NSCI 2101 Exam 4 (Final)
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
120 Terms
What is the primary function of myelin?
increases the conduction velocity of action potentials
The two hemispheres of the brain are separated by which of the following?
Interhemispheric fissure
Where is the occipital lobe?
Posterior cerebral cortex
In the peripheral nervous system, groups of neuronal somata are called ________, and bundles of axons are called _________.
ganglia, nerves
The dorsal root (spinal) ganglia, part of the peripheral nervous system, develop from what embryonic cell group?
neural crest
Failure of the caudal (tail) end of the neural tube to close completely in the embryo will result in a condition in the infant called...
spina bifida
Motor neurons that send their axons out of the central nervous system and connect to muscles develop from cells in what region of the embryonic neural tube?
basal plate
Which of the primary germ layers gives rise to the nervous system in development?
ectoderm
Which layer of the meninges is tightly adherent to the surface of the brain?
pia mater
The lateral ventricles derive from which secondary neural vesicle?
telencephalon
Cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) in the subarachnoid space normally drains into the ....
dural venous sinuses
What structure produces most of the cerebrospinal fluid?
Choroid plexus
Blood to the brain enters the skull mainly via what arteries?
Internal carotid arteries and vertebral arteries
Blood from the brain leaves the skull mainly via what pair of veins?
internal juglar veins
In a normal healthy person, approximately what percentage of the blood flow is to the brain?
20%
What effect will increased CO2 have on blood circulation to the brain?
Vasodilation
Which of the following is true regarding Schwann cells?
They myelinate axons in peripheral nerves.
Synthesis of mRNA from DNA in the nucleus is a process called…
Transcription
How many chromosomes do humans normally have?
22 pairs plus two sex chromosomes
Which of the following statements is true regarding protein synthesis?
Proteins are synthesized by linking together amino acids in a specific sequence.
Which of the following is a result of the refractory period?
Ensures that the action potential is only propagated in one direction
Activation of excitatory synapses is likely to have what effect on a neuron?
The neuron will initially depolarize.
An axon with which of the following characteristics would be expected to have the fastest conduction velocity?
5μm diameter, myelinated
Action potentials are due mainly to which of the following?
Sodium channels opening when a cell becomes sufficiently depolarized.
SNARE proteins on synaptic vesicles are activated by..
Ca++
In humans, which of the following neurotransmitters is released by motor neurons to initiate contraction of muscles?
acetylcholine
After the neurotransmitter glutamate is released, it typically …
is recycled through astrocytes back to the presynaptic terminal.
Pick the best answer.
Metabotropic receptors, when activated by an appropriate neurotransmitter, will…
activate an enzyme cascade inside the neuron that leads to opening or closing of nearby ion channels.
What level of the spinal cord has the most white matter?
cervical
Which tract in the spinal cord carries pain information to the brain?
spinothalamic tract
Where do axons of the spinocerebellar tract synapse?
cerebellum
Where in the vertebral column does the spinal cord end in the adult?
Upper lumbar
Which of the following structures cannot be seen in a ventral view of the human brain?
thalamus
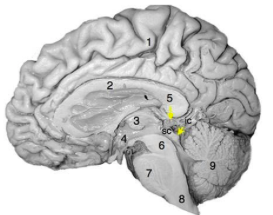
Which of the following statements regarding the photograph of the medial surface of the human brain to the right is true?
#4 is a part of the diencephalon
Which of the following lists of brain structures is in the correct rostral-to-caudal order?
