AQA A Level Biology Paper 1
1/207
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
208 Terms
Water removed from the reactants joining two molecules together forming a chemical bond
Condensation
The addition of water to the reactants to break a chemical bond between 2 molecules
Hydrolysis
1. Add Benedict's reagent. 2. Heat the solution in a water bath for 5 minutes at 95 degrees Celsius. 3. Change from blue to brick red as CuO formed
Test for Reducing Sugars (3)
Smaller units from which larger molecules are made
Monomer
1. Add 2cm³ of food sample then add 2cm³ of dilute HCl and heat.
2. Add 2cm³ of hydrogen carbonate then do test for reducing sugars.
add benedicts test and heat= if red none reducing starch is present
Non-Reducing Sugars (2)
Add drops of iodine to starch solution. Colour change to blue-black
Test for Starch (1)
1. Mix Test solution with ethanol.
2. Shake for 1 minute then add water.
3. Cloudy white emulsion
Test for Lipids (3)
1. Obtain equal volumes of test solution and NaOH then add a few drops of biuret solution (dilute copper (II) sulphate solution).
2. Colour change to mauve/purple
Test for Proteins (2)
1. Very high resolution.
2. Needs thin and dead specimen.
3. Artefacts can occur (remnant left on object during prep, such as air bubbles)
4. Uses magnets to focus on specimen
5. Uses electrons fired at sample.
6. Is not in colour
Transmission Electron Microscope (5)
1. Inhibitor is similar in shape to substrate so it impermanently binds to the active site.
2. Prevents ESC from forming, slowing rate
Competitive inhibition (2)
1. Molecule will bind to allosteric site.
2. Binding causes a change in active site.
3. Permanently preventing further ESC.
Non-competitive inhibition (3)
1. DNA helicase breaks the hydrogen bonds between the base pairs
2. 2 single strands formed as the double helix "unzips".
3. Free DNA nucleotides in the nucleoplasm bond to the complementary bases on the strand.
4. DNA polymerase forms phosphodiester bonds between adjacent DNA nucleotides via condensation reaction with the hydrolysis of ATP, forming the phosphate backbone
DNA Replication: Semiconservative (4)
1. ATP stores or releases only a small amount of energy at a time, so no energy is wasted as heat.
2. Small and soluble so easily transported
3. Easily broken down, so energy is released instantaneously
4. Can be quickly re-made
5. Can make other molecules more reactive via phosphorylation
6. ATP can't pass out of cell, so the cell always has an immediate supply of energy.
Describe 6 properties of ATP that make it a good energy source. (6)
Prevents the cell from drying out. Allows bacteria to stick to each other
Slime capsule (2)
Used for attachment of a cell to a surface
Fimbria
Involved in bacterial conjugation
Pilli
Invagination of cell membrane. Site of cell respiration (prokaryotes)
Mesosome
The ability to distinguish two points apart
Resolution
1. Lower resolution than TEM
2. 3D image
3. Does not require thin samples
Scanning Electron Microscope
The mass of organelles at the bottom of the test tube after centrifugation.
Pellet
Cold. Low temperature slows enzyme activity, minimising self digestion by reducing metabolic rate. Isotonic. Salt and sugar concentration kept the same, minimising organelle size change due to osmosis. Buffered. Minimum changes in pH, so prevents enzymes in organelles denaturing.
Solution Required for cell fractionation (6 Marks)
1. Homogenisation. Breaking up cells by blending the sample to create a homogenate.
2. Filtering. Filtering the large, unwanted sil, producing the filtrate.
3. Ultracentrifugation. Spin in a centrifuge so components separate out by weight. Heavier near the bottom of the tube.
4. Supernatant is removed and spun again at higher speed.
Separation of Organelles From The Cells (4)
The solution not including the pellet at the bottom of the test tube after centrifugation.
