Muscles, TMJ, Heart, Tongue
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
Superficial Cervical muscles (located close to surface of skin)
Sternocleidomastoid, Trapezuis
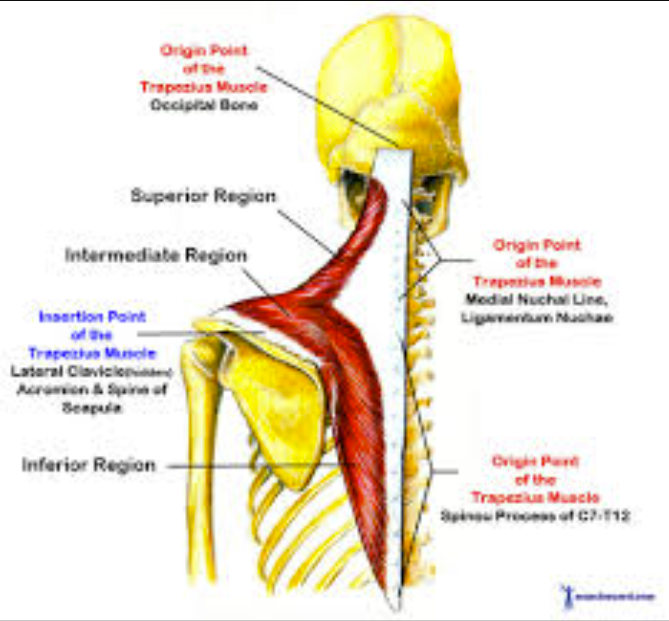
Trapezius Origin and Insertion
Origin - external surface of the occipital bone at the superior nuchal line and the posterior midline of the cervical and thoracic region.
Insertion - 1/3rd of the clavicle and parts of the scapula
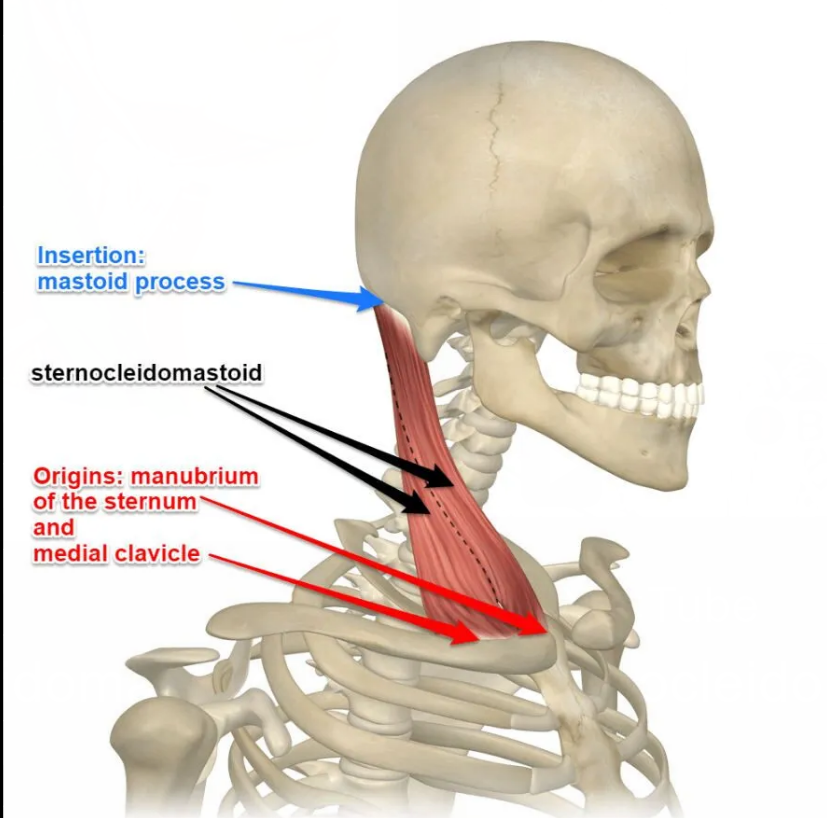
sternocleidomastoid Origin and insertion
Origin- Superior and lateral part of the sternum (bones that connect ribs) and medial portion of the clavicle (collar bone)
insertion - mastoid process of the temporal bone
Suprahyoid Muscles
Mylohyoid, geniohyoid, digastric, and stylohyoid muscles
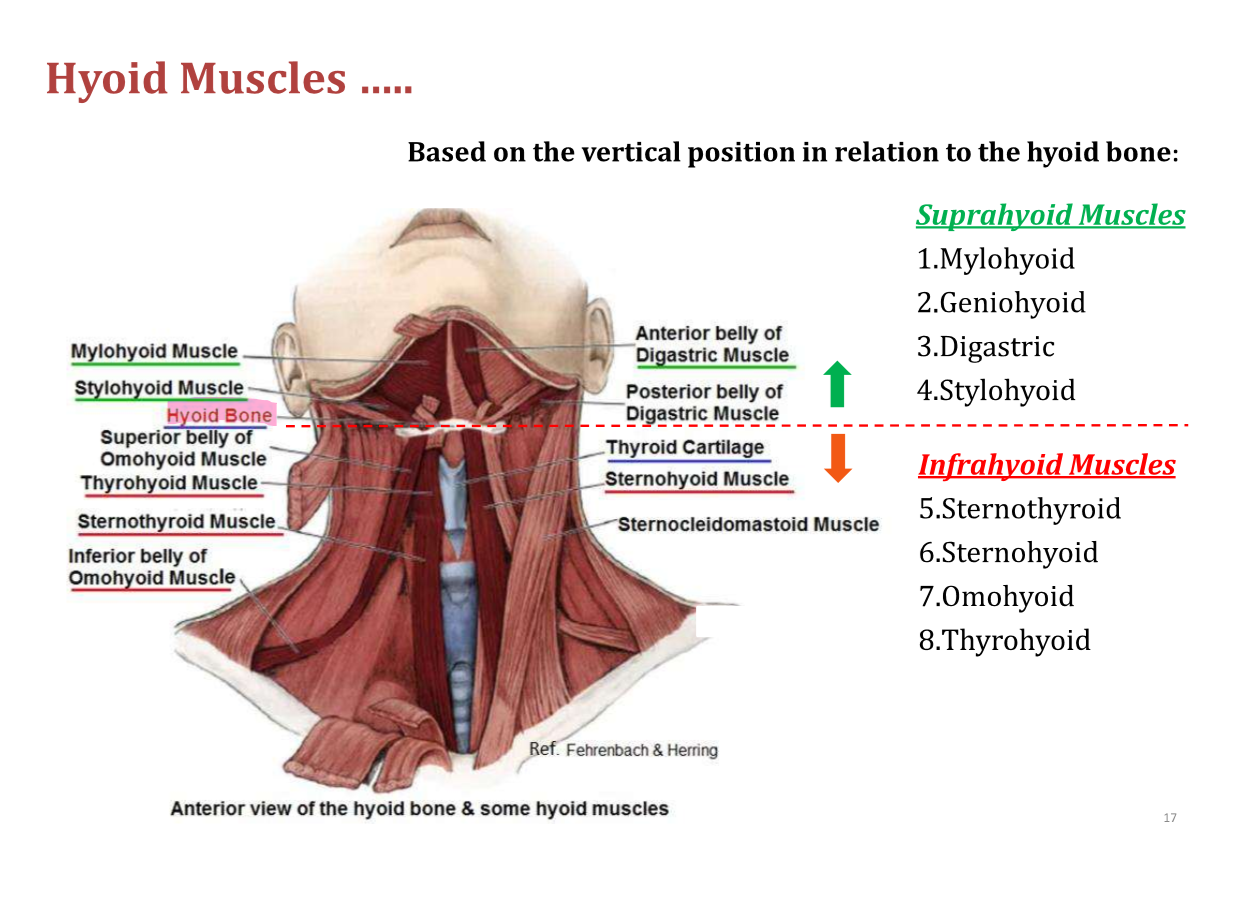
Infrahyoid Muscles
Sternothyroid, sternohyoid, omohyoid, and thyrohyoid muscles
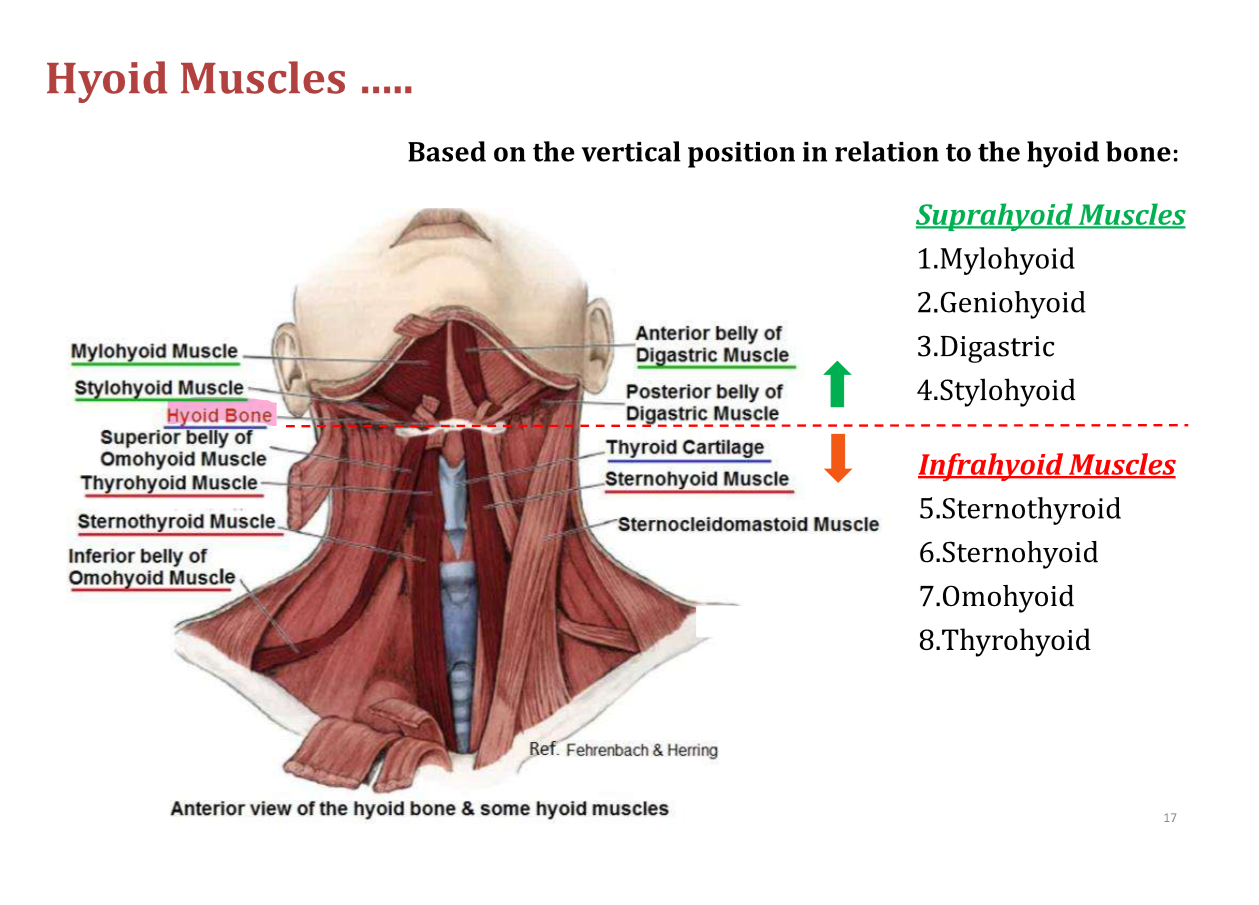
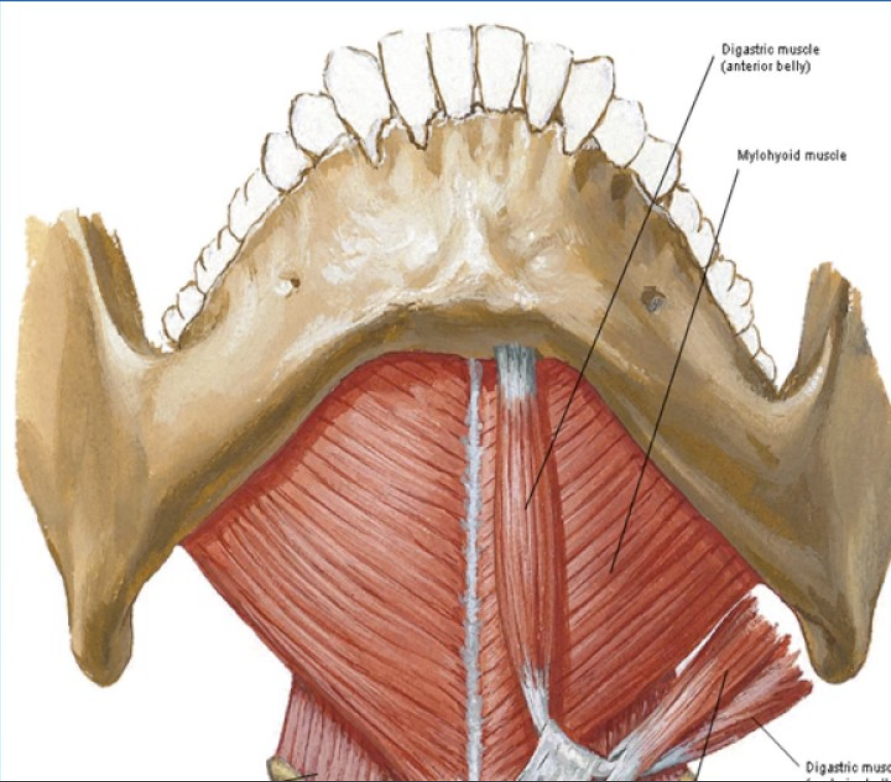
Mylohyoid Muscle origin and insertion
origin - mylohyoid line of the mandible
