Exam 3: Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves (complete)
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
What are the functions of the spinal cord?
conduction, locomotion, reflexes
Conduction
communication between body & brain
Locomotion
the continuation of walking controlled by the spinal cord (initiation, speed, and direction is from the brain)
Reflexes
involuntary responses to stimuli, does not necessarily go to the brain.
What are the regions of the spinal cord?
cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, coccygeal
What is different between the cervical and lumbar regions?
Cervical region has cervical englarment, it supplies nerves for the upper extremities. Lumbar region has lumbar/lumbosacral enlargement, supplies nerves for lower extremities.
What are the structures of the spinal cord?
-Conus medullaris
-Cauda equina
-Terminal filum
-Anterior median fissure / Ventral median fissure
-Posterior median sulcus / Dorsal median sulcus
Conus medullaris/ medullary cone
end of spinal cord
Cauda equina
nerves extensions from spinal cord that looks like horses tail
terminal filum
extension of the pia matter to anchor to coccyx
Anterior median fissure / Ventral median fissure
deeper, wider groove on the anterior side of spinal cord
Posterior median sulcus / Dorsal median sulcus
narrow groove on the posterior side of the spinal cord
What are the meninges and spaces within the spinal cord?
➢ Epidural space
Dura mater
➢ Subdural space
Arachnoid mater
➢ Subarachnoid space
Pia mater
Epidural space and its mater
between vertebra and dura matter; contains blood vessels, adipose tissue, and areolar connective tissue;
Dura mater
Subdural space and its mater