Supernatant
1. Cell wall forms, dividing the two genetically identical daughter cells.
2. Same circular DNA.
Binary Fission 3
Nuclei, Chloroplasts, Mitochondria, Lysosomes, Endoplasmic Reticulum, Ribosomes
Order of Organelles
(Pass me a taco chief)
Mitosis acronym
Cell grows and carrys out its normal function
Interphase
Cells grow to normal size. Organelles replicate and genes are expressed to make proteins needed.
Interphase G1
DNA and histones replicated.
Interphase S
Spindle fibres are made
Interphase G2
1. DNA winds up making chromosones from chromatin.
2. Centrioles appear at opposite poles of the cell. 3. Nucleolus disappears
Prophase (3)
1. Nuclear envelope disappears.
2. Chromosomes align along the equator of the cell.
3. Spindle fibres connect centrioles to chromosomes
Metaphase (3)
1. Spindle fibres contract pulling daughter chromosomes to opposite poles of the cell.
Anaphase (1)
1. Spindle fibres disperse.
2. Nuclear envelope forms.
3. Chromatids uncoil to chromatin
Telophase (3)
1. Cytoplasm constricts separating the cells into two.
2. Membrane forms creating two new genetically identical daughter cells.
Cytokinesis (2)
number of cells in mitosis/total number of cells
Mitotic index
1. Circular DNA replicates and both copies attach to the cell membrane.
2. Plasmids also replicate.
Binary fission 1 (2)
Cell membrane grows between the two DNA molecules and pinches them inwards dividing the cell into 2.
Binary Fission 2 (1)
1. Attach to host cell via attachment protein and inject nucleic acid into the cell.
2. This gives the instructions to construct the virus
Virus Replication 1 (2)
1. The virus is then assembled and leaves the cell, taking the phospholipid bilayer with it.
2. This creates holes in the cell and kills it.
Virus Replication 2 (2)
Fluid: All the components can move around. Mosaic: Many different components all fit together
Fluid mosaic Structure [Fluid][Mosaic] (2)
The passive transport of large molecules such as amino acids and sugars, but they require integral proteins to pass through.
Facilitated Diffusion
The passive movement of particles from a high concentration to a region of low concentration, down a concentration gradient.
Diffusion
1. Add antibody that is specific to antigen. After leaving them to bind, wash the surface to remove unattached antibodies.
2. Add a second antibody with an enzyme attached.
3. Second antibody binds with first antibody
4. Add colourless substrate of enzyme, which the enzyme will act upon to give a coloured product.
5. The intensity of the colour is relative to the amount of antigen present.
ELISA Test (Enzyme linked Immunosorbent Assay) (5)
Small, non-polar molecules (excluding water) freely diffuses in and out of cells through gaps between phospholipids.
Simple Lipid Diffusion
The passive movement of water molecules across a partially permeable membrane from a high water potential to a low water potential, down a concentration gradient. (Distilled water = 0Ψ)
Osmosis
Equal concentration solution to the cell
Isotonic
Solution of higher concentration to cell.
Hypertonic
Solution of a lower concentration to cell.
Hypotonic
The movement of substances across a cell membrane through a carrier protein against a concentration gradient, from a low to high concentration with the expenditure of ATP.
Active transport
1. The simultaneous transport of two different substances through one carrier protein.
2. One substance (usually an ion) moves down its concentration (passive) whilst the other substance is transported against its concentration gradient (active transport)
Co-transport (2)
A molecule, usually a glycoprotein or protein that stimulates an immune response.
Antigen
A protein molecule that can bind specifically to an antigen
Antibody
1. Ingestion (phagocytosis).
2. Antigen Presentation.
3. Clonal Expansion.
4. Differentiation (T-cells and cell mediated immunity).
5. Differentiation (B-cells and antibody mediated immunity)
Stages of response to a non-self antigen found in body fluid
Vaccination of a significant portion of a population providing a measure of protection for the individuals who have not developed immunity/have not been vaccinated.
