CHEM2 - Lab Equipment
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
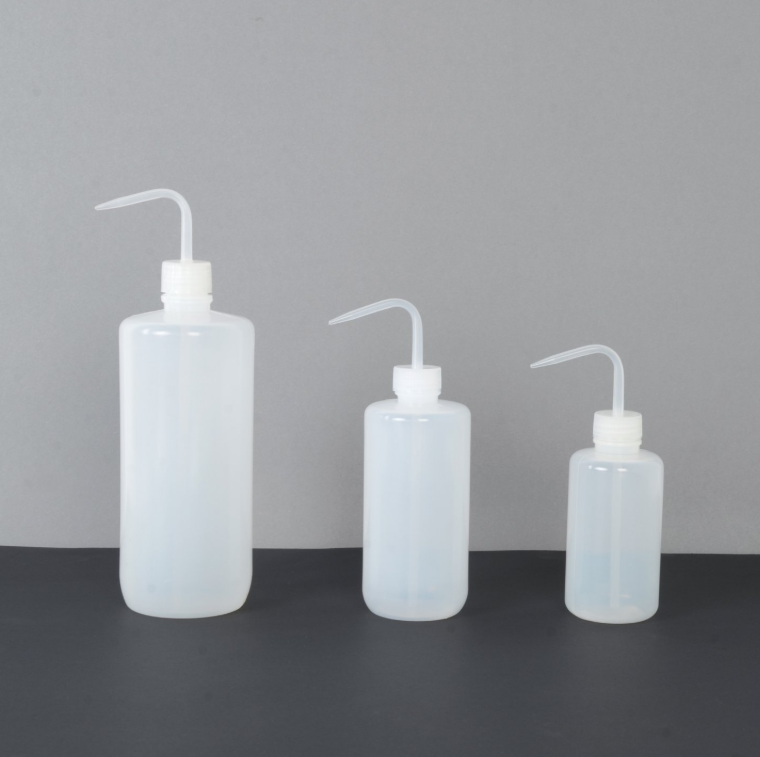
Wash Bottle
Used to rinse various pieces of laboratory glassware such as test tubes and beakers. Usually filled with solvents or distilled water.

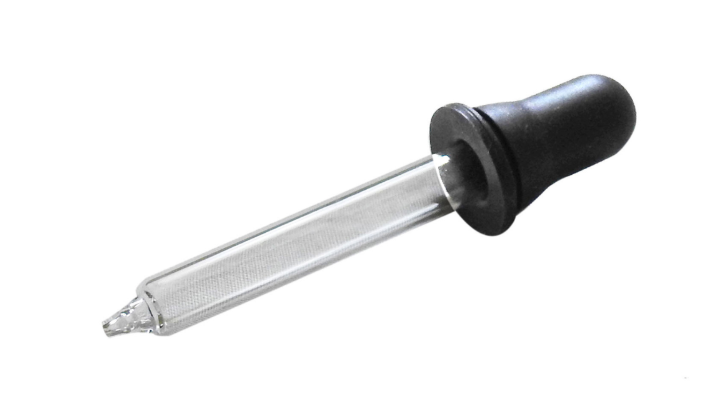
Dropper
Dispenses small amount of liquids, usually drop by drop. Useful for adding reagents or indicators precisely.

Test Tube Rack
Holds multiple test tubes upright for safe storage and organization. Convenient for conducting multiple experiments simultaneously.

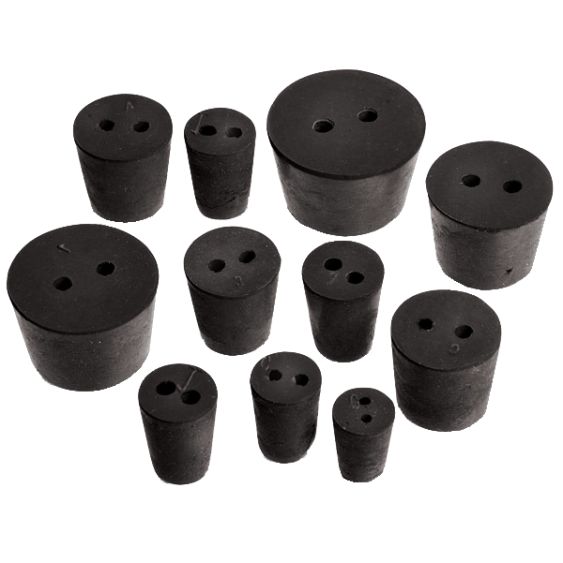
Stopper
Seals the opening of flasks, test tubes, and other containers. Prevents spills and contamination.

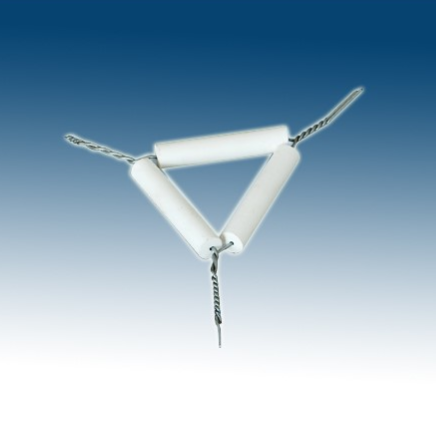
Clay Triangle
Supports crucibles and other objects during heating. Allows for even heat distribution

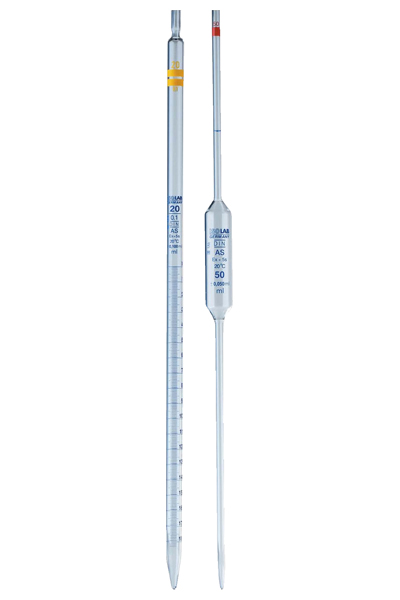
Pipette
Measures and transfers precise volumes of liquids. Available in various types such as volumetric and graduated
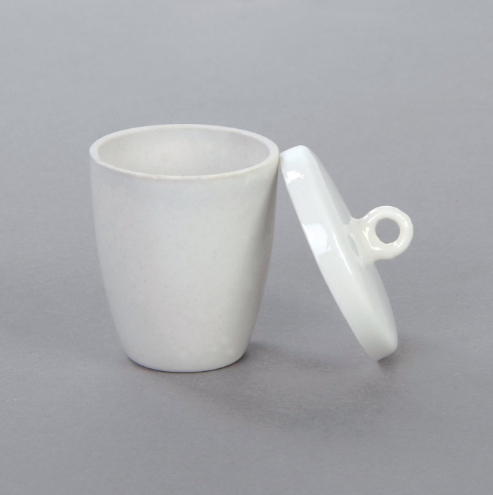
Evaporating Dish
Used to evaporate liquids from solutions, leaving behind a solid residue.

