Issues in Global Politics-EI - S25 - Darr Final Study Guide
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
Migrants
typically choose to move to another country or region, can be temporary or permanent,
Refugees
forced to flee, have international law to have certain rights and protections, might not have had time to plan without belongings
Does cultural similarities drive migrant flows
no
does economic opportunity drive migrant flows
yes
remittances
largest cash flow from rich to poor countries
How can we define slavery
the legal ownership of persons, unpaid forced labor, total control of one person by another for economic exploitation,
Define colonialism
the direct political control of a group of people by a foreign state, the control by one group over another inhabiting a separate territory, an empire that was developed for settlement by individual communities or for commercial purposes,
neo-colonialism
still exits in various forms, and has many of the same motivating forces
deproletarianization
slavery still exists in different forms, and often as a way to cut labor costs.
Cash crops
forced labor system for agricultural commodities, coffee, cocoa, cotton in Ivory Coast
Supply chain controlled
by colonial companies’ example, Ivory Coast: CFDT in the past; today, Nestle?
unequal exchange
raw materials exported, finished goods imported; Ivory Coast: cotton going out, textiles coming in
IMF
International “lender of last resort” which lends money to countries in economic crisis
IMF puts conditions on loans
desperate borrowing country must sign on to certain things in order for the loan to come through
Liberalism
the political system in which the government is legally bound not to cross certain boundaries, Individualism and rights (Property rights), limited government (checks and balances), importance of proper legal procedures, a preference for markets as a way to distribute goods
free market
system of voluntary exchange of goods and currencies wherein every transaction benefit both parties
demand
will determine supply and price, keeping them appropriate to fulfil demand
liberalism’s implications for political economy
the market ought to function on its own as much as possible to distribute goods efficiently
Neoliberalism (liberal globalism)
an ideology which advocates for applying free-market policies globally and at all levels “globalizing the market”
Neoliberalism DLPA
Deregulation: of economy (environment, labor, finance) Liberalization of markets: toward smaller government (free trade and free financial flows) Privatization: of public (state-owned) services (opposite of nationalization, when a state buys up an industry) Austerity: balancing gov’t budgets through spending cuts
nationalization
when a state buys up an industry
class struggle
The antagonism and competition between those who own for a living (bourgeoisie) and those who must work for a living (proletariat)
surplus-value of labor
value of a worker’s labor that is not paid back in wages and instead goes to the capitalist as profit (under capitalism, you’ll never be paid what you’re worth)
exploitation
workers’ wages go to the capitalist as profit
Workforce segmentation
strategic division of the working class into subgroups (gender, race, employment) to prevent revolution
labor “free Market”
one-sided and unfair to laborers, “work or starve” is not freedom, “reserve army” of the unemployed
Marxist critiques of liberal capitalism
dominant ideology legitimizes class domination (material base produces ideological superstructure), the market makes economically unequal societies more unequal
Capitalist industrialization
Began in the 15th century Europe, manufacturing became the dominant part of the economy, gradually moved out of the household and into the factory, agriculture became less prominent, urbanization and other social changes
Globalization
integration of the world economy (more specifically: spread of industrial capitalism across the globe)
Gender segmentation
masculine activities tend to be valorized and rewarded, famine activities tend to be overlooked and un(der)paid
Flexibilization of labor
Work is becoming less secure, more poorly paid, and adjunct professors see flexibilization as feminization. Most informal (uncounted, unregulated) labor is done by women
What do superhero stories tend to tell us about conflict and peace?
conflict happens between good and evil, and active hero rescues a passive crowd, conflict is resolved through violence
International law and state sovereignty
comes mainly from treaties: agreements between sovereigns, bilateral treaties, multilateral treaties
international law is legally binding
all treaties made, or which shall be made, under the authority of the United States, shall be the supreme law of the land, but
U.N charter
centerpiece of international law
collective security pact
the UN’s big idea
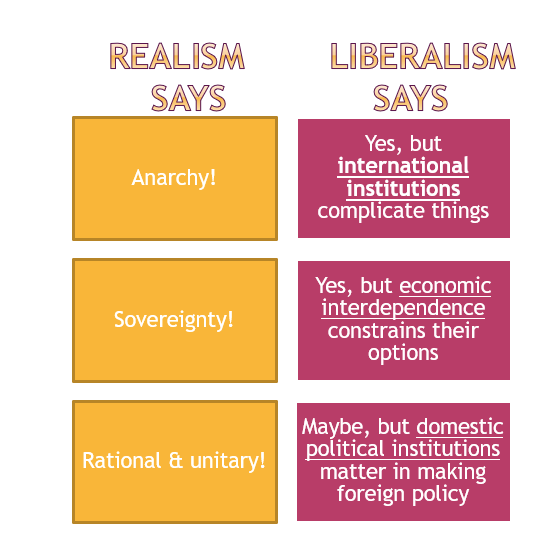
4 fundamentals of realism
The world is an anarchic “state of nature”, states are sovereign (nobody can legitimately tell them what to do) states are rational, unitary actors (rational: states have goals and use foreign policy as a means to achieve them, unitary: states act like autonomous individuals, how policy is formed is irrelevant) states operate according to their interest, not moral precepts (morality is a propaganda tool to preserve power)
Classical realism (human nature realism)
Believes there will always be war between states because humans crave power and seek it through violence
structural realism (neo-realism)
Believes there will always be war between states because states seek security in anarchy, and power is the best means to security
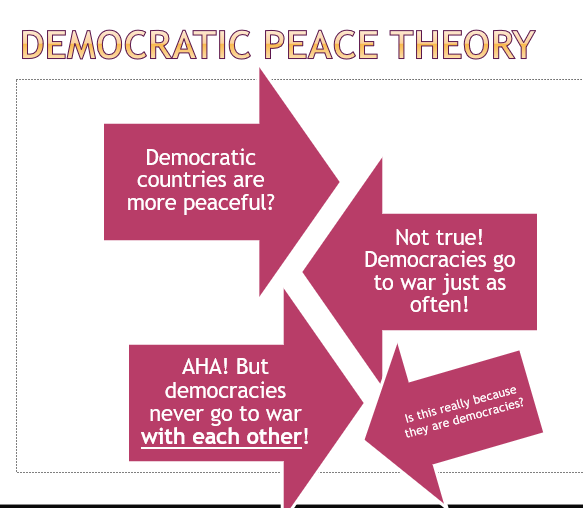
liberalism: 4 fundamentals
states can cooperate through international institutions, international commerce makes states less willing to fight, the spread of democracy makes war less likely, some states are just, and others are not (states can and should be judged by common standards of morality)
realists
states are not cooperative because they face security dilemmas again and again
liberals
precisely because they face the security dilemma again and again, they learn to cooperate
economic liberalism
economic interdependence (makes states less prone to violence) trade partners are less likely to go to war with each other
agenda-setting
deciding what is news and what is left out
newsworthiness
standard by which agenda setting is determined
framing
putting a story into a frame, different frames use different facts (some left out) framing can narrow the scope of debate
propaganda blitz
attacking and discrediting ‘official enemies’ preparing the way for action or intervention
Problem-solving theory
points itself at a problem and tries to solve it, works within certain assumptions, started or not
critical theory
steps back from solving the problem, questions the volubility of the assumptions (stated or not) of the problem, also asks the question: who benefits?