Herd immunity
Antibodies produced from cloned plasma B lymphocytes
Monoclonal Antibodies
1. Hydrogen bonds between DNA base pairs are broken
2. One DNA strand acts as a template
3. Free RNA nucleotides align by complementary base pairing (uracil is used instead of thymine)
4. RNA polymerase forms phosphodiester bonds between adjacent RNA nucleotides joining them together.
5. Pre-mRNA is spliced, removing introns then joining the exons.
6. mRNA moves out of nucleus via nuclear pore
Polypeptide synthesis (In nucleus) (6) [Transcription]
Adaptation. How it works. Example. Repeat twice for 6 marks
6 marker layout for Xerophytic plants
1. mRNA attaches to ribosome
2. tRNA molecule with complementary anticodon and desired amino acid moves to the ribosome and binds to the codon.
3. Amino acids join by peptide bonds with the use of ATP
4. tRNA released after amino acid joined to polypeptide
5. The ribosome moves along the mRNA to form the polypeptide
Polypeptide synthesis (In ribosomes) (5) [Translation]
1. Substrate binds to active site
2. ESC forms
3. Active site changes shape slightly distorting hydrogen bonds in the substrate.
4. Reduces activation energy
Describe the Induced fit model of enzyme action and how an enzyme acts as a catalyst. (3 marks)
A change in the nucleotide base sequence.
Mutations (Normal = BEAST)
Substitution in a codon turns it into a stop codon
Substitution (Nonsense)
Causing a different amino acid to be coded for
Missense (FEAST)
Results in a codon coding for the same amino acid creating degenerate code.
Silent
Nucleotide is gained from a DNA strand, creating a right frameshift.
Addition (BREAST)
A nucleotide is lost so frameshift to the left.
Deletion (BEST)
When one or more bases are repeated so shift to the right.
Duplication (BEEAST)
A group of bases become separated from the DNA, then join back but inverted.
Inversion (BEATS)
Breaks the end peptide bond
Exopeptidase
Breaks the middle peptide bonds
Endopeptidase
Tidal volume x Ventilation rate
pulmonary ventilation =
1. Proteins remain in the plasma
2. This reduces the water potential
3. Water moves to blood by osmosis
4. Returns to blood via lymphatic system
Tissue Fluid is formed from blood at the arteriolar end of a capillary bed. Explain how water from tissue fluid is returned to the circulatory system. (4)
1. Co-transport
2. Hydrolysis of ATP
3. Na+ and H+ bind to carrier protein
4. Protein changes shape and moves Na+ and H+ across membrane.
Sodium ions from salt (sodium chloride) are absorbed by cells lining the gut. Some of these cells have membranes with a carrier protein called NHE3. NHE3 actively transports one sodium ion into the cell in exchange for one proton (hydrogen ion) out of the cell. Use your knowledge of transport across cell membranes to suggest how NHE3 does this. (4)
1. High salt results in low water potential in tissue fluid
2. Less reabsorbed back into capillaries at venule end by osmosis
High absorption of salt from the diet can result in a higher than normal concentration of salt in the blood plasma entering capillaries. This can lead to a build-up of tissue fluid. Explain how. (2)
1. To digest protein
2. So they can absorb amino acids for growth OR destroy toxins.
Some proteases are secreted as extracellular enzymes by bacteria. Suggest one advantage to a bacterium of secreting an extracellular protease in its natural environment. Explain your answer. (2)
1. In metaphase II, homologous chromosomes are randomly aligned along the equator.
2. They are randomly pulled to different poles of the cell
Variation in Meiosis [Independent assortment of homologous chromosomes] (2)