Porcelain Crucible
Heats small amounts of solid substances to high temperatures. Used for processes like melting, calcination, and ignition.

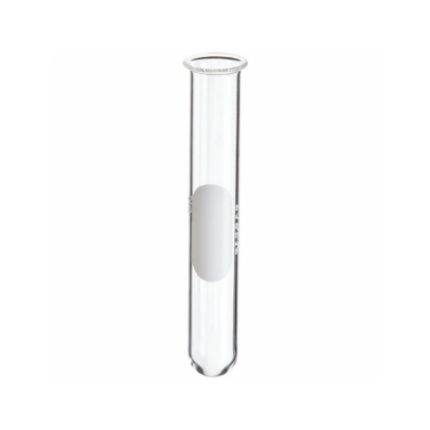
Test Tube
Holds small amounts of liquids or solids for various experiments and reactions. Can be heated, cooled, or mixed.

Beaker
Simple container for mixing, stirring, and heating liquids. Available in various sizes.

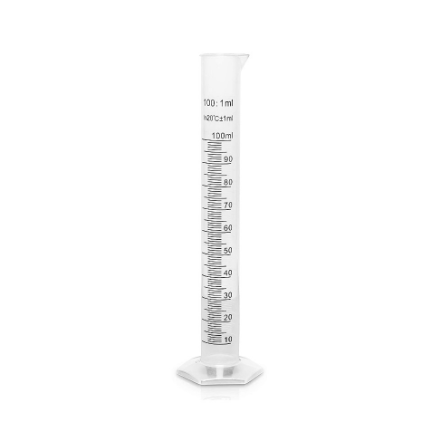
Graduated Cylinder
Measures the volume of liquids. More Accurate than beakers.

Distilling Flask
Separates liquids based on their boiling points through distillation

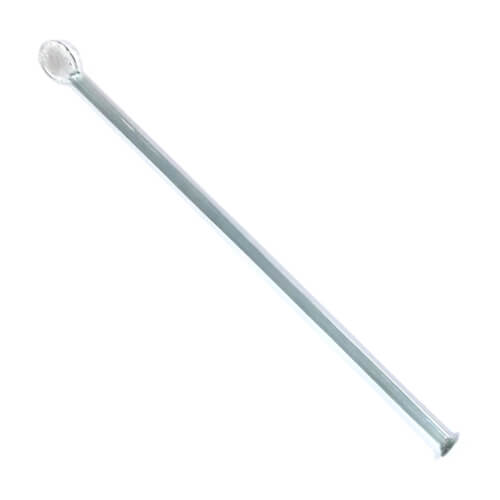
Glass Rod
Stirs and mixes liquids and chemicals. Can also be used to transfer liquids or induce crystallization.

Iron Ring
Supports laboratory apparatus, such as flasks and funnels, on a ring stand.

Universal Clamp
Attaches to a ring stand and holds various laboratory apparatus, such as test tubes and flasks, at different angles.