potential space between the dura matter and the arachnoid matter; Arachnoid mater
Subarachnoid space and its mater
filled with CSF;
Pia mater
Dura mater
outermost meninges layer for stability
Arachnoid mater
meninges made of simple squamous epithelium + mesh of collagenous and elastic fibers
Pia mater
innermost meninges layer that is on the surface of the spinal cord made of elastic and collagen fibers. Includes terminal filum
epidural injection vs spinal tap
Epidural goes into epidural space, spinal tap is taken between the vertebrae of the lower lumbar spine
Gray matter
inner part of the spinal cord and contains little myelin, but mostly somas, dendrites, and proximal portions of axons; location where information is processed (synapses)
White matter
outer part of the spinal cord with highly myelinated axons called tracts, carrying information to different parts of the CNS.
What are the different parts of gray matter in the spinal cord?
Posterior horns / Dorsal horns
Anterior horns / Ventral horns
Lateral horns
Gray commissure
What type of structures/neurons will you find in different parts of gray matter in the spinal cord?
Multipolar neurons
What is the space within the spinal cord called? How is it different from adults vs children?
Central canal; space filled with CSF that contain ependymal cells in children but mostly collapsed in adults.
Posterior horns / Dorsal horns
Axons (not cell bodies) of sensory neurons and cells bodies of interneurons are located here (multipolar neurons)
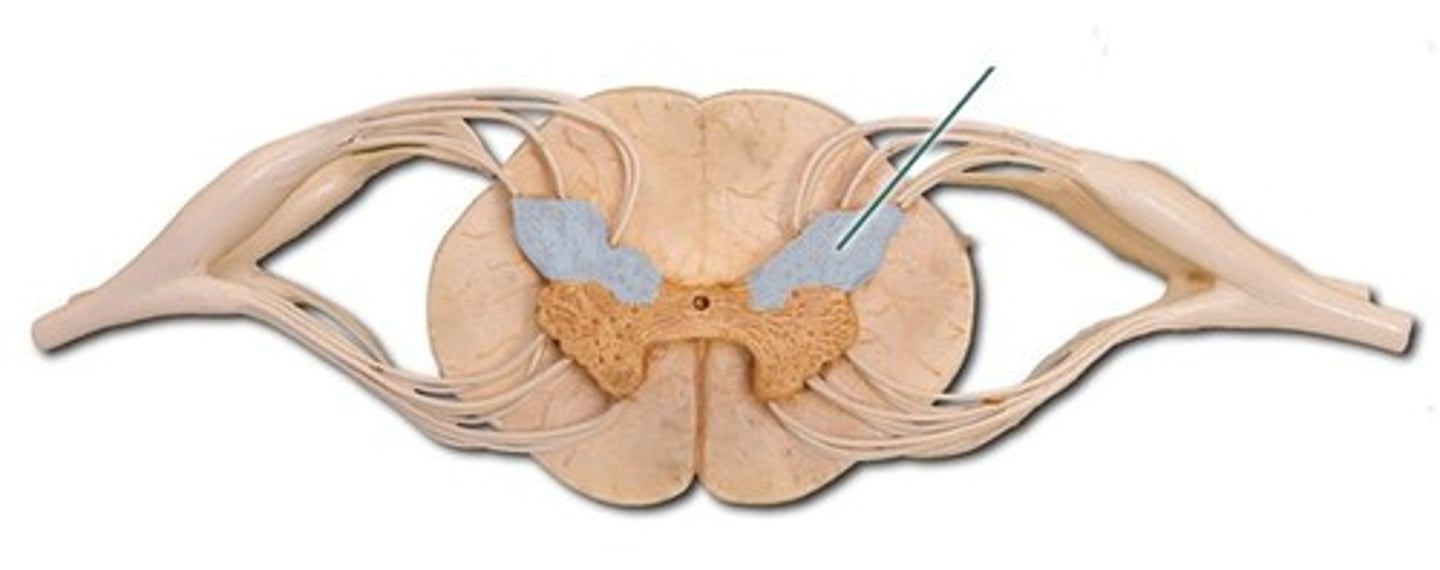
Anterior horns / Ventral horns
Cell bodies (nuclei) of somatic motor neurons are located here to send information out of the spinal cord (multipolar neurons)