1. External intercostals contract
2. Diaphragm contracts
3. Pressure decreases in ribcage as thorax volume increases.
4. Air moves from high to low pressure
(Forced Expiration is just the opposite of this)
Inspiration (4)
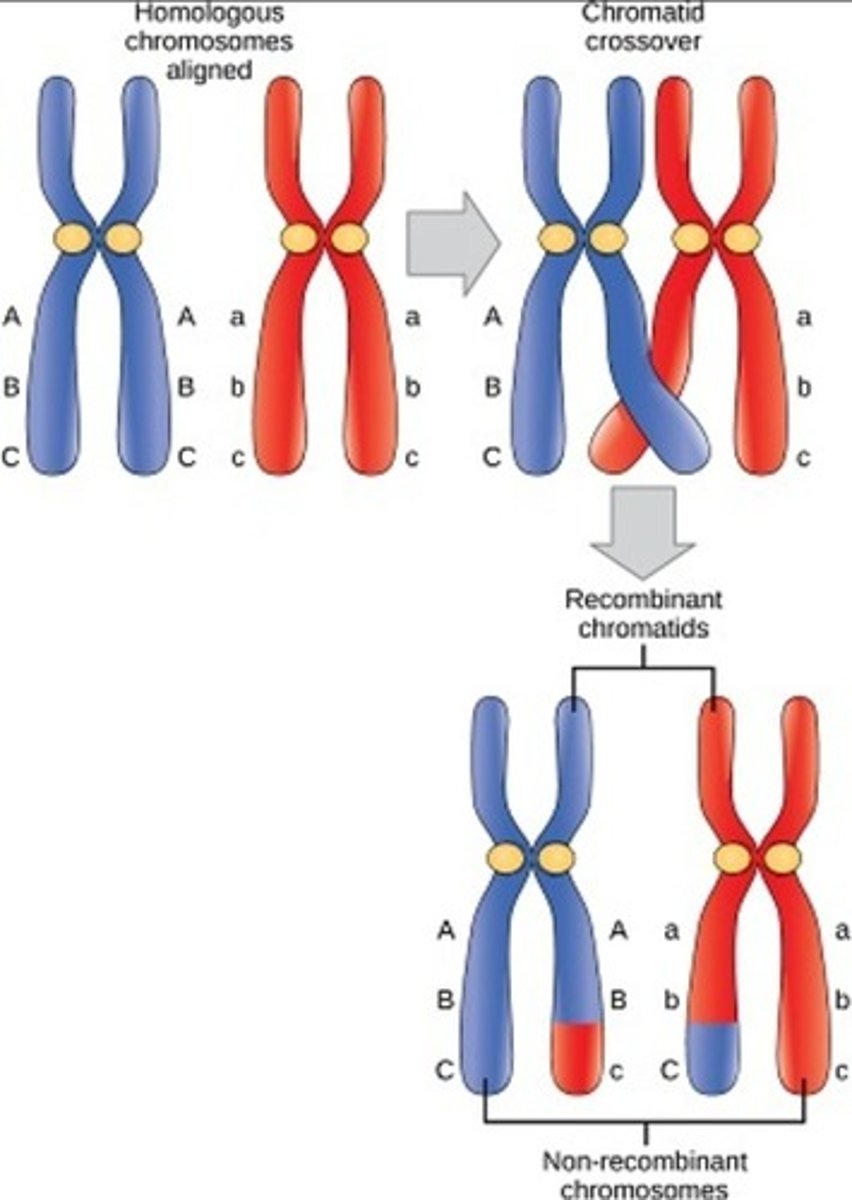
1. In meiosis I/II, chromatids of each pair become twisted and form bivalents.
2. Chiasmata form causing tension in parts of chromatin, thus equal parts if chromatids break off and rejoin, forming recombinants chromatids with a new allele combination.
Variation in Meiosis (Crossing over) (2)
1. The rate of diffusion is directly proportional to the membrane surface area
2. Concentration gradient is inversely proportional to the membrane thickness.
Fick's Law (2)
Domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species
Taxonomy order (King phillip came over for good spaghetti)
The number of different species in a community
Species richness
The relationship between the number of species in a community and the number of individuals in each species
Index of diversity
The number of different alleles in each gene.
Genetic Diversity
A group of similar organisms that can breed and produce fertile offspring.
Species
Anatomical, physiological, behavioural
Types of adaptations (3)
Alleles towards the mean more likely to survive.
