R3.4.5 Addition reactions of alkenes
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
Due to the carbon-carbon double bond (alkene group).
Double bond opens to form new bonds in addition reactions.
Electrophilic addition.
Two reactants combine to form one product.
Double bond breaks during reaction.
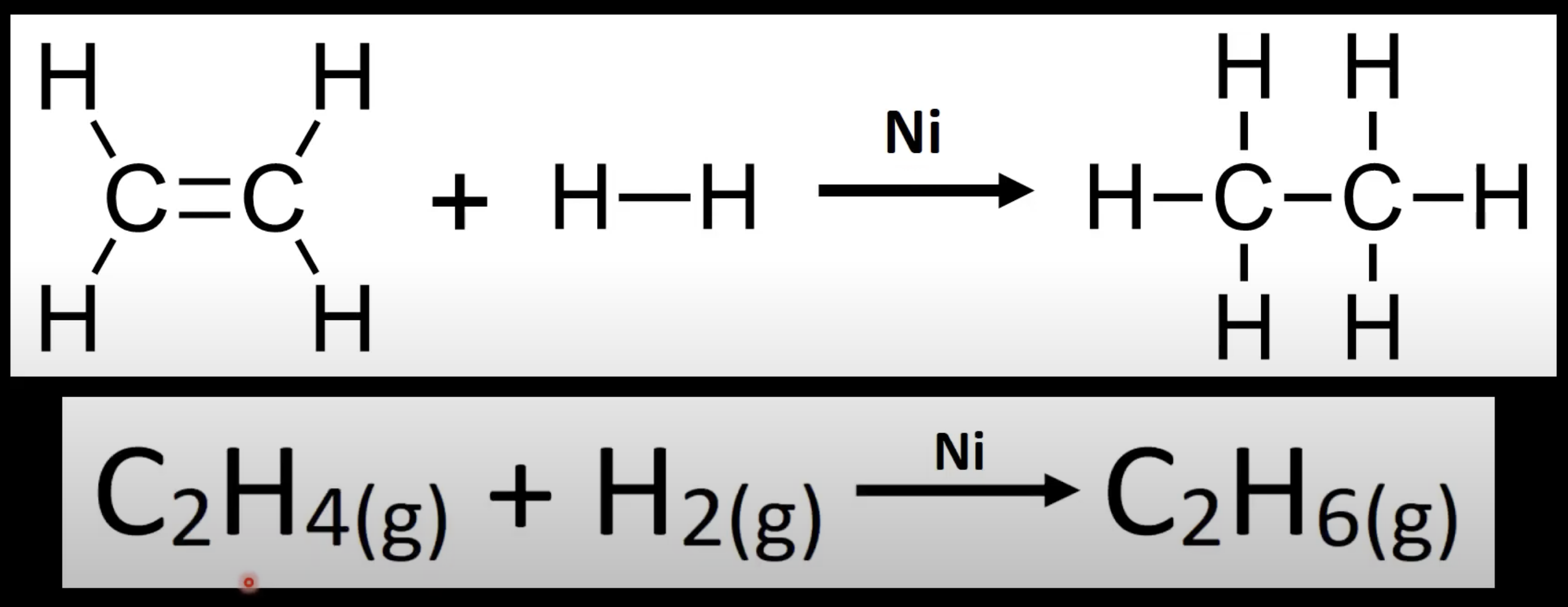
Alkene + H₂ → alkane.
Uses nickel catalyst.
Adds hydrogen atoms to saturate the molecule.