insertion - mylohyoid raphe of the hyoid bone
action - depress the mandible and elevate the hyoid and tongue
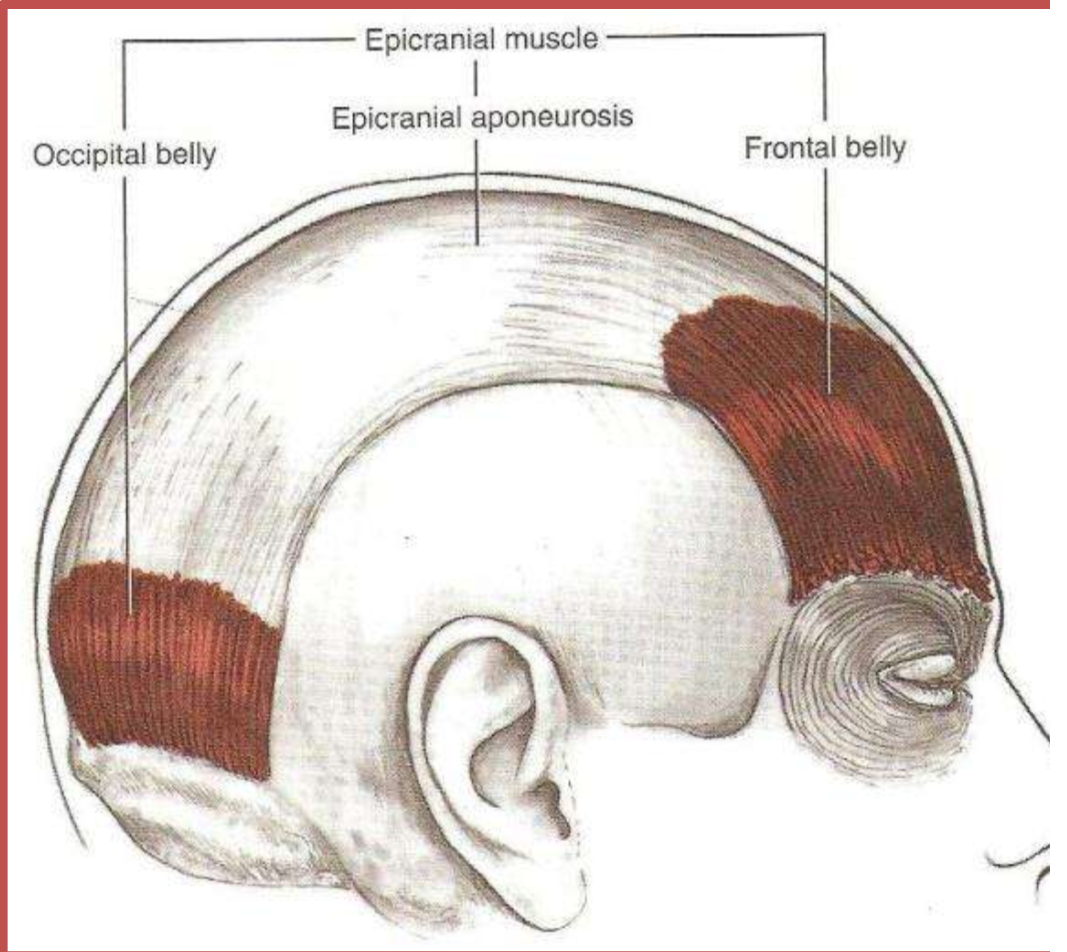
Scalp region (2 bellies and action)
1) Occipital belly
2) frontal belly
Epicranial aponeurosis (large tendon)
action - raises eyebrows
eye region action
orbicularis oculi
action - closes eyelid
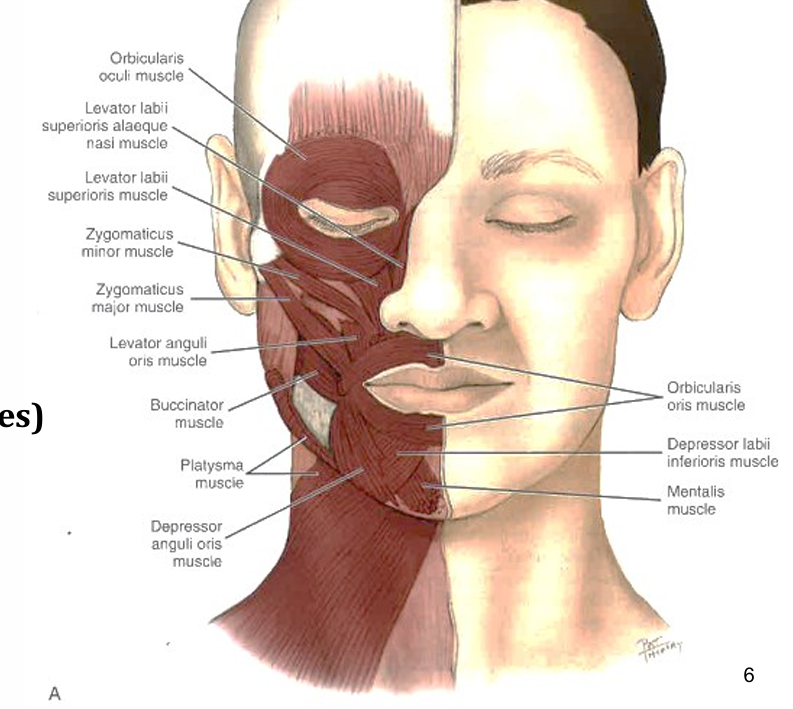
Orbicularis oris origin/insertion and action
origin - facial modiolus
insertion- vermillion zone (ensures the mouth) and non-vermillion zone (skin tissue)
Action- closing, rolling forward
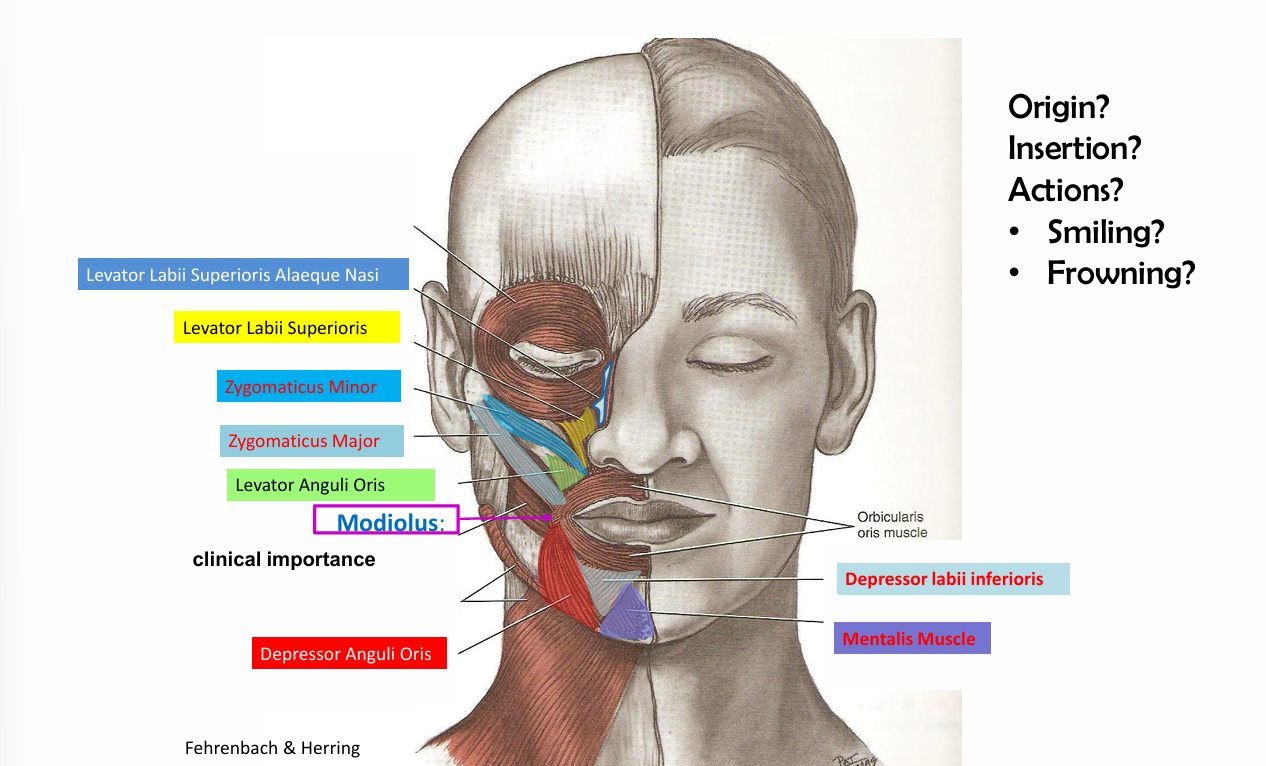
6 muscles supplied by the facial nerve (VII) supply
Buccinator, zygomatic major, zygomatic minor, levator labii superioris alaeque nasi, levator labii superioris
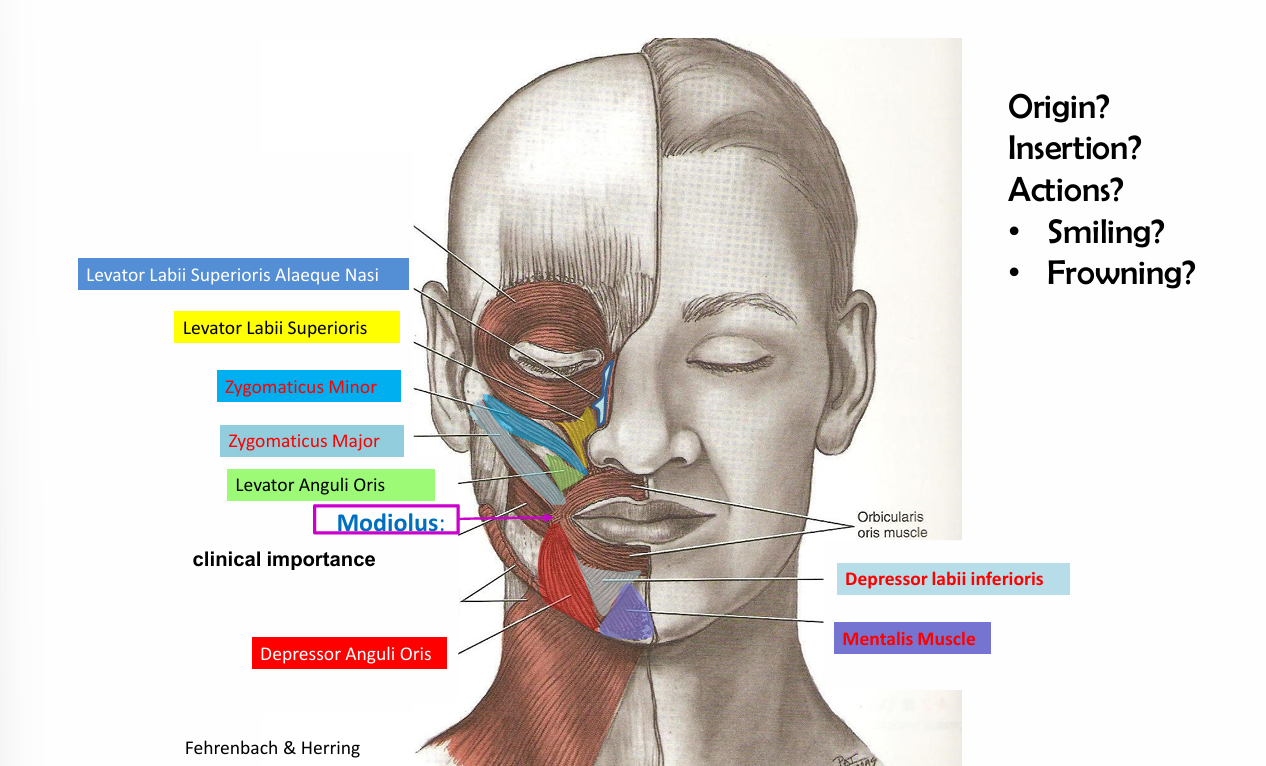
Buccinator origin, insertion and action
Origin- alveolar processes of maxilla and mandible pterygomandibular raphe
insertion- skin tissues at the angle of the mouth
action- pulls the angle of the mouth laterally
Zygomatic Major origin, insertion and action
Origin- zygomatic bone