Environment conditions are stable
Human birth weight
Stabilising Selection
Transport of sap (a very concentrated solution of dissolved sucrose and amino acids) in the phloem vessels.
Translocation
stroke volume x heart rate
Cardiac output
1. Phagosome fuses with lysosome;
2. Virus destroyed by lysozymes
3. Antigen (from virus) are displayed on
the cell membrane
Describe how phagocytosis of a virus leads to presentation of its antigens. (2)
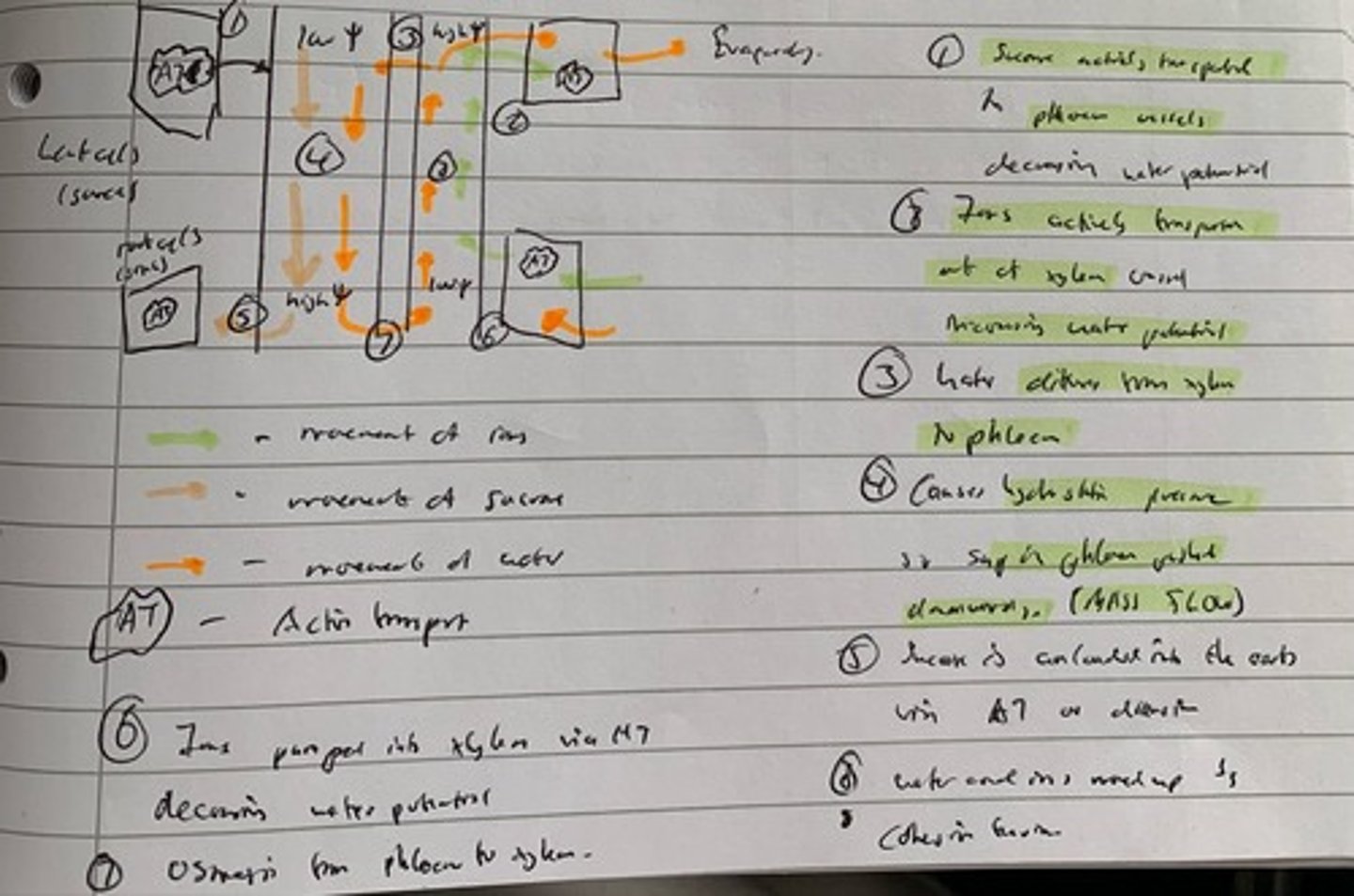
1. Transpiration.
2. Water leaves the leaf creating low pressure.
3. Water is sucked up from a high pressure (roots) to a low pressure.
4. Column of water does not break because of high tensile strength.
5. Strong lignin walls preventing xylem vessels from collapsing.
Xylem movement (5)
