GIT Histology
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
The goal of the GIT CAL is for the students to familiarize themselves with the overall histology of the GIT and to be able to identify some key histological features of the major tissues in this important physiological system. Please see the video below for instructions on how to engage with the CAL material.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms

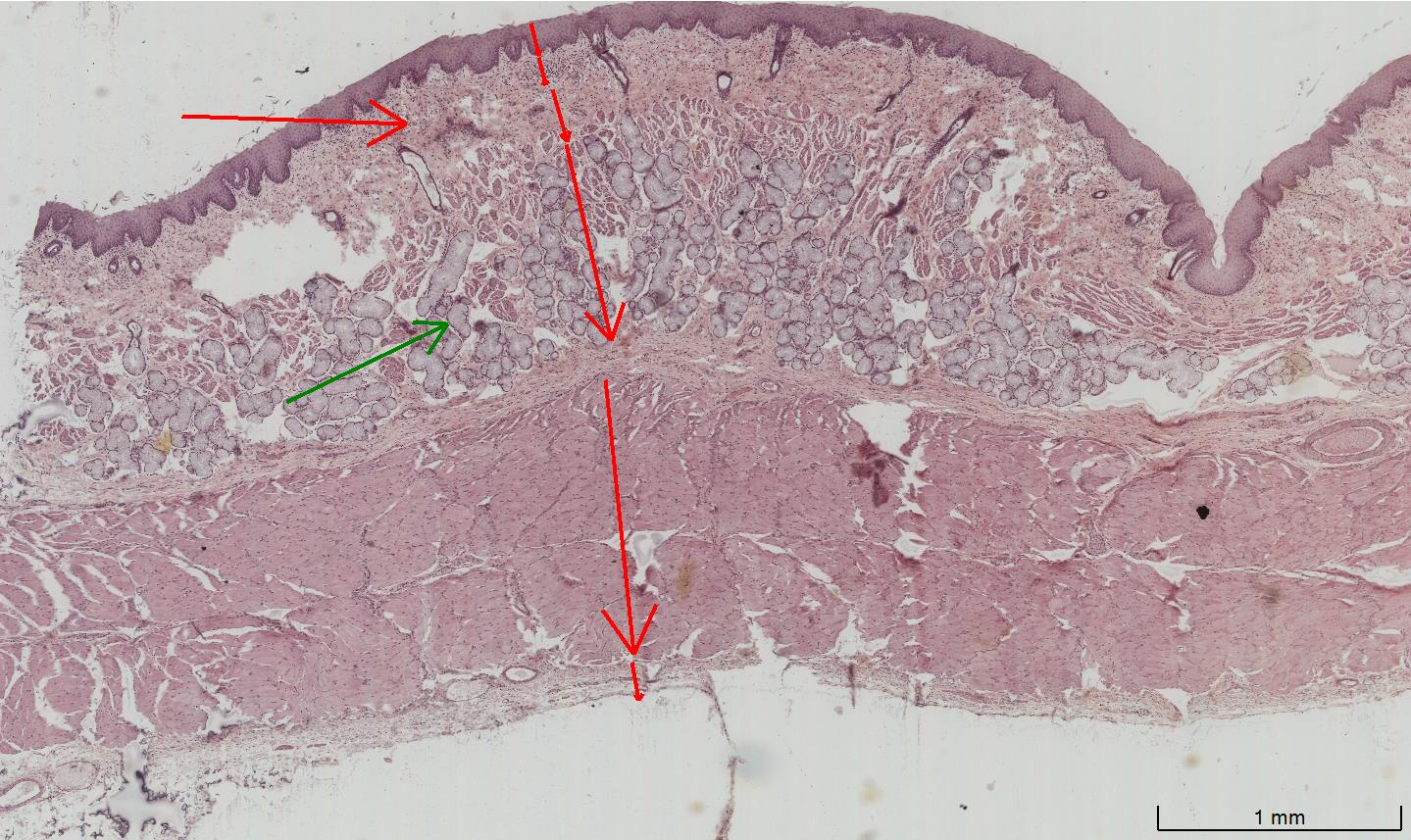
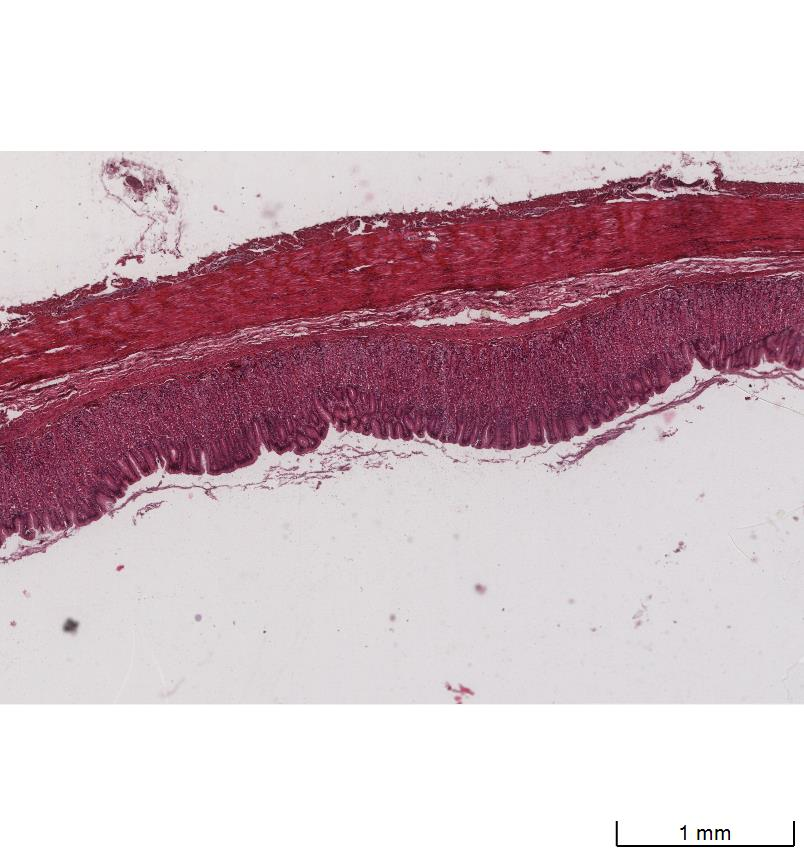
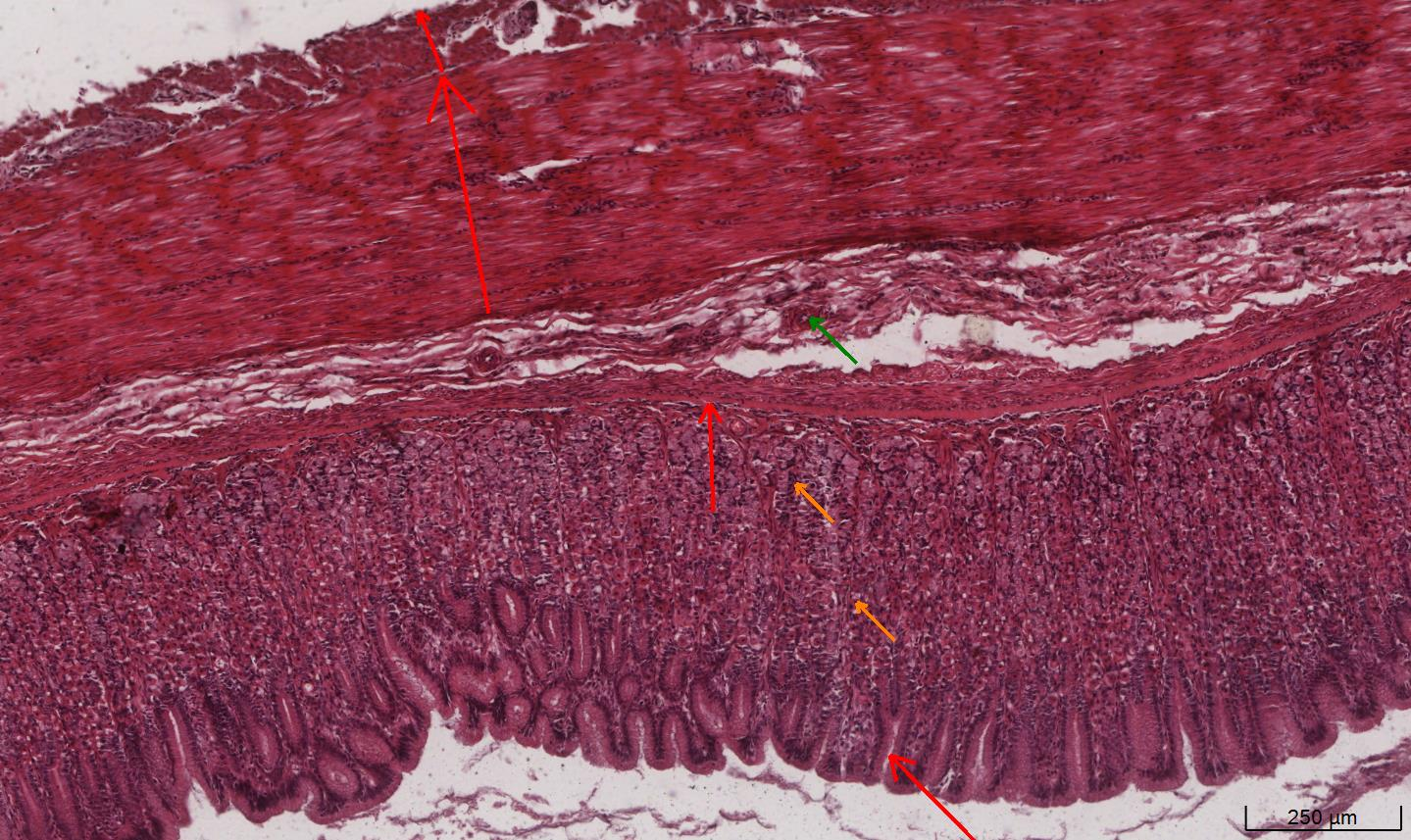
Oesophagus
Mucosa
Epithelium, lamina propria below and the muscularis mucosa (if present)
