Unit 10: Social and Economic Change
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Brown v. Board of Ed.
A supreme court case ended segregation in public schools. It overturned Plessy v. Ferguson, which said public facilities could be separate but equal. The Brown decision said "separate but equal is inherently unequal".

segregation
A policy of having separate public facilities for white people and "colored" people.
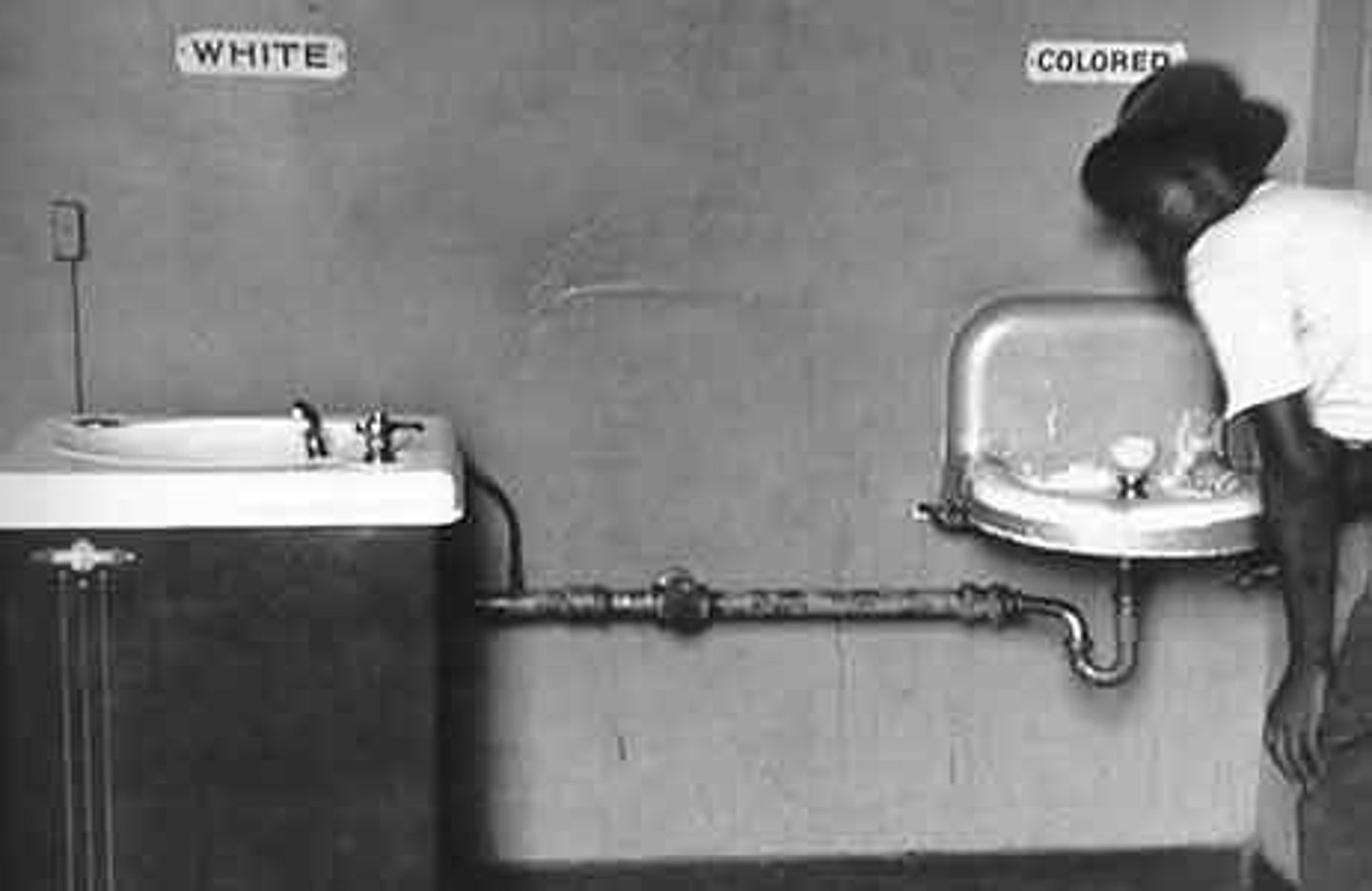

