BCHE 3200 Exam 1 Banerjee
1/366
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
367 Terms
Polar molecule
part of the molecule isslightly positive while the other partis slightly negative
H-O-H bond angle
104.5
What kind of bond has a nearly tetrahedral arrangement of orbitals around oxygen, bonds with 4 neighboring water molecules?
Hydrogen bonds
How many H-bonds does each molecule form in a liquid state?
3.4
In ice, each molecule forms bonds with ____ water molecules → lattice structure
4
T/F: Water interacts electrostatically with charged solutes
True
Hydrophilic
dissolves in water
Do polar compounds dissolve in water?
Yes
Which of the following is NOT hydrophilic?
a) Glucose
b) Glycine
c) Aspartate
d) Lactate
e) Glycerol
f) All are hydrophilic
f) All are hydrophilic
hydrophobic
do not dissolve in water
T/F: lipids and waxes are non-polar molecules
true
Water interacts ____________ with charged solutes
electrostatically
Amphiphilic
Part hydrophilic/hydrophobic
➢ Surfactants and detergents, phospholipids, cholesterol, fatty acids
the property of water molecules to be attracted to each other, which causes them to stick together
cohesion
Adhesion
the property of water molecules to be attracted to molecules other than water
A homogeneous mixture of one or more ________ dissolved in a ________
solutes, solvent
A substance that can be dissolved into a solution by a solvent
solute
A substance in which a solute is dissolved
solvent
a concentrated solution of a chemical substance that is used tomake more dilute solutions
stock solution
stock solution equation
N1V1 = N2V2
N1 = Concentration of the stock solution
V1 = Volume of the stock solution
N2 = Concentration of the solution to be prepared
V2 = Volume of solution to be prepared
Any substance that can donate a proton
acid
Anyy substance that can accept a proton
base
T/F: Water acts as both an acid and a base
TRUE
Can water be a strong acid or a strong base?
No
pH=-log[H+]
pH equation
What is the fold difference inH+ from pH 6 to pH 10?
10,000
a solution that resists changes in pH when an acid or base is added,even in small amounts.
buffer
T/F: Strong acids completely dissociate in water.
TRUE
What is pKa?
inherent property of a particular substance.
Indicates whether an acid is a strong acid or a weak acid
How is Ka related to pKa?
pKa = -logKa
a number that measures how acidic a molecule is, or how tightly a proton is held by an acid
pKa
Is a high Ka acidic or basic?
acidic
Is a high pKa acidic or basic?
basic
T/F: Ka and pKa are inverersley proportional
TRUE
Henderson-Hasselbalch equation
pH = pKa + log [A-]/[HA]
The point at which the acid and conjugate base are in balance, the pH of the solution is equal to the pKa of the acid
half equivalence point
T/F: More carbonic acid we have in the blood, less likely is the reaction of CO2 with H2O to form carbonic acid.
True
Buffer system of blood
carbonic acid and bicarbonate
What are proteins?
Most versatile macromolecules in living systems that serve crucial functions in almost all biological processes
What do amino acids consist of?
a carboxyl group, an amino group, and a side chain, all attached to a central carbon atom
What kind of reaction does a peptide bond have?
Dehydration-condensation reaction
Peptide bond formation is accompanied by the loss of a __________ molecule
water
T/F: The polypeptide chain consists of a constant backbone and variable side chains.
True
Largest known protein
titin with 27,000 letters (amino acids)
In what ways do amino acids vary?