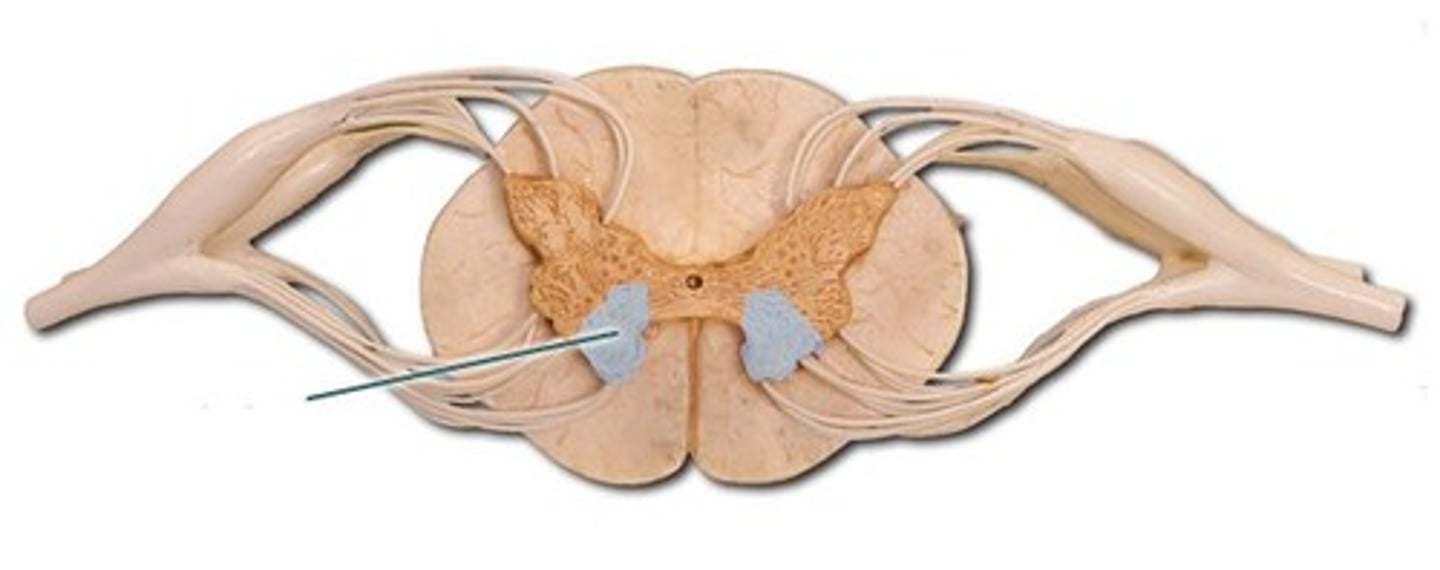
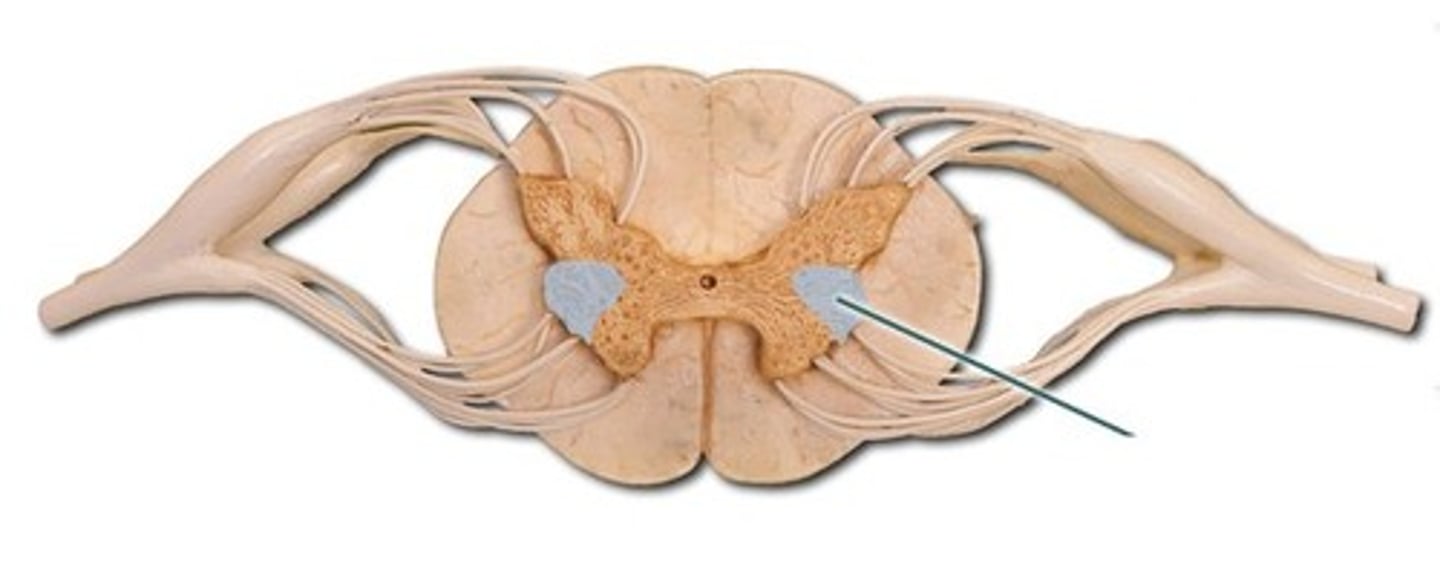
Lateral horns
(only in T1-L2) contains cell bodies (nuclei) of the autonomic nervous system (multipolar nuerons)
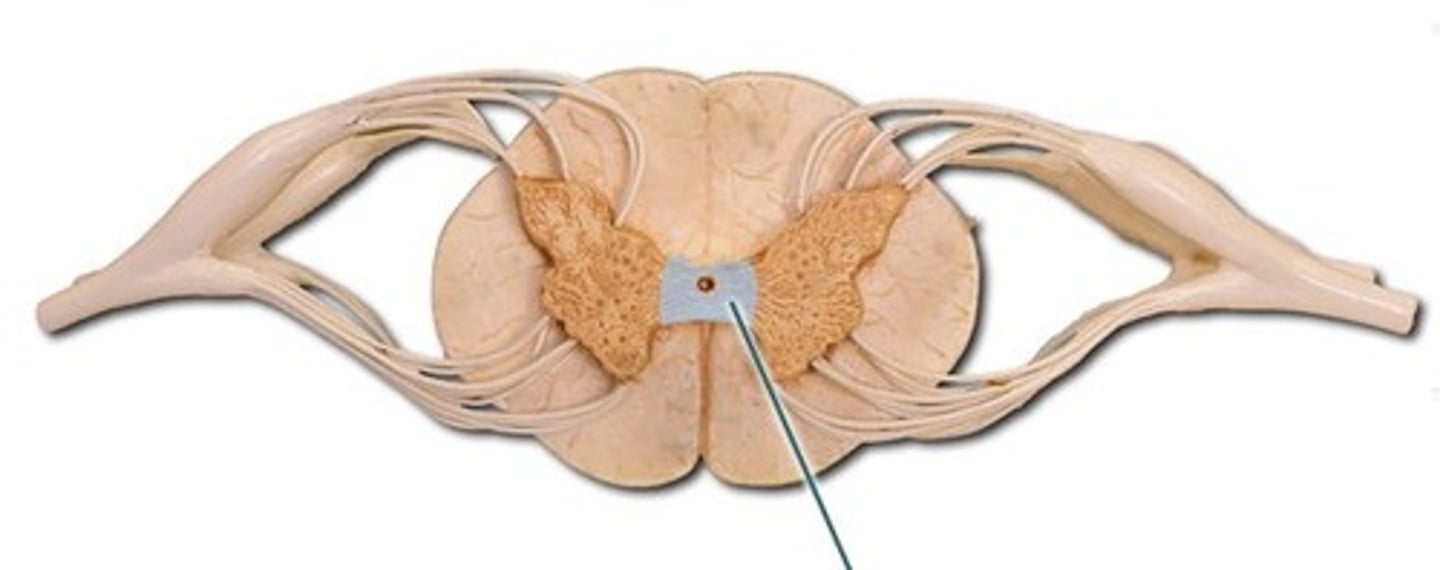
Gray commissure
structure that connects the right and left parts of gray matter of the spinal cord, surrounding the central canal
What are the different parts of white matter?
-Posterior/dorsal columns / funiculi
-Anterior/ventral columns / funiculi
-Lateral columns / funiculi (only in T1-L2)
What information do ascending vs descending tracts carry?
Ascending tracts – carry sensory information up the SC
Descending tracts – carry motor information down the SC
What are decussation, ipsilateral, contralateral?
Decussation - when neurons cross over to opposite side of the body
Ispilateral - no decussation occurs so tracts stay on the same side
Contralateral - decussation occurs so tracts cross over to opposite side
How many spinal nerves do we have? What type of nerves are they?
31 pairs of spinal nerves that extend from spinal cord; mixed nerves
Where does the first spinal nerve go through?
First pair between skull and atlas (C1), while the rest pass through intervertebral foramina
How many spinal nerves for each region of the spinal cord have?
8 cervical (C1-8), 12 thoracic (T1-12), 5 lumbar (L1-5), 5 sacral (S1-5), 1 coccygeal (Co)
What type of information goes through the spinal nerve proper?
Carries information from sensory AND motor neurons to and from the spinal cord, and is made of several nerve fibers (axons)
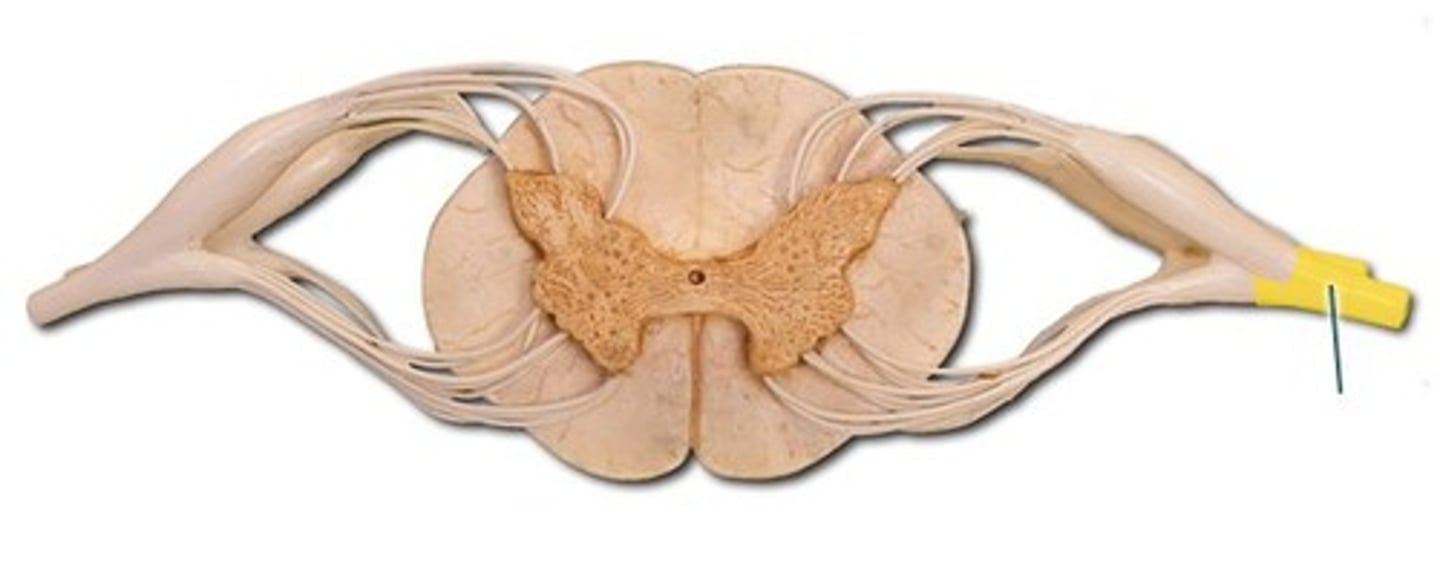
If sensory info is sent to spinal nerve proper, structures will it go to next?