insertion- skin tissue at the angle of the mouth
action-elevate the angle of the supper lip and pulls laterally when smiles
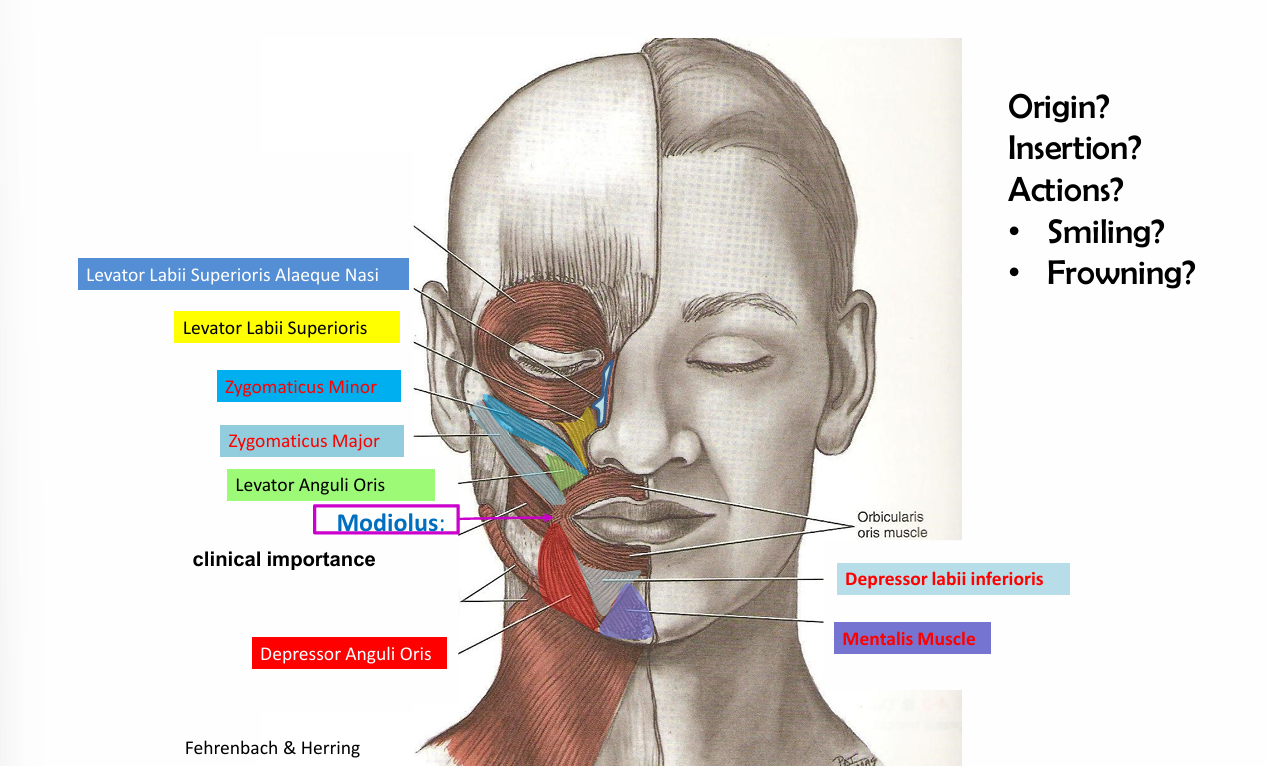
zygomatic minor origin, insertion and action
origin- zygomatic bone
insertion- skin tissues of upper lip
action- elevate the upper lip (smile)
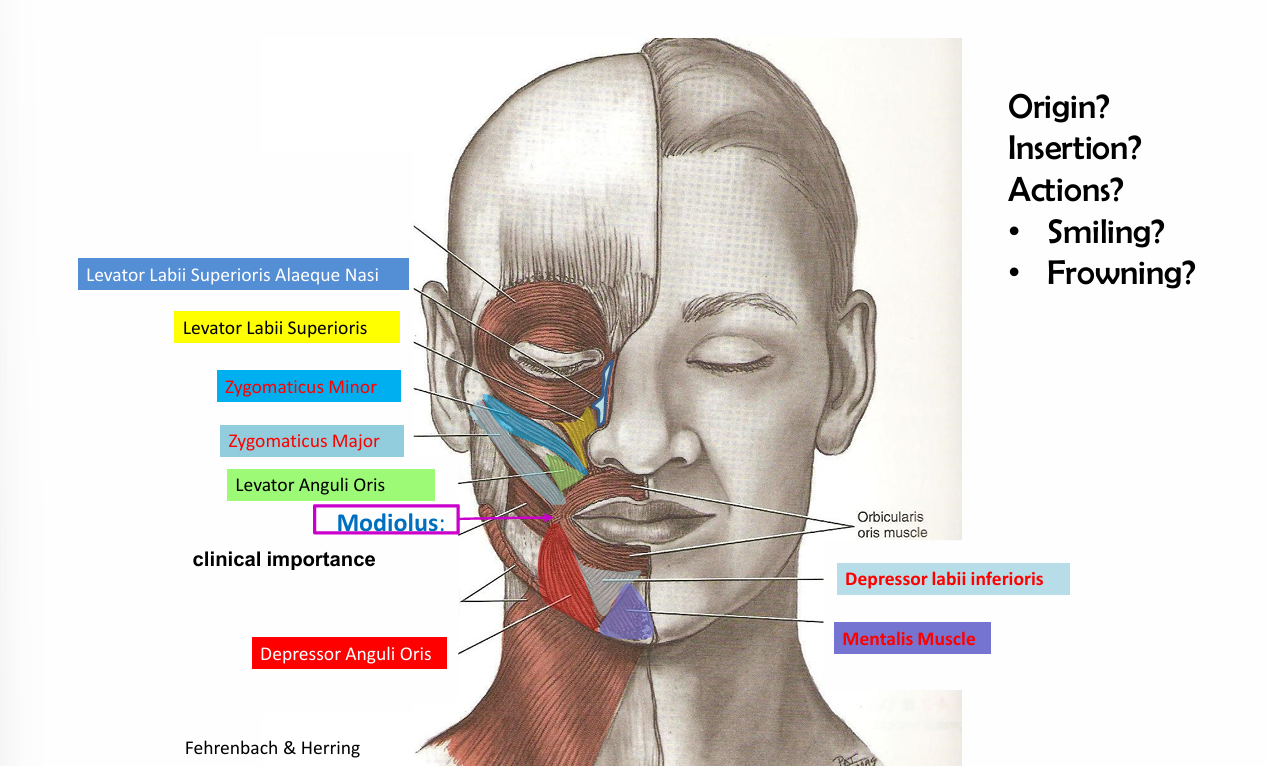
Modiolus definition
Point at the corners of lips where several muscles converge
Modiolus muscle examples
Orbicularis oris
Buccinator
Zygomatic major
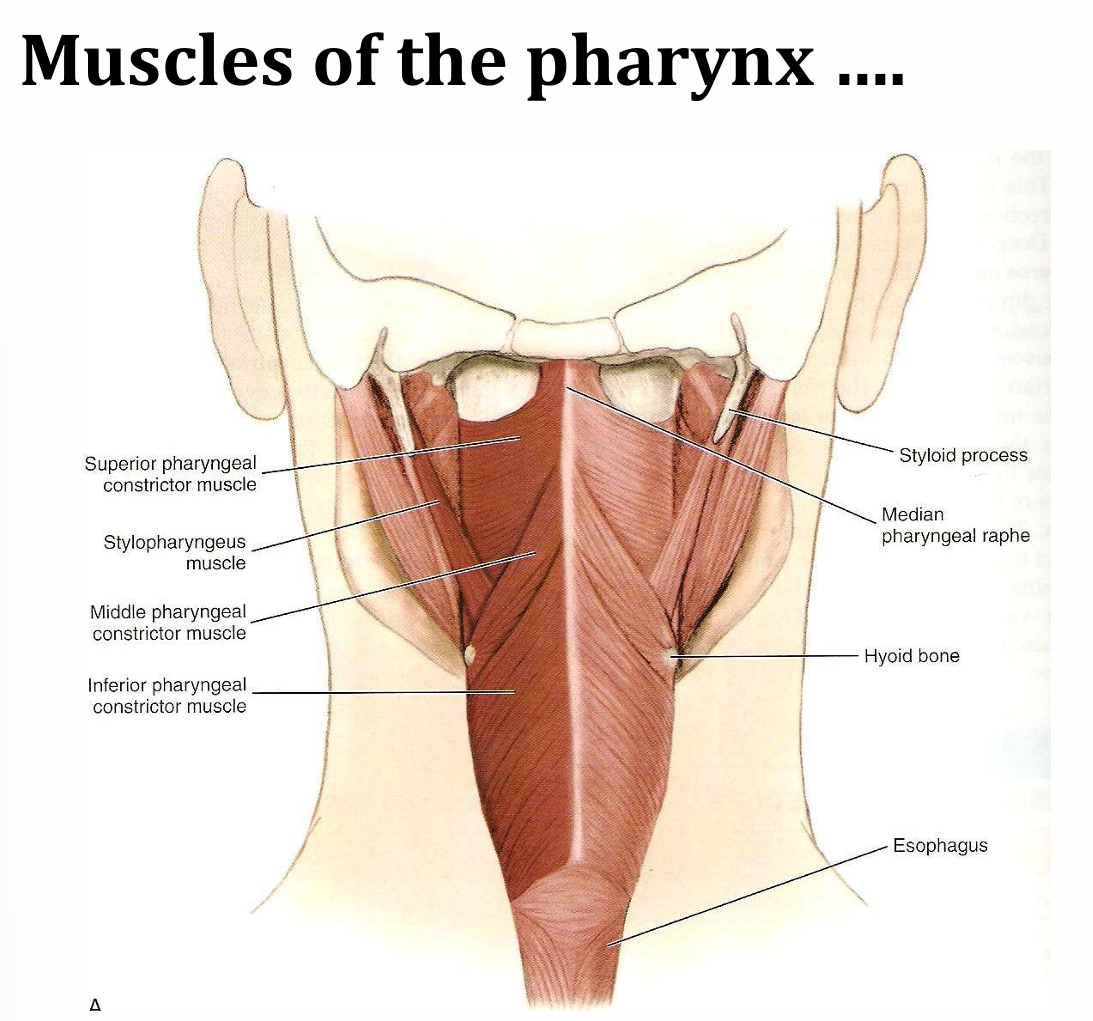
muscles of the pharynx
superior, middle and inferior pharyngeal constrictor muscle
muscles of the soft palate
Palatoglossus and palatopharyngeal
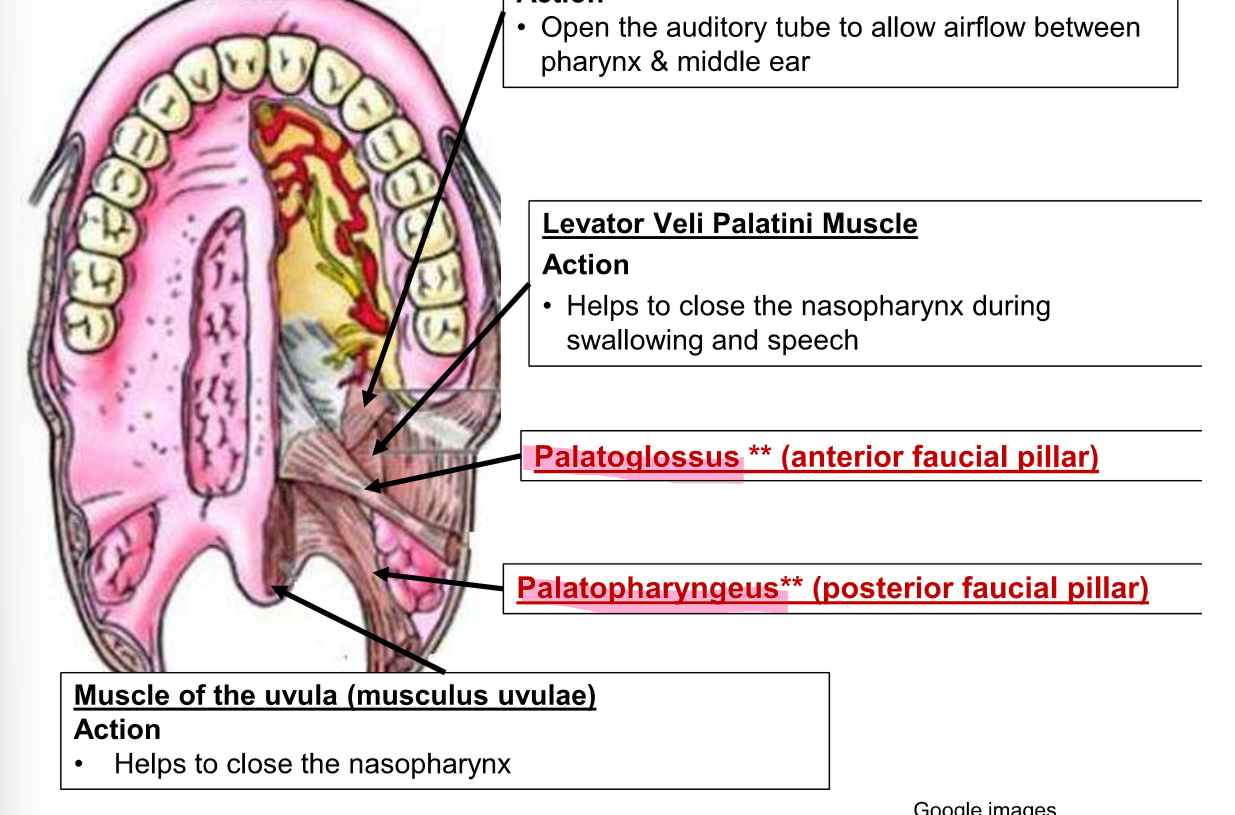
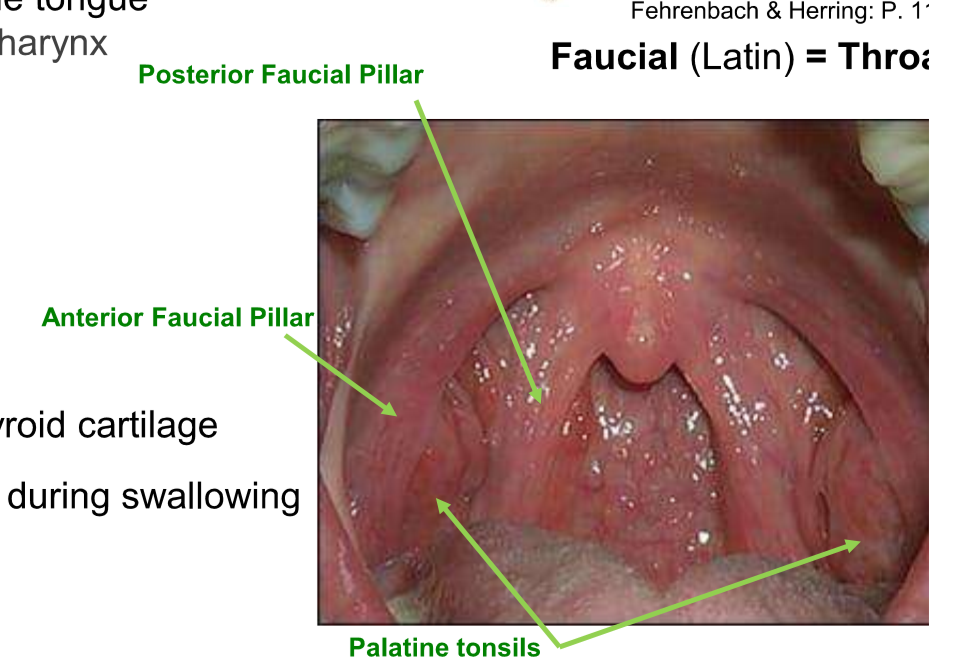
palatoglossus
forms anterior faucial pillar

palatopharyngeus
Posterior faucial pillar
what happens when muscles of the soft palate are relaxed
palate extends posteriorly over the anterior oropharynx
How does the nasopharynx and oropharynx separate during swallowing
Combines action of the soft plate.
