Section 6.2 Phospholipid Bilayers
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
2 sheets of phospholipids align with heads and tails facing
heads: out and tails: in
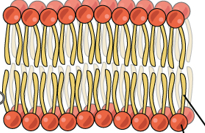
Form spontaneously
Form spontaneously: No outside
Vesicles form in the lab
phospholipids and liposomes
liposomes
Artificial membrane-bound vesicles
Small bubble-like structures surrounded by
phospholipids
Vesicles are important for
vaccine delivery
vesicles are in what form
liquid
Liposomes are not formed in
cells
lipid bilayers have what permeability
selective
what crosses through the lipid bilayer easily
Gases
what passes through relatively easy
small uncharged polar molecules (H2O, glyercol)
what moves through the lipid bilayer but it is hard
large, uncharged polar molecules
What can not pass through lipid bilayer
small ions
can move but its hard: that’s why there are ? channels to make it easier
Glucose
to measure permeability of lipid bilayers
Tendency of given substances to pass through and substance on one side and measure it on the other side
what is more MORE PERMEABLE
Unsaturated Hydrocarbon Chains, Shorter Tails, No Cholesterol, and High Temperatures
Less permeable
Saturated Hydrocarbon Chains, longer tails, with cholesterol, low temperatures
Lipid bilayer with short and unsaturated hydrocarbon tails =
higher permeability and fluidity
Lipid bilayer with long and saturated hydrocarbon tails =
lower permeability and fluidity
Hydrophobic interactions become stronger as saturated hydrocarbon tails
increase in length
Adding cholesterol to membranes
increases the density of the hydrophobic section
increases the density of the hydrophobic section =
decreases membrane permeability
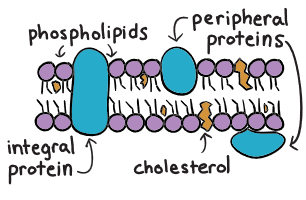
Very hydrophobic or hydrophilic ; takes up space or less space and adds or removers to the density
hydrophobic ; takes up space; adds to the density
Glycerol is polar or nonpolar
polar