Non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
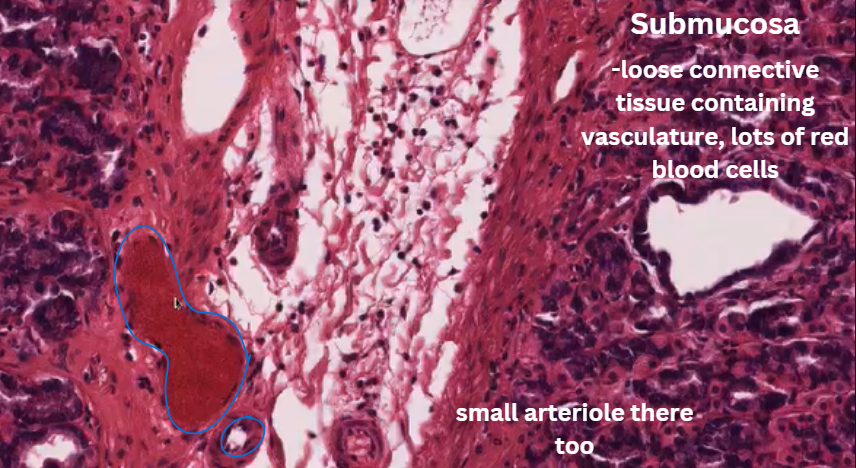
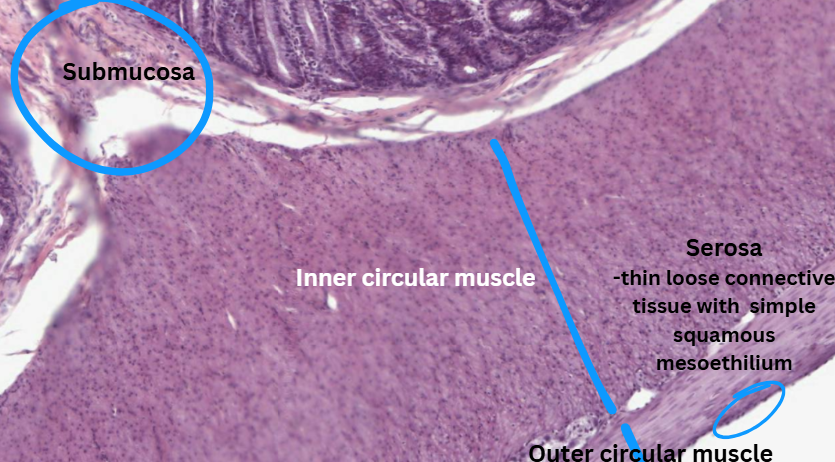
Submucosa
The area below the mucosa
Contains small mucous secreting cells, vascular supply and innervation.
Muscularis externa
Muscle layers
Has different composition depending on its location within the oesophagus.