Posterior/ dorsal root: carries the sensory nerve fibers entering the posterior horn
Posterior root ganglion: has somas of sensory neurons (unipolar neurons)
If motor information is sent to spinal nerve proper, what structures did that motor information come from?
Anterior/ ventral root – carries somatic motor axons from anterior horn (and lateral horn) and eventually to the skeletal muscles.
Posterior/dorsal ramus
Innervates the muscles and joints in spine (ie:erector spinae) and back skin
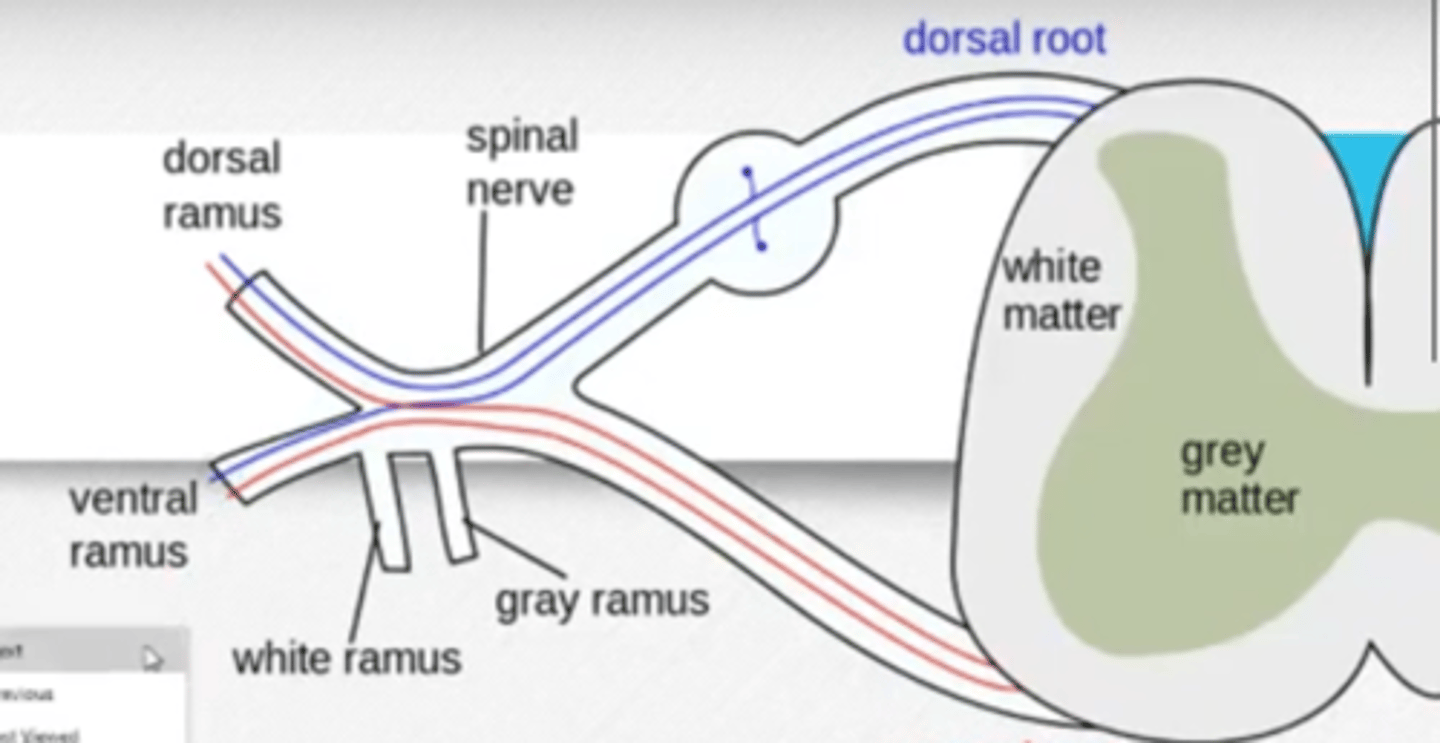
Anterior/ventral ramus
Innervates the anterior & lateral skin, muscles of the trunks, and nerves of limbs. Has white & gray communicating rami.