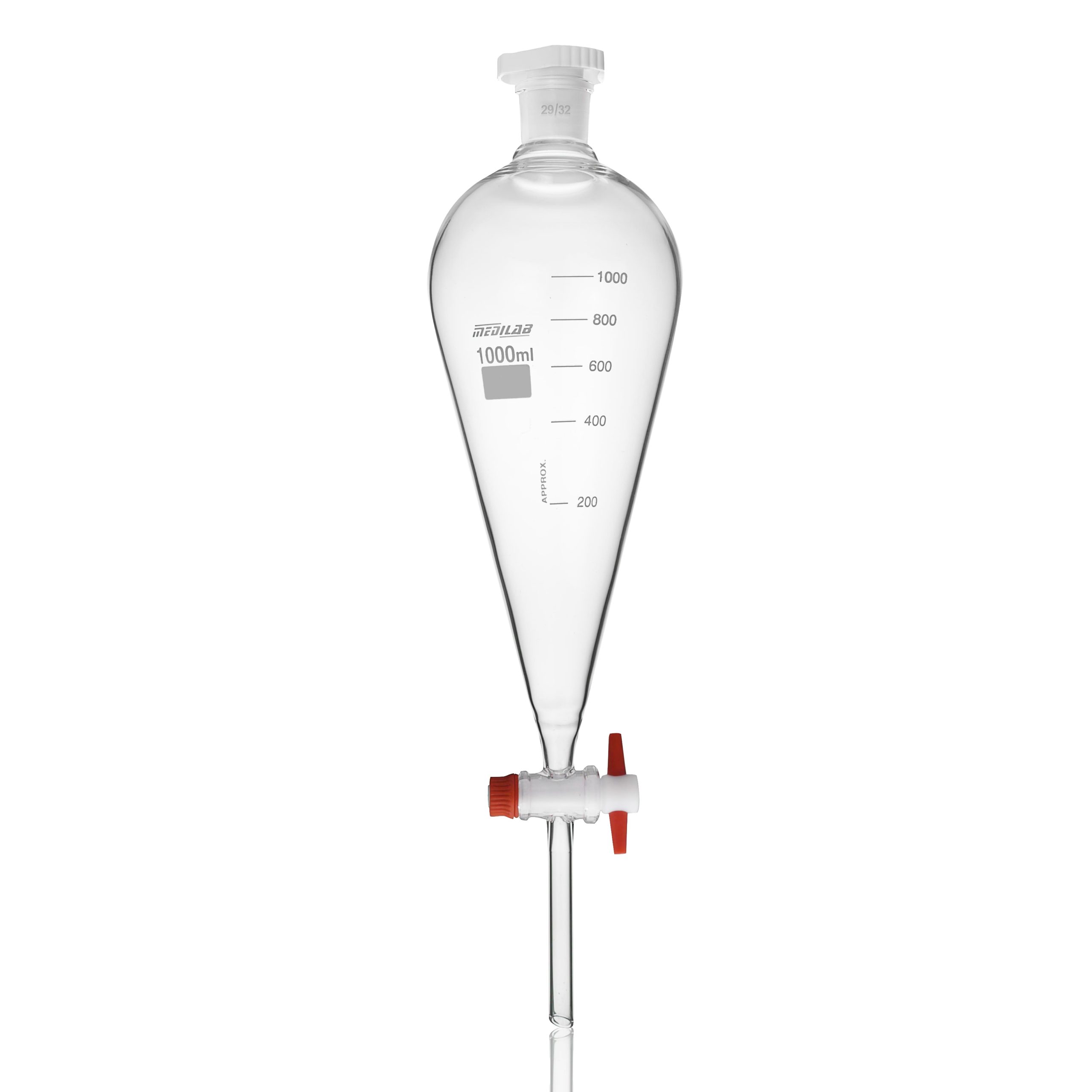
Separatory Funnel
Separates immiscible liquids based on their densities
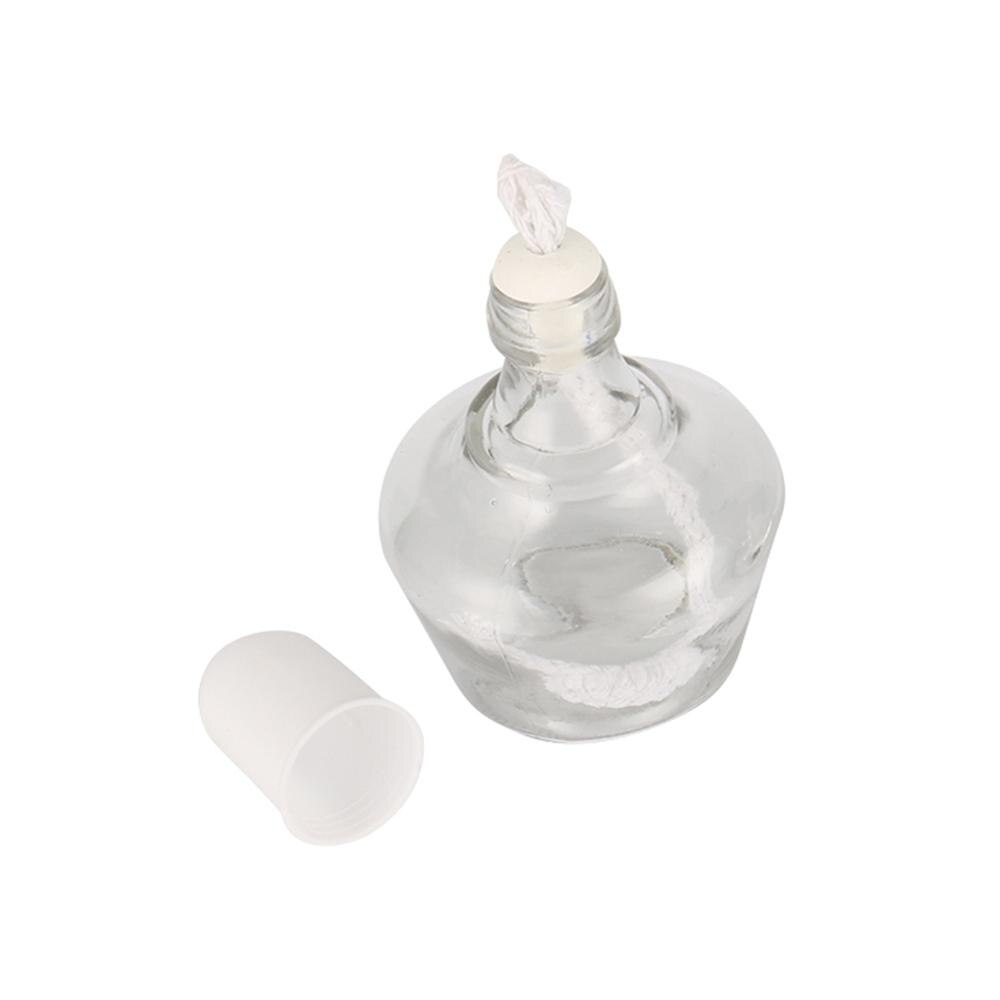
Alcohol Lamp
Provides a heat source for various laboratory processes such as heating, sterilization, and combustion