frontal lobe, thalamus, cerebellar vermis, medulla, spinal cord
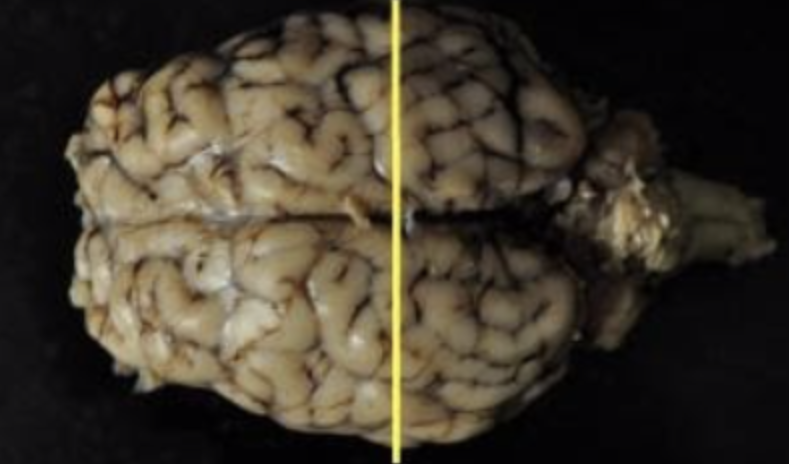
What is the name of the plane of section indicated by the yellow line?
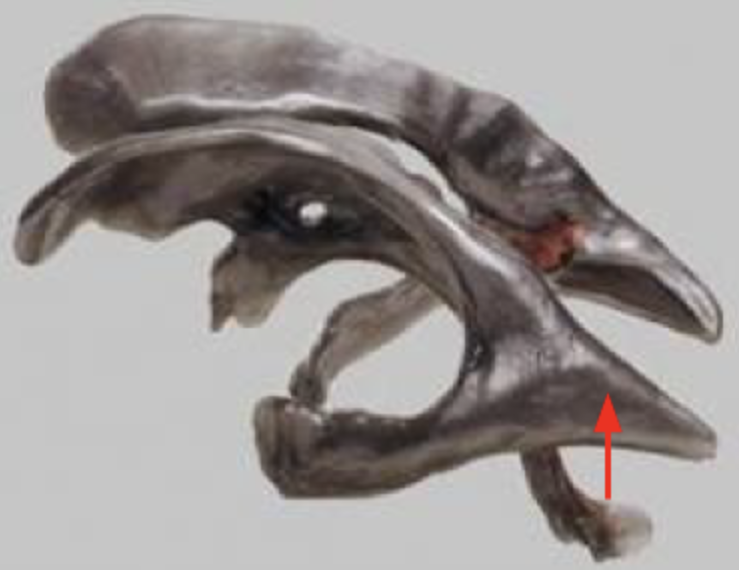
What structure is indicated by the red arrow in this cast of the ventricular system of the human brain?
Lateral ventricle
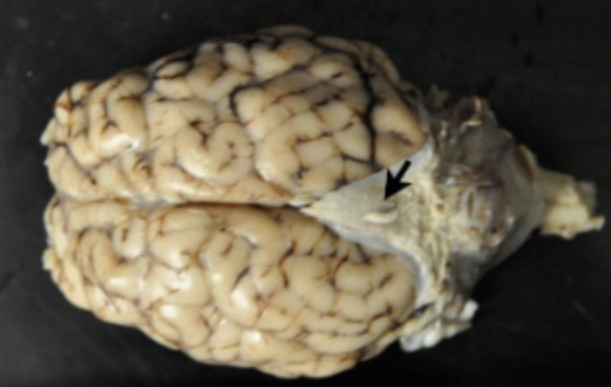
Which of the following statements is TRUE regarding the structure indicated by the arrow in the image below?
It is part of the dura.
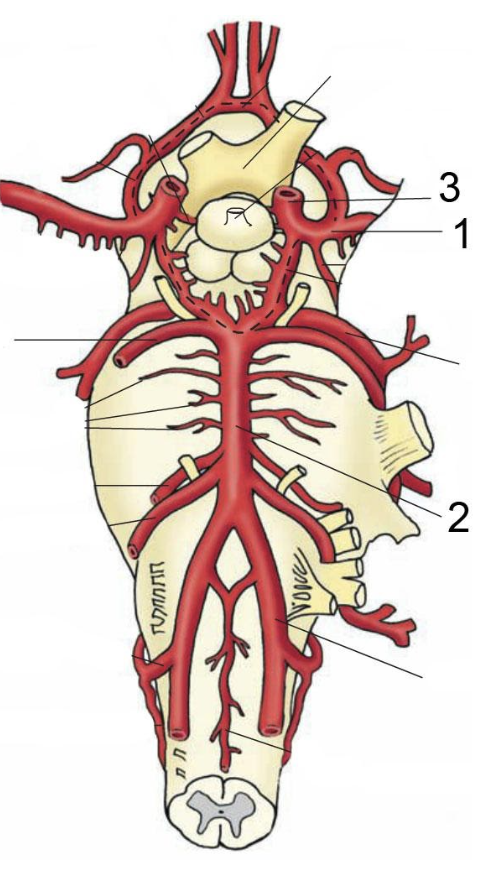
What artery is indicated by the # 2 in the diagram below?
