Auditory System, Visual Processing, and Higher Cortical Functions
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards focused on the auditory system, visual processing, and higher cortical functions.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
What role do hair cells play in the auditory system?
Hair cells serve as mechanoreceptors in the auditory system, converting mechanical sound waves into electrical signals.
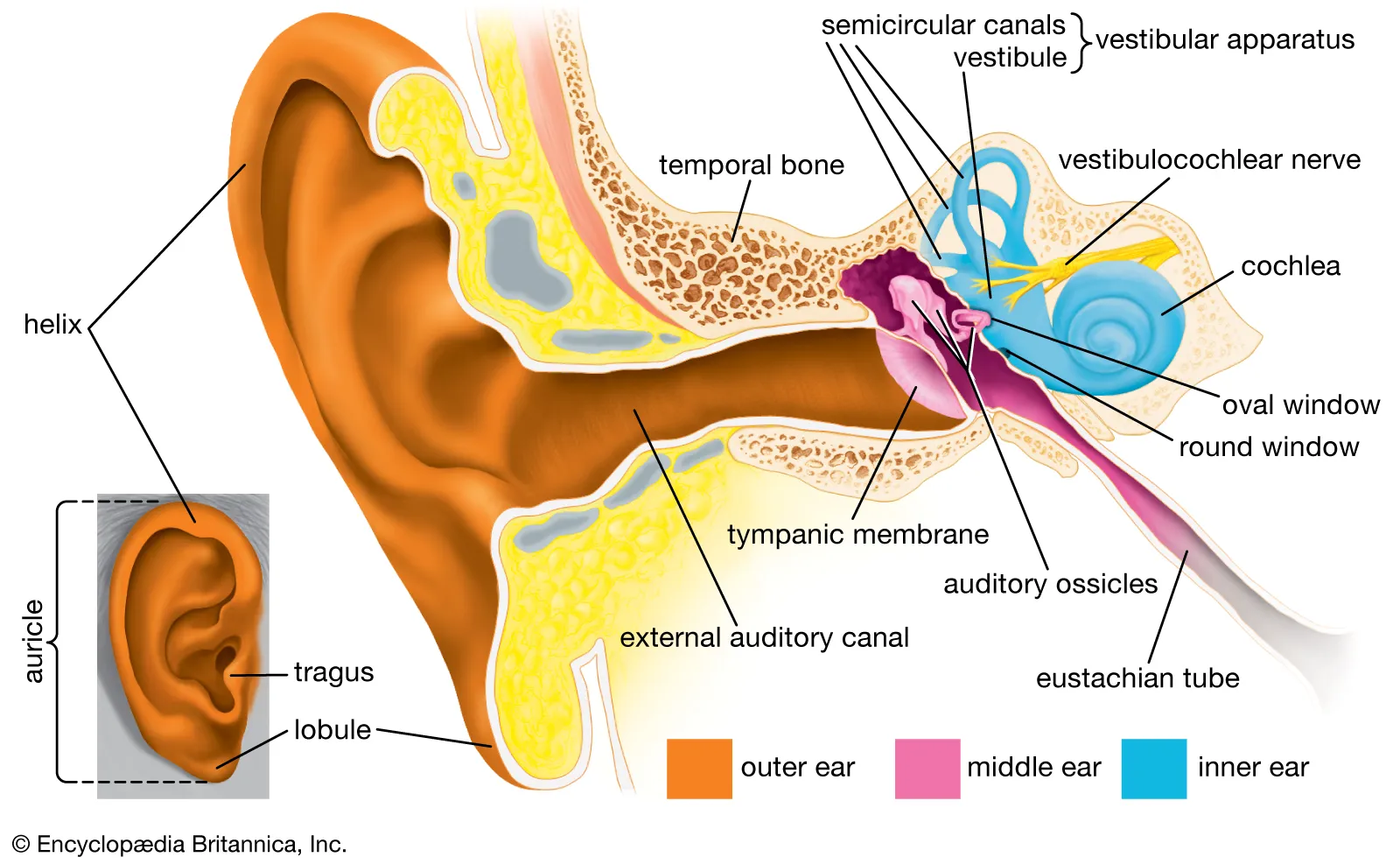
What structures are involved in sound transmission in the middle ear?
The ossicles (malleus, incus, stapes) transmit vibrations from the tympanic membrane to the oval window of the cochlea.