Top = skeletal muscle
Middle = smooth and skeletal muscle
Bottom = smooth muscle
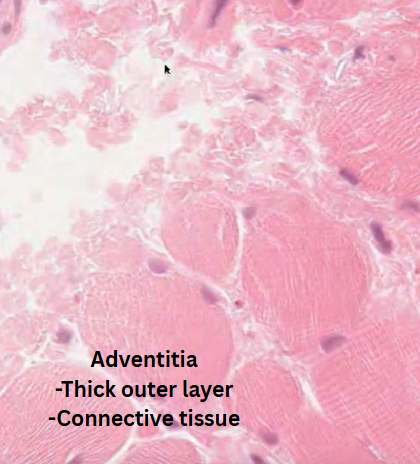
Adventitia
Outer connective tissue layer
The outer layer of the organ is called serosa which is a thin layer of loose connective tissue with a simple squamous mesothelium e.g. stomach
Stomach
Fundus
Surface mucosal cells
Parietal cells → fried egg shape/pyramidal. Cells can be found mid way down the gland. = HCl
Chief cells → These can be found in the bottom third of the gland. = Pepsinogen producing cells
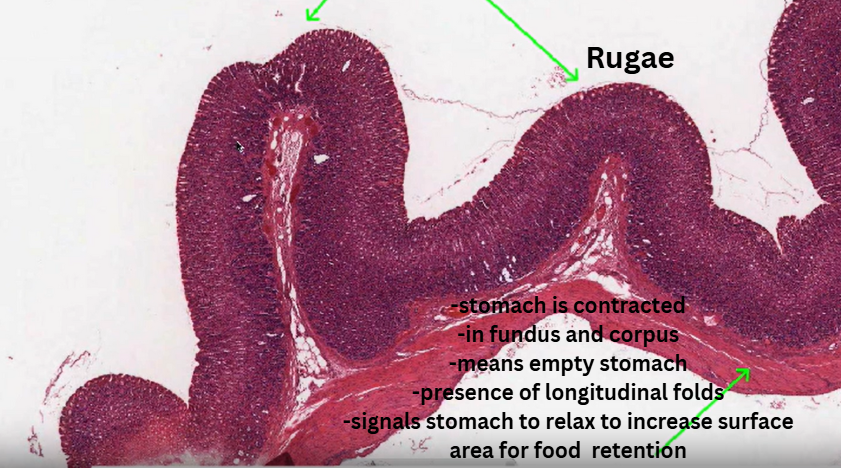
Rugae
Folds; presences of contracted stomach = on an empyt stomach.
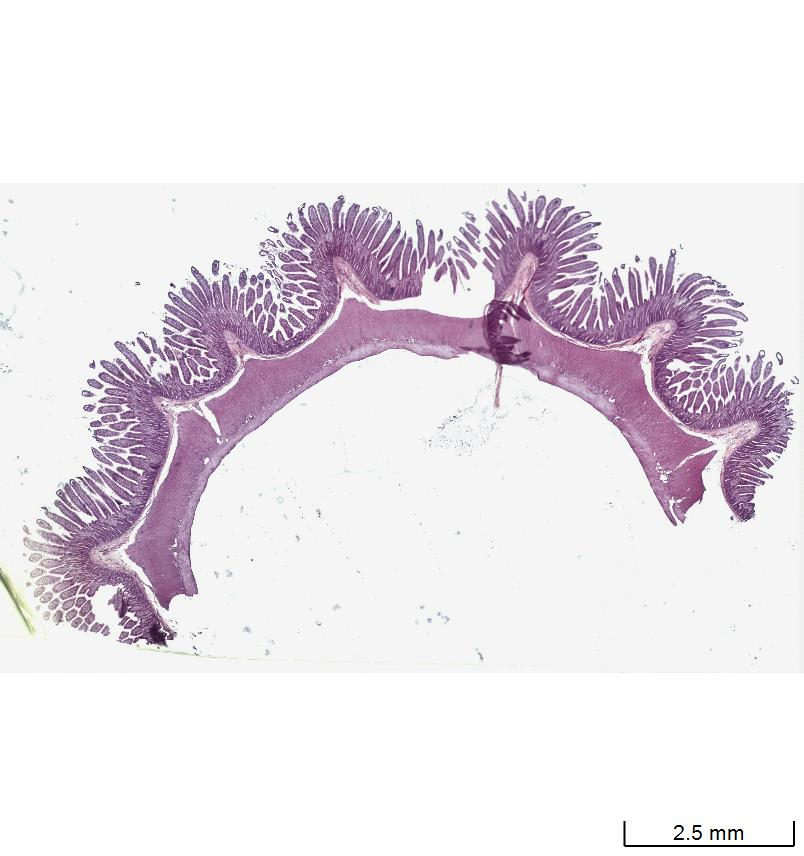
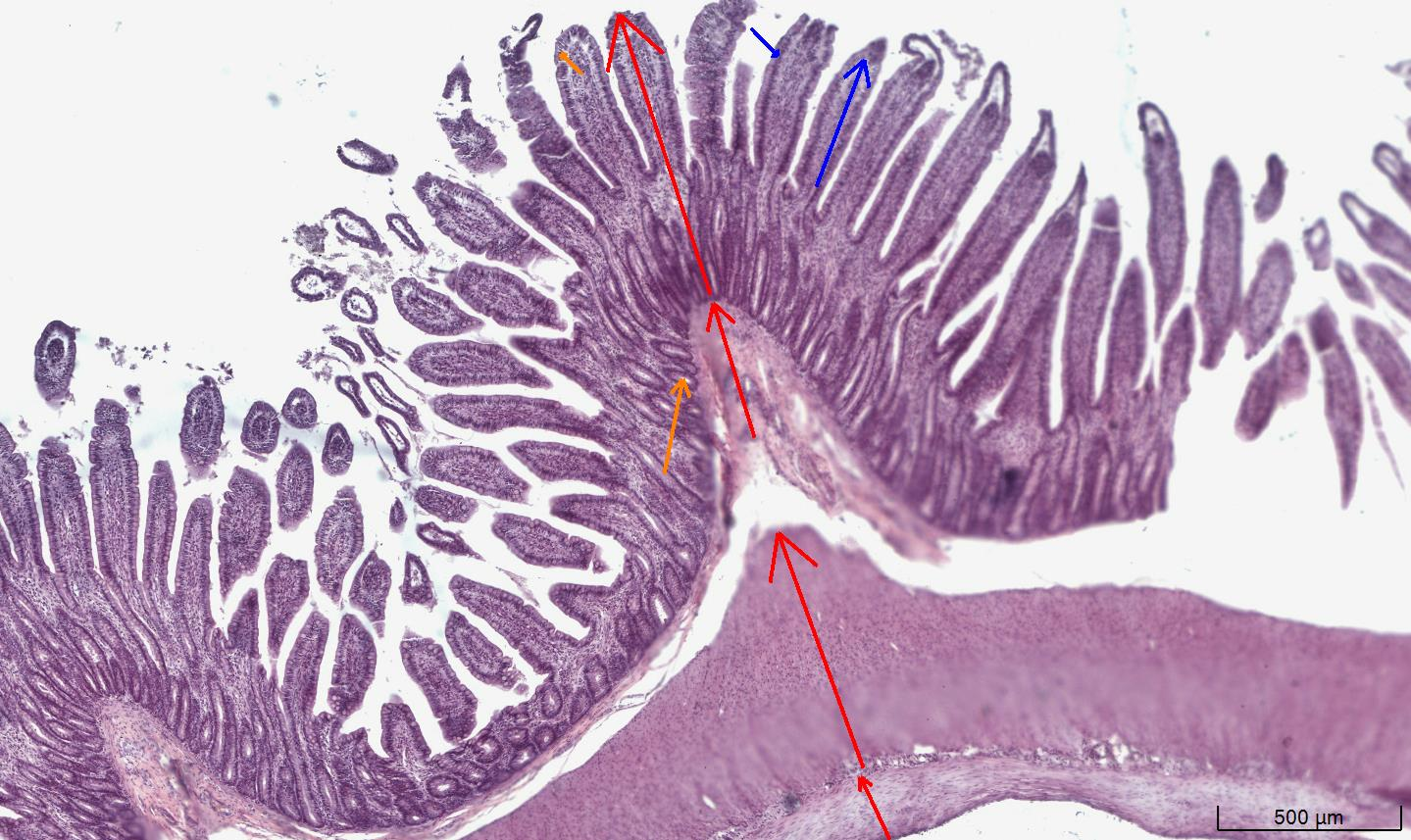
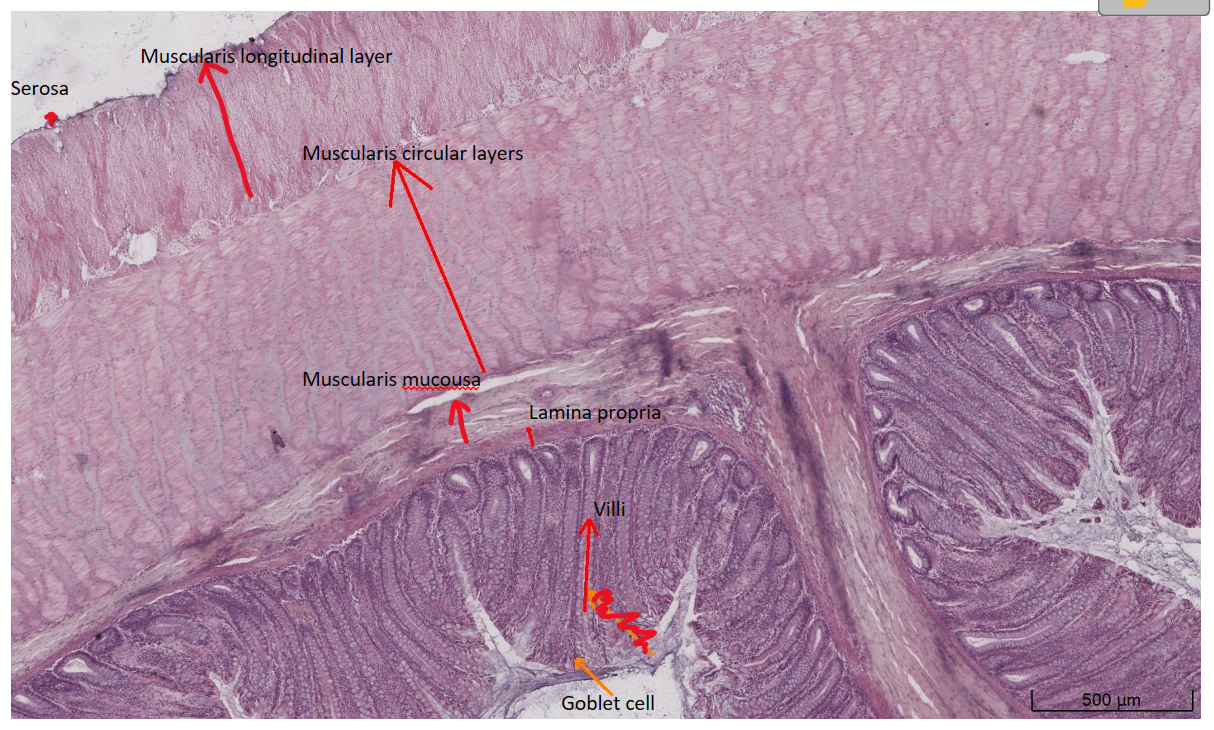
Small intestine
Jejunum
Plica circularis → outfolds of tissue
Villus → hundred villi on a songle plica circularis
Enterocyte →
Crypt of Lieberkühn →
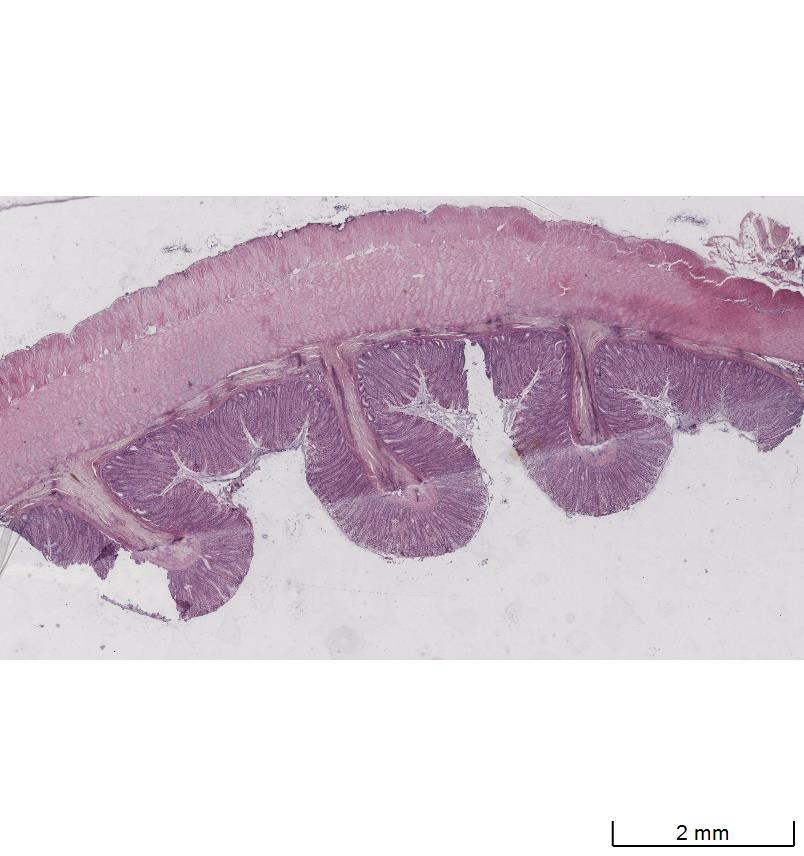
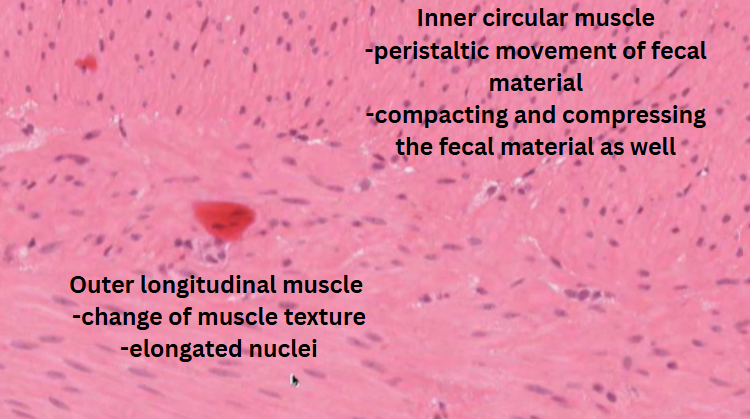