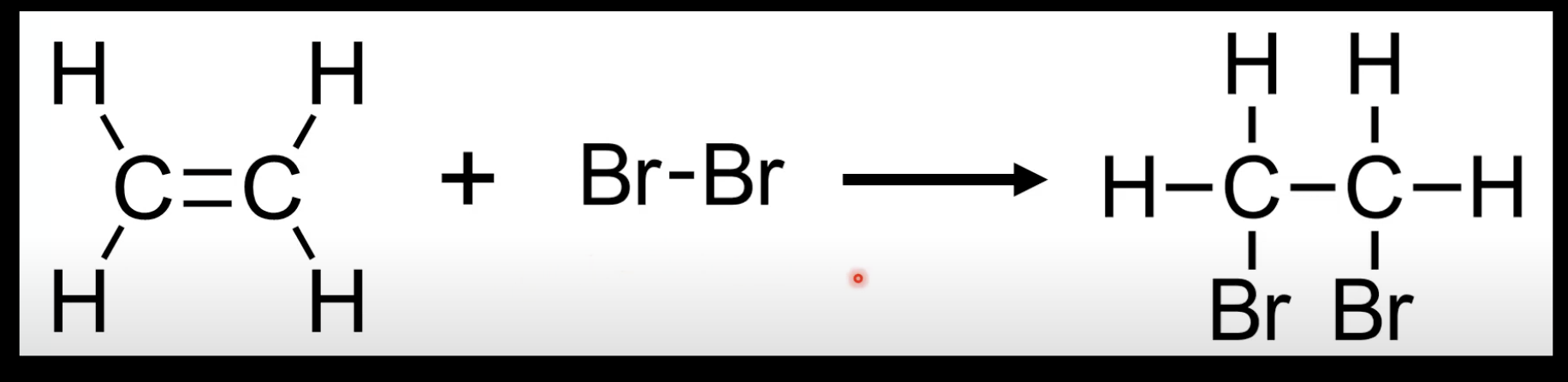
Alkene + X₂ → dihalogenoalkane.
Example: Ethene + Br₂ → 1,2-dibromoethane.