Montgomery Bus Boycott
A boycott to end bus segregation that lasted over a year. It successfully integrated the public buses in Montgomery, Alabama.
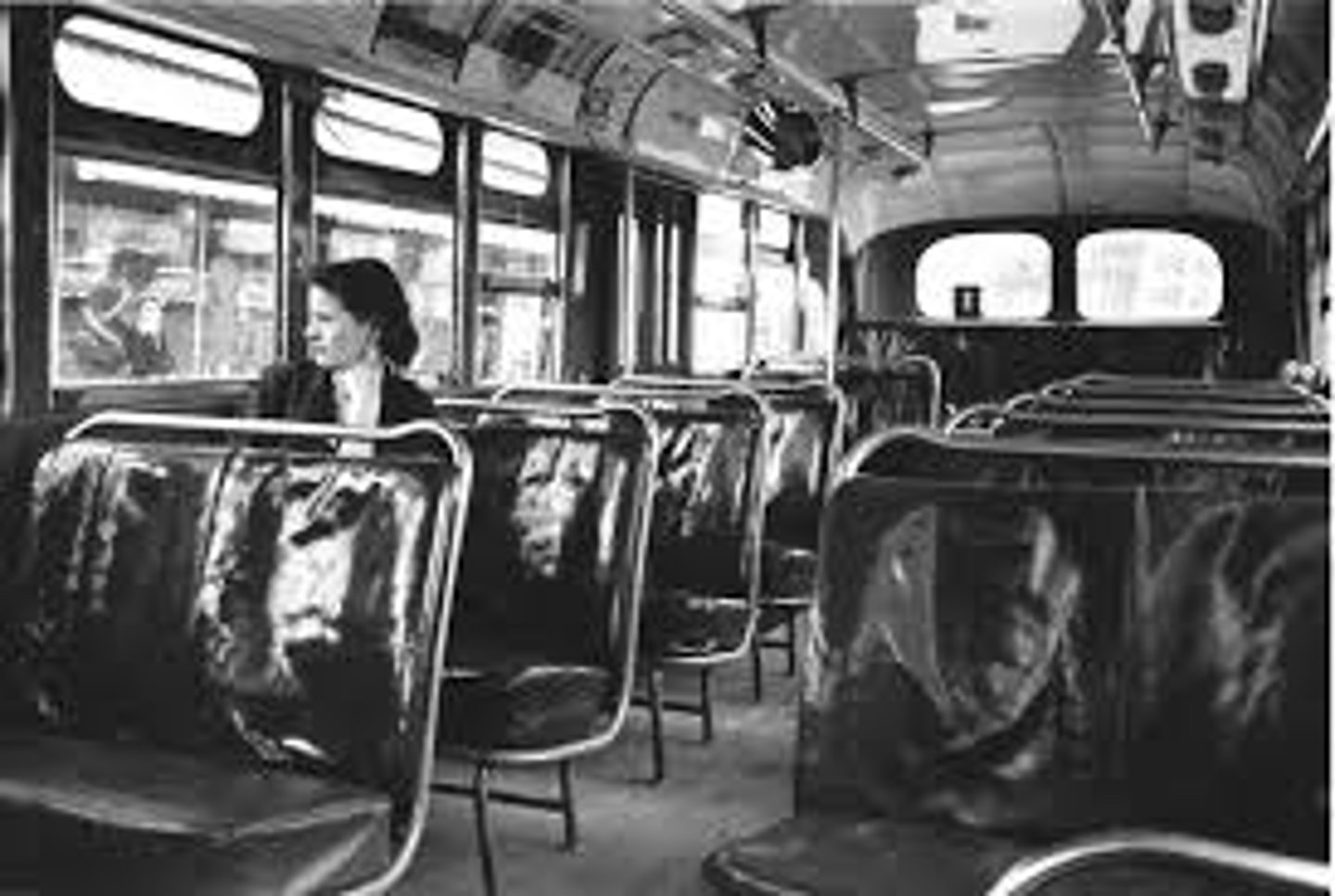

desegregation/integration
The process of bringing black and white people together in public spaces. Many white people were against desegregation.
Voting Rights Act of 1965
Laws that protected African-American's right to vote by banning literacy tests, poll taxes, and intimidation that prevented African-Americans from voting.