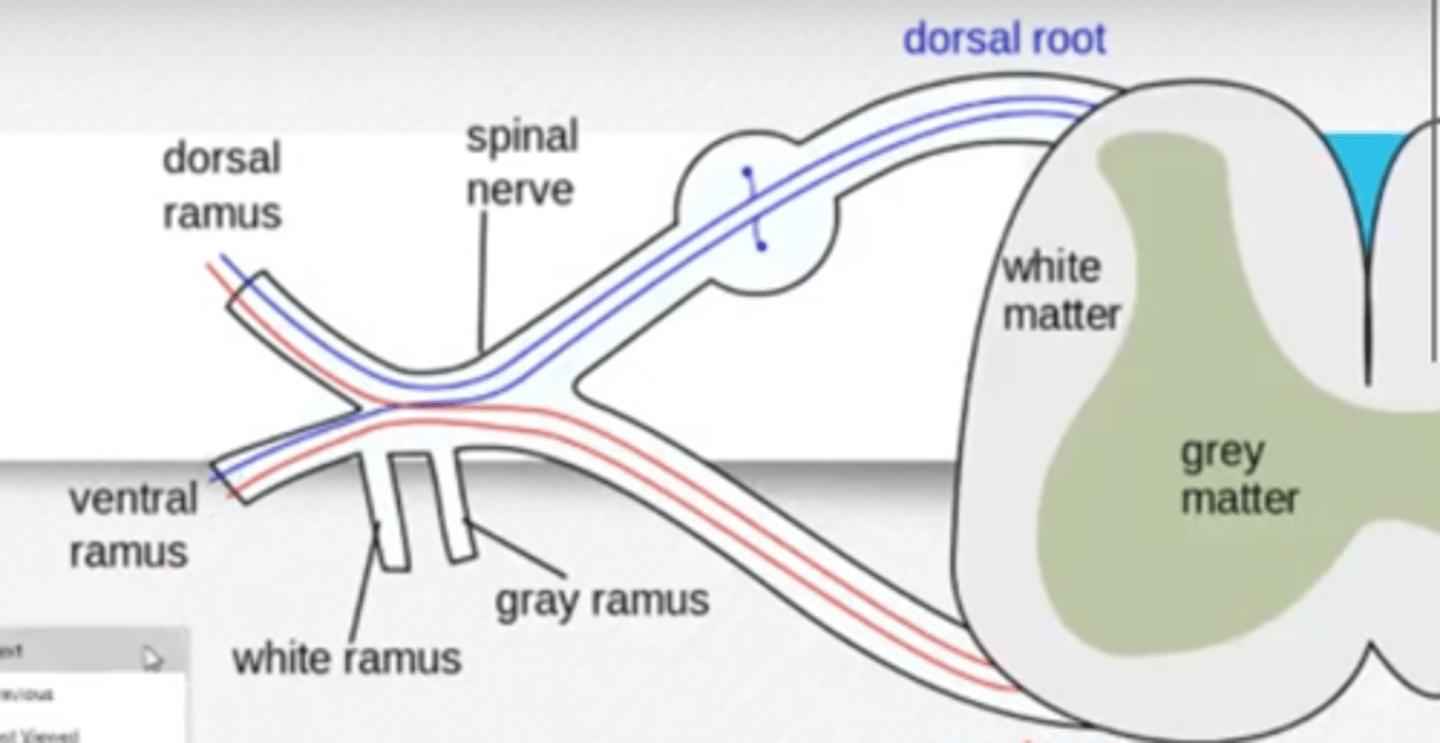
What structures comes off of/goes through the anterior ramus?
Communicating rami (white & gray)- connects to sympathetic chain ganglia
Intercostal nerves – thoracic region innervating skin and intercostal muscles, and abdominal muscles
Nerve plexuses – group of spinal nerves coming and dispersing
Communicating rami
Extend from anterior ramus: connects to sympathetic chain ganglia of SNS; includes white ramus and gray ramus
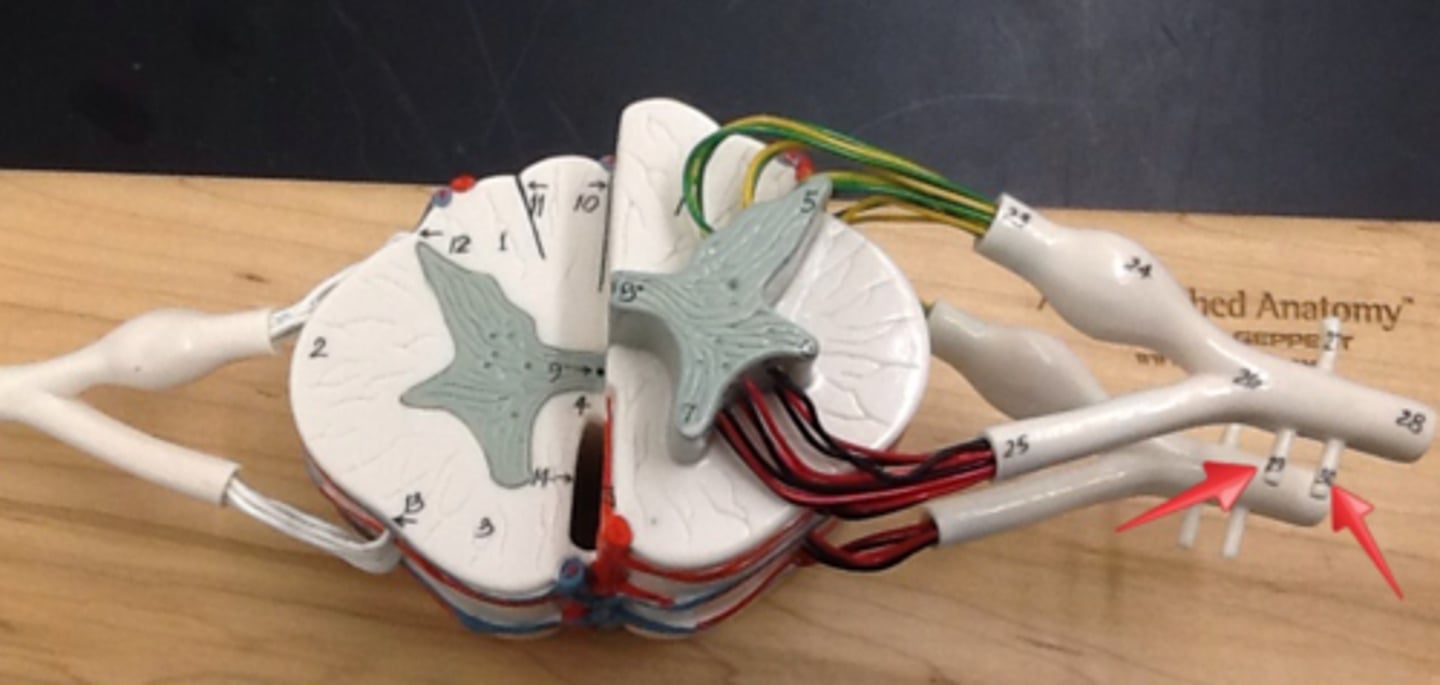
Intercostal nerves
come from anterior ramus: Nerves between ribs in the thoracic region, innervating skin, intercostal muscles, and abdominal muscles