The soft plate moves superiorly and posteriorly to contact the posterior pharyngeal wall.
4 main muscles for mastication
Masseter, temporalis, medial pterygoid and lateral pterygoid muscle
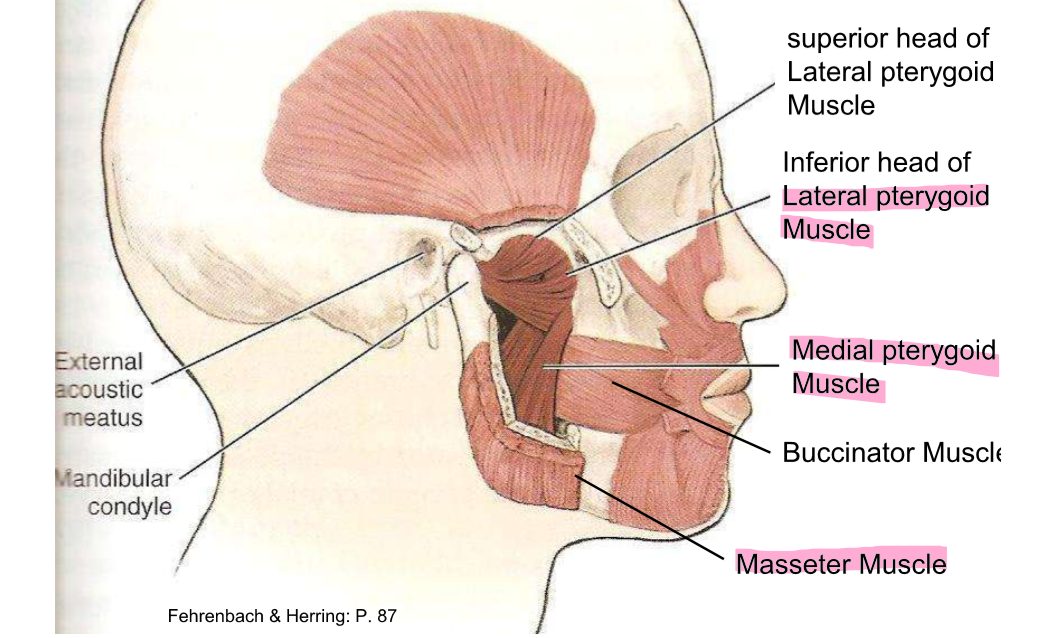
Masseter origin, insertion and action
Origin- zygomatic arch
insertion- lateral surface of the angle and ramus of the mandible
Action- elevates the mandible
The masseter blood and nerve supple
Masseteric artery and nerve
Temporalis origin, insertion and action
Origin- temporal fossa
insertion- coronoid process of the mandible
action: elevate mandible
Neck surface features
hyoid bone, thyroid notch, laryngeal prominence
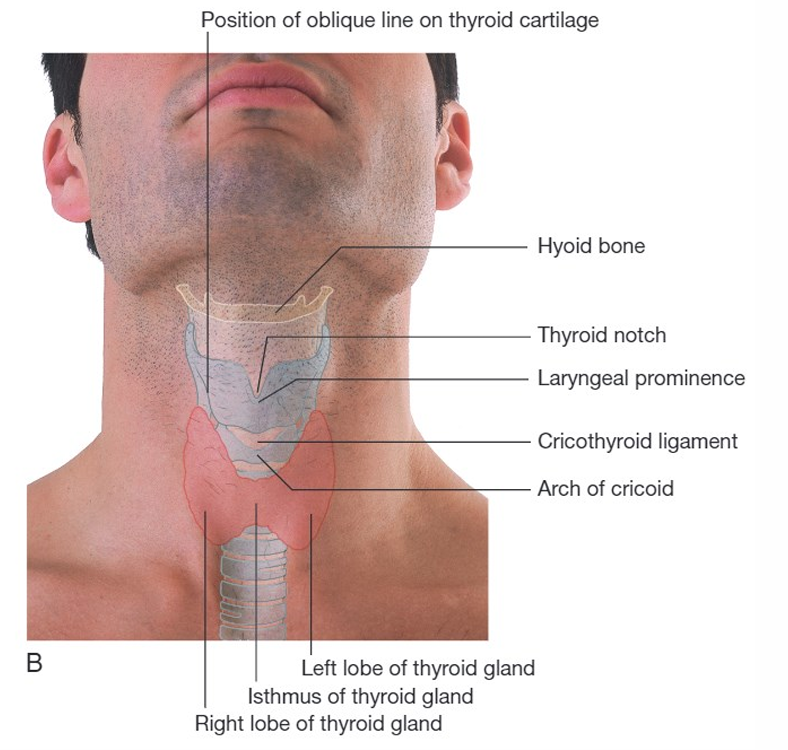
What Cervical triangles does the sternocleidomastoid muscle separate
Occipital and posterior triangle
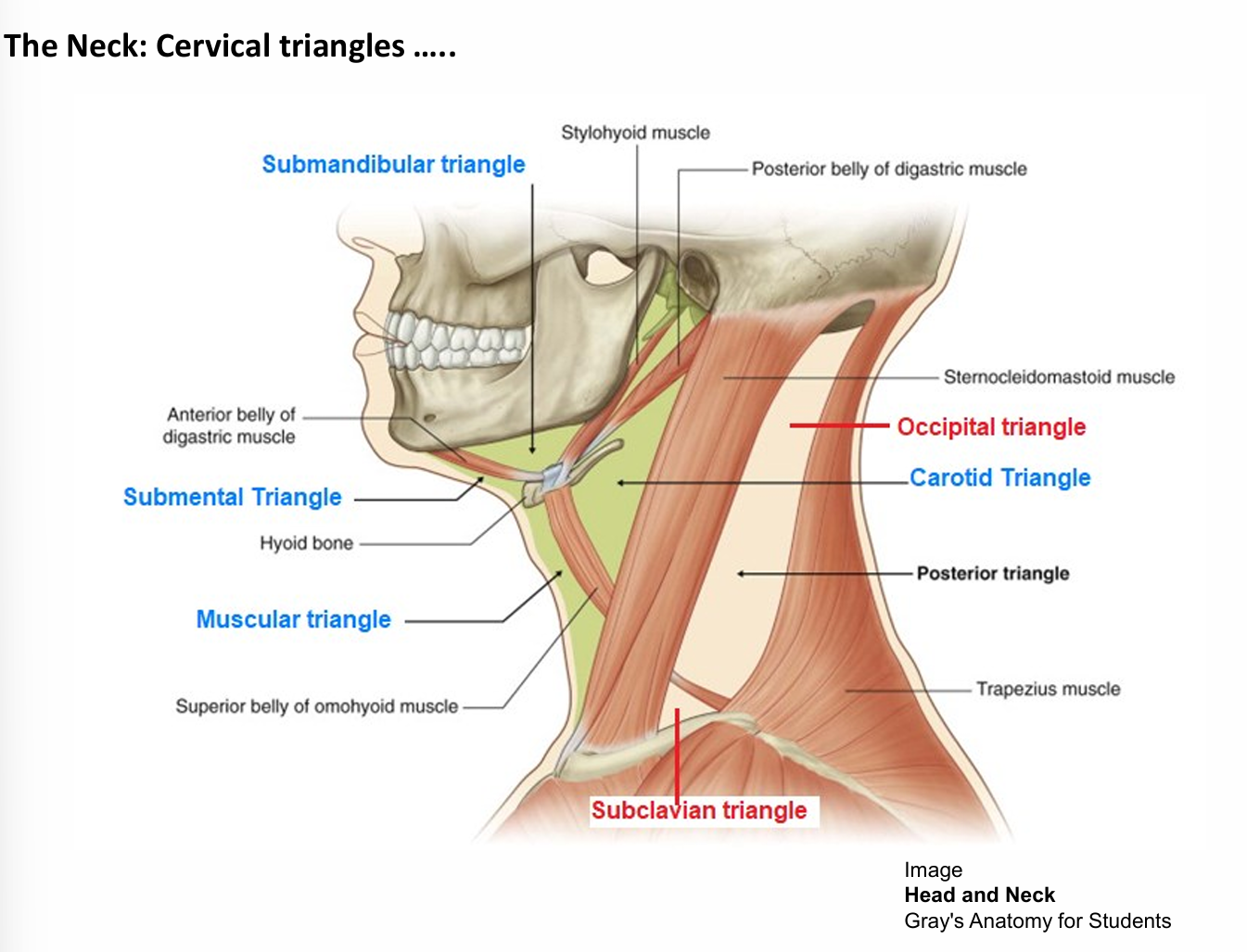
Cervical triangle of the chin
Submandibular and submental triangle
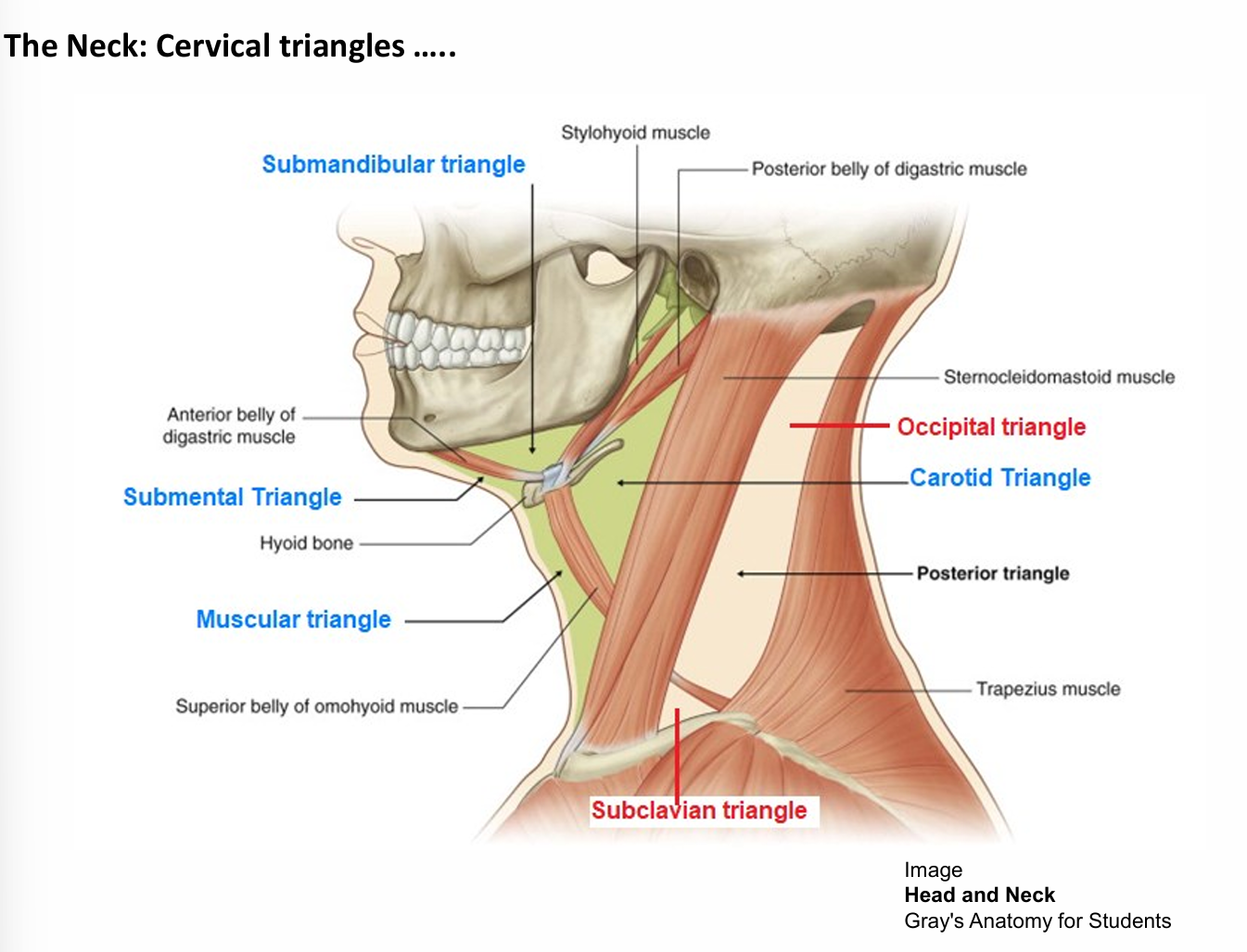
cervical triangle of the neck
Muscular triangle
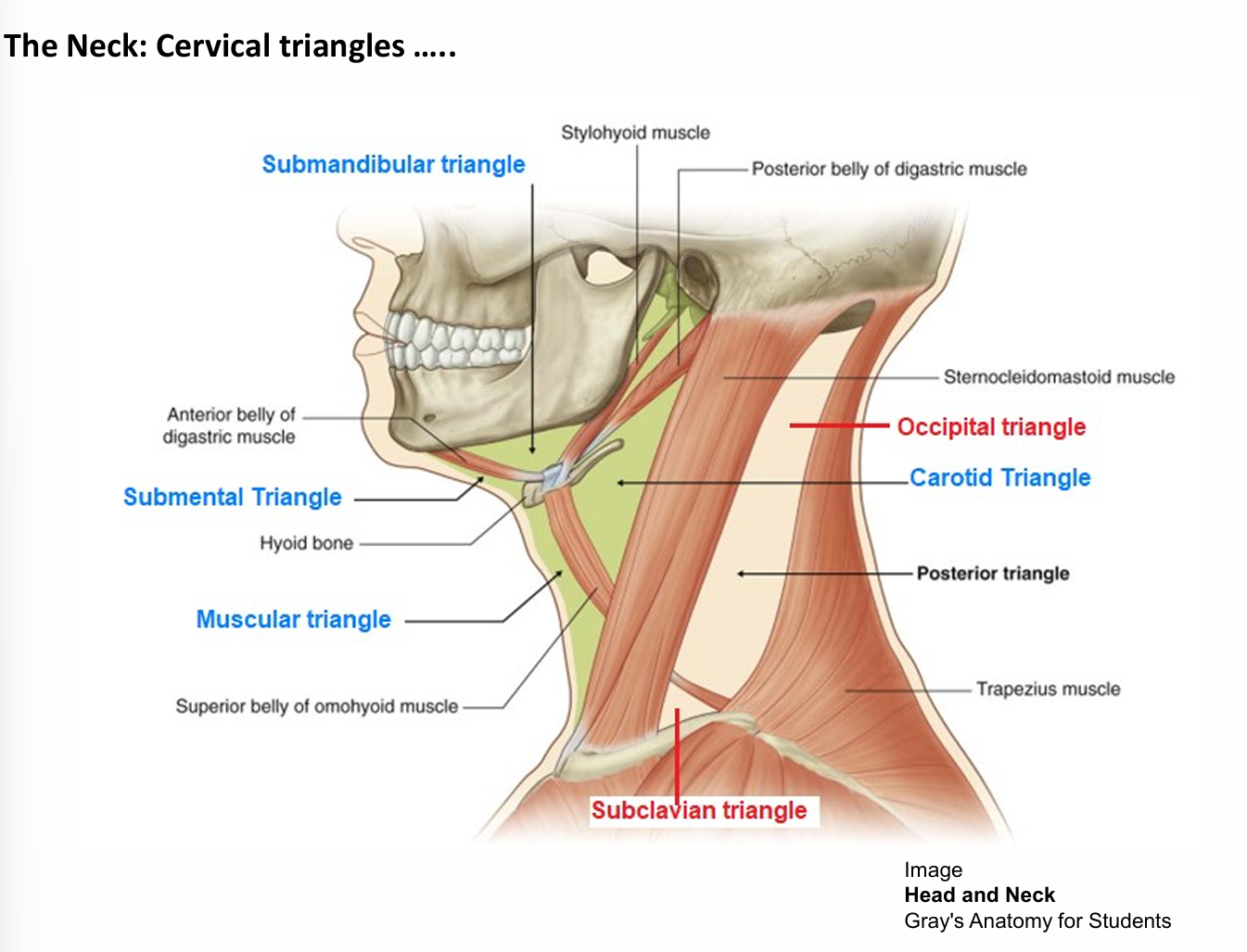
Submandibular triangle features
submandibular glands
supplied by the facial artery
Carotid sheath
fibrous tunnel in the neck