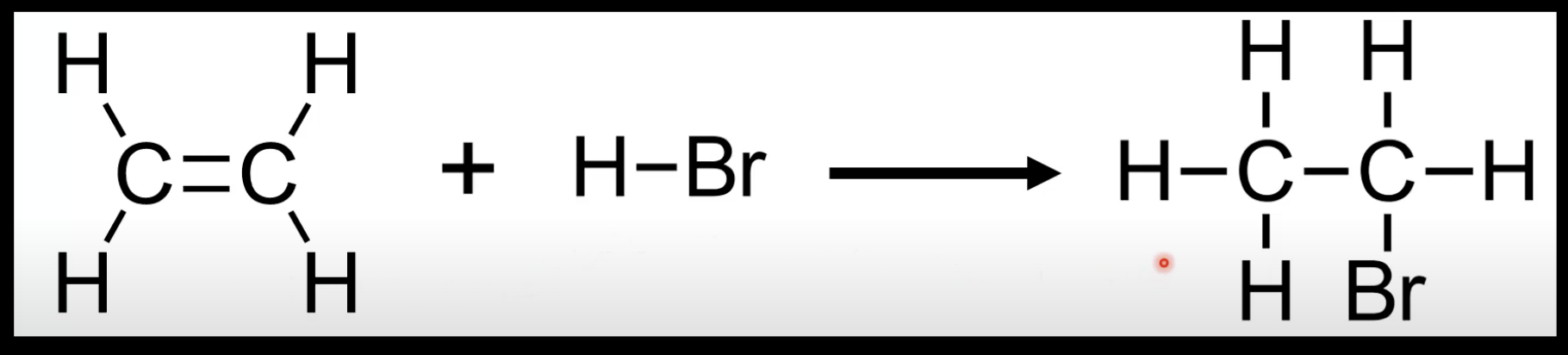
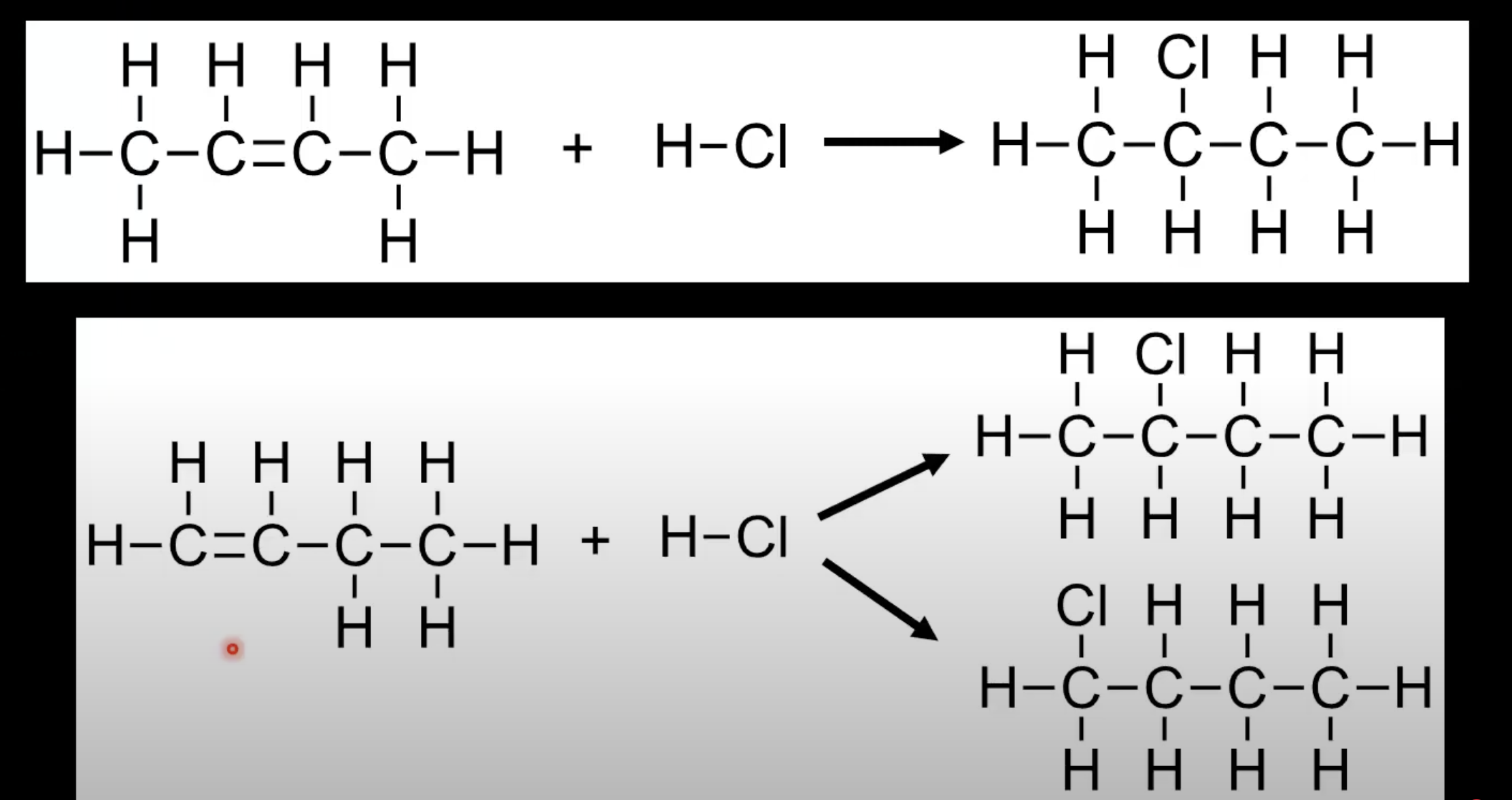
Alkene + HX → halogenoalkane.
Example: Ethene + HBr → bromoethane.
