BIO 111 - Unit 5: Module 1 (Ecology)
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
What is Ecology?
The study of how organisms interact with each other and their environment
What is organismal ecology?
- The study of individual morphological, physiological, and behavioral adaptations
- How individuals interact with each other and their physical environment
Functions of animal communication
Signal from one individual modifies the behavior of a recipient individual
- Sender: Individual making the signal
- Receiver: Individual responding to signal
ex: ground squirels tail flagging/snakes heat detection
What is Population ecology?
Study of the number and distribution of individuals in a population over time
What is a population?
A group of interbreeding (or potentially interbreeding) individuals of same species in same area (at same time)
What are life history trade-offs?
- Limited resources (and time) lead to fitness trade-offs in resource allocation to growth, reproduction, survival
- universal, but the best strategy is different for different species
R-selected species
- Grow quickly
- small adults
- short lifespan
- Reproduce early in life
- Produce many offspring, low investment in each
- Few of which survive to adulthood
ex: mice
K-selected species
- Grow slowly
- large adults
- long lifespan
- Reproduce when older
- Produce few, expensive offspring (and often care for them to ensure survival)
ex: humans, elephants
What is Community ecology?
Study of the nature of the interactions between different species in a community
− Species interactions
− Community Structure
− Community Dynamics
What is a community?
All the populations of different species that are interacting in a certain area
What defines species interaction?
Defined by whether the species in the interaction incurs a fitness cost (-) or gains a fitness benefit (+) or is unaffected (0)
What do species interactions do?
- Affects distribution/abundance of a species
- Coevolution can occur during interactions
- Outcome of interactions is dynamic and conditional
Consumption (+/-) / types of consumption
One organism eats part or all of another
Types:
1. Predation: A predator kills and eats an animal
2. Herbivory: An herbivore eats a plant
3. Parasitism: A small organism eats small amount of host tissue
Defenses against consumption (Mimicry)
- Evolution favors sending signals to predators to avoid getting eaten (Aposematic coloration)
- Predators are more likely to recognize a signal if it is common
- Batesian mimics: look dangerous, are not dangerous
- Müllerian mimics: look dangerous, are dangerous
Predator adaptations
- Weapons
- Deception
- Hunting in groups
- Eavesdropping
What is the coevolution arms race?
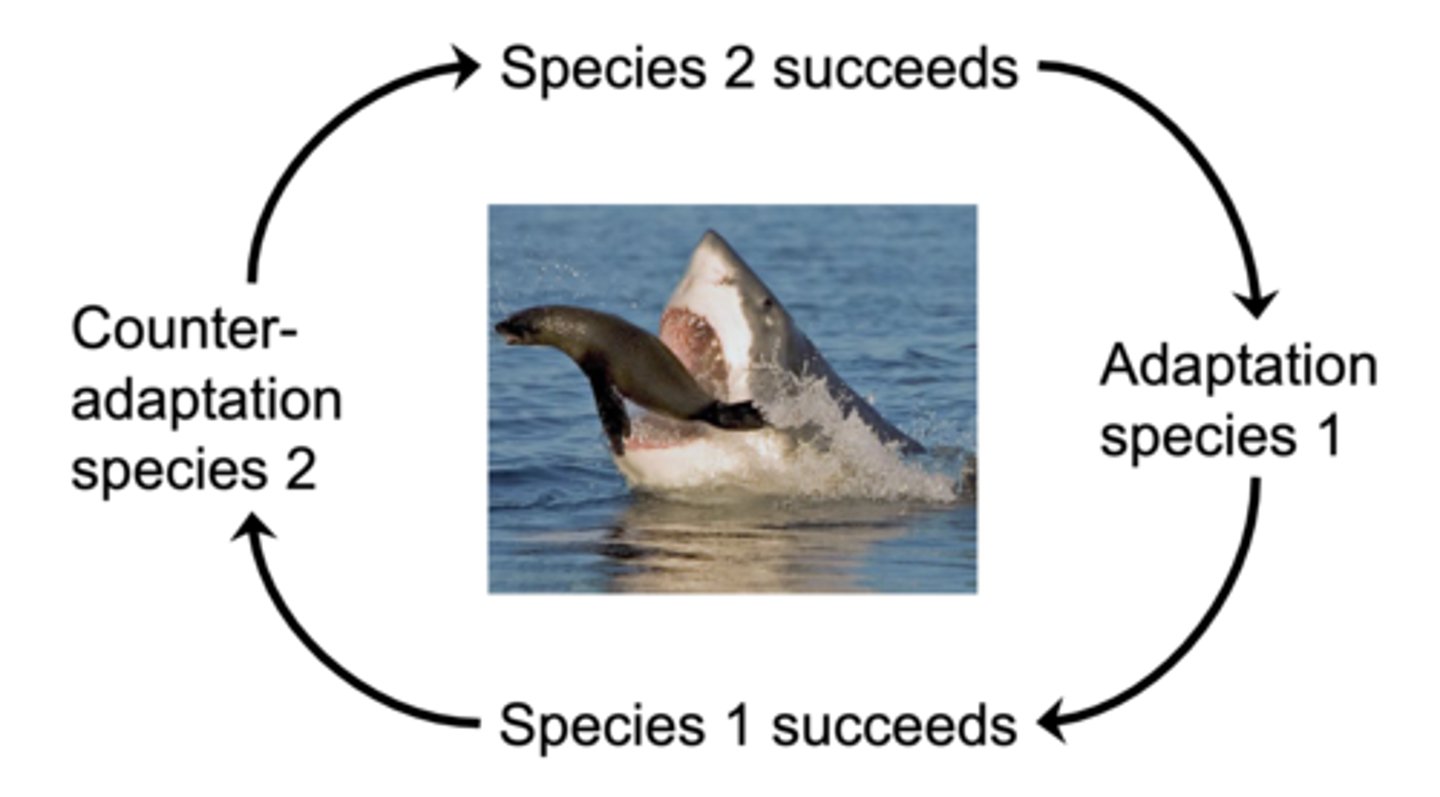
What is Ecosystem ecology?
Study of nutrient and energy movement among organisms and
surrounding atmosphere/soil/water
What is an ecosystem?
- Community of interacting species present in a region, along with the abiotic components of the soil, water, and atmosphere
- Everything is linked to everything else by flow of energy and nutrients
Trophic structure
- Trophic Level: Organisms all obtaining energy from the same type of source
- Food chains become food webs to account for complexity