carotid sheath structures
internal jugular vein, common carotid and internal carotid arteries, vagus nerve
TMJ bony components
Articular fossa and articular eminence of the temporal bone
condyle head the of the mandible
TMJ connective tissue parts
articular disk, joint capsule and ligaments
Meniscus (articular disc) functions
Compressive forces are cushioned or distributed to a large area to protect the articular surfaces
Articular disc age changes
Become thinner, calcified
Synovial fluid functions
Lubrication to reduce friction
Nutrional to avascular tissues
Ligament function
helps stabilise the joint
TMJ ligament function
prevents excessive retraction of the mandible
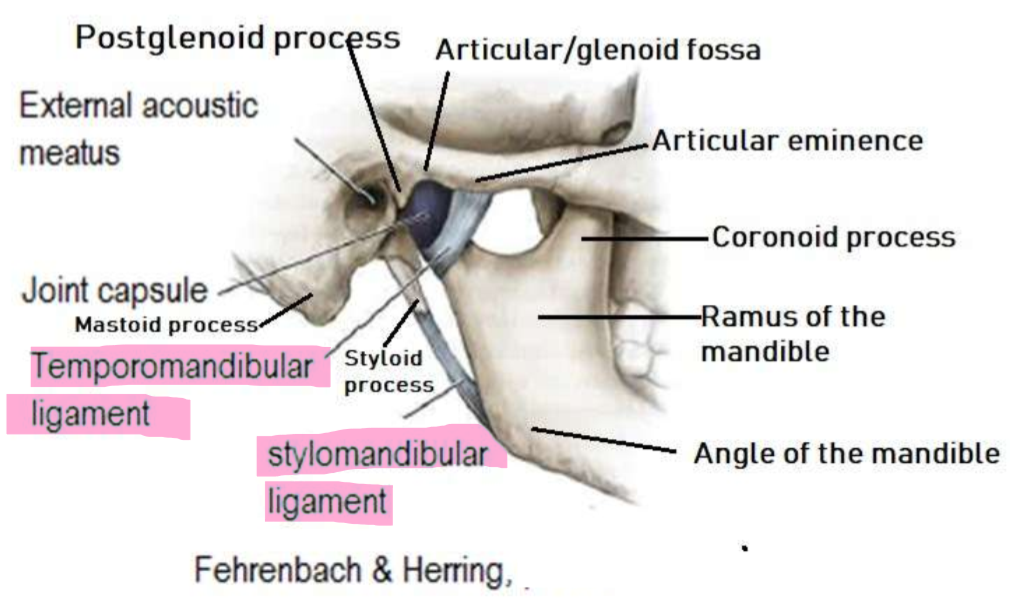
Sphenomandibular ligamnet and stylomandibular ligament function
become taut (tight) when the mandible is protruded

Between what part of the TMJ helps with Gliding movement.
Occurs mainly between disc and articular fossa in the supper synovial cavity
protrusion (forward) - lateral pterygoid muscle
protrusion (backwards) - posterior fibers of the temporalis muscle
Between what part of the TMJ helps with rotational movement.
