correlations
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
types of correlation
- correlation illustrates the strength and direction of an association between two or more co-variables (things that are being measured)
- correlations are plotted on a scatter gram
- one co-variable forms the x-axis and the other the y-axis
- each point or dot on the graph is the x and y position of each co-variable
positive correlation
a correlation where as one variable increases, the other also increases, or as one decreases so does the other. Both variables move in the same direction.
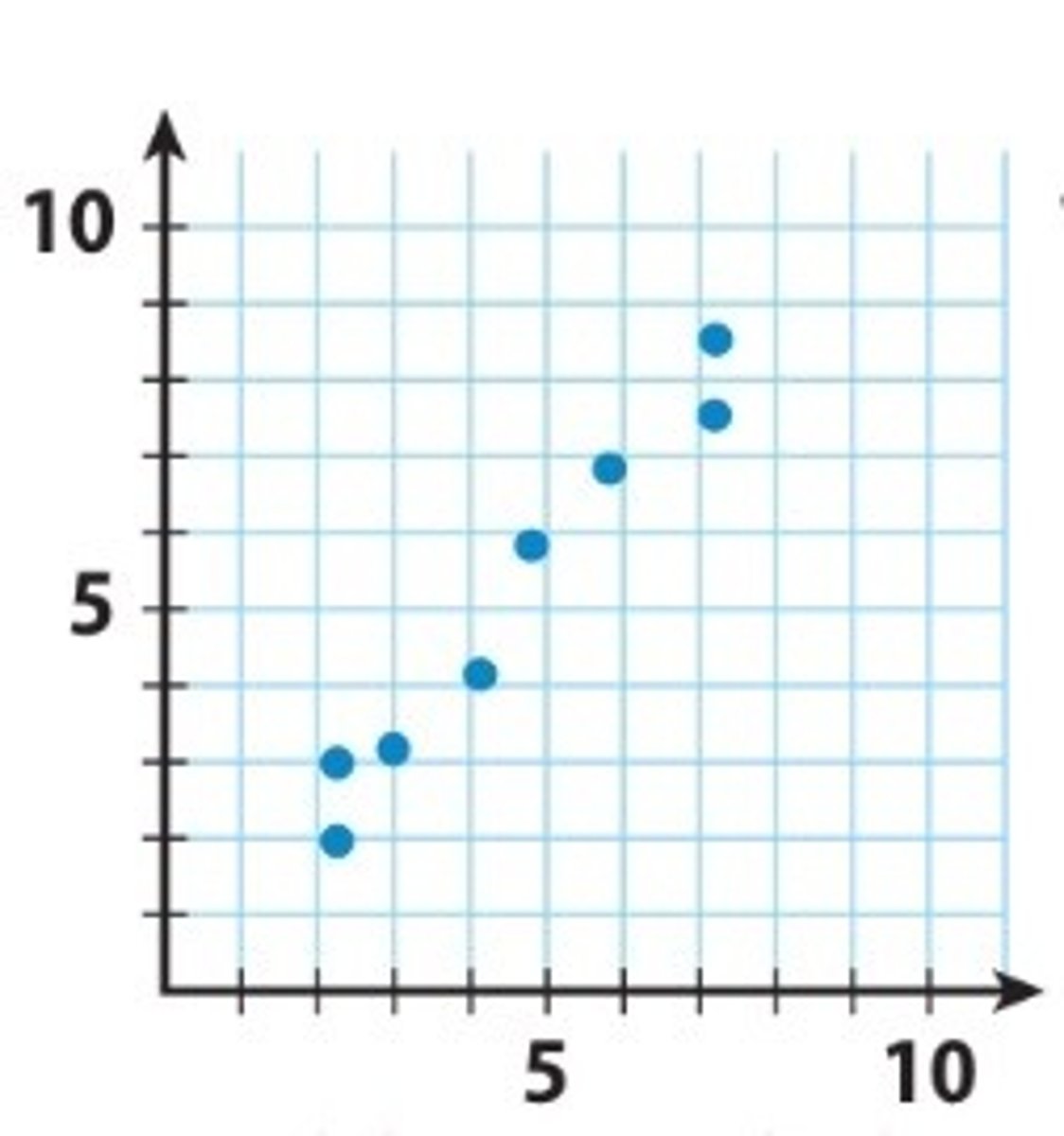
negative correlation
as one variable increases, the other decreases
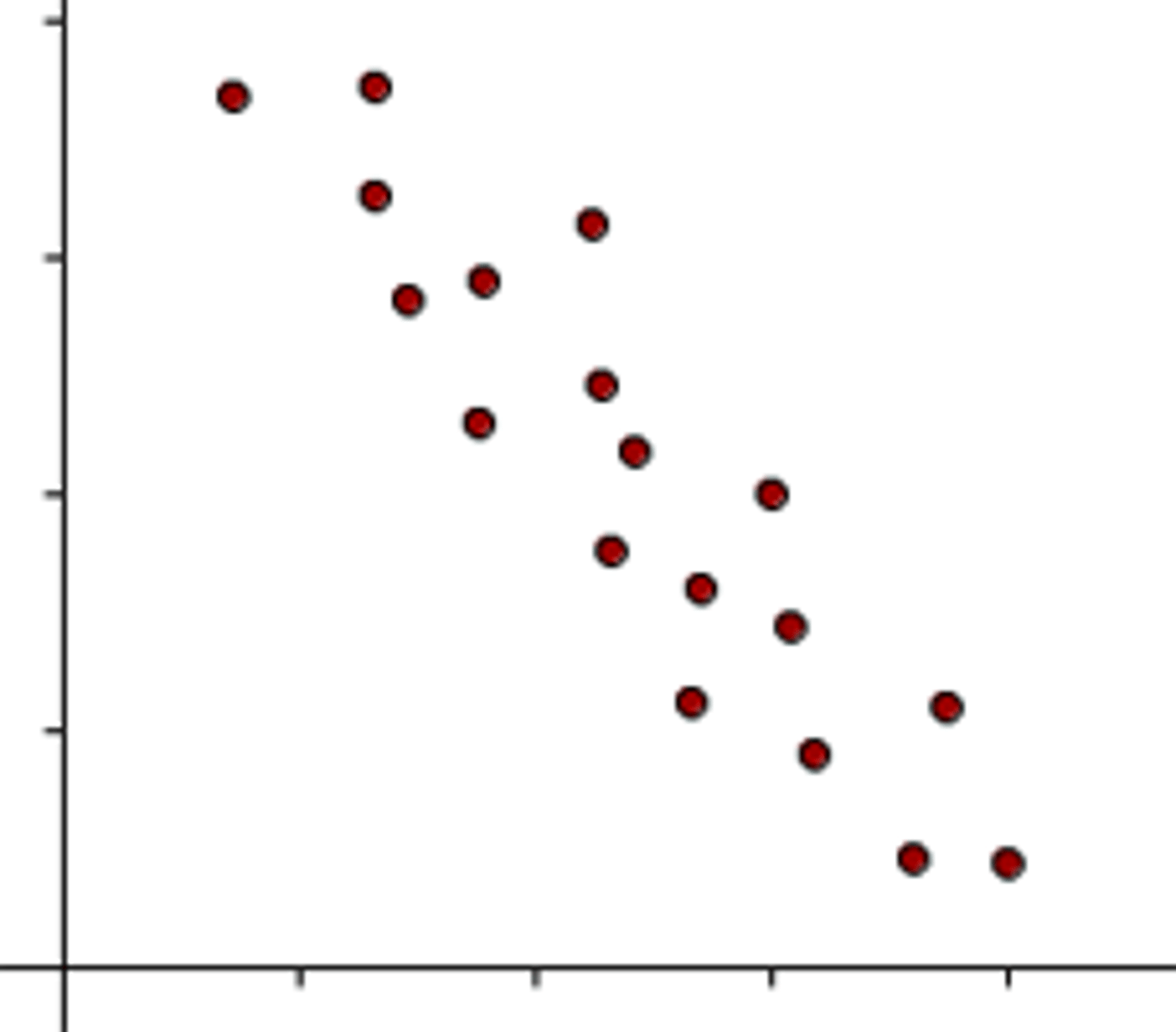
no correlation
close to zero correlation between two variables