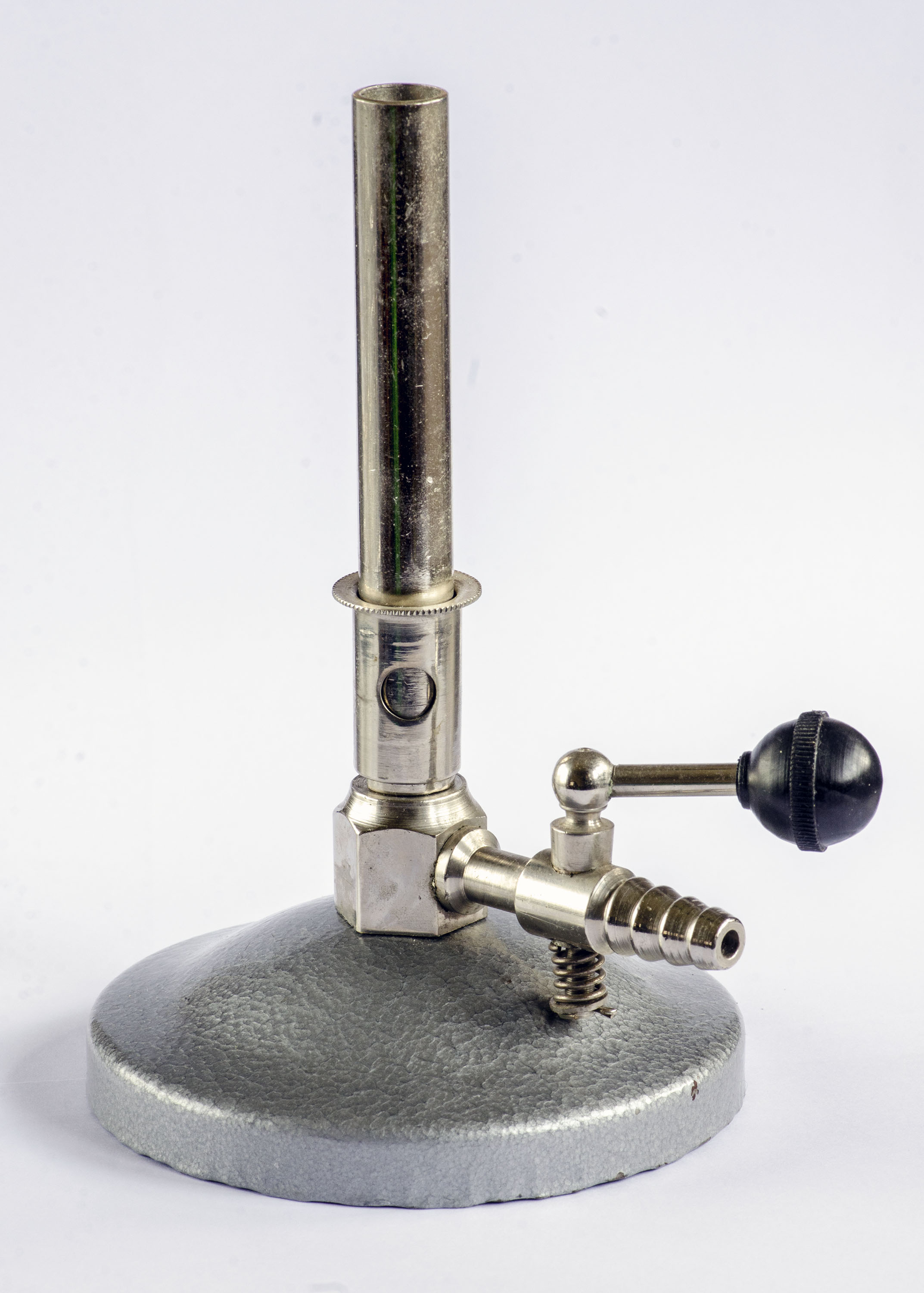
Bunsen Burner
Provides a heat source that can be concentrated and adjustable for various laboratory processes such as heating, sterilization, and combustion.

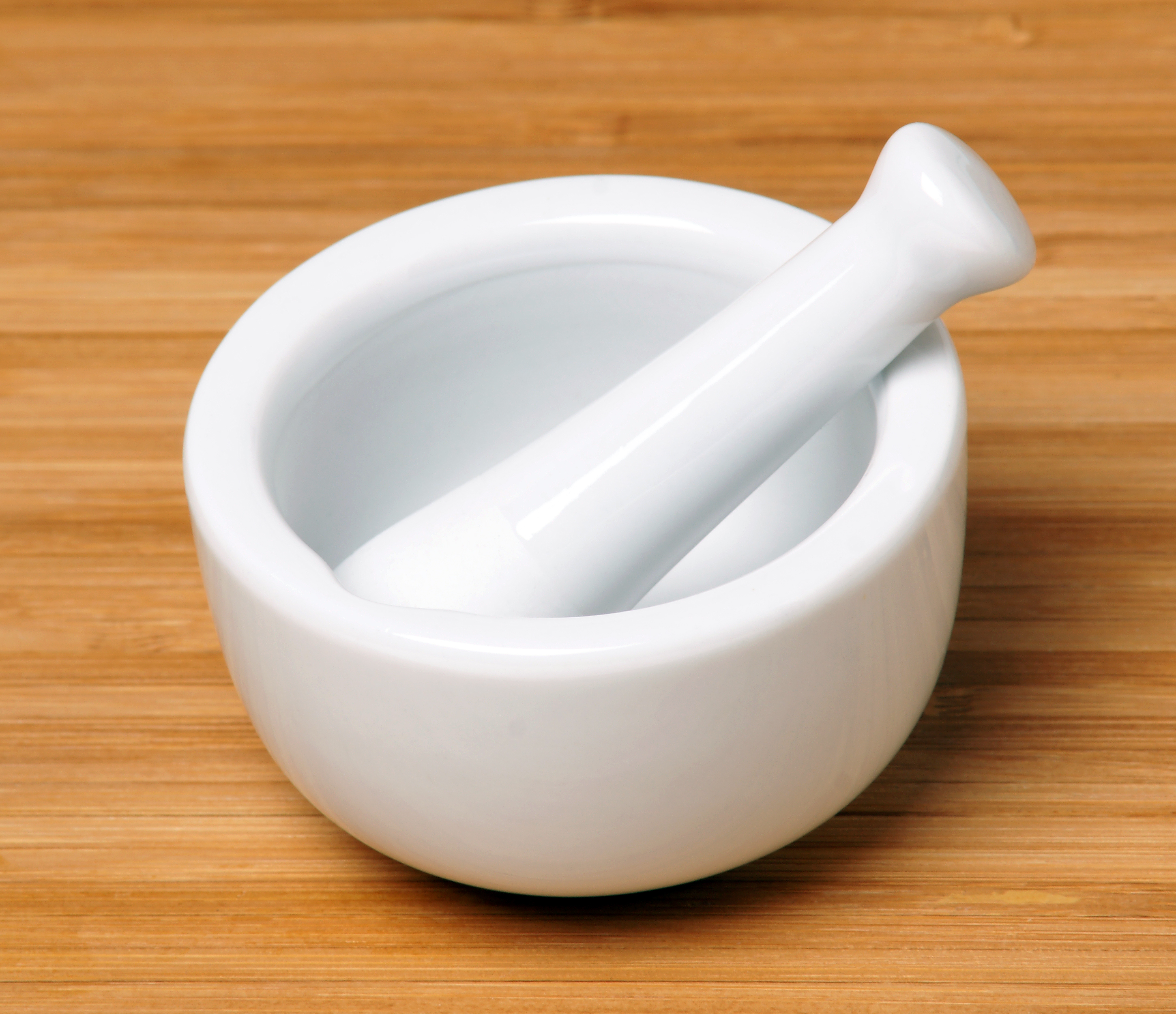
Mortar and Pestle
Grinds and crushes solid substances into powders or small pieces

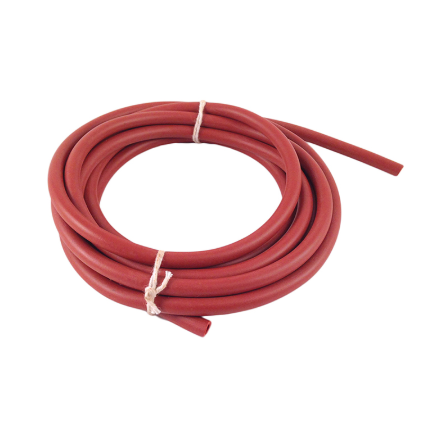
Rubber Tubing
Connects laboratory apparatus such as flasks and condensers. Flexible and resistant to many chemicals.