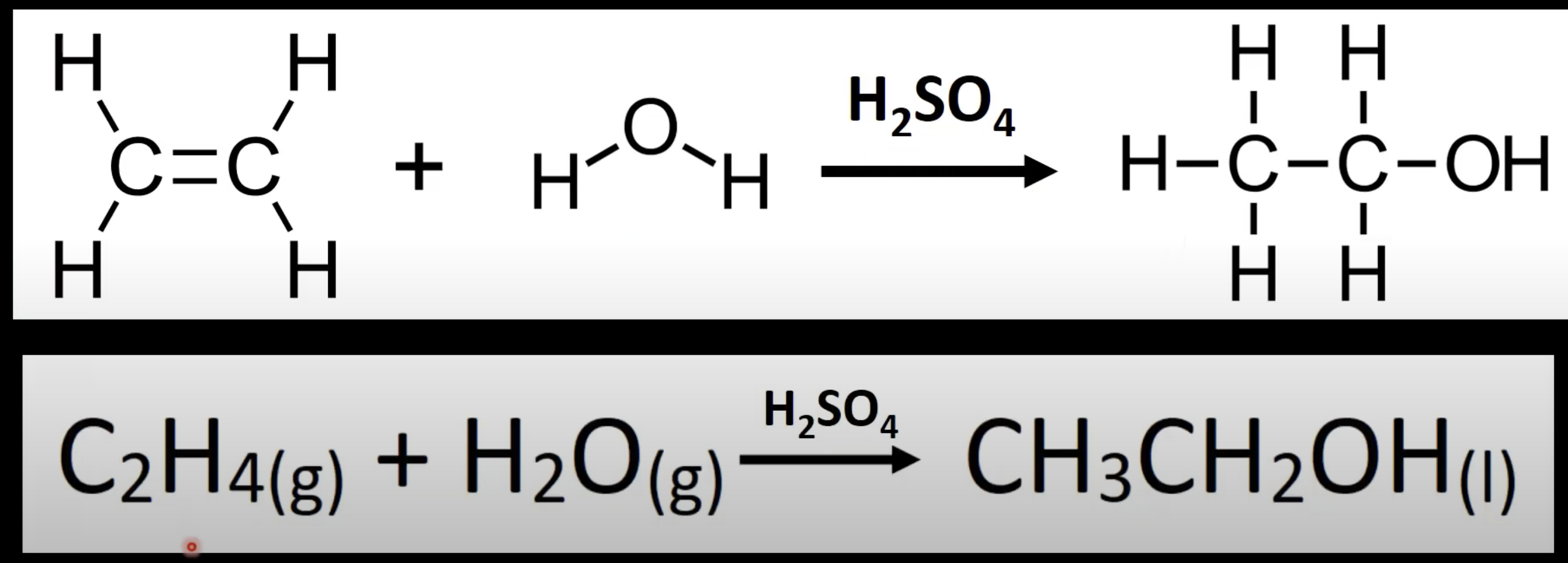
Alkene + steam → alcohol.
Uses H₂SO₄ catalyst.
Example: Ethene + H₂O → ethanol.
Symmetrical alkenes form one product.
Unsymmetrical alkenes may form two products.
Saturated: only C–C single bonds (alkanes).
Unsaturated: contains C=C or C≡C bonds (alkenes, alkynes).
