Psychopathology Chapter 7: Mood Disorders
1/68
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards based on chapter 7 and powerpoints.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
Depression
involves feelings of extraordinary sadness and dejection.
Mania
often characterized by intense and unrealistic feelings of excitement and euphoria.
Unipolar Depressive Disorder
a person experiences only depressive disorders.
Bipolar Disorder
a person experiences both depressive and manic episodes.
Depressive Episode
when a person is markedly depressed or loses interest in formerly pleasurable activities for at least 2 weeks.
Manic Episode
markedly elevated, expansive, or irritable mood for at least 4 days.
Hypomanic Episode
abnormally elevated, expansive or irritable mood for at least 4 days; the person must also have at least 3 other symptoms similar to those involved in mania.
Diagnostic criteria suggests that a person but be in a major depressive episode and never had a manic, hypomanic or mixed episode with what disorder?
Major Depressive Disorder
Relapse
return of the symptoms within a fairly short period of time.
Recurrence
the onset of a new episode of depression.
Reoccurrence happens in ___ of people who experience a depressive episode.
40-50 percent
Specifiers
different patterns of symptoms or features.
Major depressive disorder with melancholic features:
includes loss of interest, not reacting to usually pleasurable stimuli or desired events.
Severe major depressive episode with psychotic features:
depression is accompanied by psychotic symptoms.
Major depressive episode with catatonic features:
includes a range of psychomotor symptoms.
Recurrent major depressive episode with a seasonal pattern:
includes at least 2 episodes of depression in the past 2 years at the same time of year.
Persistent Depressive Disorder
characterized by persistently depressed mood most of the day, for more days than not, for 2 years.
Double depression
moderately depressed on a chronic basis but undergo increased problems from time to time, during which person also meets the criteria for a major depressive episode.
What are the four phases of normal response to the loss of a spouse or close family member?
Numbing and Disbelief
Yearning and searching for the dead person
Disorganization and despair
Reorganization
Depressive symptoms of grief and loss tend to peak ____ after the loss.
2-6 months
Postpartum Blues
symptoms include interchangeable mood, crying easily, sadness and irritability, often intermixed with happy feelings.
Postpartum blues occur in up to…
50-70% of women within 10 days of giving birth.
Family studies have shown that the prevalence for a mood disorder is…
about 2-3 times higher among blood relatives of a person with clinically diagnosed unipolar depression.
The serotonin-transporter gene is involved in…
the transmission and reuptake of serotonin. One of the key transmitters involved in depression.
Monoamine Theory of Depression
depression is at least sometimes due to an absolute or relative depletion of serotonin and norepinephrine at important receptor sites of the brain.
Damage to the left, but not the right, anterior prefrontal cortex often leads to ___.
Depression
REM Sleep
Categorized by rapid eye movement and dreaming.
Patients who are depressed have:
early morning waking, periodic waking and difficulty falling asleep.
Abnormalities in the Circadian Rhythm in patients with depression include:
drastic changes to mood, sleep, appetite and social interactions.
A distinction must be made between
independent life events and dependent live events.
Hypothesis that minor events may play more of a role in the onset of (1)___ than in the (2) ___ episode.
Recurrent
Initial
Neuroticism/Negative Affectivity:
stable and heritable personality trait that involves a temperamental sensitivity to negative stimuli.
Freud and colleague Karl Abraham both hypothesized that:
when a loved one dies, the mourner regresses to the oral stage of development.
Beck’s Cognitive Theory
the cognitive symptoms of depression often precede and cause the affective or mood symptoms, rather than vice versa.
Underlying dysfunctional beliefs, known as _____, are rigid, extreme and counterproductive.
Depressogenic Schemas
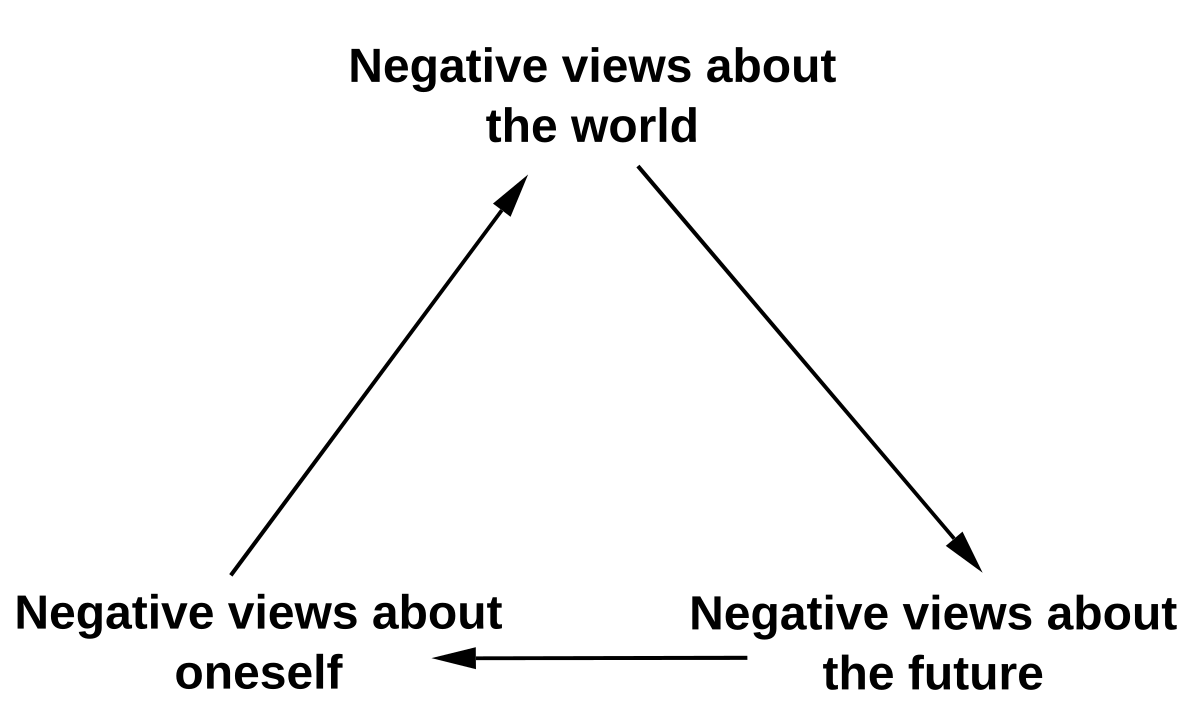
Negative Cognitive Triad
includes negative thoughts about the self, the world and the future.