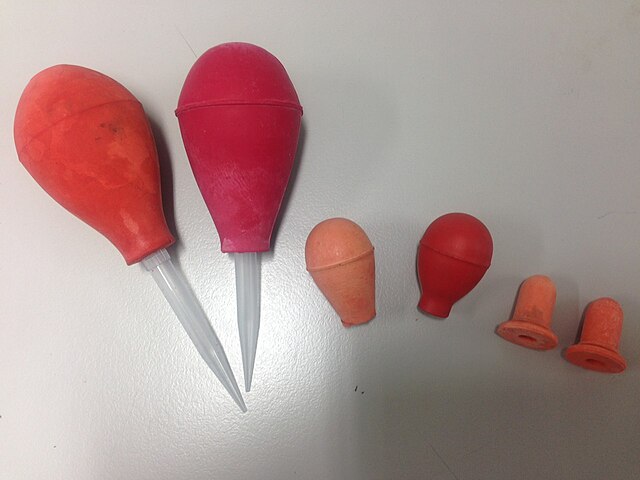
Rubber Bulb Aspirator
Creates a vacuum to draw liquids into pipettes or other apparatus

Burette
dispenses precise volumes of liquids, typically used in titrations.

Reagent Bottle
Stores chemicals and solutions

Test Tube Holder
Holds test tubes during heating or when they are too hot to handle

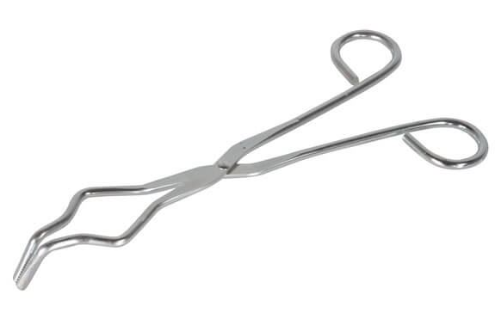
Crucible Tong
Holds and manipulates hot crucibles and other objects.
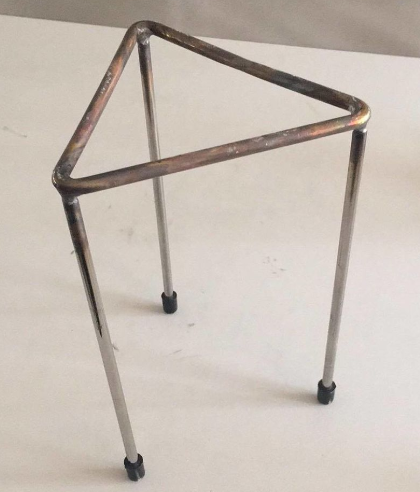
Tripod
Supports objects such as beakers and flasks, during heating

Wire Gauze
Provides a flat surface for heating objects on a tripod. Distributes heat evenly.

Watch Glass
Holds small amounts of solids or liquids. Can also be used as a cover for beakers

Volumetric Flask
Prepares solutions with precise volumes

Erlenmeyer Flask
Used for mixing, heating, and storing liquids. Its conical shape prevents spills.

Florence Flask
Holds liquids, often used for boiling. Round bottom allows for even heating

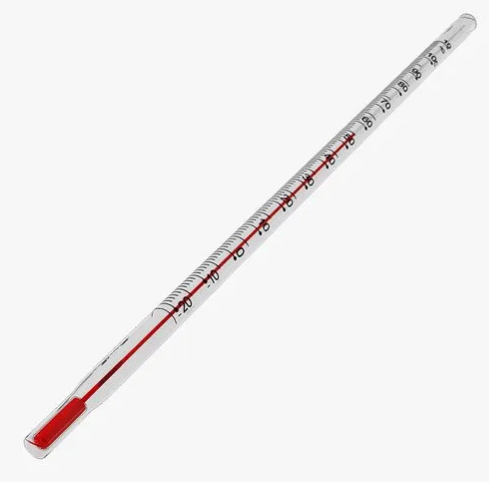
Laboratory Thermometer
Measure the temperature of liquids and solids.
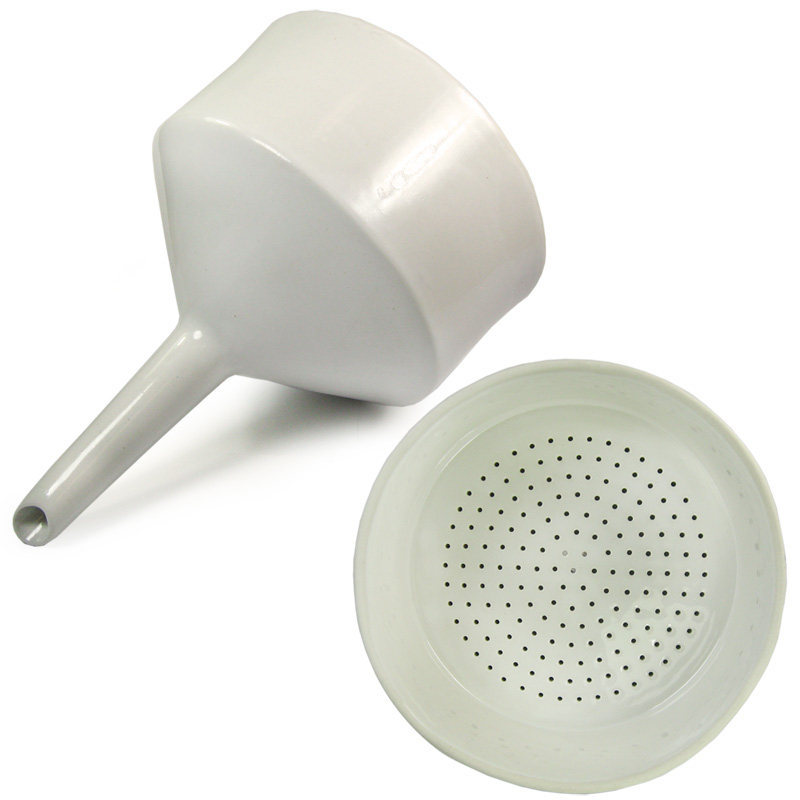
Buchner Funnel
Used for vacuum filtration to separate solids from liquids.

