Lecture 16: Advancing Tumour Surgery through the Enhancement of Intraoperative Precision
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
what is cancer?
Cancer (neoplasia) occurs when abnormal cells divide in an uncontrolled way. Some cancers may eventually spread into other tissues (metastasis).
Types of cancer treatment
Surgery- heavy reliance
Radiation Therapy
Chemotherapy
Immunotherapy to Treat Cancer
Targeted Therapy
Hormone Therapy
Stem Cell Transplant
Precision Medicine
Tumour Architecture
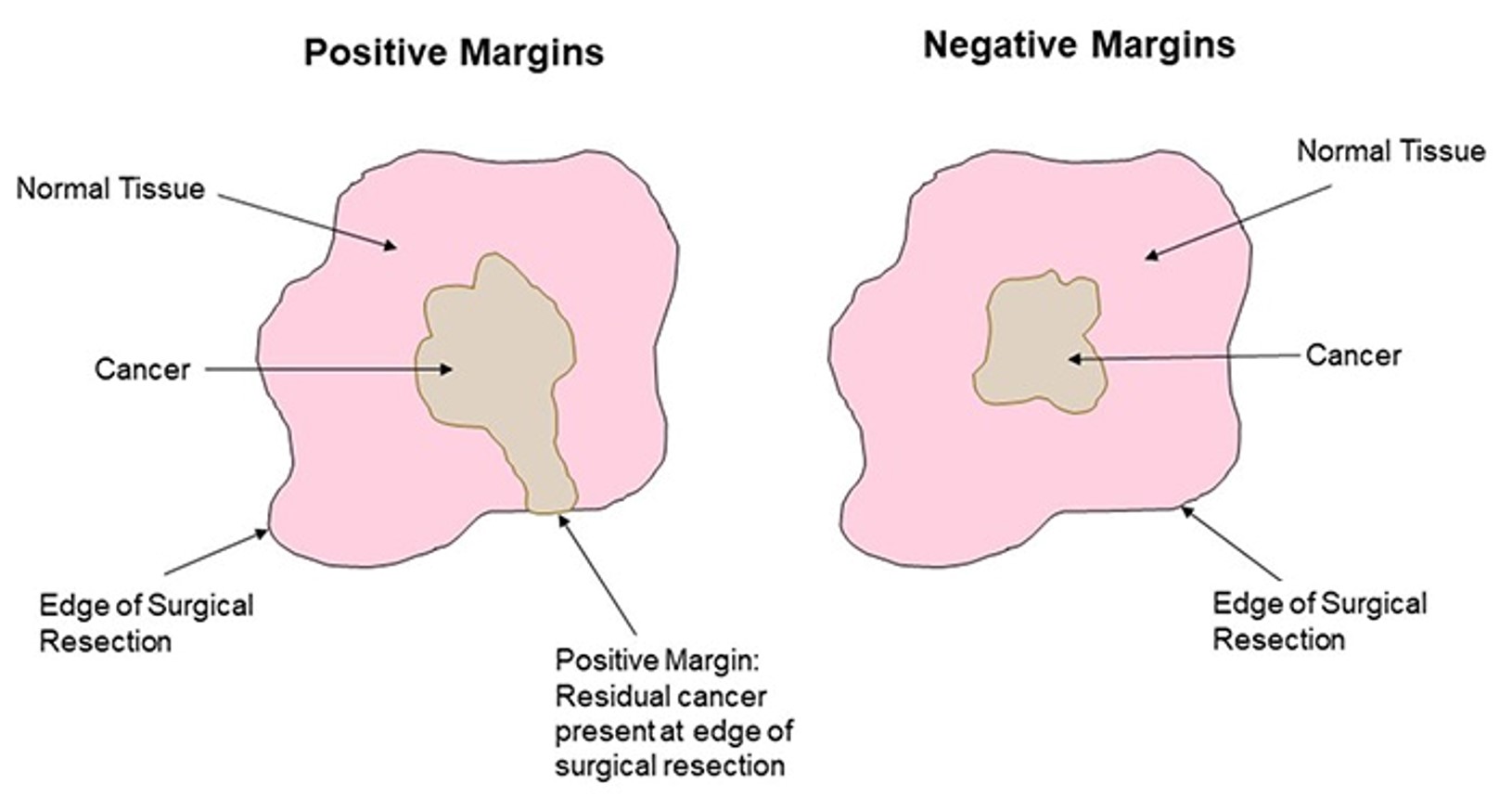
The accurate definition of surgical resection margins is an critical prognostic factor in cancer surgery
40% of cancers treated following removal of “tumour margin with clearances”
Positive and Negative margins have consequences
+ve = residual cancer on edge of surgical resection
-ve = cancer contained inside surgical resection
Margins currently defined by sight and feel
Unmet clinical need
Current Intra-operative Imaging Solutions
biopsy: tissue dehydrated and mmbeded in parafin
Microtome: cut into wafer thin section
attach to slide
remove wax
stain tissue
Frozen Sectioning - Cryostat
to speed up tissue processing
deep freeze tissue instantly to cut tissue
30-40min
Cons of cryostat
Poor quality section: Frozen tissue sections are not easy to cut compared to paraffin embedded sections (especially brain and other fatty tissues)
Bloated cell morphology: Tends to cause the cells to be larger and appear (water freezes)
Poorly stained section: As pathologist depends on colours as well as morphology, studying cells and its surrounding tissues, this factor may affect diagnosis bloated
paraffin embedded vs frozen tissue section
paraffin:
fixed tissue
time consuming:24-48hrs
clear morphology
pathological diagnosis
freezing:
fresh tissue
30-40 mins
opaque morphology
intraoperative consultation
Fluorescence Based Imaging
Fluorescent compound absorb (λex) and emit light (λem) at specific wavelengths
Stokes Shift: the difference, in nanometres, between the peak excitation and the peak emission wavelengths
must have good peak separation to avoid overlap and confusion
Each fluorophore has a distinct and individual Stokes Shift
Method for Fluorescence Based Imaging
white light shined through filter to select specific wavelength
light hits dichroic mirror
reflects light of certain wavelength onto sample
sample fluoreses and is detected
Fluorescence Guided Surgery
patient given fluorophore to bind to tumour cells
Fluorescent dyes (ICG) are not tumour specific – false positives
Diathermy Cutting Blade
The iKnife: not in clinical practice
food industry
Diathermy cutting blade used in surgery to minimise intraoperative bleeding - hot blade cauterises blood vessels
major byproduct = smoke
previously been considered to be a toxic irritant – extracted to waste
authors suggest that this is a rich source of biological information
used mass spectrometry to measure the metabolomic composition of this vapour
could provide new chemical information that describes the tissue and its associated pathology
diagnosic markers in smoke
Glycerophospholipids are overexpressed in all cancers
degree of of over expression can determine cancer type
The basic structure of important phospholipids detected during MS vapour analysis
limitations to diathermy smoke suction
Slow in sergery (30-60secs per analysis)