Large intestine
Colon
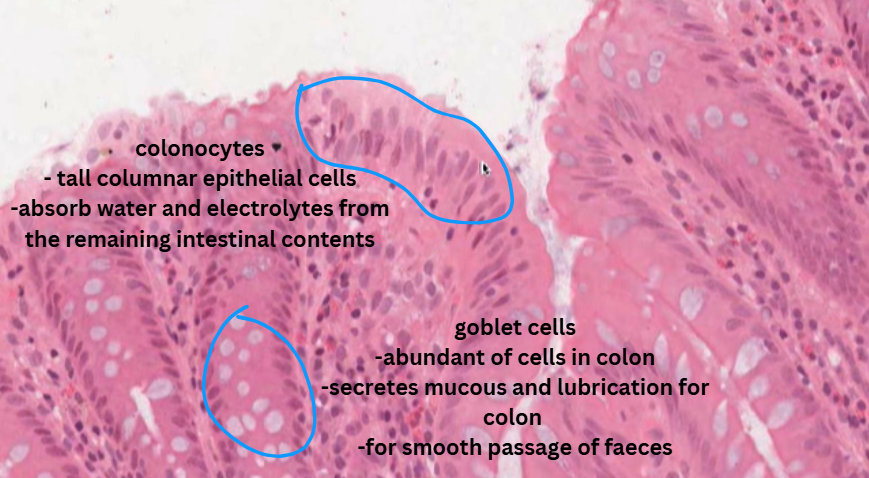
Colonoic epithelial cell or colonocyte → protection from luminal contents of the colon (faeces, bateria etc). Columnar epithelial cells
Lamina propria → has lumphoid cells and sometimes lymphoid aggregates.
Muscularis mucosa → state of agitation and movement
Crypt/Colonic gland
Myenteric ganglion
Colonocyte
Goblet cell → lubricative and protective function.
![<p>I. Oesophagus GIT video tutorial [4 main layers]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/b4435e2a-0481-4637-a921-1df1bc859008.png)
I. Oesophagus GIT video tutorial [4 main layers]
Mucosa
Submucosa
Muscularis externa
Adventitia
Mucosal specialization in particular here
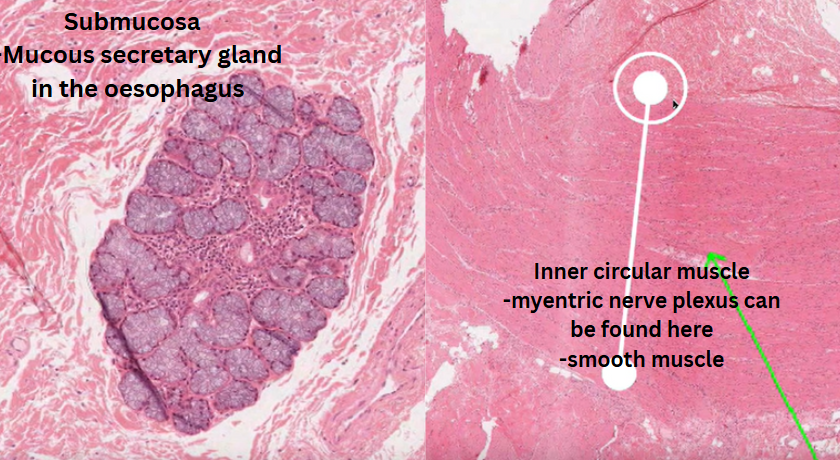
![<p>II. Oesophagus GIT video tutorial [4 main layers]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/f68e77d6-89f3-4bd9-b312-ff648f558b4b.png)
II. Oesophagus GIT video tutorial [4 main layers]
Mucosa
Submucosa