• Size
• Charge
• Shape
• Hydrogen-bonding capacity
• Hydrophobic character
• Chemical reactivity
Amino Acids: Nonpolar, aliphatic R groups
GAVLIMP
glycine, alanine, proline, valine, leucine, isoleucine, methionine
Amino Acids: Non-polar, aromatic R groups
First Year Writing
phenylalanine, tyrosine, tryptophan
Non-polar amino acids
GRANDMA ALWAYS VISITS LONDON IN MAY FOR WINSTON'S PARTY
Glycine, Alanine, Valine, Leucine, Isoleucine, Methionine, Phenylalanine, Tryptophan, Proline
Glycine feature
Simplest amino acid. Achiral
Alanine feature
Has a CH3 methyl for its R-group
Valine, Leucine, and Isoleucine feature
Branched chain amino acid
Methionine feature
contains sulfur
Proline feature
R group bound directly to the alpha-amino group
Phenylalanine feauture
Precursor for other amino acids and neurotransmitters
Tyrosine feature
Formed by the hydroxylation of phenylalanine in the liver
Tryptophan feature
R group of 9 carbons and one nitrogen in a structure known as an indole ring
Amino acids: polar uncharged
Santa's Team Crafts New Quilts
serine, threonine, cysteine, asparagine, glutamine
Amino acids: Negatively charged
Dragons Eat
aspartate, glutamate
Amino acids: Positively charged
Knights Riding Horses
lysine, arginine, histidine
Cysteine feature
Form of an SH group known as sulfhydryl
serine features
Body's proteins, enzymes and muscle tissue
What is threonine a precursor to
glycine and serine
Histidine feature
• Often found in the activesites of enzymes
•Positively charged
aspartate feature
A precursor to threonine biosynthesis also connected to the TCA cycle through fumarate and oxaloacetate
glutamate feature
The most abundant excitatory neurotransmitter in the vertebrate nervous system
What is a chiral carbon?
Carbon atom with four different groups attached
Isomer
Compounds with the same formula but different structures.
constitutional isomer
compounds with the same molecular formula but different connections among their atoms
Stereoisomers
molecules that have the same structural formulas and bonding patterns but different arrangements of atoms in space
Diastereomers
stereoisomers that are not mirror images
enatiomers
isomers that are mirror images of each other
Is R/S configuration absolute or relative?
absolute
Is D/L configuration absolute or relative?
relative
Rules of R/S configuration
1. Rank your substituents, highest to lowest atomic number
2. Make sure number 4 is at the back(dashed line)
3. Cross out number 4
4. Trace direction of 1 → 2 → 3
a chemical property of chiral molecules that measures howmuch plane-polarized light rotates as it passes through a sample of the molecule
Specific rotation [𝛼]
light with an electric field that is limited to a single plane
polarized light
dextrorotatory
clockwise rotation (+)
levorotatory
counterclockwise
Specific rotation depends on...
Pathlength- Longer the pathlength, the greater the rotation Concentration- Higher the concentration, the greater the rotation
Temperature- Higher is the temperature, faster is the specific rotation
Lightbulbs- Different bulbs will have different light emission
Specific rotation equation
[a] = a/cxl
[a] = specific rotation
a = observed rotation
c= concentration (g/ml)
l = pathlength (dm)
T/F: Peptide bonds are planar and usually assume the trans-configuration
True
Can peptide units rotate?
yes
Structure of each amino acid can be adjusted by rotation about how many single bonds?
two
Rotation of these bonds can be specified by torsion angles called phi and psi
...
T/F: The freedom of rotation about two single bonds of each amino acid allows proteins to fold in many ways
TRUE
Are all combinations of φ and ψ possible?