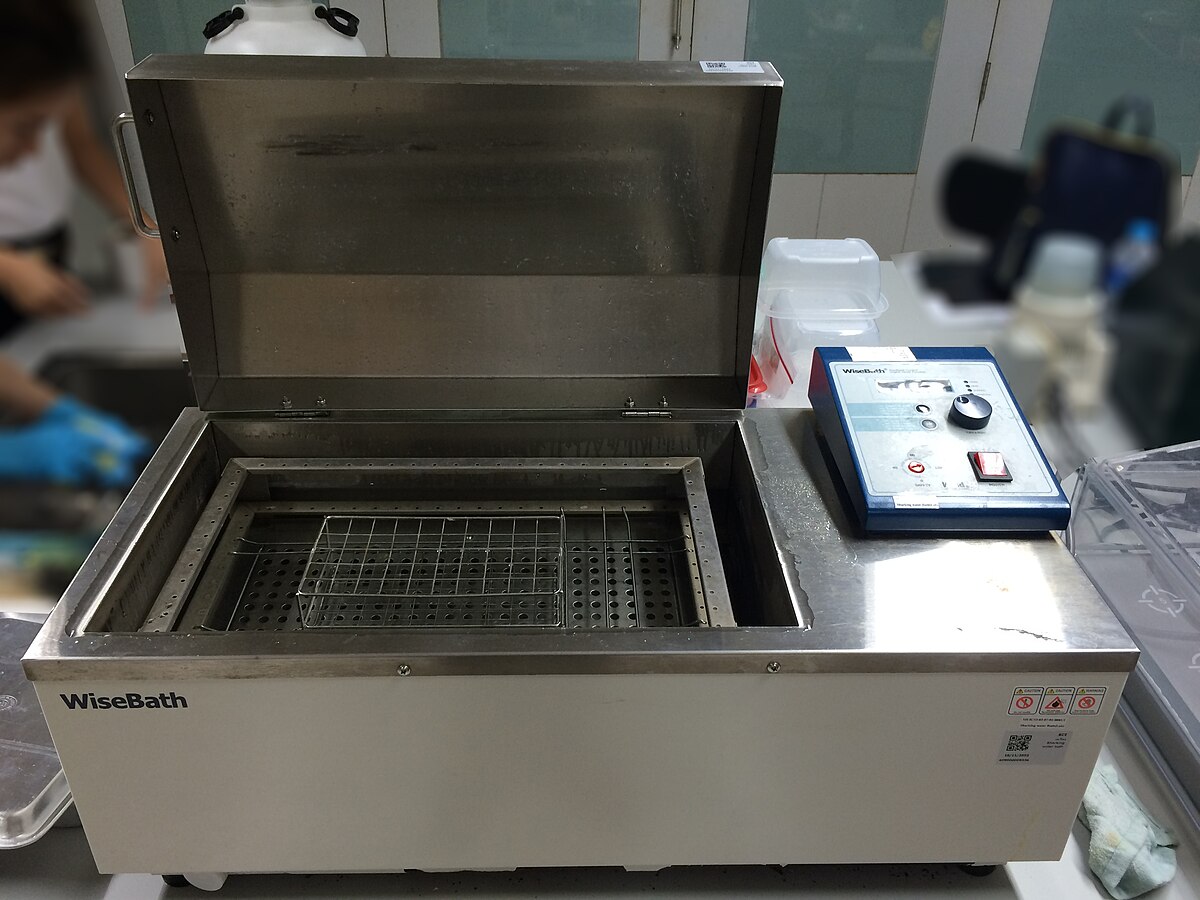
Water Bath
Provides a controlled temperature environment for heating or incubating samples

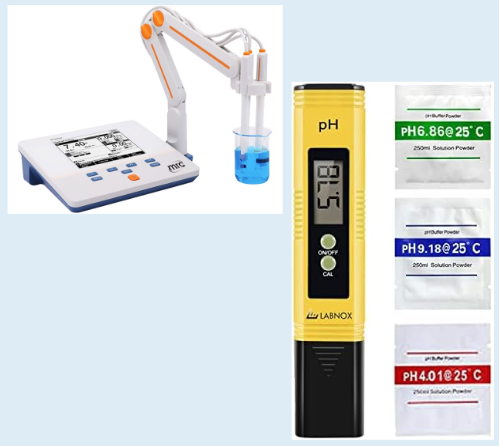
pH Meter
Measures the acidity or alkalinity (pH) of a solution.

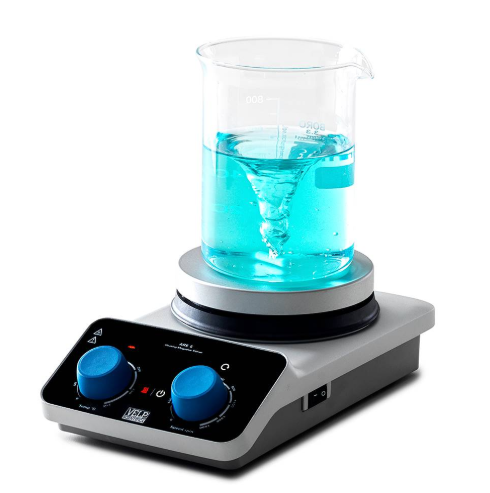
Hot Plate with Stirrer
Heats and stirs liquids simultaneously. The stirrer looks like a capsule