Occurs mainly between disc and the condyle in the lower synovial cavity
Depression (lowering) - lateral pterygoids muscle
Elevation (raising) - masseter and temporalis
Valves of the heart
mitral valve, pulmonary valve, tricuspid valve
Where does the blood get oxygenated back into the heart
through pulmonary arteries to the lungs and back into the pulmonary veins
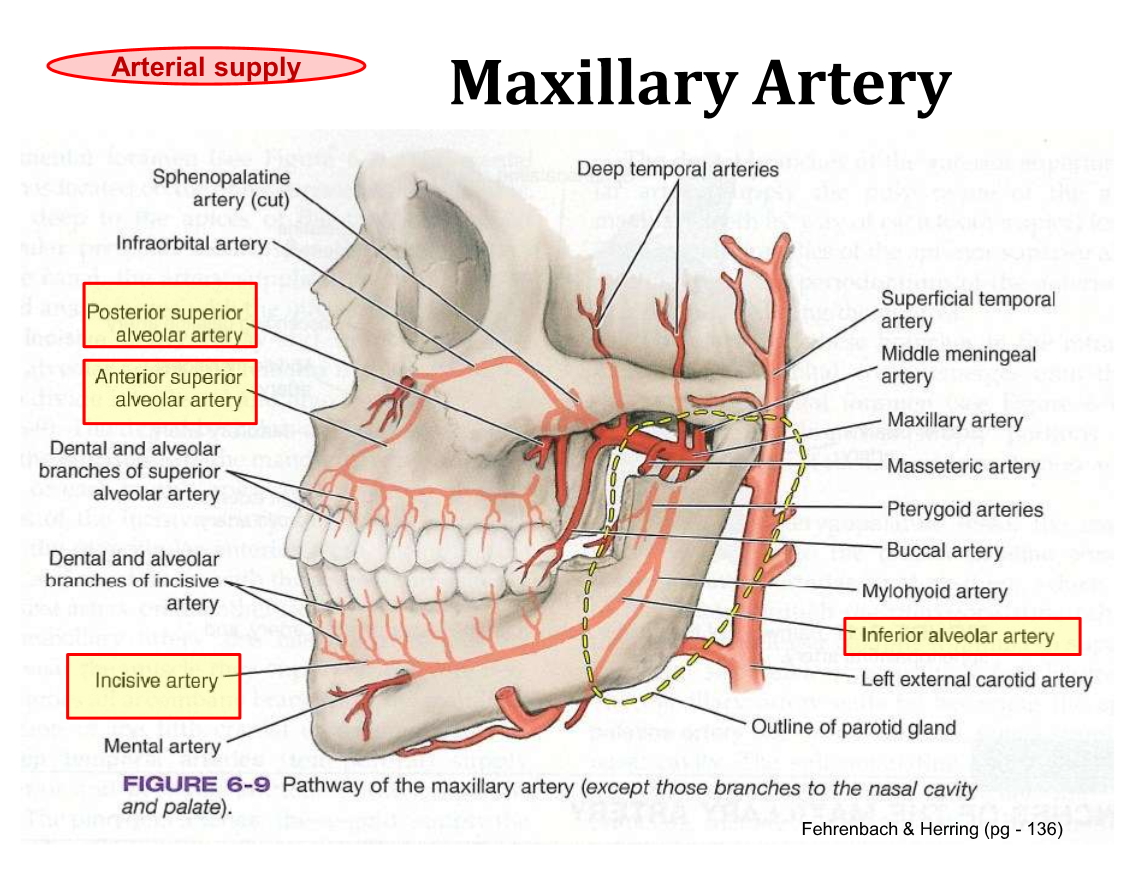
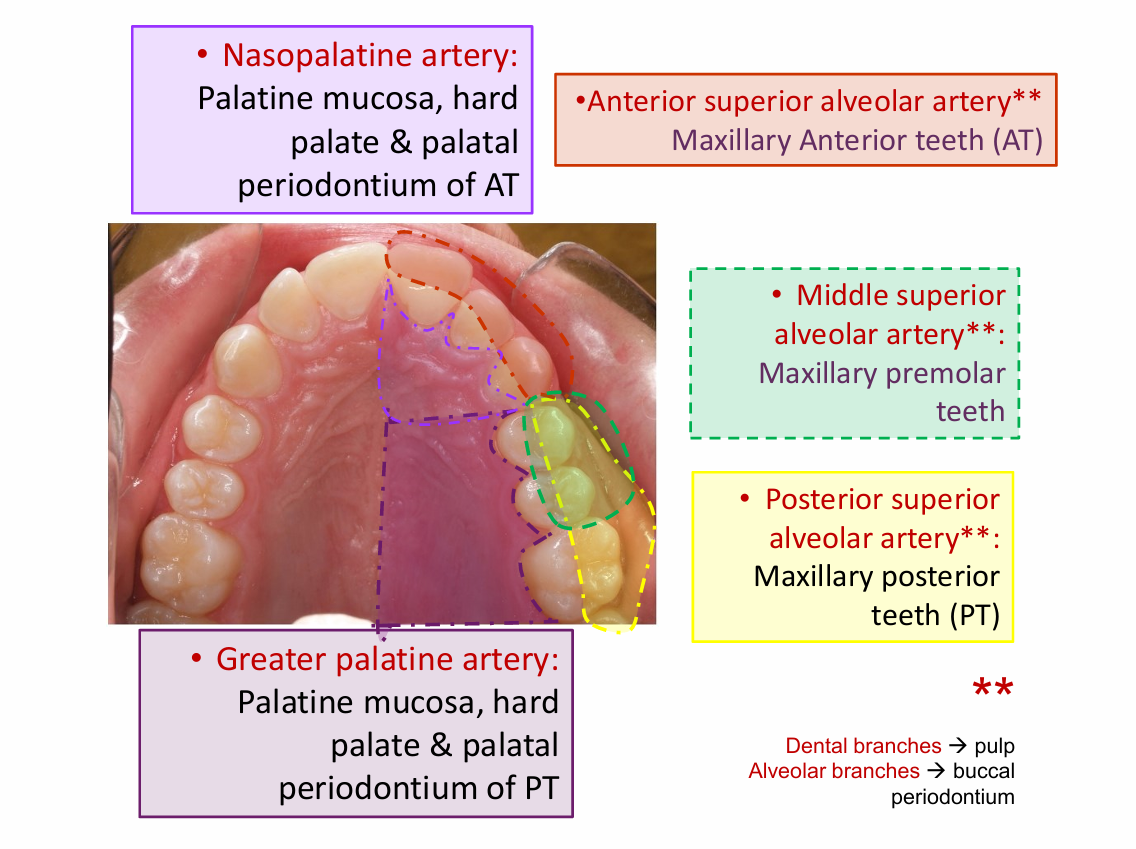
Maxillary arteries - away from heart
Posterior superior alveolar artery
Anterior superior alveolar artery
incisive artery
inferior alveolar artery
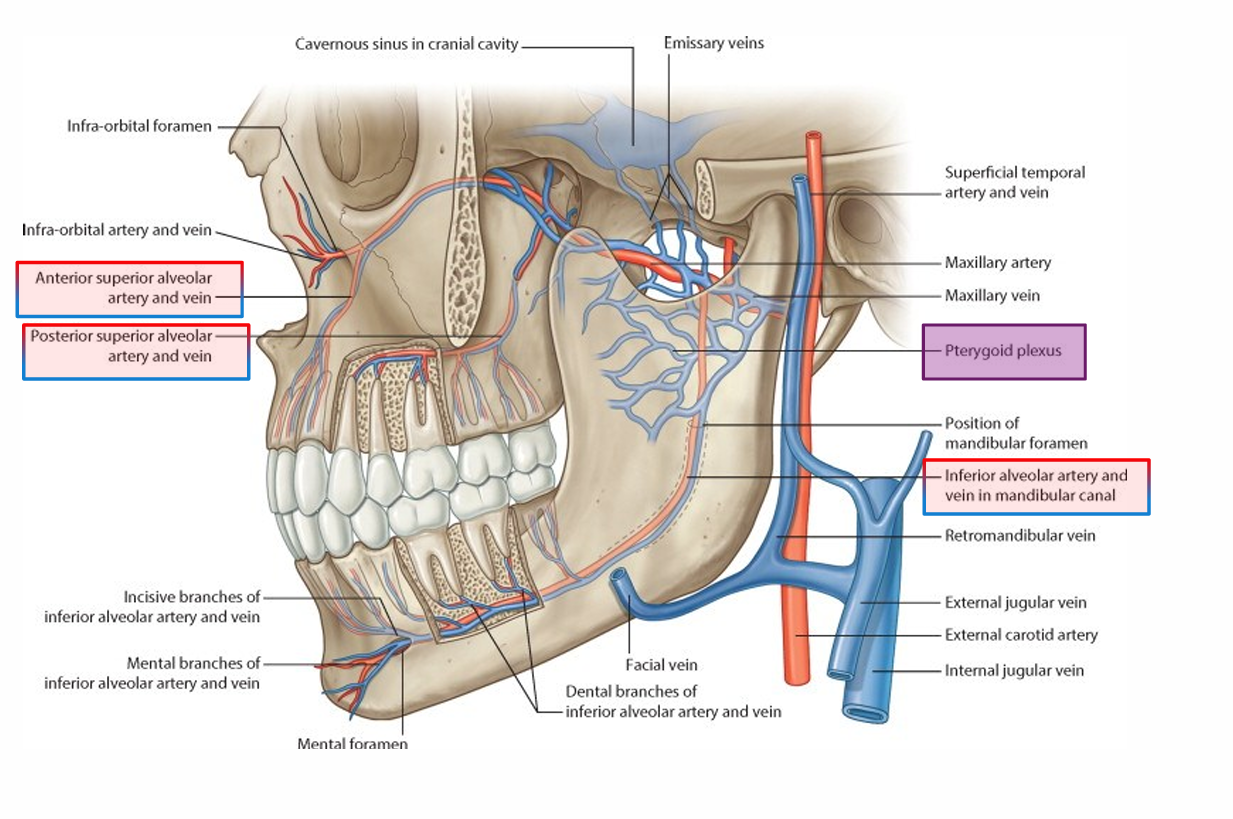
Facial veins and artery
Anterior superior alveolar
posterior superior alveolar
inferior alveolar artery
vein in mandibular canal
Anterior superior alveolar artery blood supply of teeth
Maxillary anterior teeth
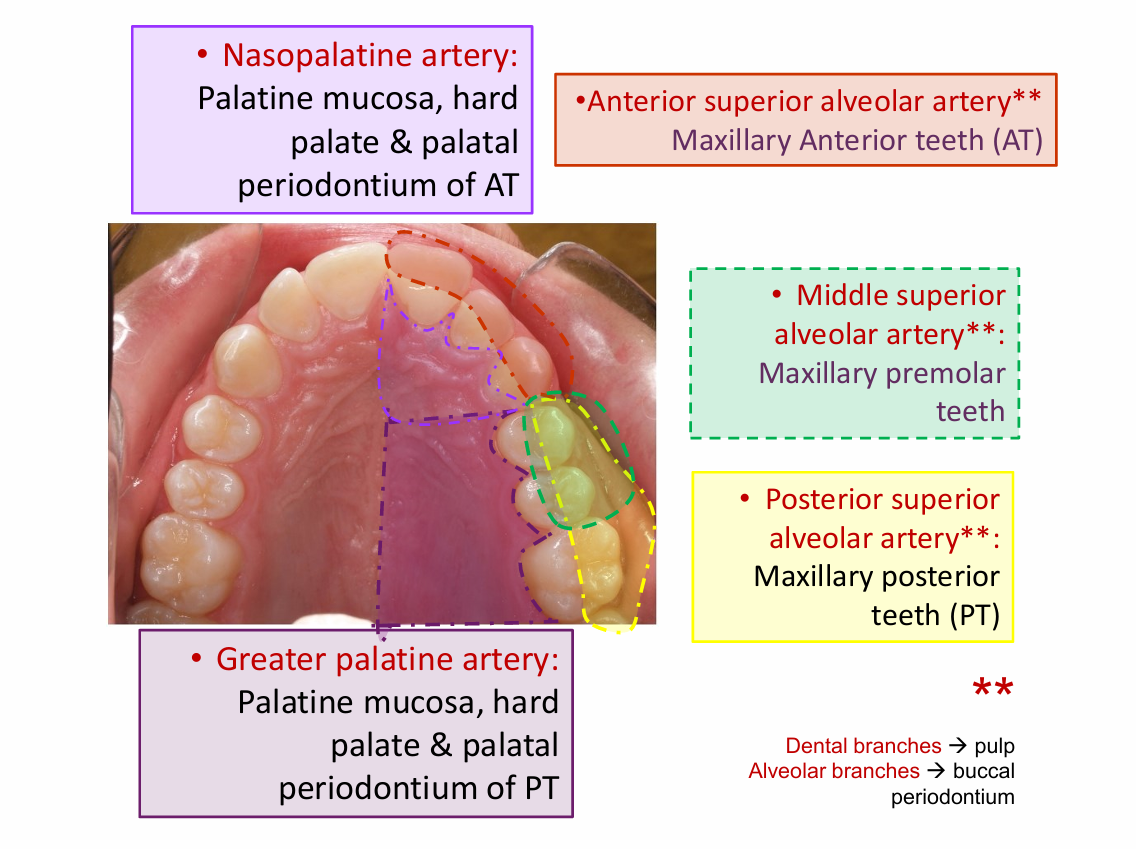
middle superior alveolar artery
Maxillary premolar teeth
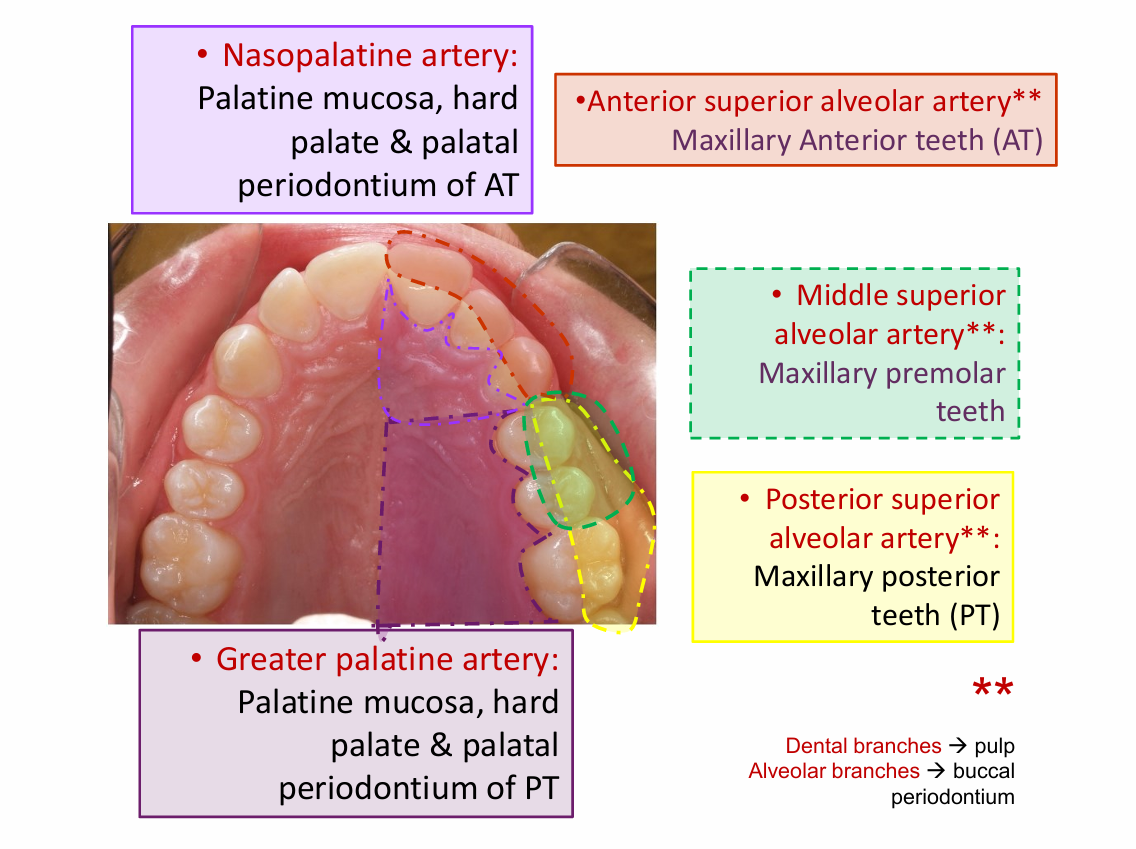