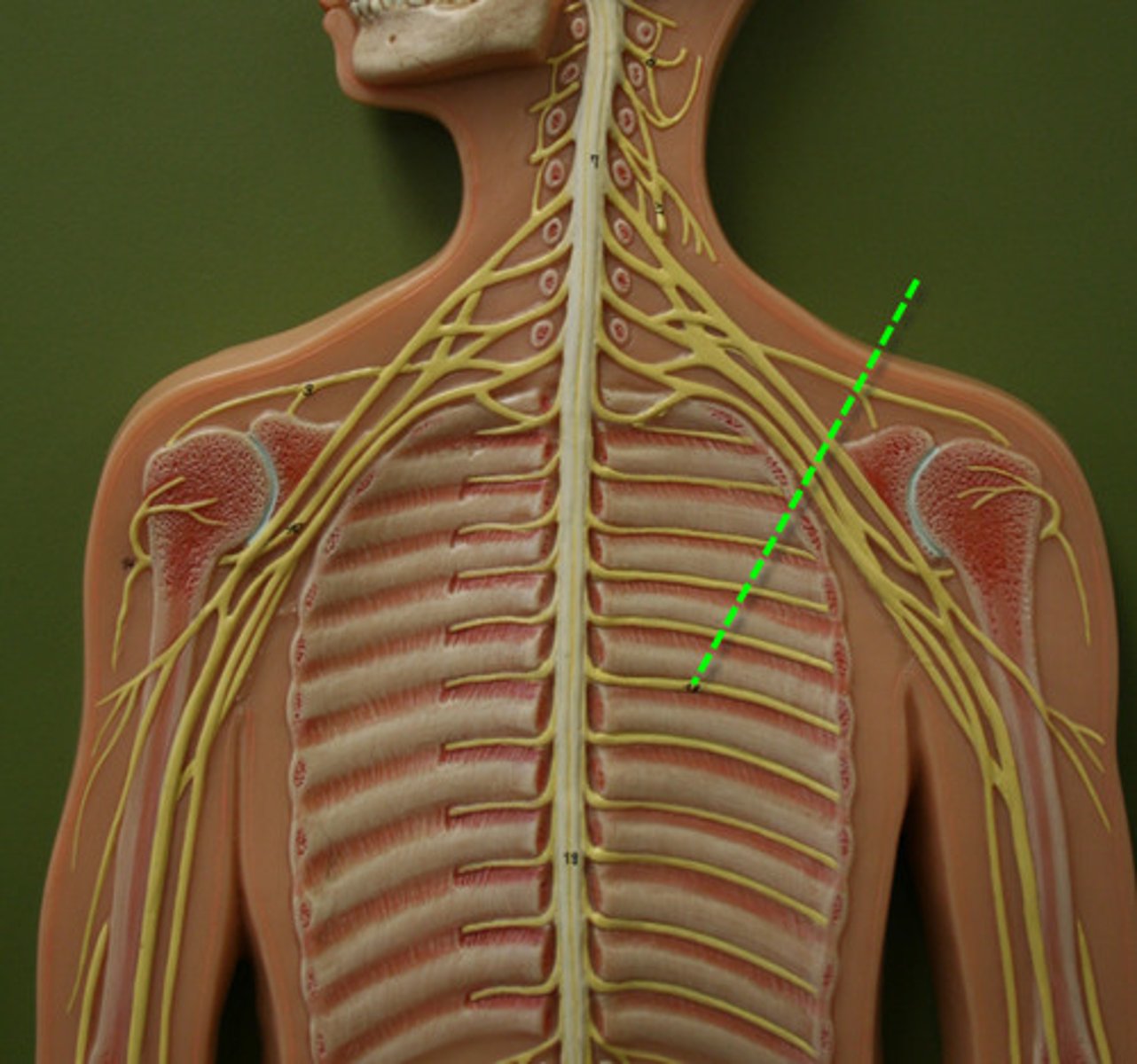
From anterior ramus: group of spinal nerves coming and dispersing
Nerve plexuses
Dermatome
The area of skin where each spinal nerve innervates
Referred visceral pain
Pain from an organ that is referred to a dermatone.
What are nerve plexuses?
Network of nerves from anterior rami that contains somatosensory info (from bones, joints, muscles, skin), motor function (for contracting skeletal muscles and autonomic fibers for blood vessels (smooth muscle)
What are the different nerve plexuses?