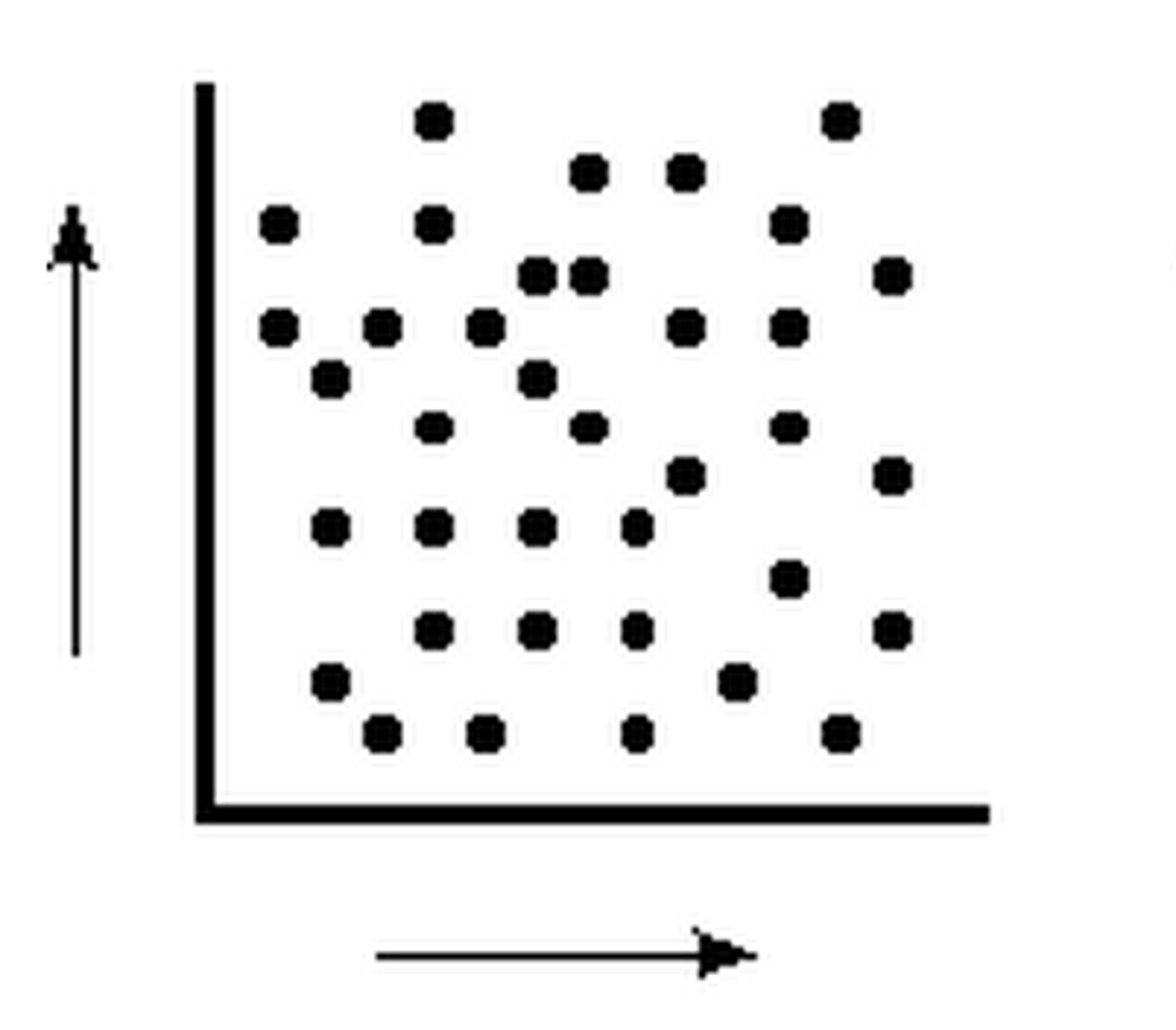
difference between correlation and experiments
- in an experiment the researcher controls or manipulates the iv in order to measure the effects of the dv
- as a result of this deliberate change in one variable, it is possible to infer that the iv caused any change observed in the dv
- in contrast, in a correlation there is no manipulation of one variable so therefore it is not possible to establish cause and effect between a co-variable and another
- even if we found a strong positive correlation between the co-variables we cannot assume one was the cause of another
- the influence of other variables cannot be disregarded, these other variables are known as intervening variables
correlation
a mathematical technique in which a researcher investigates an association between two variables, called co-variables.
co-variables
The variables investigated within a correlation, for example height and weight. They are not referred to as the independent and dependent variables because a correlation investigates the association between the variables, rather than trying to show a cause and effect relationship.
correlation evaluation (+)
- they provide a precise and quantifiable measure of how two variables are related
- used as a starting point before researchers commit to a study
- relatively quick and economical to carry out
- no need for controlled environment and no manipulation of variables, secondary data can be used
correlation evaluation (-)
- cannot demonstrate cause and effect between variables
- intervening variables could effect results
- correlations can be misused or misinterpreted