science revision (electromagnetism)
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
i dont have the symbols on ts
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
whats a magnetic field?
the region around an object in which a magnetic force affects other magnets
whats a conductor?
a material that allows the flow of electricity through it with very little resistance.
what is a electron?
a particle with a negative charge that orbits the nucleus of a atom
whats a switch?
a device used to open or close a circuit
whats a natural magnet?
a magnet that occurs naturally in the earth.
whats a geographical pole?
the earth’s northernmost and southernmost points.
what direction does the force begin?
from the north pole to the south pole
where is magnetic property maximum?
at the poles
what are field lines?
a visual tool that represents the direction of the magentic field, that curve in towards the magnetic poles and indictaes the strength of the field, the closer the lines are to one another, the stronger the field.
what is a permanent magnetic field?
a permanent magnetic field is a persistent magnetic field generated by a material without needing an external power source.
can all elements form a permanent magnetic field? t/f
f. only some elements can form a permanent magnetic field, such as iron, nickel and cobalt.
what is a temporary/induced magnetic field?
a temporary magnetic field is a magnetic field that exists only while an electric current is flowing through it or while the material is in the presence of another external magnetic field.
does magnetic field always exists around a wire carrying an electrical current? t/f
t, it follows a circular pattern
how does the strength of field decrease?
with a greater distance from the source (wire)
how does the strength of field increase?
with a higher current.
what is a current?
the flow of charge (typically electrons) through a material.
what does a electric circuit consist of?
a power supply, wires and a load
whats a closed circuit?
a unbroken path for electrons to move through
how is current measured?
amps (A)
what is a anmeter?
an instrument for measuring electric current in amps.
what is voltage?
the amount of electrical potential energy per charge.
how is voltage measured?
volts (V)
what is a voltmeter?
an instrument for measuring electric potential in volts.
what does resistance measure?
a measure of how difficult it is for electric current to flow through a material.
how is resistence measured?
a multimeter (ohms)
what is a solenoid?
wrapping a wire into coils, which produces a solenoid.
how can the strength of a solenoid increase?
using more turns of wire, using a smaller radius or turns or wrapping a wire more compactly.
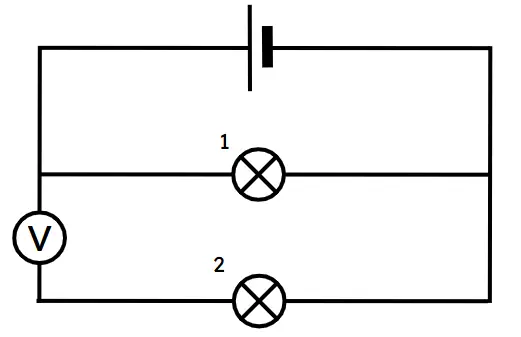
whats a parallel circuit?
an electrical pathway that branches, forming multiple paths for current to flow.
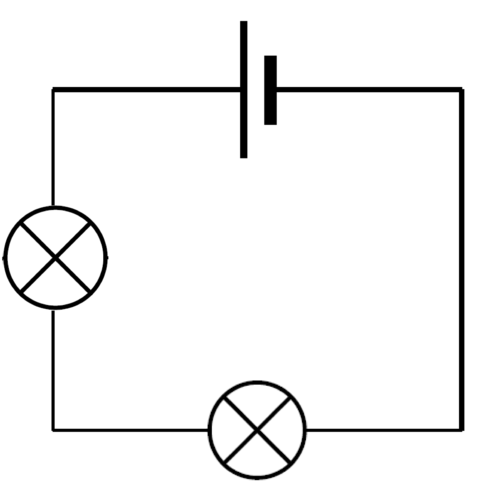
whats a series circuit?
a single electrical pathway which all of the current flows through
whats a voltage drop/potential difference?
the reduction in voltage as electric current flows through the circuit.
what is the voltage drop across each branch on a parellel circuit?
the same as the v oltage proivded by the power supply
whats an electromagetic wave?
energy that travels through space in the form of electric and magnetic fields.