cervical, brachial, lumbar, sacral, coccygeal
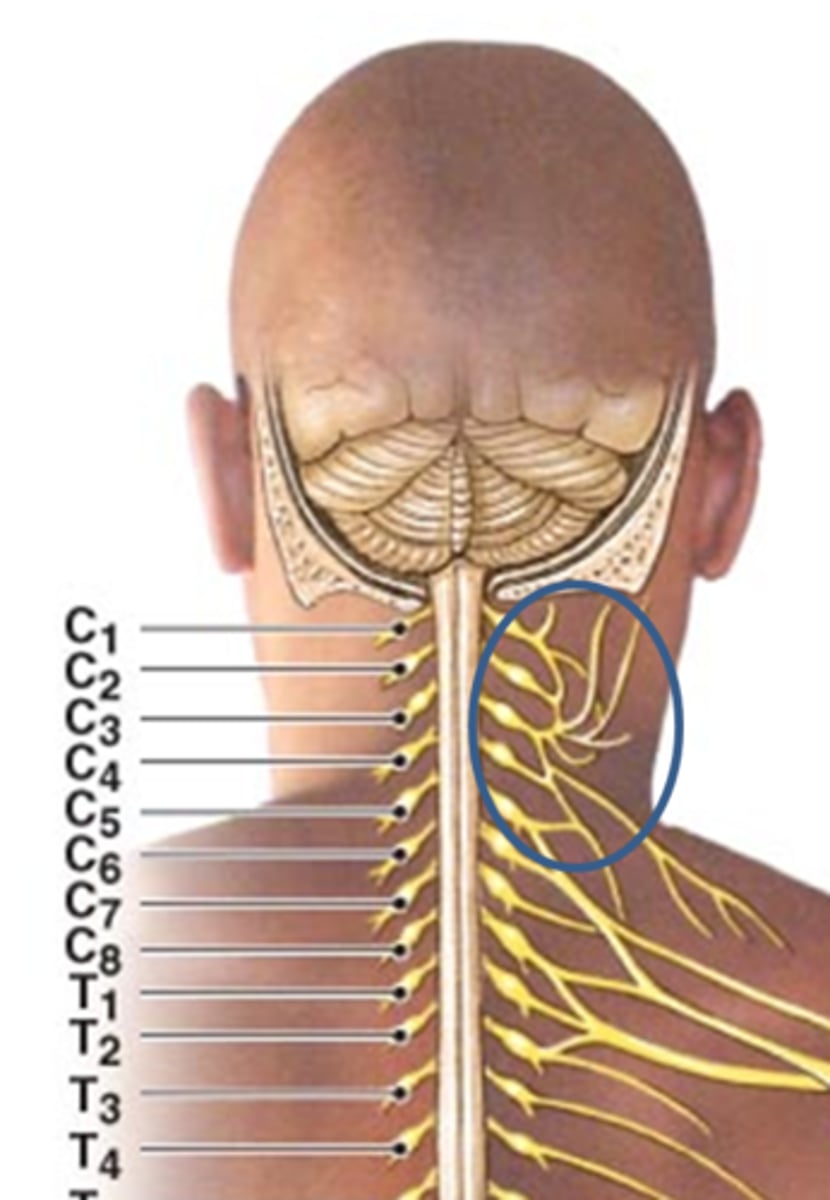
Cervical plexus
plexus from anterior rami of C1-C4 innervating anterior neck muscles, skin of the neck, and parts of the head & shoulder
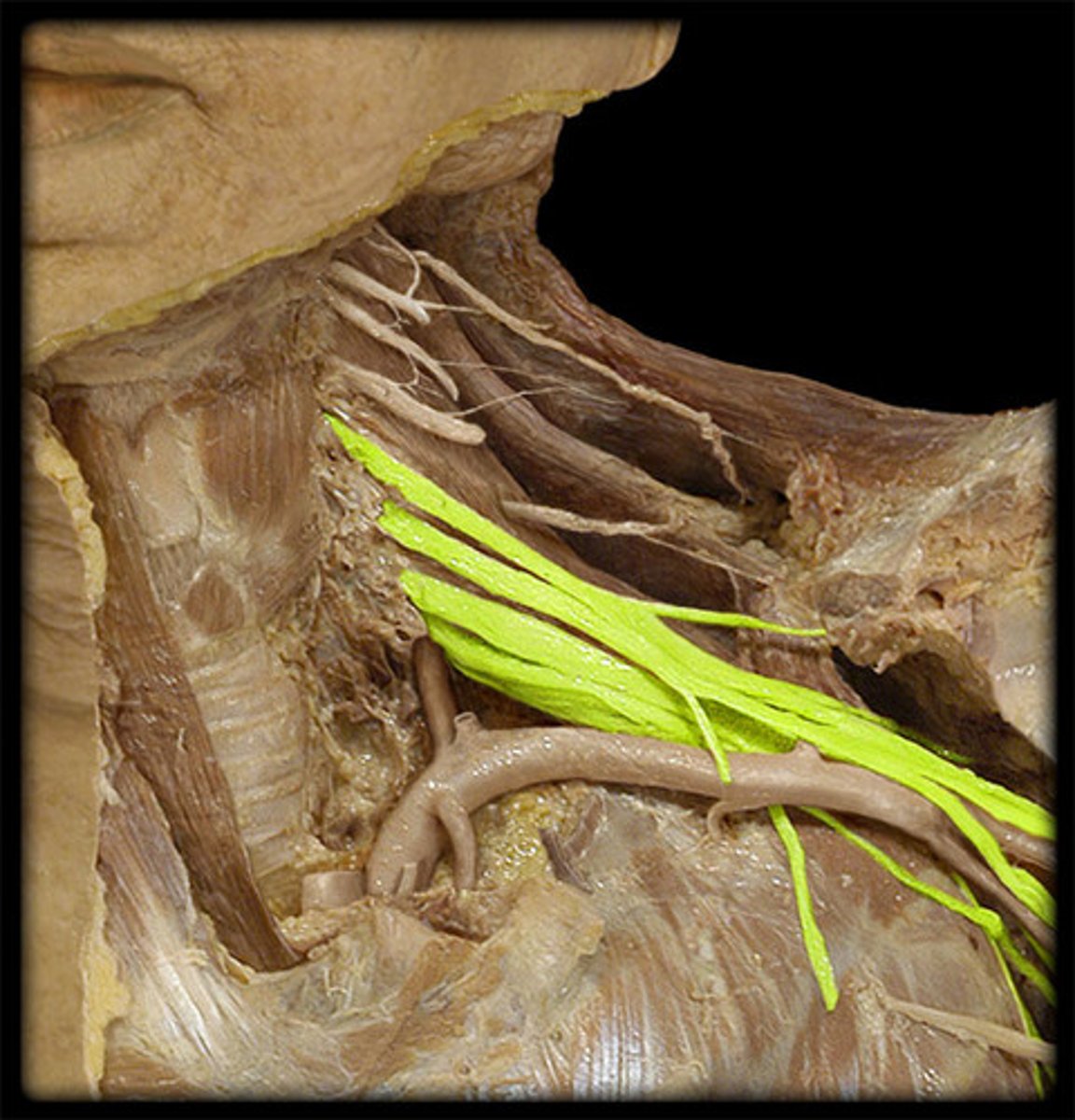
Brachial plexus
plexus from anterior rami C5 - T1 which supplies innervation of the upper extremities
Lumbar plexus
plexus from anterior rami L1 - L4 that contains the femoral nerve
Sacral plexus
plexus from anterior rami L4 - S4 that contains the sciatic nerve
Coccygeal plexus
plexus from anterior rami of S4-Co
What nerve comes off of the cervical plexus and its function? Which spinal nerves make up this nerve?