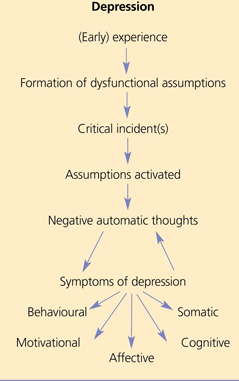
Beck’s Cognitive Model of Depression
certain kinds of early experiences can lead to the formation of dysfunctional assumptions that leave a person vulnerable to depression later on in life if critical incidents active those assumptions.
Learned Helplessness
a psychological phenomenon where individuals, after repeated exposure to uncontrollable negative situations, come to believe they are helpless to change their circumstances, even when opportunities to do so arise.
People with a ______ have a vulnerability for depression when faced with uncontrollable negative events.
Pessimistic Attributional Style
Rumination
involves a pattern of repetitive and relatively passive mental activity.
Cyclothymic Disorder
the repeated experience of hypomanic symptoms for a period of at least 2 years.
Mixed Episode
symptoms of both manic and major depressive episodes for at least a week, either intermixed or alternating rapidly every few days.
Bipolar I
Person has full blown mania. Person experiences episodes of mania and depression. Even if the episodes of depression do not reach the threshold for a major depressive episode, the diagnosis is still given.
Bipolar II
Person experiences periods of hypomania, but symptoms are below threshold for full blown mania. Person experiences periods of depressed mood that meet the criteria for major depression.
Increased levels of ___ may be related to manic symptoms.
Dopamine
____ activity appears to be low in both manic and depressive phases of Bipolar Disorder.
Serotonin.
PET scans reveal that blood flow is reduced in…
the left prefrontal cortex during depression, and increased to other parts of the prefrontal cortex during mania.
The basal ganglia and amygdala are enlarged in ____ but reduced in size in
____.
Bipolar Disorder, Unipolar Disorder
In the 1950s, the first category of antidepressants were:
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MNOs)
Drug treatment of choice from the 1960s - early 1990s were:
Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs)
The side effects of TCAs led to the prescription of:
Selective Serotonin Re-uptake Inhibitors (SSRIs)
Drugs usually take ____ to take affect.
3-5 weeks
Around ___ of patients don’t respond to the first drug prescribed.
50%
____ has been widely used to treat manic episodes.
Lithium
Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) is often used…
in patients who are severely depressed and may be at immediate suicide risk.
The most common side effects of ECT are:
confusion, amnesia, and slowed response time.
Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
focuses on the here and now problems; teaches people to systematically evaluate their dysfunctional beliefs and negative automatic thoughts.
Behavioral Activation Treatment
is a relatively new and promising treatment for unipolar depression. Goals are to increase levels of positive reinforcement and to reduce avoidance and withdrawal.
Interpersonal Therapy (IPT)
Focuses on current relationship issues, trying to help the person understand and change maladaptive interaction patterns.
It is important to distinguish suicide from ____.
non-suicidal self-injury behaviors.
Nonsuicidal Self-Injury (NSSI)
refers to direct, deliberate destruction of body tissue in the absence of any intent to die.
Perceived burdensomeness and thwarted belongingness…
interact to produce suicidal thoughts.
Sophie from the textbook was suffering from what mood disorder?
Major Depressive Disorder and drinking issues which are common with a mood disorder.
Jennifer from the textbook was suffering with what mood disorder?
Major Depressive Disorder with anxiety, and no desire to carry out every day tasks.
Rosa, the 20 year old college student from the text book was suffering with what mood disorder?
Persistent Depressive Disorder for over 2 years throughout high school and college.
Hippocrates (c. 400 b.c.) hypothesized that…
depression was caused by an excess of “black bile” in the system.
Double Depression is classified as what in the DSM-5?
Classified as Persistent Depressive Disorder.
How long do depressive episodes last if untreated?
usually 6-9 months.