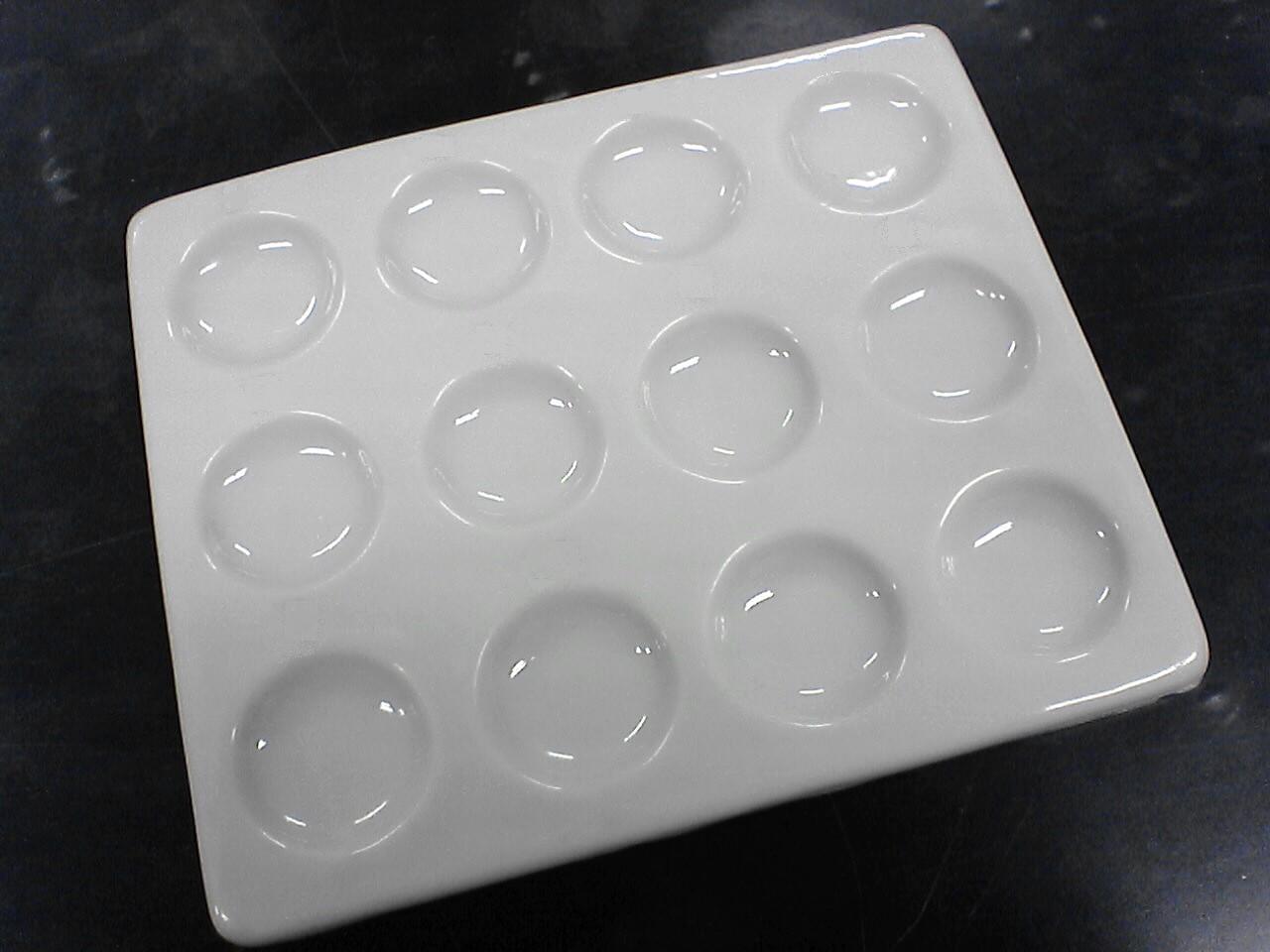
Spot Plate
Has multiple small wells for performing small-scale reactions or tests.

Spatula
transfers solids, particularly powders and crystals
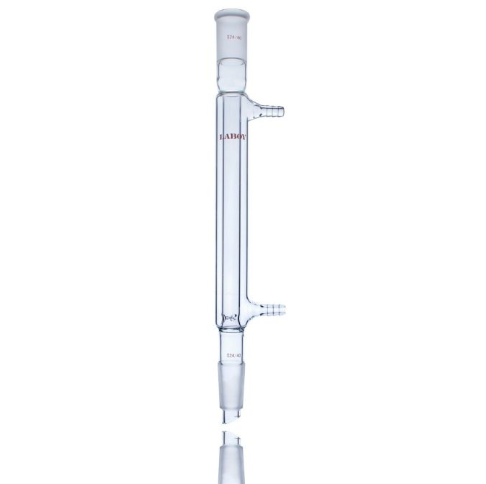
Distillation Condenser
Cools down generated vapours and convert them back into the liquid form in a distillation setup.

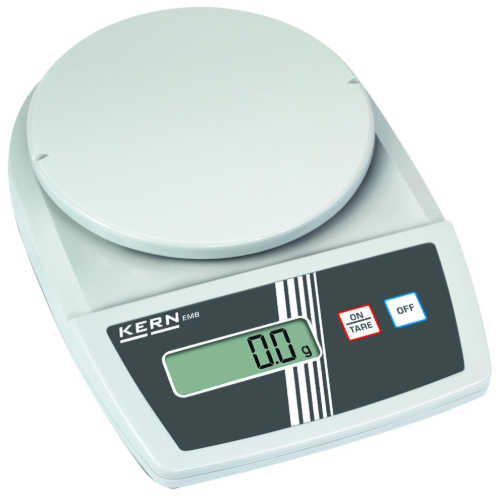
Electronic Weighing Scale
Measures the weight or mass of an object

Calorimeter
Measures the heat transfer associated with chemical reactions or physical changes.