civil disobedience
To peacefully break laws that are not fair as a way to protest them and create social or political change (ex: sit-ins)
nonviolence
The use of peaceful means, not force, to make political or social change.
Martin Luther King, Jr.
A civil rights leader who used nonviolent protest. He is famous for his speeches, including "I Have a Dream", and his writings such as "Letters from a Birmingham Jail".
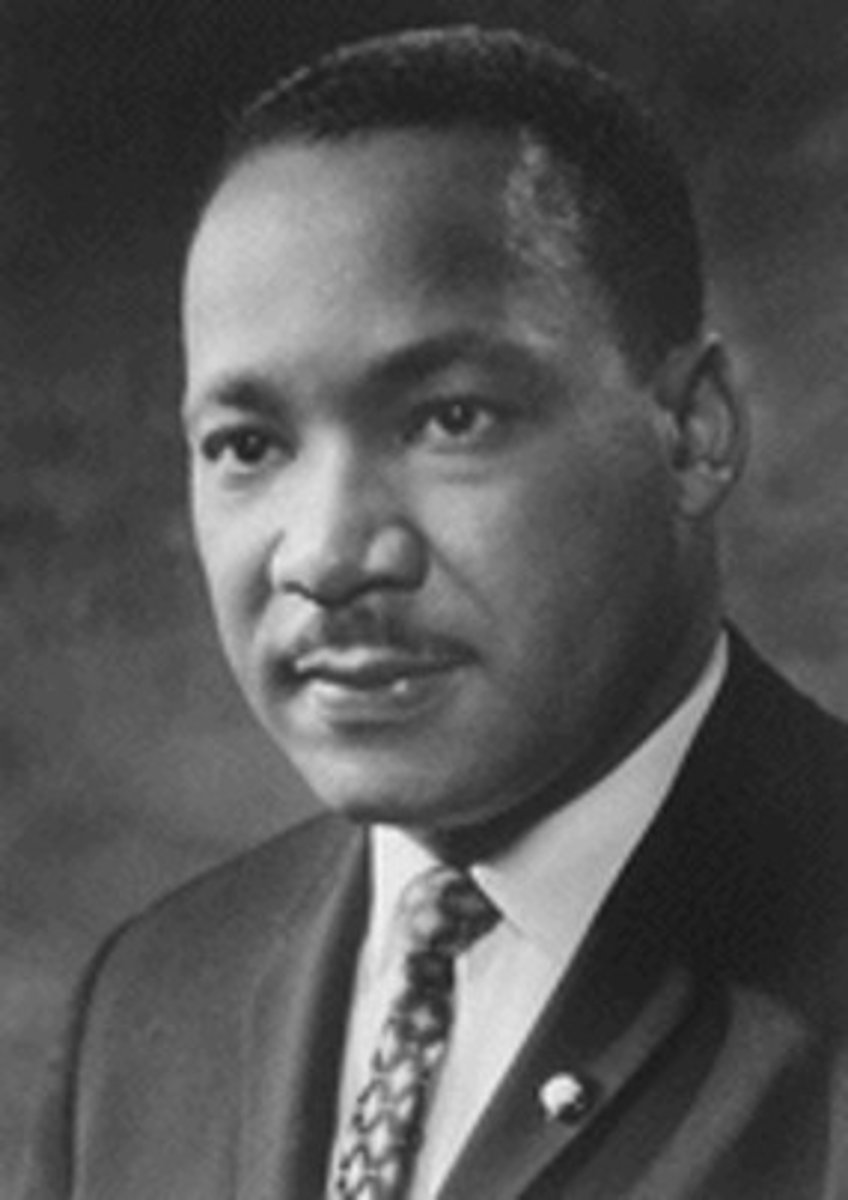

Malcolm X
A civil rights leader who said African-Americans should defend themselves in any way, even using violence if necessary.