posterior superior alveolar artery
Maxillary posterior teeth
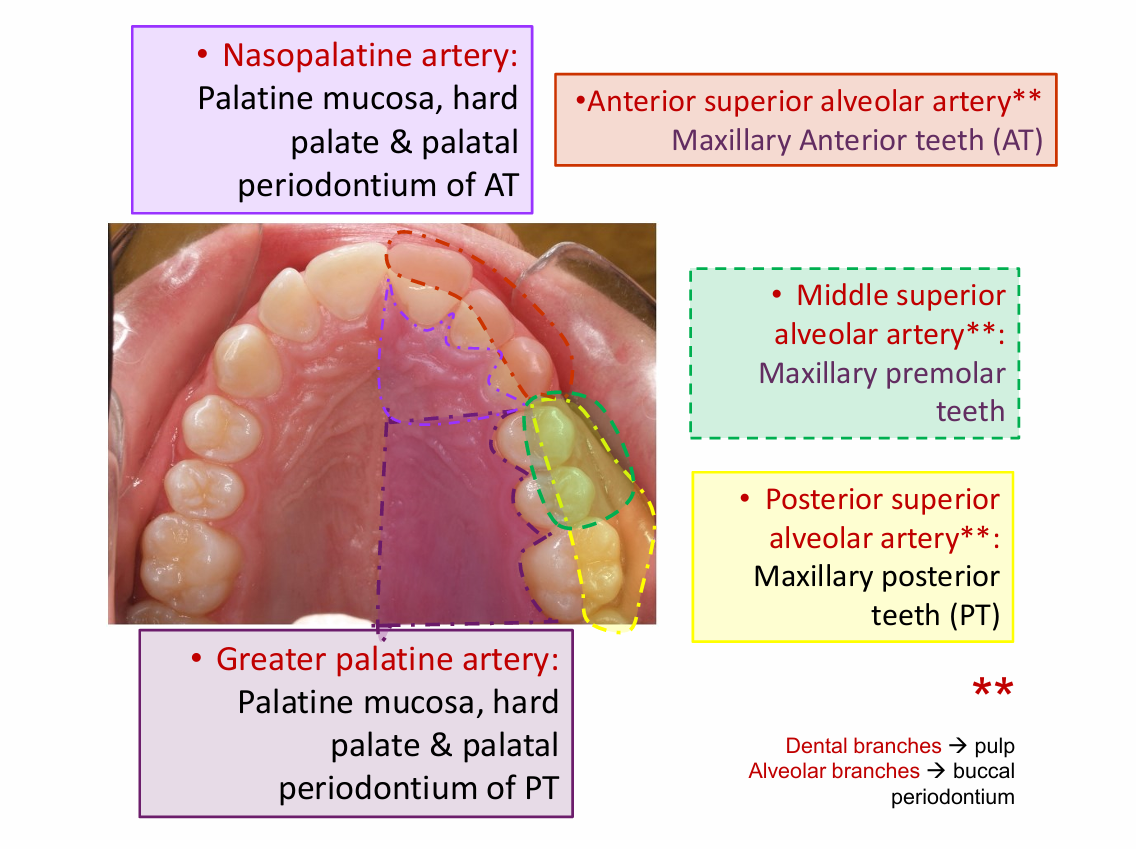
greater palatine artery
Palatine mucosa
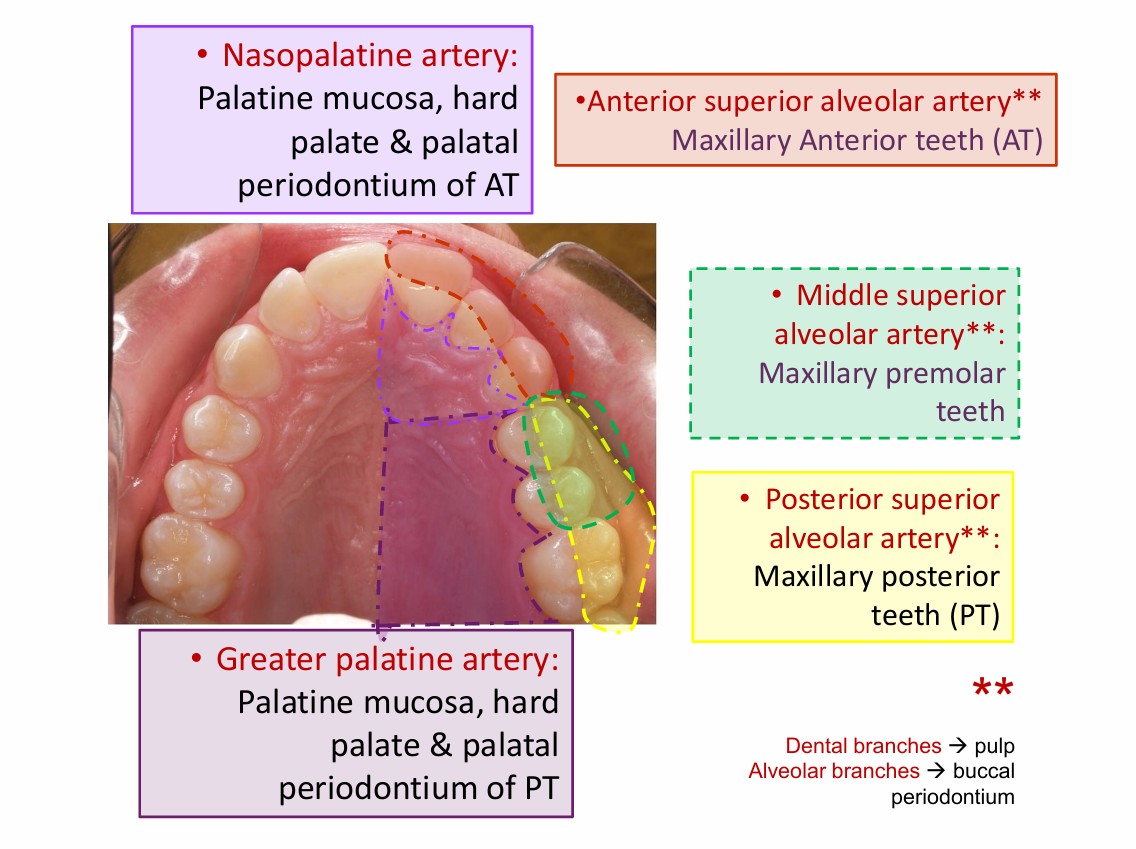
Nasopalatine artery
palatine mucosa
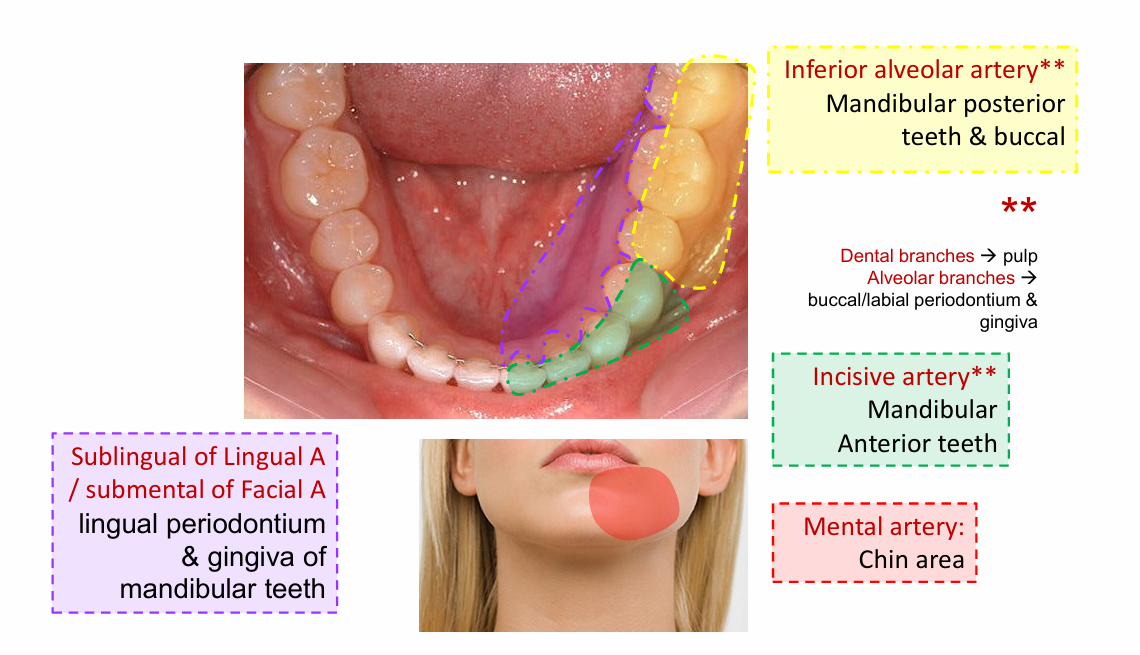
Inferior alveolar artery
Mandibular posterior teeth and buccal
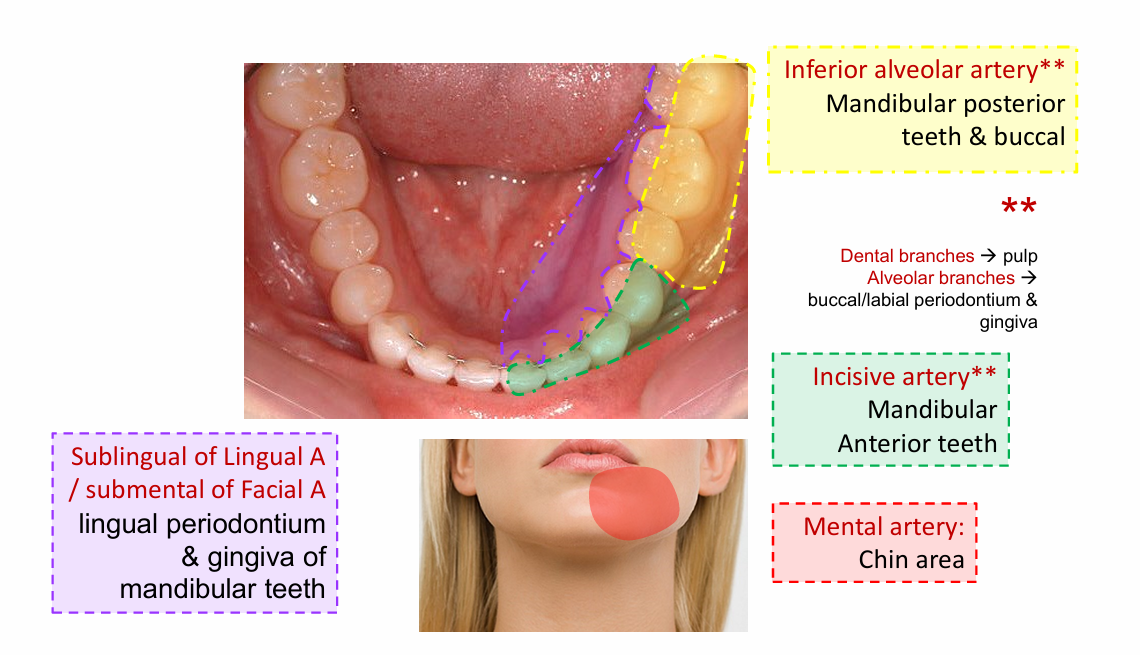
Incisive artery
Mandibular anterior teeth
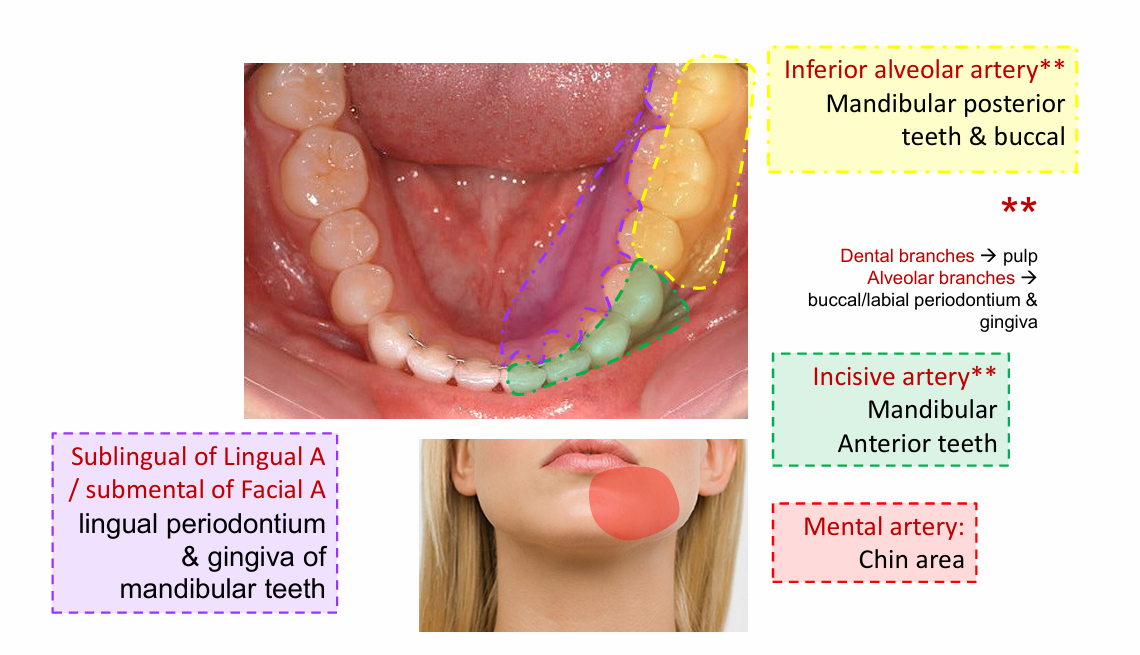
Mental artery
chin area
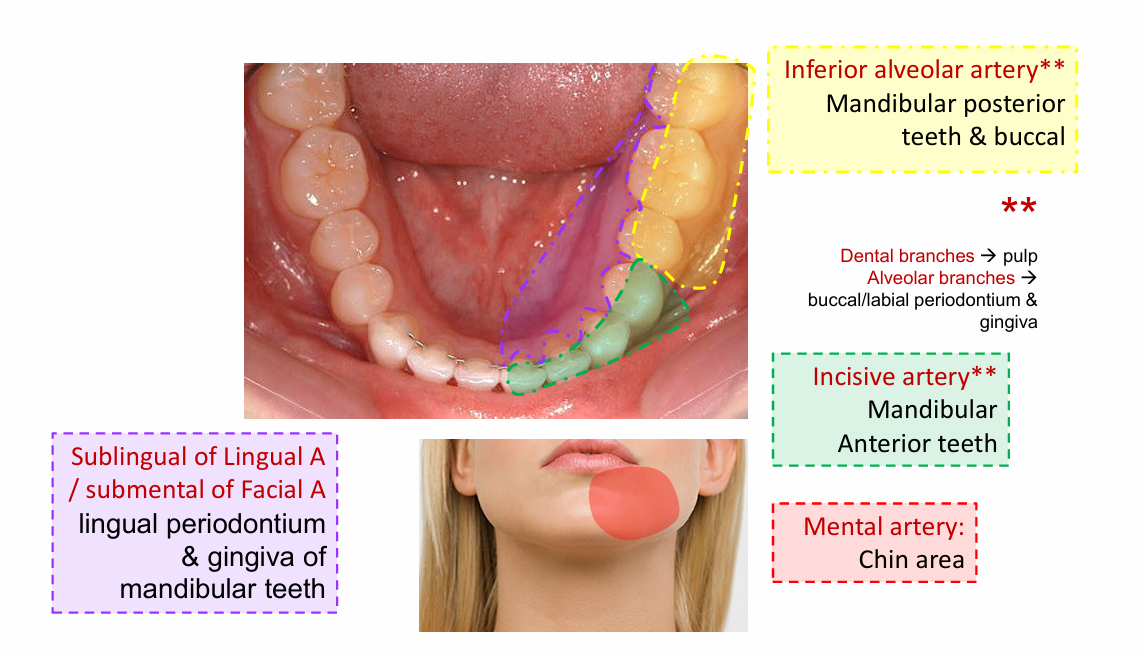
Sublingual of lingual artery
lingual periodontium
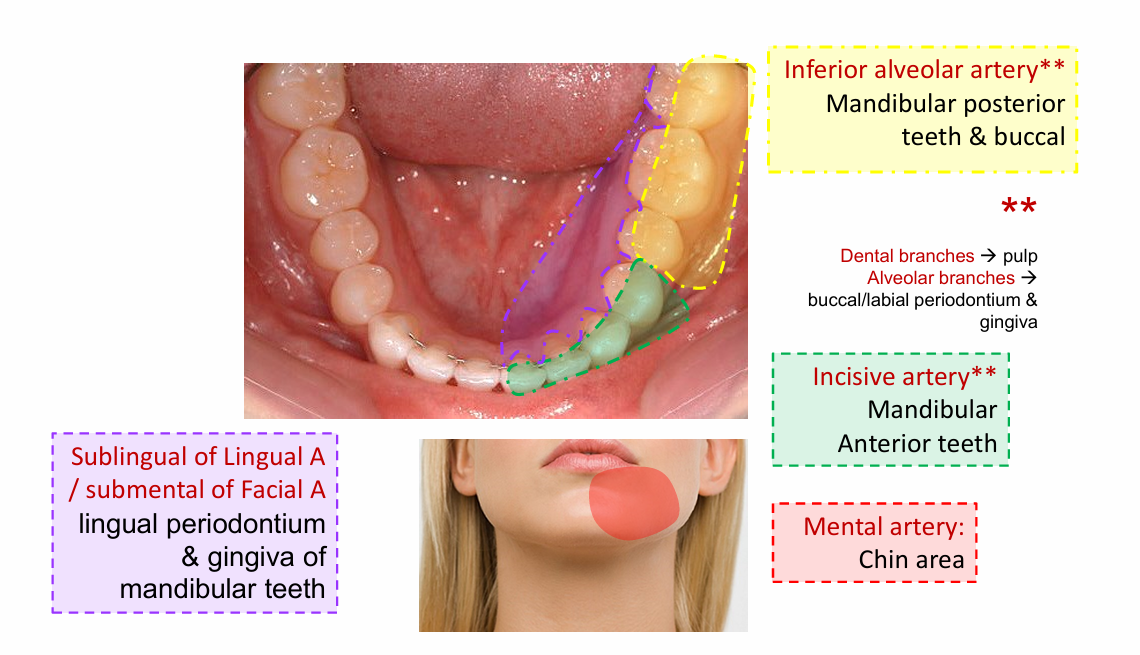
submental of facial artery
gingiva of mandibular teeth
Tongue functions
Speech, mastication, taste, oral cleaning
base (root) of tongue - vertical plane
Posterior 1/3rd - pharyngeal part
attaches to the floor of the mouth
Body - horizontal plane
anterior 2/3rd - oral part
apex of tongue
tip of tongue
lingual papillaes of tongue
fungiform
filiform
foliate
circumvallate
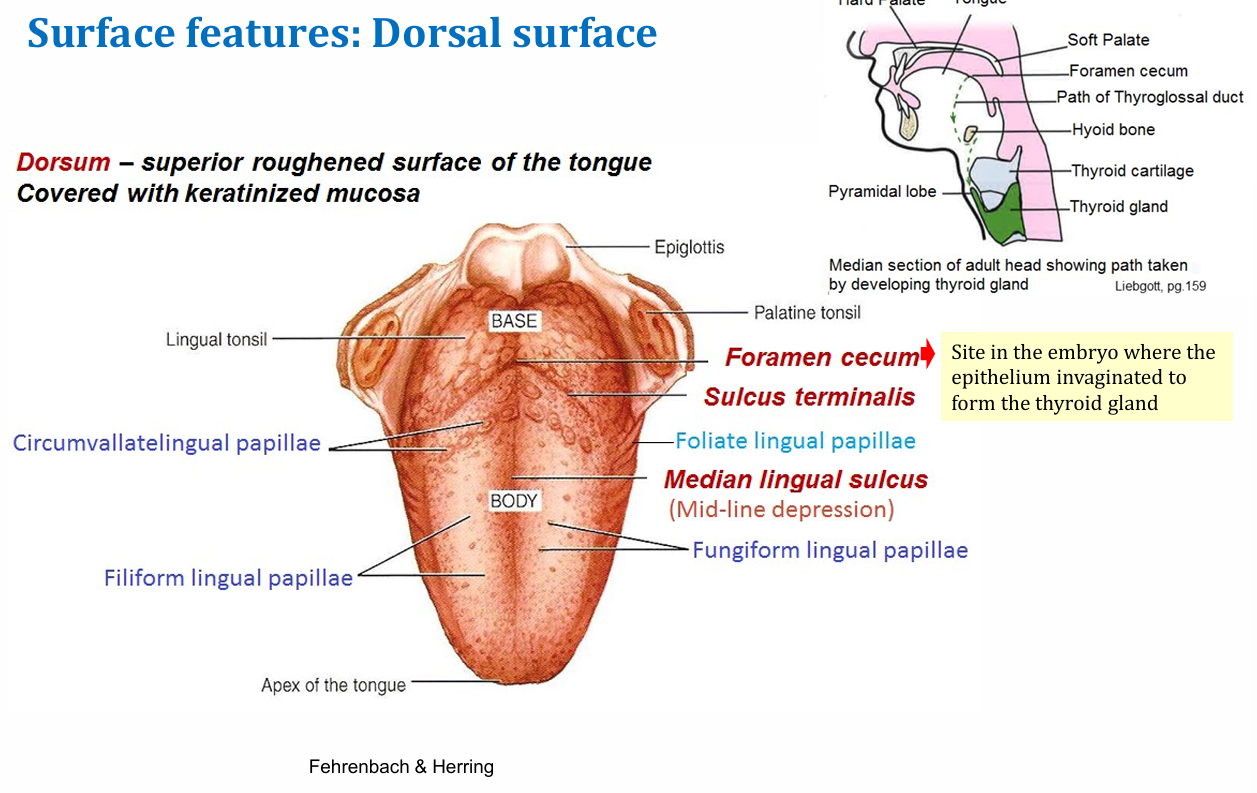