Muscularis externa
Adventitia
Mucosal specialization in particular here
![<p>I. Stomach GIT tutorial video [4 main layers]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/f1fdcc83-73b2-46dc-bf22-010fc656d6d2.png)
I. Stomach GIT tutorial video [4 main layers]
Cardia
Fundus
Corpus
Pylorus
Secretory mucosa: acid and mucosa producing
Parietal cells
Chief cells
Gastric pits
Submucosa
Muscularis externa
Serosa
![<p>II. Stomach GIT tutorial video [4 main layers]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/b5163d58-1889-4a86-9e79-bb4c09af7b65.png)
II. Stomach GIT tutorial video [4 main layers]
Cardia
Fundus
Corpus
Pylorus
![<p>III. Stomach GIT tutorial video [4 main layers]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/e591e54f-966b-4534-8dcd-2397f5121997.png)
III. Stomach GIT tutorial video [4 main layers]
Cardia
Fundus
Corpus
Pylorus
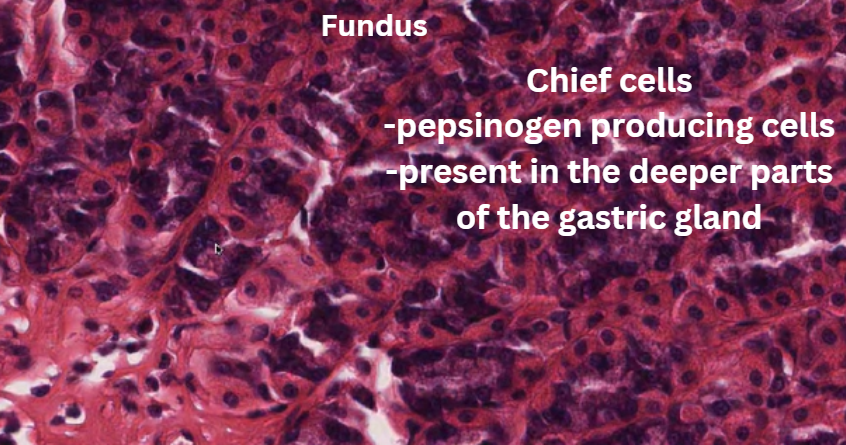
