Things I did not know
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Why does denaturation happen at a high temperature
The contribution of TΔS becomes more important when the temperature increases
Why does denaturation happen at a low temperature
The strong hydrophobic bond decreases, ΔHbond becomes less positive and consequently ΔG decreases
Why does denaturation happen at extreme pH values?
The electrostatic repulsion in the shell increases, the outer shell of the globule becomes more stretched, and can even be broken open. This implies that ΔHbond is less positive at extreme pH
Why does denaturation happen when the quality of the solvent is altered?
If a solvent is added that is a good solvent for the hydrophobic core, the core of the globule may swell. Again ΔHbond becomes less positive due to the fact that the hydrophobic interaction decreases. Moreover, we get back the interaction of the nucleus with a good solvent. This provides an additional enthalpy change that is negative
Why does denaturation happen when surfactants are added that attach themselves to the hydrophobic core?
This results in the hydrophobic interaction within the core decreasing and ΔHbond will be less positive. In addition, we will gain the enthalpy change due to core-surfactant interactions which is negative. Therefore ΔG decreases when surfactants are added.
Why does denaturation happen when reactants are added?
Reactants may break bonds, when the strength of the internal structure decreases as a result of eliminating covalent bonds, ΔHbond becomes less positive and ΔG decreases.
What is necessary for stability?

What radius do you use for change in volume
Calculated with effective segments!
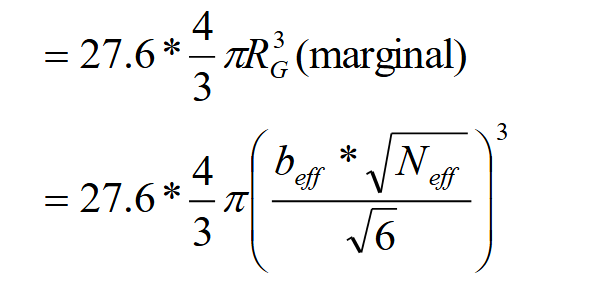
name three flour based sauces
Espagnole, Velouté and béchamel
Name three emulsion based sauces
Hollandaise, Béarnaise and mayonnaise
What determines the crystallinity of the starch granule?
Ratio between the two constituents
Describe what happens to a starch granule in water when it is heated (distinguish two stages, and mention the temperatures that define these two stages).
First melting, losing the crystalline structure of the granule, and afterwards the dissolution of the molecules into the surrounding liquid
Give one important distinction between wheat starch and corn starch in terms of their ingredients, and explain how that affects their appearance once they are thickening the solution they are in.
Wheat starch contains proteins, while corn starch does not. First is non-transparent, while the second is transparent and glossy upon cooling
Why can an emulsion sauce that is stored at cold temperature be destabilized upon heating?
Too cold may deprive the droplets from their emulsifiers, thus leading to
coalescence while heating again
Describe the colloidal structure of whipped cream. What aspects of the colloidal
structure lead to the stabilisation of the system
Cream suitable to be whipped is an oil in water emulsion (fat content higher than 30-35%) of fat globules covered by a membrane and dispersed in a water phase consisting of skimmed milk. (2 points) As a consequence of whipping, the fat globules are absorbed at the air/ water interface and partly coalesce. This results in the formation of a network of fat globules, which leads to the stabilization of the system
Thickening of Natural starch vs. Modified starch
Natural: thick because of swollen starch granules + some leached amylose
Modified (are more resistant to high temperatures): thick because of swollen starch granules
Force of gravity
F = mass * gravity (9.81)
Force of surface tension
F = surface tension * 2 pi r
The experiment is repeated a third time, again with a new sample, and again with a force of 10 N, but now the upper plate moves at twice the speed. Do you expect the value of G to be higher or lower than your answer in b). Explain your answer
The material is viscoelastic; at a higher speed less relaxation will occur during the deformation process, and more energy is reversibly stored in the structure.
Would in general the Gibbs adsorption equation also applicable to protein solutions?
No because:
Conformational Changes: Unlike simple surfactants, proteins usually change their conformation (unfold) once they reach a fluid/fluid interface.
Irreversible Adsorption: The Gibbs equation assumes a state of reversible equilibrium partitioning between the bulk phase and the interface.
Denaturation: In some cases, the change in configuration at the interface is so extreme that the protein effectively denatures
Write down the Gibbs adsorption equation and explain the symbols used.
Tm denotes the surface coverage in units of moles per m2
X1 the concentration surfactant
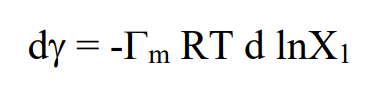
What is the meaning of C*
the specific concentration of polymer segments per unit volume where the individual polymer coils first begin to touch or overlap with one another
therefore the lower C*, the more viscosity because the solution already becomes thick at a lower concentration.