1. Sucrose actively transported to phloem vessels decreasing water potential.
2. Ions actively transported out of xylem vessel, increasing water potential.
3. Water diffuses from xylem to phloem.
4. Causes hydrostatic pressure so sap in phloem pushed downwards (mass flow).
5. Sucrose is unloaded in the roots via active transport or diffusion.
6. Ions pumped into xylem via active tranport, decreasing water potential.
7. Osmosis from phloem to xylem
8. Water and ions made up by cohesion tension.
Mass flow Hypothesis (8)
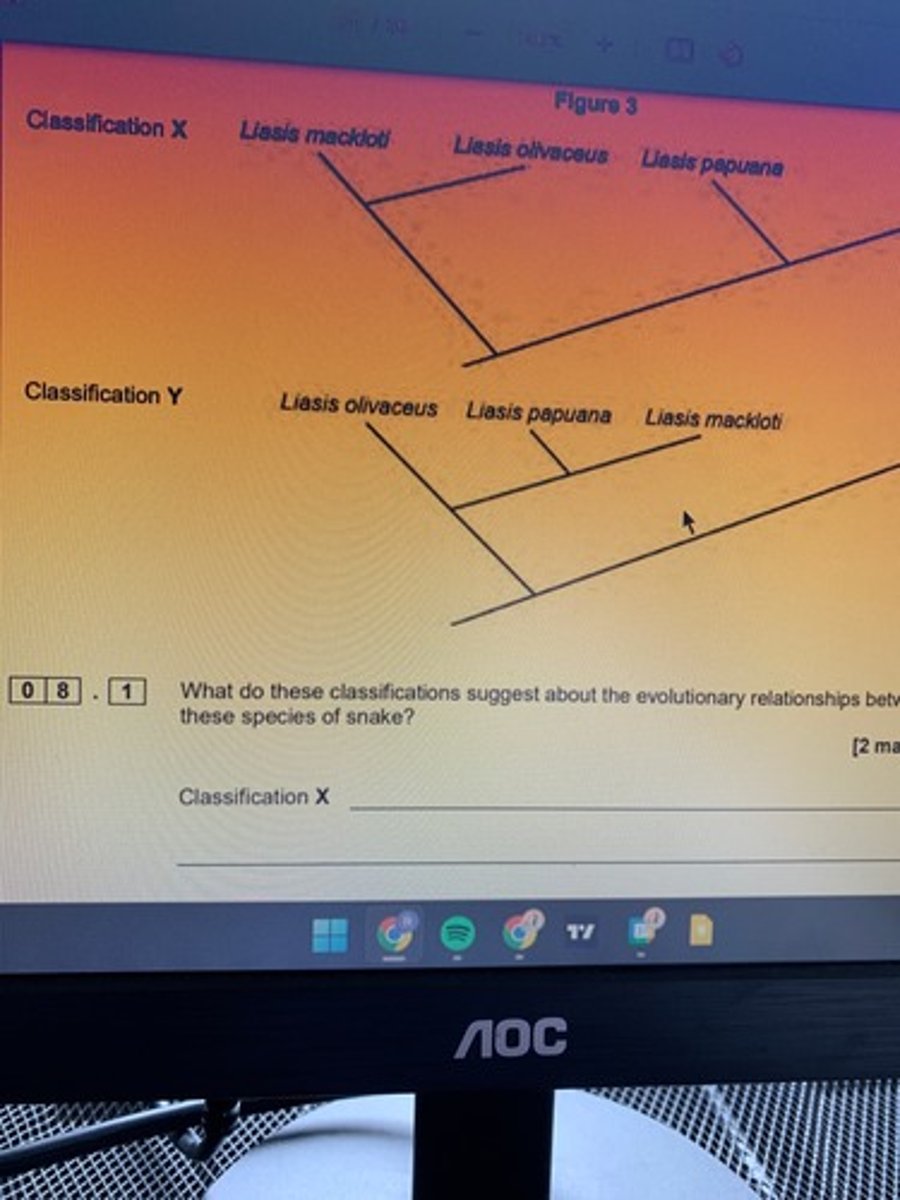
1. The base sequence of DNA
2. The base sequence of mRNA
3. The amino acid sequence of proteins
State three comparisons of genetic diversity that the scientists used in order to generate classification Y. (3)