Phrenic nerve (C3-C5): innervates diaphragm to cause it to contract for inhalation.
What categories/divisions come off of the brachial plexus?
Anterior rami – sensory and motor information will be sent through the ventral ramus to and from the spinal cord.
Trunks – anterior rami merge forming 3 trunks.
Divisions – each trunk split into anterior vs posterior divisions
Cords – the six divisions converge forming three chords.
Anterior/ventral rami of brachial plexus
from brachial plexus: sensory & motor information will be sent through here to and from the spinal cord.
Anterior rami of brachial plexus merge forming 3 of these:
Trunks
Each trunk of the anterior rami of the brachial plexus splits into:
anterior and posterior divisions of the brachial plexus
the divisions of the brachial plexus converge forming:
3 Cords (of the brachial plexus)
What nerves come from each of the brachial plexus divisions?
Posterior division:
Axillary nerve & Radial nerve
Anterior division:
Musculocutaneous nerve, Median nerve, & Ulnar nerve
Axillary nerve
supplies sensory info from shoulder and arm; innervates deltoid & teres minor muscles
Radial nerve
supplies sensory info from the posterior arm & forearm; innervates extensor muscles of arm & forearm (triceps brachii, extensor carpi ulnaris, extensor carpi radialis)
Musculocutaneous nerve
supplies sensory info of the lateral forearm; innervates anterior arm muscles (biceps brachii, brachialis)
Median nerve
supplies sensory info from hand & digits; innervates forearm flexors (flexor carpi radialis, flexor digitorum superficialis)
Ulnar nerve
supplies sensory info of the medial part of hands & digits; innervates forearm flexors (flexor carpi ulnaris, flexor digitorum profundus)
What nerve comes off the lumbar plexus and what does it do?
Femoral nerve: supplies sensory info from anterior thigh; innervates iliacus, pectineus, quadriceps, and sartorius muscles.
What nerves come off the sacral plexus and its functions?
Sciatic nerve: largest & longest nerve; innervates hamstring muscles; divides around popliteal region into tibial nerve and common fibular/ peroneal nerve.
What nerves does the sciatic nerve become and its functions?
Tibial nerve – supplies sensory info from posterior leg & sole of foot (calf muscles)
Common fibular nerve – splits into two nerves; innervates lateral and anterior leg muscles; supplies sensory info from dorsum of foot, distal 1/3 leg, & dorsal interspace between 1st & 2nd toes
What are reflexes?
Quick, involuntary, stereotyped reactions of glands or muscles
What are the properties of reflexes?
Stimulation (reflexes respond to stimulus), Quick (bc little to no interneurons), Involuntary (occur without higher brain centers involved), and Sterotype (occurs the same way everytime)
What are the components of a somatic reflex arc and its order?
1. Stimulus
2. Receptor (somatic sensory receptor/muscle spindle)
3. Afferent/sensory nerve fibers
4. Integrating center
5. Efferent/motor neuron
6. Effector Response
Stimulus
stimulus stimulates Somatic sensory Receptor ie. muscle spindle
Somatic Sensory Receptor
detects stimulus within the skin, muscle or tendon
Afferent/sensory nerve fiber/neuron
carries sensory info to the posterior horn of the spinal cord or brainstem
Integrating center
synapse between afferent/sensory nerve fiber in the gray matter of the SC or brainstem; determines whether or not to signal efferent nerve fibers (can also include interneurons)
Efferent/motor nerve fibers/neurons
carries motor impulses to effector
Effector
skeletal muscle or gland that carries out response
Response
the action caused by an effector (skeletal muscle or gland)
What are the different proprioceptors?
muscle spindles, golgi tendon organs, and Joint kinesthetic receptors
Muscle spindles
proprioceptors that sense organ & muscle length for coordinated movement, muscle tone, & posture
Golgi tendon organs
Proprioceptors that are nerve endings in tendons
Joint kinesthetic receptors
Proprioceptors that are sensory receptors within joints
Stretch/mytatic reflex
When muscle is stretched, muscle spindles detect it & cause contraction to help maintain posture
Name a specific example of a stretch/mytatic reflex.
Patellar/ knee-jerk reflex: tapping patellar ligament stretches quadriceps, causing them to contract
What type of reflex arc is the patellar/ knee - jerk reflex?
Monosynaptic reflex arc – when primary afferent/sensory neuron synapses directly on the motor neurons
Monosynaptic reflex arc vs polysynaptic reflex arc
Monosynaptic reflex arc: only ONE synapse; only two neurons involved. Primary afferent neuron synapses directly onto motor neuron. Faster
Polysynaptic reflex arc: involves multiple synapses; slower
What is a withdrawal/flexor reflex? What type of reflex is this?
Contracts flexor muscles to withdraw limb from injury, also causing reciprocal inhibition. Is a polysynaptic reflex arc.
polysnaptic reflex arc
Slower reflex arc involving multiple synapses