Biology Midterm
5.0(2)
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/94
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
1
New cards
How does a plant respond to the environment
by turning towards the sun
2
New cards
Example of an adaption
Abmeoba has a structure that allows it to pump out excess water from it's body
3
New cards
what does a horse gain energy from
the grass it eats
4
New cards
when does a Caterpillar undergo dramatic changes
as it grows and develops
5
New cards
what are all organisms composed of
cells and cells are the smallest unit of life
6
New cards
levels of organization from simple to complex:
molecular, cellular, tissue, organ, organ system, organism
7
New cards
cells work together to form
tissues
8
New cards
tissues that function together make
organs
9
New cards
the molecular level:
DNA, proteins, carbs, and lipids
10
New cards
genetics
the study of heredity
11
New cards
Anatomy
The study of body structure
12
New cards
Botany
study of plants
13
New cards
Ecology
the study of the environment
14
New cards
what is a hypothesis
an attempt to explain an event or a set of observations
15
New cards
what are carefully designed experiments useful for
testing hypotheses
16
New cards
what are the 2 parts of an experiment
the experimental set up and the control set up
17
New cards
what is a microscope
an instrument that produces enlarged images of a specimen. The best light microscope can magnify up to 1500 times.
18
New cards
the parts of the microscope:
body tube, revolving nose piece, scanning, high power objective, low power objective, stage clips, diaphragm, light source, ocular lens, arm, stage, coarse focus, fine focus, and base
19
New cards
ocular lens:
10x magnification
20
New cards
low power objective:
10x magnification, 100x total magnification
21
New cards
high power objective:
40x magnification, 400x total magnification
22
New cards
what does good resolution mean
the image is clear
23
New cards
what is an atom
the smallest particle of an element that has the element's properties
24
New cards
what are the 3 particles that make up an atom
proton, neutron and electron
25
New cards
first energy level in an atom:
can hold a maximum of 2 electrons
26
New cards
atomic number:
determined by the number of protons in an element
27
New cards
atomic mass:
determined by the number of protons and neutrons in an element
28
New cards
organic molecules:
any molecule with carbon including the carbs, proteins, lipids and nucleic acids
29
New cards
inorganic molecules:
water, carbon dioxide or CO2, and carbon monoxide or CO are inorganic molecules
30
New cards
carbon:
has 6 electrons - 4 are available for bonding
31
New cards
functional groups:
groups of atoms that carry out chemical reactions
32
New cards
monomer:
small building block molecules
33
New cards
polymers:
molecules made by linking 2 or more monomers
34
New cards
dehydration:
process of removing water to form a compound
35
New cards
hyrolysis
process of splitting a molecule with water
36
New cards
what are 3 elements that make up carbohydrates
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
37
New cards
What are monosaccharides
glucose (blood sugar), fructose (fruit sugar), and galactose
38
New cards
what are the disaccharides
sucorse (table sugar), and lactose (milk sugar)
39
New cards
What are polysaccharides
chitin, cellulose, glycogen, and starch
40
New cards
chitin:
exoskeleton of certain animals
41
New cards
cellulose:
cell walls of plants, gives plants support
42
New cards
glycogen:
how animals store excess sugar
43
New cards
starch:
how plants store excess sugar
44
New cards
what are the lipids
fats, waxes, steroids, and phospholipids
45
New cards
peptide:
consist of 2 or more amino acids and they make up proteins
46
New cards
saturated fats:
like butter are made of fatty acids containing no double bonds
47
New cards
aminoo acid:
contains an amino functional group and a carboxyl functional group and the peptide bond forms between these two groups when amino acid bond to each other
48
New cards
enzymes:
proteins that speed up chemical reactions in the body
49
New cards
cell theory:
all biological organisms are composed of cells; cells are the unit of life and all life comes from preexisting cells
50
New cards
diffusion:
net movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
51
New cards
osmosis:
diffusion of water
52
New cards
hypotonic solution:
the concentration of solutes is lower than the concentration f solutes inside the cells so water moves into the cell
53
New cards
hypertonic solution:
the concentration of solutes is higher than the concentrations of solutes inside the cells so the water moves out of the cells
54
New cards
isotonic solution:
concentration of solutes is equal
55
New cards
active transport:
uses energy to take molecules across the membrane
56
New cards
bulk transport:
moves large molecules across the membrane
57
New cards
endocytosis:
brings in large molecules in bulk
58
New cards
exocytosis:
removes large molecules in bulk
59
New cards
cell cycle:
phases of the life of the cell
60
New cards
interphase:
period of growth prior to division
61
New cards
cell division:
made up of mitosis and cytokinesis
62
New cards
what happens during the s phase of interphase
the chromosomes replicate
63
New cards
phases of mitosis:
prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
64
New cards
gametes:
sexual reproductive cells that result from meiosis
65
New cards
zygote:
single cells that result from sexual reproduction
66
New cards
what are homologous pairs
matching pairs of chromosomes
67
New cards
Meiosis 1:
separates homologous pairs of chromosomes
68
New cards
meiosis 2:
separates sister chromatid
69
New cards
trait:
any characteristic that can be passed from parent to offspring
70
New cards
hybrid:
gets different genetic information from each parent
71
New cards
each of Mendel's traits:
occurred in 2 distinct observable forms
72
New cards
purebred plants:
produce only plants like themselves when they self fertilize
73
New cards
recessive trait:
what Mendel called the trait that did not show up in the hybrid
74
New cards
allele:
different versions of a gene for the same trait
75
New cards
genotype:
the actual genetic makeup of an organism
76
New cards
heterozygous:
an organism with 2 alleles for a trait that are different
77
New cards
Punnett Square:
a grid that shows all the possible results of a genetic cross
78
New cards
incomplete dominance:
not dominant or recessive alleles, the heterozygote shows an in between of the 2 homozygous phenotypes
79
New cards
co dominance:
when both homozygous phenotypes show up in the heterzygous
80
New cards
example of co dominance:
AB blood type
81
New cards
examples of polygenic traits:
eyes, skin and hair color
82
New cards
(Know how to work all types of genetic problems that we have covered up to midterm.)