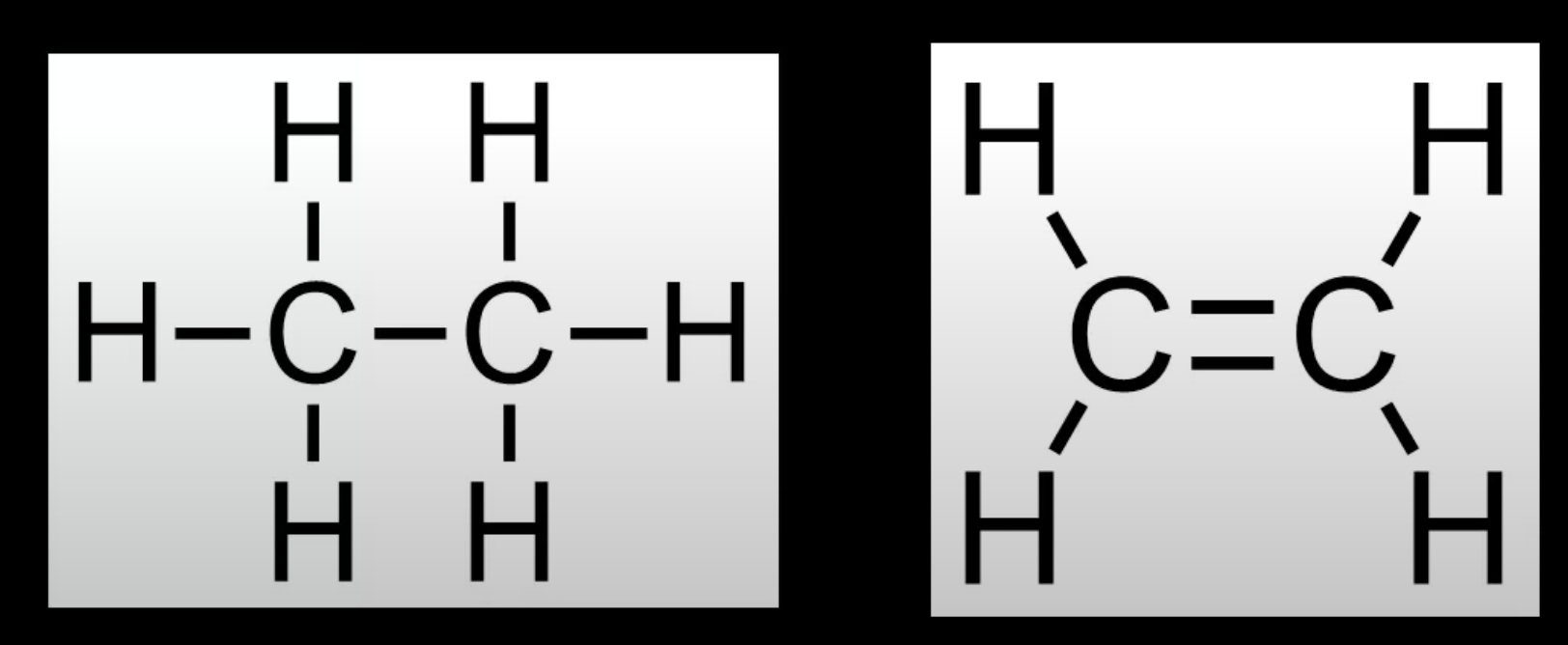
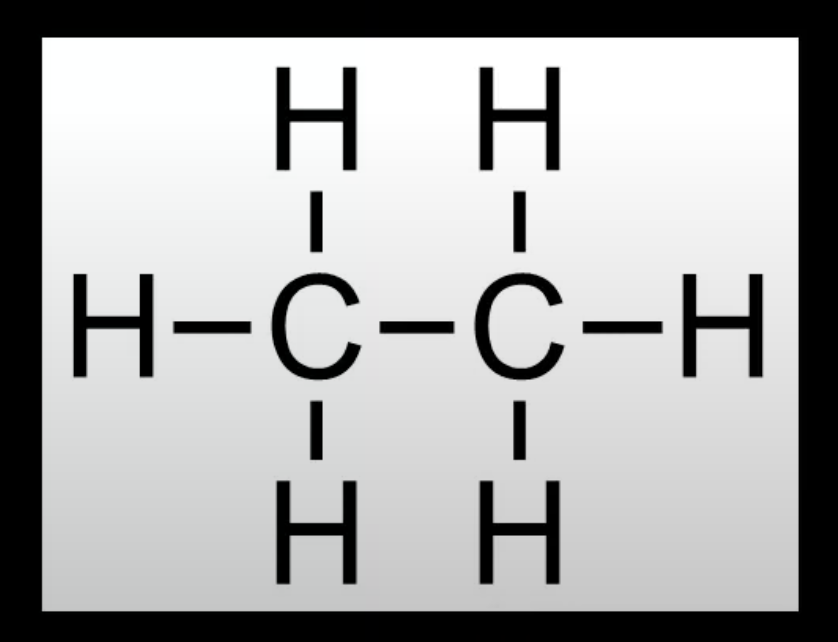
Ethane (C₂H₆). Has only single bonds between carbon atoms.