basilar
What artery supplies much of the lateral surface of the cerebral cortex?
middle cerebral artery
The fourth ventricle is on the dorsal surface of what part of the brain?
pons and medulla
The superior colliculus is on the …
dorsal surface of the midbrain
The olive and inferior olivary nucleus are major landmarks for what part of the central nervous system?
Upper medulla
Axons from thalamus project to the cerebral cortex via what major bundle of axons?
internal capsule
To which layer(s) of neocortex does the thalamus project?
Layer IV
What layer of myelinated axons divides the thalamus into medial, lateral, and anterior regions?
Internal medullary lamina
What is the function of the thalamic reticular nucleus?
It inhibits the output of other thalamic nuclei to the cerebral cortex.
What is the only cranial nerve that exits from the dorsal surface of the brainstem?
Trochlear (CN IV)
Which of the following cranial nerves is most important for pointing your eyes at the text when you are reading?
Trochlear
Which cranial nerve carries somatosensory information from most of the face?
Trigeminal
What part of the retina is specialized for high acuity vision?
fovea
The ciliary muscle in the eye is important for what function?
adjusting the diameter of the pupil, focusing the lens
What happens when photoreceptors are exposed to light?
They hyperpolarize.
The axons from retinal ganglion cells on the nasal (nose) side of the left retina …
synapse in the right lateral geniculate nucleus.
The main nucleus in the thalamus for relaying visual information to primary visual cortex receives axons of retinal ganglion cells. Which of the following best describes this input?
The input to the thalamus on one side of the brain comes from both eyes, but the axons from the two eyes are segregated into separate layers in the nucleus.
Which of the following nuclei is particularly important for the pupillary light reflex?
pretectal nucleus
Vision is processed in the cortex in two main streams. Which of the following statement best describes the ventral stream from primary visual cortex?
It projects to temporal lobe for recognition of objects and faces
Cutting the right optic tract would be expected to result in
Loss of the left half of one's visual field
Axons in the right dorsal column of the spinal cord carry primarily what information?
proprioception and touch information from the right side of the body
which cranial nerve controls the lateral rectus muscles of the eyes?
abducens (CN VI)
Which of the following accurately describes Piezo2?
It can form a channel through which ions pass, causing the cell to depolarize.
Sensory neurons associated with muscle spindles are activated by what?
Stretch of the muscle
Where is the cell body (soma) of a primary afferent neuron sensing pain in the skin of the leg?
Dorsal root (spinal) ganglion
Stimulation of the periaqueductal gray results in…
analgesia
Which of the following statements regarding the dorsal column pathway and spinothalamic pathway is TRUE?
Information relayed by these two pathways is carried to the same cortical region.
Which of the following describes pain that outlasts healing?
Chronic pain
Suppose a tone with a frequency of 220 hz. resonates 2 mm from the apex of the cochlea. A tone with a frequency of 440 hz resonates 5 mm from the apex of the cochlea. Roughly where will a tone with a frequency of 880 hz resonate?
8 mm from the apex of the cochlea
Sound is conducted through the middle ear by vibration of several structures. What is the correct sequence of these structures from the external ear to the inner ear?
tympanic membrane – three bones – oval window
The sensory apparatus in the semicircular canals are most sensitive to what?
Rotation
The primary auditory cortex, which is important for the conscious perception of sound, is in what lobe of the brain?
Temporal lobe
How many odorant receptors are expressed by one olfactory primary afferent neuron?
1
Where do axons of olfactory receptor neurons synapse?
olfactory bulb
Which of the following taste(s) are innately aversive to humans? Mark all that are correct.
