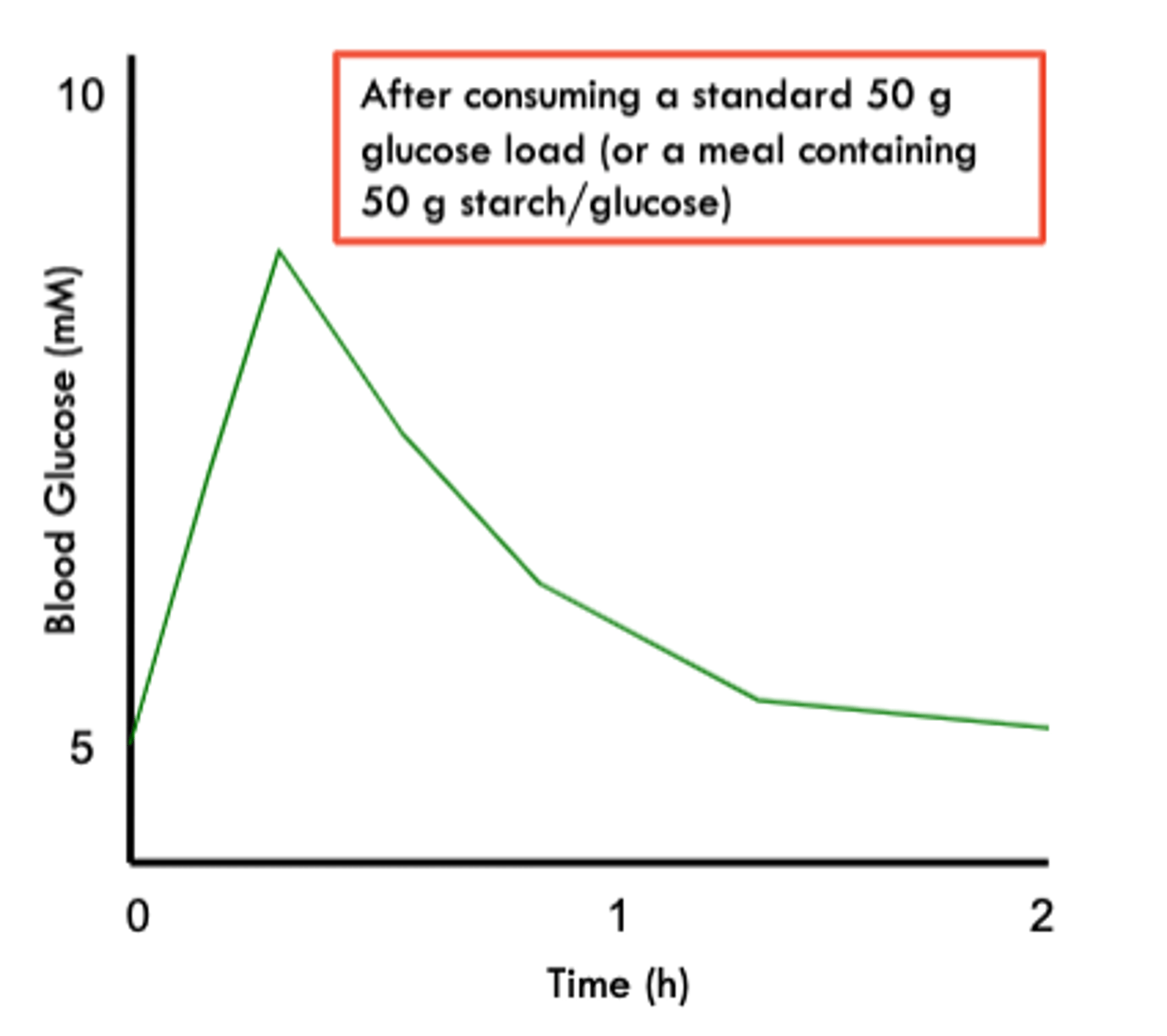
glucose homeostasis
"4-5nm": maintaining glucose levels in the body at a near-constant level
starch
"main carbohydrate source": glucose polymer
amylose starch
"alpha 1,4' glycosidic linkage": a chain of glucose molecules
amylopectin starch
1,6 linkage; branched; easy hydrolysis
glycemic index
classifying foods according to their potential for raising blood glucose
glucose disposal
"decrease blood glucose": via glycolysis/TCA
- glycogenesis (glycogen synthesis)
- hexose monophosphate shunt
OR
FA synthesis/urinary excretion (insulin-independent path)
glycogen synthase
rate limiting enzyme of glycogenesis
glucokinase
enzyme that adds a phosphate group to a molecule of glucose exclusively
glycogenesis
formation of glycogen from glucose
liver glycogenesis
"form of glycolysis - push mechanism":
excess bloodstream glucose enters liver cells regardless of G6P concentration;
phosphorylation upon entry into the cell;
more efficient than the muscle at lowering blood glucose;
2 ATP
muscle glycogenesis
"form of glycolysis":
more G6P present in the cell the slower the glucose entry and phosphorylation of glucose less active hexokinase;
2 ATP
lipogenesis
"synthesis of fatty acids from acetyl CoA": acetyl CoA from glucose, consuming ATP & 2 NADPH; insulin as main stimulant