![<p>IV. Stomach GIT tutorial video [4 main layers]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/e263486d-1f1c-4527-9449-f4d52f0c31cb.png)
IV. Stomach GIT tutorial video [4 main layers]
Cardia
Fundus
Corpus
Pylorus
![<p>Small intestine → Jejunum GIT tutorial video [4 main layers]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/d3e7266c-5555-4271-9cea-16366a0d865b.png)
Small intestine → Jejunum GIT tutorial video [4 main layers]
Mucosa
Submucosa
Muscularis externa
Serosa
Highlight key differences between the small intestine and stomach. Also the small intestine and large intestine.
Differences are evident with respect to the surface area, musculature, epithelia, immune cell density
![<p>Small intestine → Jejunum GIT tutorial video [4 main layers]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/f44ff575-c4be-42b6-8623-e66cc6035ad4.png)
Small intestine → Jejunum GIT tutorial video [4 main layers]
Mucosa
Submucosa
Muscularis externa
Serosa
Highlight key differences between the small intestine and stomach. Also the small intestine and large intestine.
Differences are evident with respect to the surface area, musculature, epithelia, immune cell density
![<p>I. Large intestine / Colon GIT tutorial video [4 main layers]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/2e4b2c5f-89b6-4042-bda1-68be8d9c2a75.png)
I. Large intestine / Colon GIT tutorial video [4 main layers]
Mucosa
Submucosa
Muscularis externa
Adventitia/Serosa
Crypt
Goblet cell
Shallow plicae present in the large intestine and NO villi
![<p>II. Large intestine / Colon GIT tutorial video [4 main layers]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/5b4c4fcc-2d3e-4142-ac14-ce8bbe75f482.png)
II. Large intestine / Colon GIT tutorial video [4 main layers]
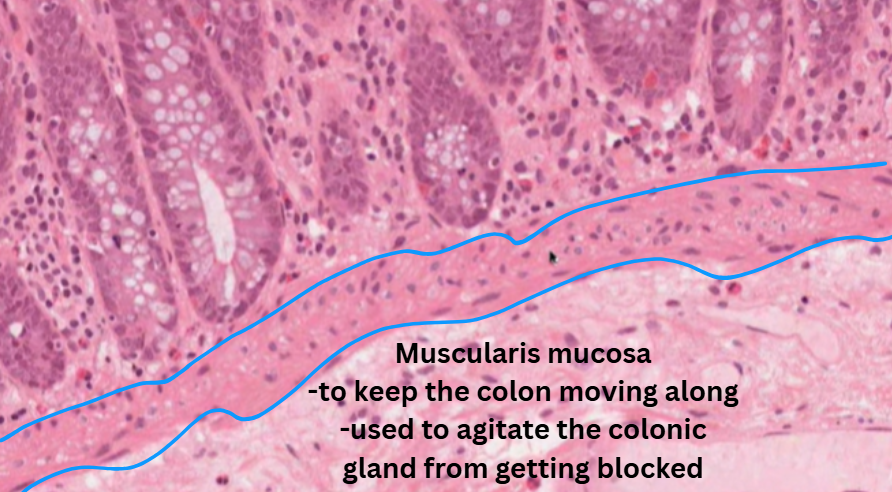
![<p>III. Large intestine / Colon GIT tutorial video [4 main layers]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/fd837f2b-78aa-4e70-ad0f-de7c4a26a54b.png)
III. Large intestine / Colon GIT tutorial video [4 main layers]