Expensive due to mass spectrometer
Not all procedures use a diathermy cutting blade
MarginProbe™
Dune Medical Devices
currently used in lumpectomy in breast cancer
Assessment of malignant margin residue on tumours removed from patient
Radio wave base assessment of cells pathophysiology
MarginProbe™ method
sergion removes lump of tissue
tissue analysed using radio waves
cancer contains more water than healthy
technition uses probe to emit radiowaves
radiowaves detect water and determine if tissue is malinant or normal
Pros and cons of MarginProbe™
pros:
Rapid, reagent free response
Additional surgical information to prevent secondary operations
cons:
measuring on tissue outside the patient
Tissue analysis rather than informing surgical decision making – Reason for quick FDA approval?
FLARE™
Fluorescence-Assisted Resection and Exploration is based on the use of a Near Infrared (NIR) fluorophore (Methylene blue) to detect tumour cells
Provides real-time guidance to surgeons for targeting tissues of interest and avoiding sensitive structures
Methylene blue injection at sight of tumour provides NIR ‘contrast reagent’
NIR Fluorescence Guided Surgery
give patient methylene blue
illuminate patient with white light and NIR
NIR causes tumour cells to fluoresce
detected by camera
FLARETM Limitations
Fluorophore is not tumour specific
Whole of abdomen is illuminated – reduced signal strength and tissue penetration
Reduced surgical precision?
Pathology Node - Biomedical Engineering Strand Objectives
‘To develop a technique or process based on Near Infrared (NIR) technology that would allow the direct, real-time intraoperative definition of tumour margins’.
Identify a tumour-cell specific target molecule that could be labelled with an antibody based NIR fluorophore
Miniaturise existing NIR sensor technology into a hand-held sensor for intraoperative use
Use the hand-held sensor to detect NIR labelled cell in vitro and in vivo
scalpel with NIR light source to fluoresce tumour cells
Selection of a Novel Target – Protein Expression Array Data
in colorectal cancer, tumour regrows at junction of tissue removed - scar tissue
protein expression array data
control: CCD-841
colon cancer: HT-29
EpCAM over expressed in cancer cells - use anti-EpCAM as AB
Conjugated Polymer Nanoparticle (CPN®)
Significantly brighter than ‘organic fluorophores’ (based on OLED technology)
Long-term photostability (years)
Multi-modal imaging potential
Biocompatibility
Familiar surface ligand chemistry
λex= 750nm – λem=1125nm
NIR Sensing Technology
Reece innovation: use NIR to detect cracks in wind turbine > Collimator to focus light cell to a point
Sagitto: handhelt NIR sensor > can detect EpCAM expression > use glasses
CPNs have Theranostic Potential
drug can be therapeutic and diagnostic
Tumour selective intraoperative imaging
NIR Responsive ROS medicated Tumour Destruction through the initiation of Apoptosis
shrink tumour mass before surgery
Market analysis
iKnife – Imperial College, London, UK.
FLARE™ Intraoperative Near-Infrared Fluorescence Imaging System – LUMC, Netherlands
LightOx – Billingham, UK.
Patent Position
Choice of NIR CPN – if unique
Choice of tumour marker antibody – if unique
Combination of the two
Novel imaging system, if sufficiently innovative
Novel integration of imaging system with surgical procedure, again if sufficiently innovative