Sour, Bitter
T2-type taste receptors are involved with sensing which of the following tastes?
Bitter
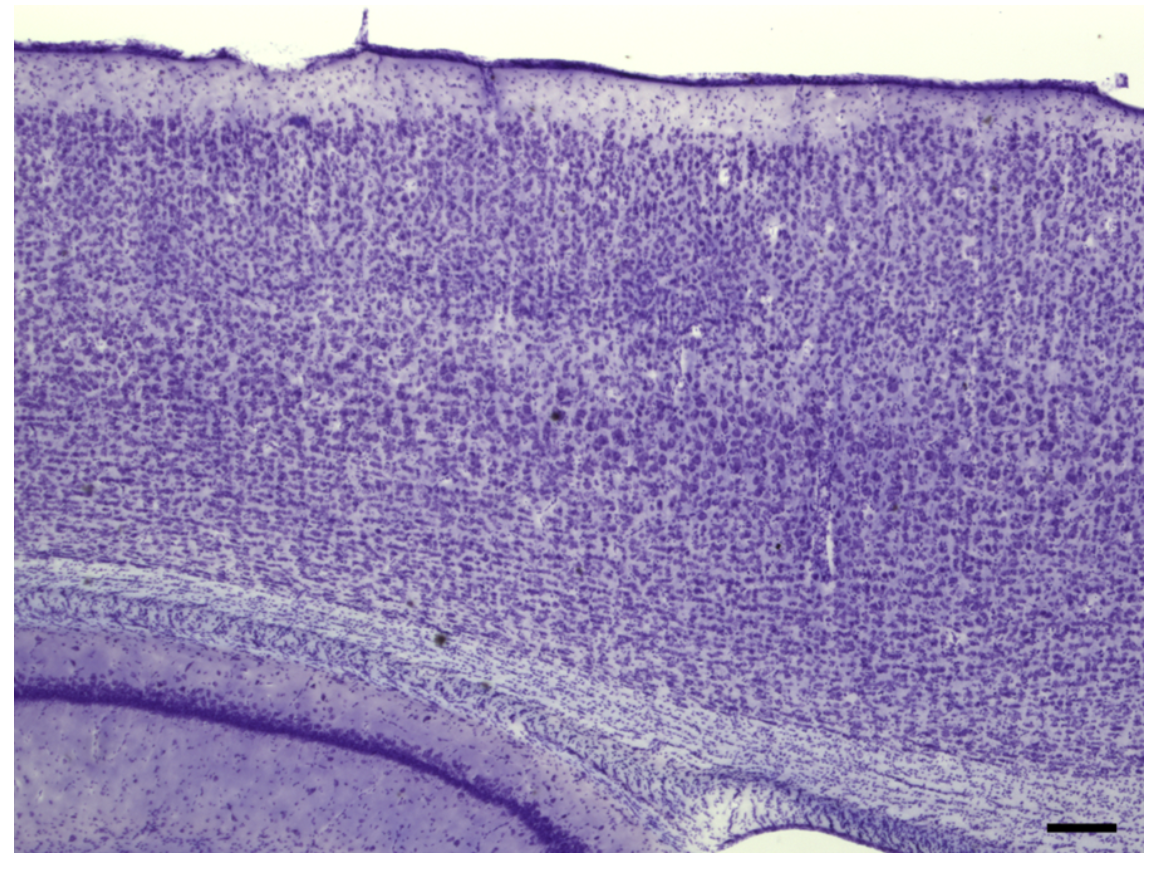
Neocortex
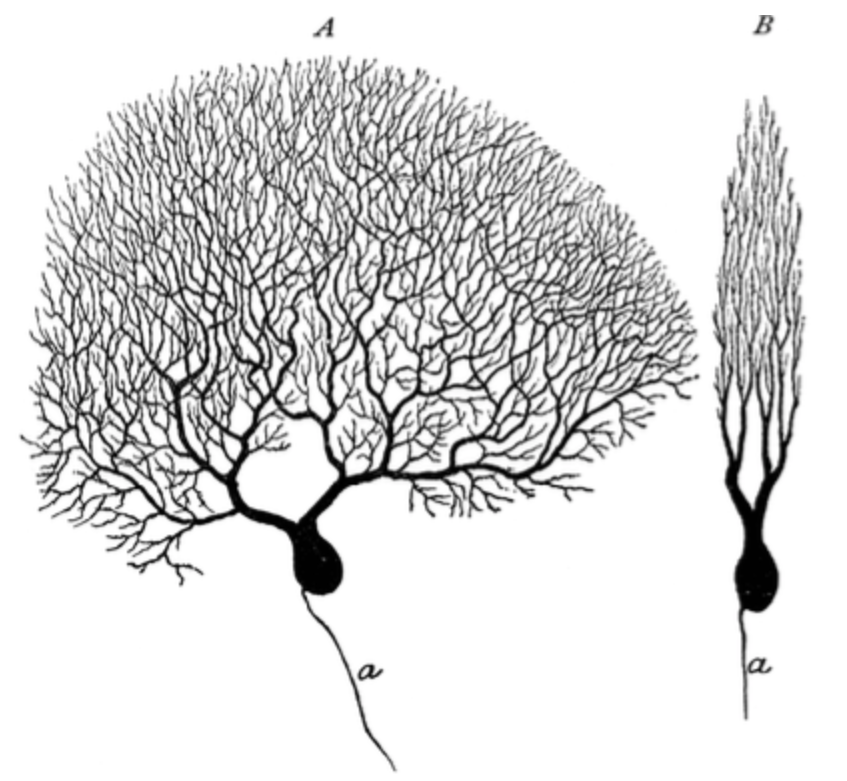
Which brain region is the most likely location for the drawing of the cell shown below? (The same cell is shown in two views.)
cerebellum
Which of the following histological staining methods is most helpful for visualizing dendritic spines?
Golgi
Which of the following statements is TRUE about action potentials?
Sodium ions enter the cell when the voltage-gated sodium channels open.
Tetrodotoxin (TTX) is a compound that blocks the action of voltage-gated sodium channels. What would be the effect of applying TTX to neurons?
It would be more difficult to generate an action potential.
The resting membrane potential of a cell is closest to the equilibrium potential of which of the following ions?
potassium
Each muscle fiber is targeted by how many neuromuscular junctions?
1
What neurotransmitter is released at neuromuscular junctions to initiate muscle contraction?
acetylcholine
Where can lower motor neurons be found?
ventral horn of the spinal cord
Unilateral damage to motor cortex leads to paralysis mainly on the ____ side of the body. Unilateral damage to the spinal cord leads to paralysis mainly on the ____ side of the body.
contralateral, ipsilateral
Degeneration of neurons in which of the following results in Parkinson's disease?
substantia nigra
The major input to the striatum is from …
cerebral cortex
Which of the following nuclei is NOT part of the striatum?