1. A reactant in hydrolysis, photosynthesis
2. High heat capacity so buffers changes in temperature.
3. Large latent heat of vaporisation so provides a cooling effect through evaporation.
4. Cohesion between water molecules so supports columns of water in plants.
5. Cohesion between water molecules so produces surface tension supporting small organisms
Explain five properties that make water important for organisms. (5)
1. Tracheoles have thin walls so short diffusion distance to cells
2. Large number of tracheoles so short diffusion distance to cells;
3. Large number of tracheoles so large surface area (for gas exchange)
4. Body can be moved (by muscles) to move air so maintains diffusion/concentration gradient for oxygen/carbon dioxide
The adult damselfly uses a tracheal system for gas exchange. Explain three ways in which an insect's tracheal system is adapted for efficient gas exchange. (3)
Glucose is high concentration in the ileum, low in the epithelial, but we want to increase the rate of transport. Sodium-potassium pump actively transports in a K+ to transport out Na+ creating a concentration gradient.
Na+ and glucose pass through a co transporter in the phospholipid bilayer of the epithelial cell.
Co-Transport (Not mark scheme specific, only here as a guidance)
Mitosis:
1. Division of body cells
2. results in 2 diploid daughter cells
3. genetically identical
4. used for growth, repair, and cell replacement
Meiosis:
1. germline cells divide into sex cells
2. 4 haploid daughter cells
3. genetic variation due to:
4. crossing over
5. random orientation
6. used for sexual reproduction
Similarities
1. Start as diploid cells
2. Same basic stages prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis [Differences Mitosis(4), Meiosis(6)][Similarities (2)]
1. A condensation reaction joins monomers by forming a chemical bond and releases water.
2. A hydrolysis reaction breaks a chemical bond between monomers by adding water.
3. Example: A-glucose —> Starch, glycogen. Alpha 1,4 Glycosidic bonds formed
4. Example: B-glucose —> cellulose beta 1,4 glycosidic bonds
Describe the chemical reactions involved in the conversion of polymers to monomers and monomers to polymers. Give two named examples of polymers and their associated monomers. (5)
1. Micelles include bile salts and fatty acids.
2. Makes fatty acids more soluble in water
3. Brings fatty acids towards the lining
4. Fatty acids absorbed by diffusion
Describe the roles of micelles in the absorption of fats into the cells lining the ileum (3).
1. Hydrolysis
2. Of glycosidic bonds
3. Starch to maltose by amylase
4. Maltose to glucose by maltase
5. Membrane-bound (disaccharidase/maltase)
(Add context to where such digestion happens in relation to digestive system)
Describe the complete digestion of starch by a mammal. (4)
1. Nuclear envelope and pores
2. Chromatin
3. Nucleolus
4. Holds genetic material to code for polypeptides
5. DNA replication occurs here
6. Production of mRNA/tRNA
7. Production of ribosomes
Describe the structure and the function of the nucleus. (4) [Structure (3)] [Function(4)]