what lingual papillae has no taste buds
filiform LP
Middle line of tongue
Median lingual sulcus
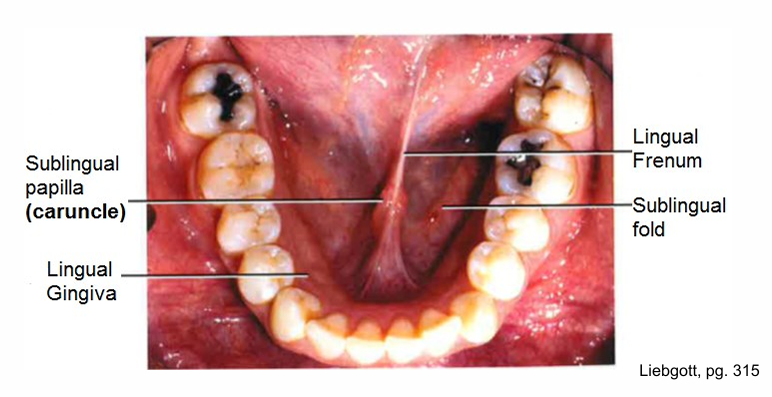
ventral surface of tongue structures
lingual frenum
sublingual caruncle
deep lingual veins
plica fimbriata
intrinsic tongue muscles
vertical, transverse, superior longitudinal, inferior longitudinal
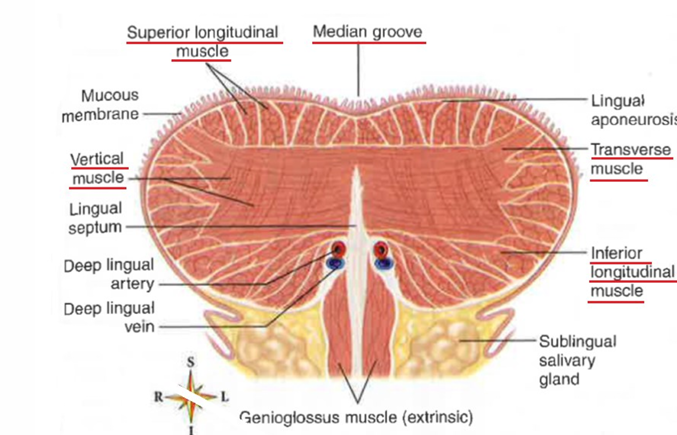
Intrinsic tongue muscle innervation (CN)
Hypoglossal nerve
extrinsic tongue muscles
hyo glossus
Stylo glossus
genio glossus
palato glossus
palatoglossus innervation
Vagus nerve (X)
hyoglossus
genioglossus
styloglossus innervation
hypoglossal nerve
anterior 2/3rd general sensation
Lingual nerve from mandibular division of trigeminal nerve
posterior 1/3rd general sensation
glossopharyngeal nerve, circumvallate and foliate papillae
Anterior 2/3rd taste sensation with fungiform papillae
facial nerve
the most posterior part near the epiglottis
General and taste sensation with the vagus nerve