.
83
New cards
linked gene:
when genes are close together on the same chromosome
84
New cards
sex-linked gene:
applies to the genes that are located on the sex chromosome
85
New cards
(know how to work sex linked problems and pedigree.)
.
86
New cards
what did Walter Sutton say
chromosomes are the basis of heredity
87
New cards
what did Theodor Boveri say
male sperm nuclei and female egg nuclei were equivalent in the amount of hereditary information
88
New cards
what did Bateson and Punnet do
they co-discovered gene-linkage and re-did Mendel's experiments
89
New cards
Recombinants:
result of crossing over
90
New cards
what did Thomas Hunt Morgan do
conducted statistical studies of the way genetic traits are passed on in fruit flies
91
New cards
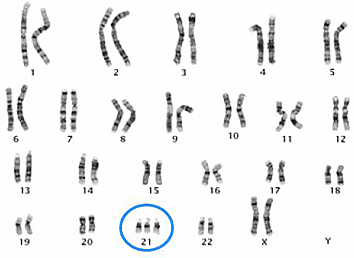
Down Syndrome mutation:
\-non-disjunction
\-trisomy 21
\-moon face
\-thick or protruding tongue
\-trisomy 21
\-moon face
\-thick or protruding tongue
92
New cards
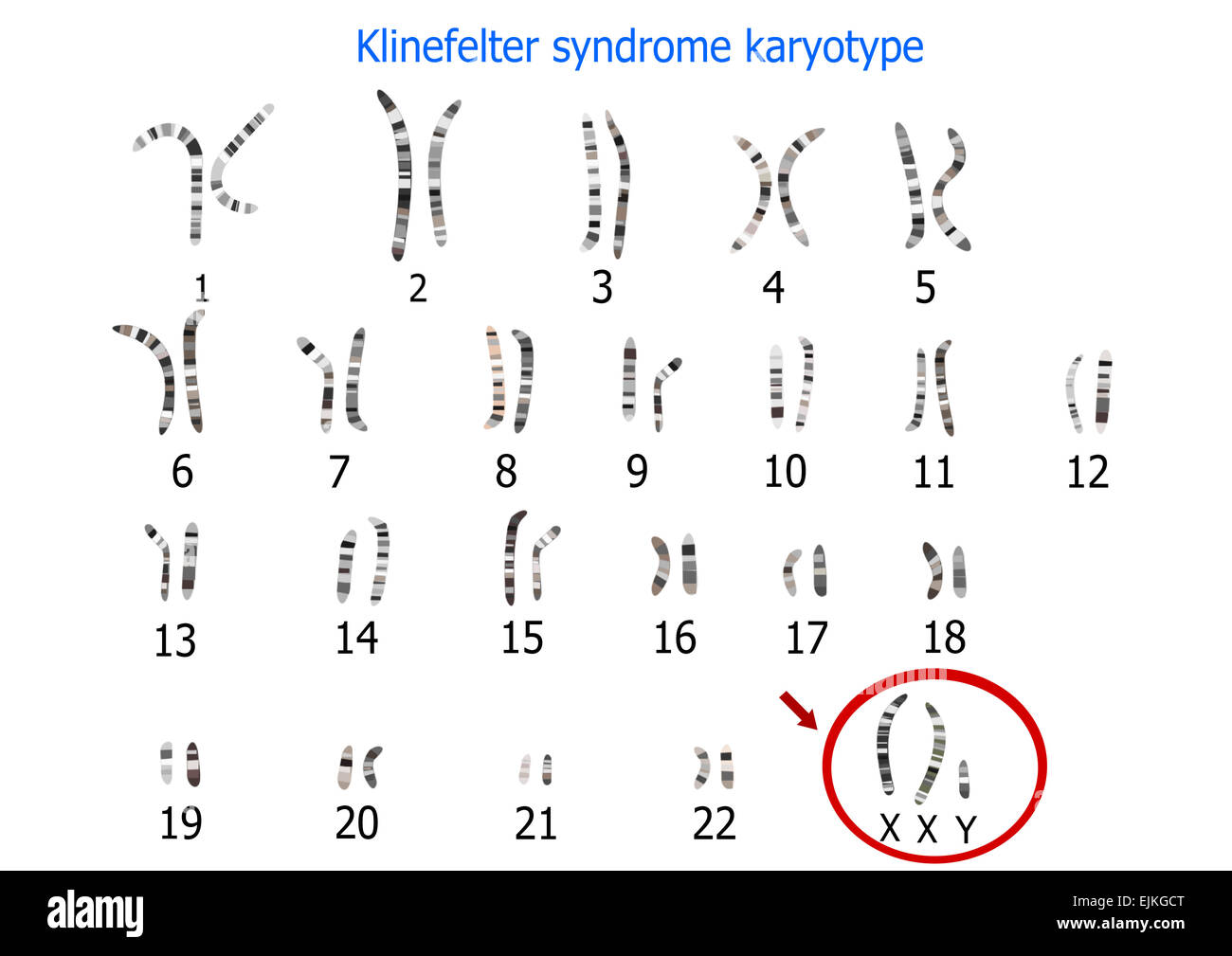
Klinefelters Syndrome mutation:
\-non-dis-junction
\-trisomy 23
\-only in males
\-have feminine features
\-trisomy 23
\-only in males
\-have feminine features
93
New cards
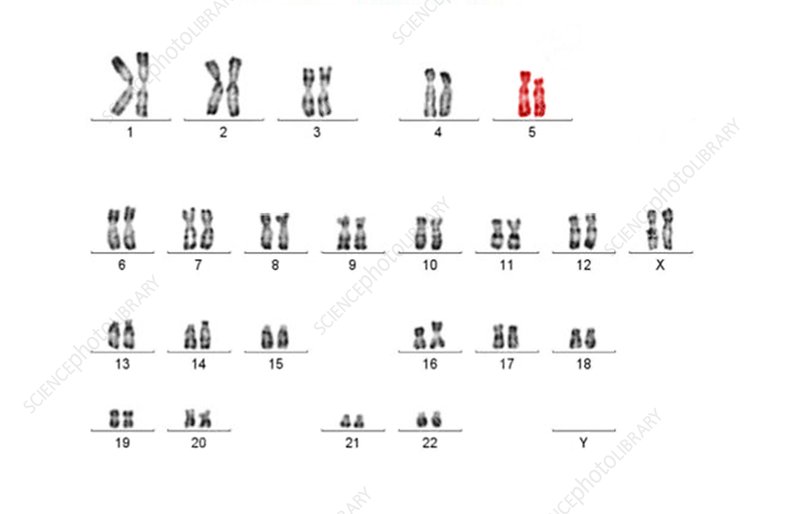
Cri du chat syndrome mutation:
\-structural
\-deletion of the 5th chromosome
\-cat like cry
\-small head, low birth weight
\-deletion of the 5th chromosome
\-cat like cry
\-small head, low birth weight
94
New cards
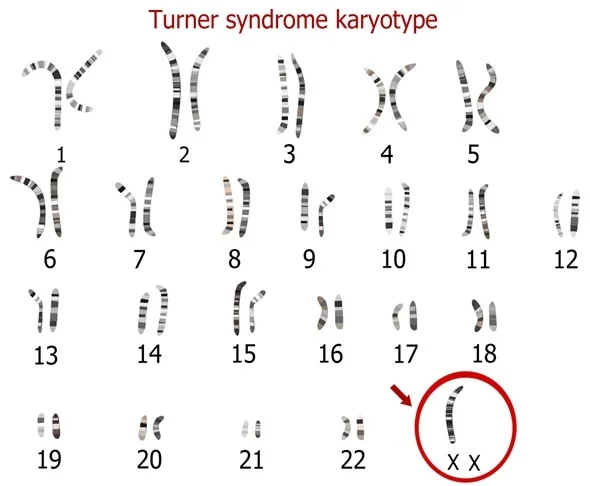
Turner's Syndrome mutation:
\-non-disjunction
\-monosomy
\-webbed neck, short stature
\-only in women
\-monosomy
\-webbed neck, short stature
\-only in women
95
New cards
What did Nettie Stevens do
one of the first scientists to find that sex is determined by a particular configuration of chromosomes