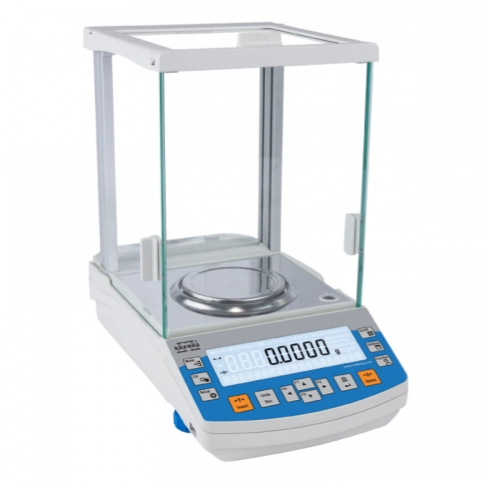
Analytical Balance
Measures the mass of very small samples with high accuracy and precision.

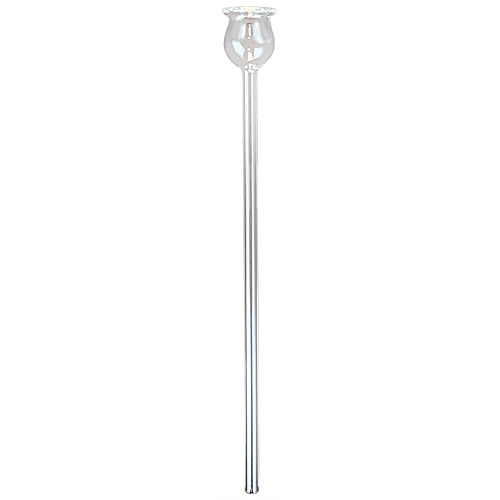
Thistle Tube
A long, slender tube with a bulb-shaped reservoir at the top, used for adding liquids to a reaction vessel or apparatus. The thistle tube allows for controlled addition of liquids, preventing spills or rapid reactions. It is often used in chemistry experiments involving gas generation or titration.

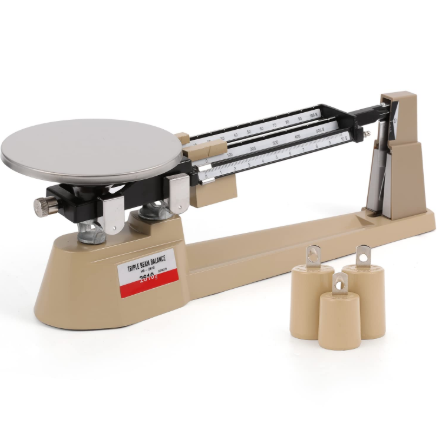
Triple-Beam Balance
A mechanical balance used to measure the mass of objects. It consists of a beam with three sliding weights (riders) that can be adjusted along calibrated scales.

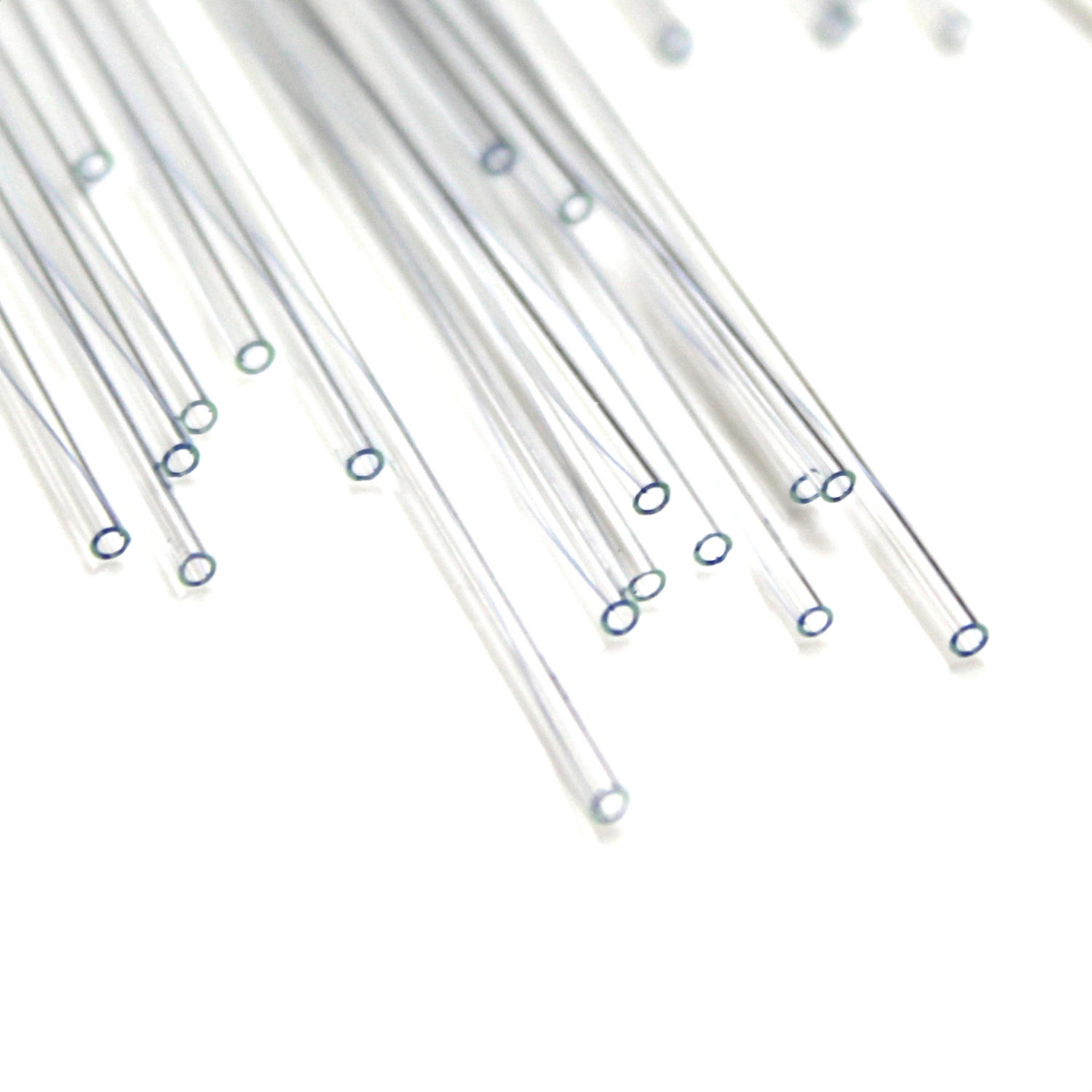
Capillary Tube
Narrow bores used for tasks such as measuring melting points, observing capillary action, or performing micro-scale experiments.