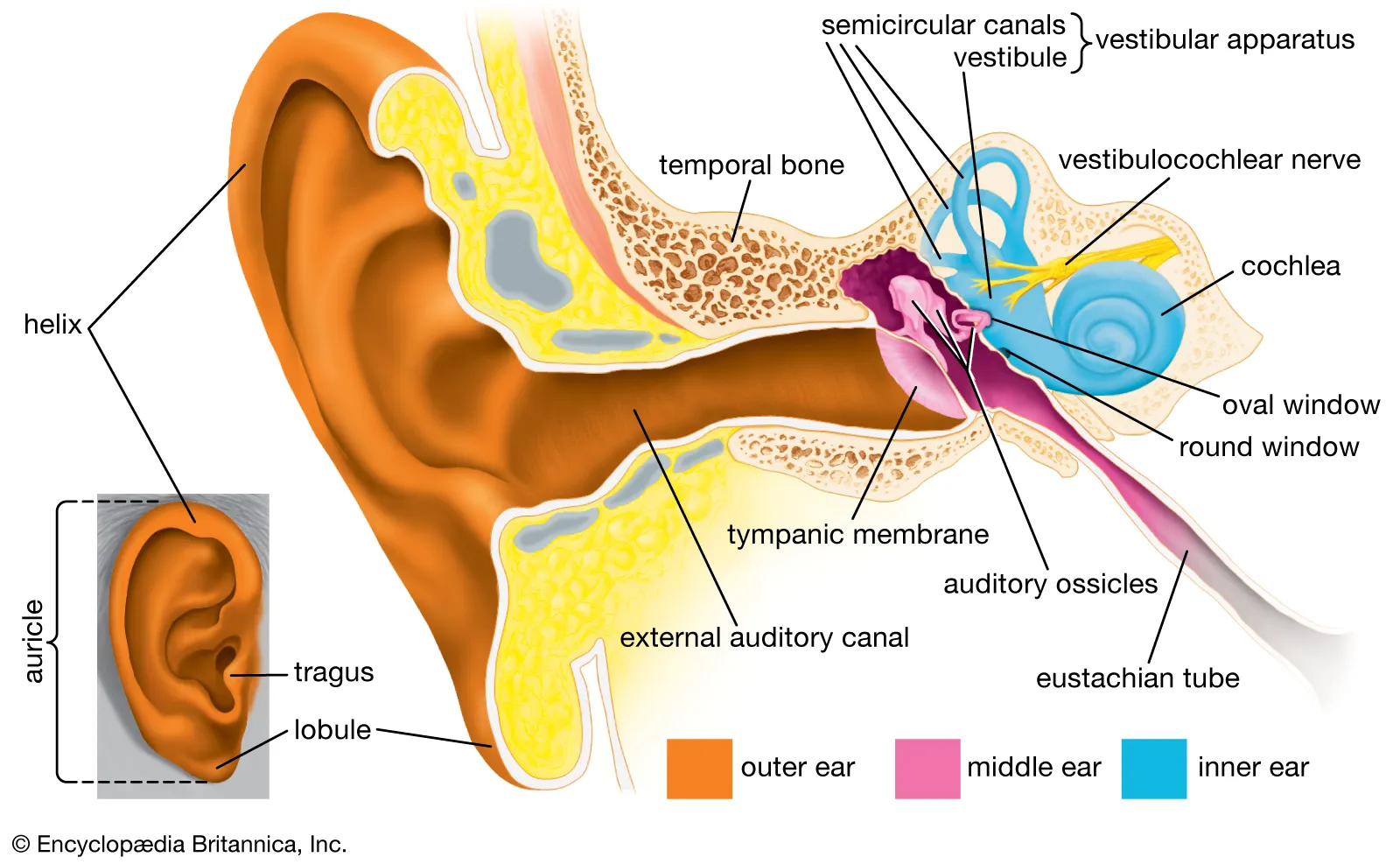
How does the cochlea exhibit tonotopic organization?
High-frequency sounds peak near the base, while low-frequency sounds peak near the apex of the cochlea.
What is the function of the Organ of Corti in the cochlea?
The Organ of Corti contains hair cells that transduce mechanical vibrations into electrical signals for sound perception.
What is the primary function of the auditory cortex?
The auditory cortex is responsible for processing auditory information and is organized tonotopically.
What happens at the neuromuscular junction?
Acetylcholine is released from motor neurons, binding to muscle fiber receptors, triggering muscle contraction.
How does the paraventricular nucleus (PVN) contribute to autonomic functions?
The PVN regulates autonomic functions by projecting to autonomic centers in the brainstem and spinal cord.
What is the significance of the fornix in the limbic system?
The fornix connects the hippocampus with various subcortical structures and is crucial for memory processing.
What distinguishes declarative memory from nondeclarative memory?
Declarative memory involves conscious recall of facts and events, while nondeclarative memory includes unconscious skills and habits.
What are the stages of cognitive development according to Piaget?
Sensorimotor, Preoperational, Concrete Operational, and Formal Operational.
What brain areas are associated with higher-order functions like problem-solving and decision-making?
The prefrontal cortex is primarily involved in planning, decision-making, and moderating social behavior.
How does the visual system process information from the retina to the brain?
Light is detected by photoreceptors, transmitted to bipolar cells, then to ganglion cells, forming the optic nerve.
What is the role of Broca's area in language processing?
Broca's area is responsible for speech production and articulating thoughts into spoken language.
What is agnosia, and what are its types?
Agnosia is the inability to recognize sensory stimuli; types include prosopagnosia, associative agnosia, and apperceptive agnosia.
How do the dorsal and ventral streams differ in visual processing?
The dorsal stream ('where' pathway) is involved in spatial awareness, while the ventral stream ('what' pathway) focuses on object recognition and form.
What is the primary function of the amygdala in the limbic system?
The amygdala integrates emotional responses and is key for emotional learning and behavior.