globus pallidus
Which of the following axon tracts divides the striatum?
internal capsule
Which of the following is a major direct input to Purkinje cells? Axons from …
cerebellar granule cells
In most regions of the cerebellum, Purkinje cells send axons to the …
a deep cerebellar nucleus.
Which of the following is a major source of axons that leave the cerebellum (i.e. output of the cerebellum)?
Deep cerebellar nuclei
Parallel fibers originate from which of the following
Granule cells
Golgi tendon organs relay information via ____ fibers about ____.
Ib, weight bearing
Typically, while walking, activation of the motor neurons for extensor muscles in one leg will roughly coincide with…
inhibition of the motor neurons for flexor muscles in the same leg.
What is TRUE about the effects of the brain on locomotion?
Descending glutamatergic pathways are required to initiate walking.
Which of the following is TRUE regarding the central pattern generator (CPG) for walking?
The CPG includes inhibitory interneurons whose axons cross the midline of the spinal cord.
Which of the following cranial nerves directly innervates the medial rectus muscle?
oculomotor (CN III)
Which type of movement is most essential for reading a street sign when you are walking down the street?
Vestibulo-ocular reflex
If you want to look to the left, which extraocular muscles must contract?
lateral rectus muscle of the left eye and medial rectus muscle of the right eye
Which of the following eye movements do you make when you are reading?
fixation followed by a saccade