Classified as saturated.
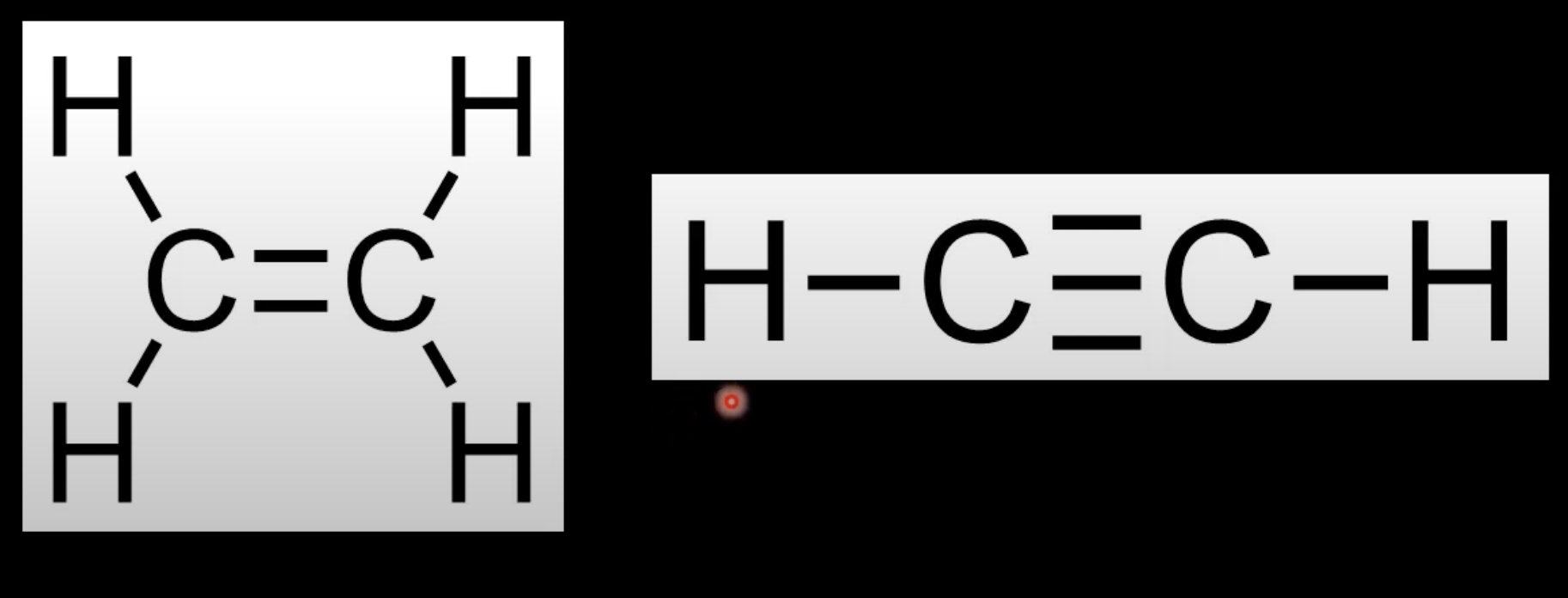
Ethene (C₂H₄) has a double bond.
Ethyne (C₂H₂) has a triple bond.
Both are unsaturated.
Use bromine water.
Brown solution turns colorless if C=C is present.
No change if saturated.

No color change.
Indicates saturated molecule with only C–C single bonds.

Turns from brown to colorless.
Indicates presence of C=C bonds, confirming unsaturation.
