Honors Natural Selection Practice
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Adaptation
An inherited trait that helps an organism survive and reproduce

genetic variation
Differences among individuals in the composition of their genes or other DNA segments

Fitness
Ability of an organism to survive and reproduce in its environment

Inheritable Traits
how heredity influences a person's abilities, character, and behavior
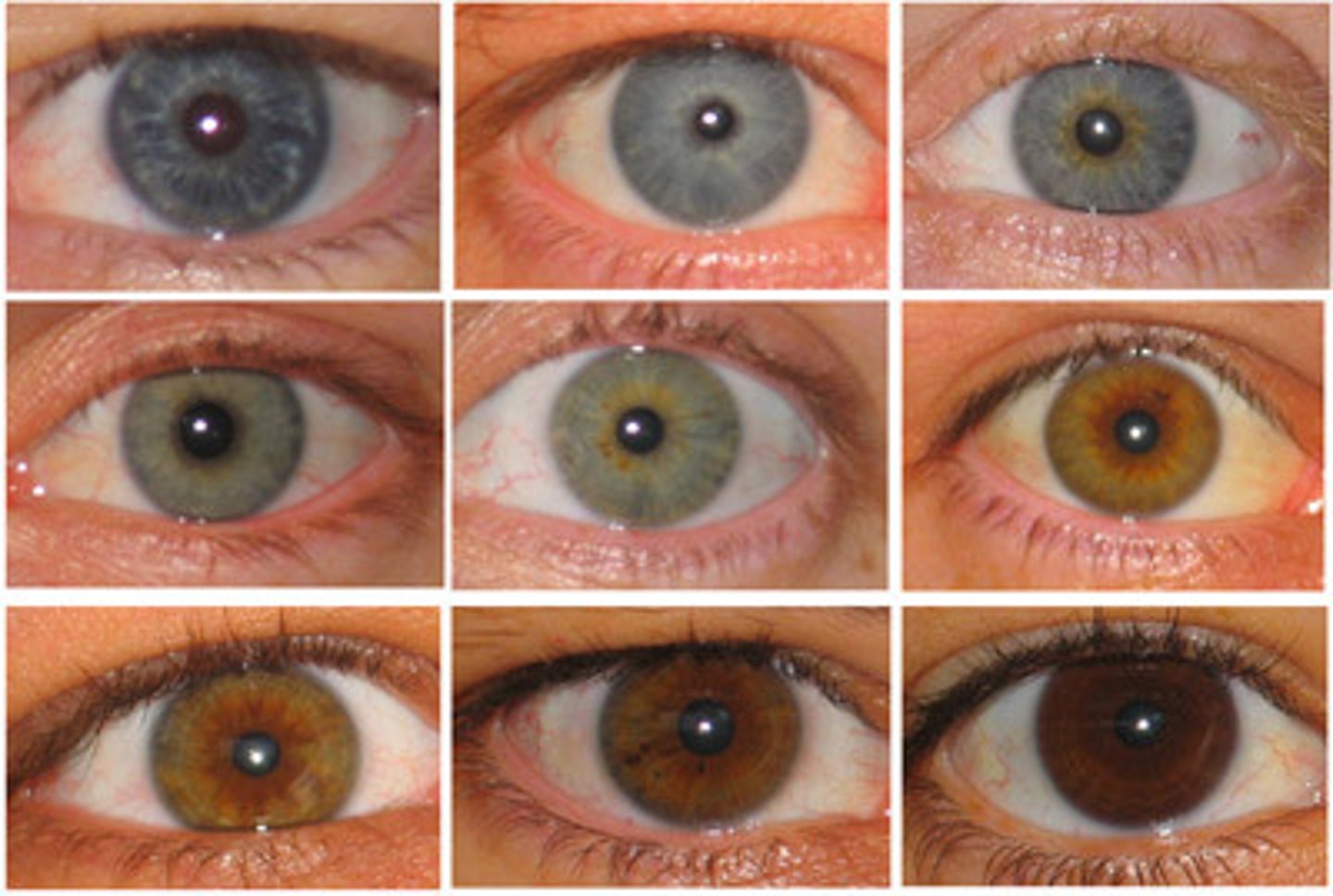
aquired traits
Traits that are acquired during lifetime are pass on to offspring

evolution
change in a population over time
overproduction
more offspring are produced than can survive
competition
the struggle between organisms to survive in a habitat with limited resources
natural selection
mechanism by which natural pressures change populations and evolution occurs
common ancestor
The shared ancestor of new, different species that arose from one population
ancestral trait
more-primitive characteristic that appeared in common ancestors
Theory of Evolution
supported by multiple lines of evidence on how life on earth has changed over time
differential survival and reproduction
Individuals possessing traits well suited for the struggle for local resources will contribute more offspring to the next generation.
Sources of variation
random mutations, genetic recombination, migration
Microevolution
Evolutionary change below the species level; change in the allele frequencies in a population over generations.
Macroevolution
large-scale evolutionary changes that take place over long periods of time
disruptive selection
favors individuals at both extremes of the phenotypic range
directional selection
occurs when natural selection favors one of the extreme variations of a trait
stabilizing selection
Natural selection that favors intermediate variants by acting against extreme phenotypes
environmental pressures
the factors (abiotic or biotic) in an ecosystem which put pressure on an organism's survival and increase competition (whether inter-species or intra-species)