Many combinations are forbidden because of steric collisions between atoms
Ramachandran plot
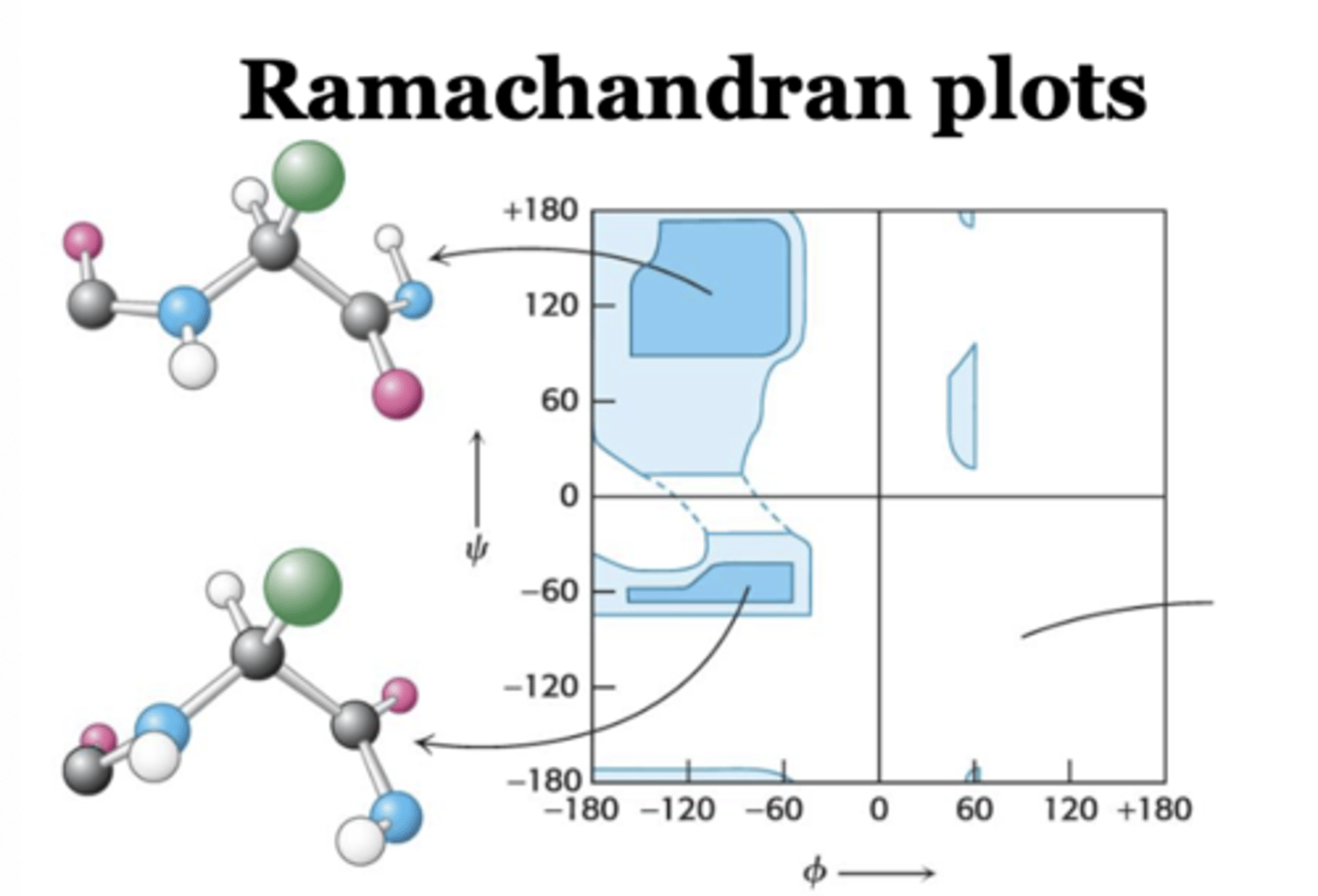
What color is the region where bond angles are easily allowed in a ramachandran plot?
dark blue
What color regions are comparatively lower in bond angles?
Intermediate blue
What does the white color represent in the ramachandran plot?
White color in between the dotted line is the region that displays the least favorable region to have bond angles
Which amino acid of a protein occupies the largest area in the Ramachandran plot?
glycine
Which amino acid of a protein occupies the smallest area in the Ramachandran plot?
proline
The ______ of the peptide unit and the restricted set of allowed φ and ψ angles limits the number of structures accessible to the unfolded form sufficiently to allow protein folding to take place
rigidity
Can a polypeptide chain fold into a regularly repeating structure?
yes
Linus Pauling and Robert Corey
Polypeptide chains can fold into regular (secondary) structures such as the alpha helix and the beta-sheet.
Structure of the right handed alpha helix
• Rod-like structure - 3.6 amino acids per turn!
• Tightly coiled backbone forms the inner part of the rod, and the side chains extend outward
• Stabilized by hydrogen bonds between the NH and CO groups of the main chain
Example of right handed alpha helix
ferritin
How is alpha helix held together?
It is held together by hydrogen bonds between the C=O of residue i and the NH of residue i+4
Is right handed alpha helix curved?
Yes
Are alpha helix hydrophilic?
No, α Helix are usually amphiphilic or hydrophobic