Civil Rights Act of 1964
A set of laws that prevented discrimination based on race or sex, supported desegregation of schools, and strengthened voting rights protections.

boycott
To stop buying or using something from a company. This is a nonviolent protest to make change.
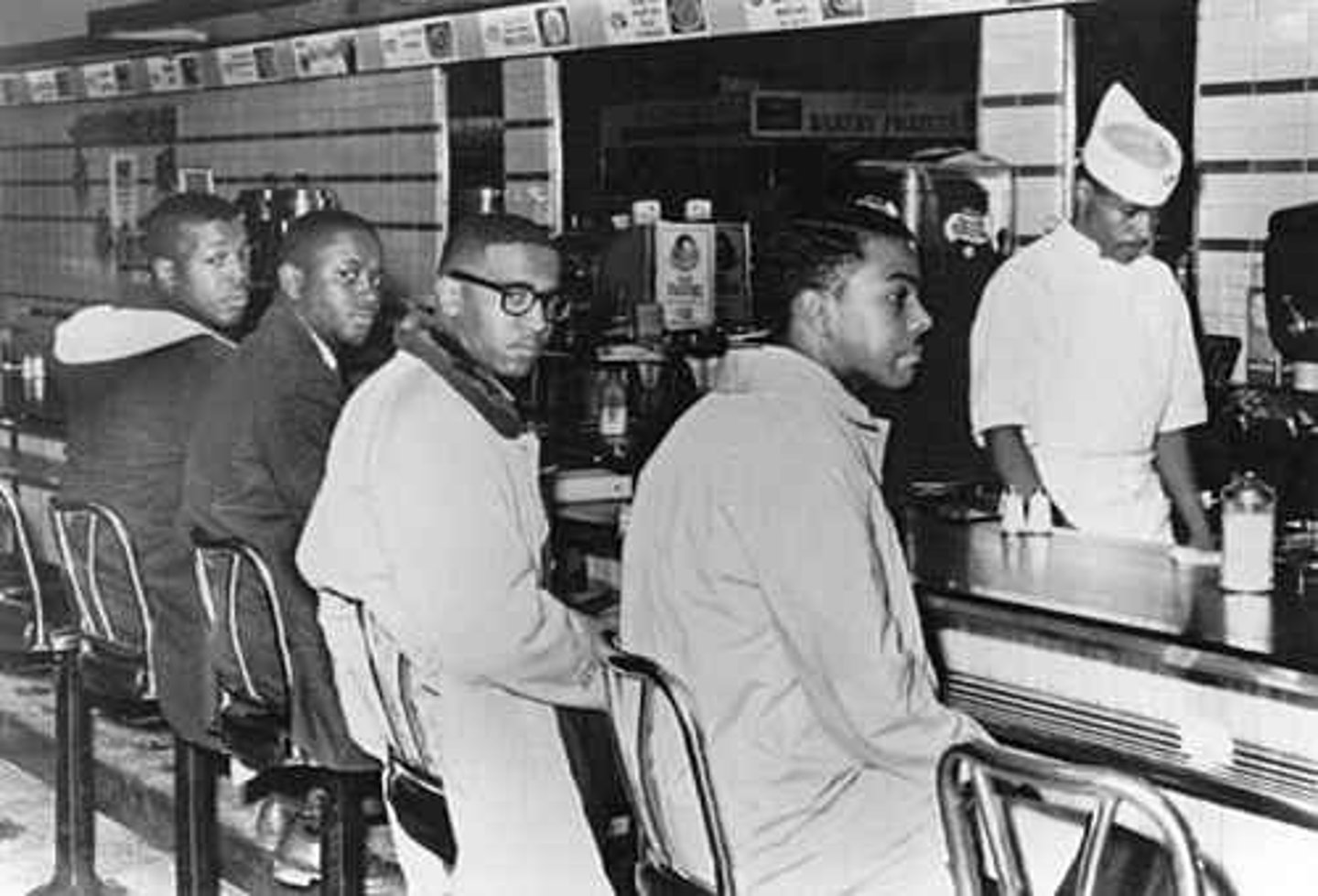
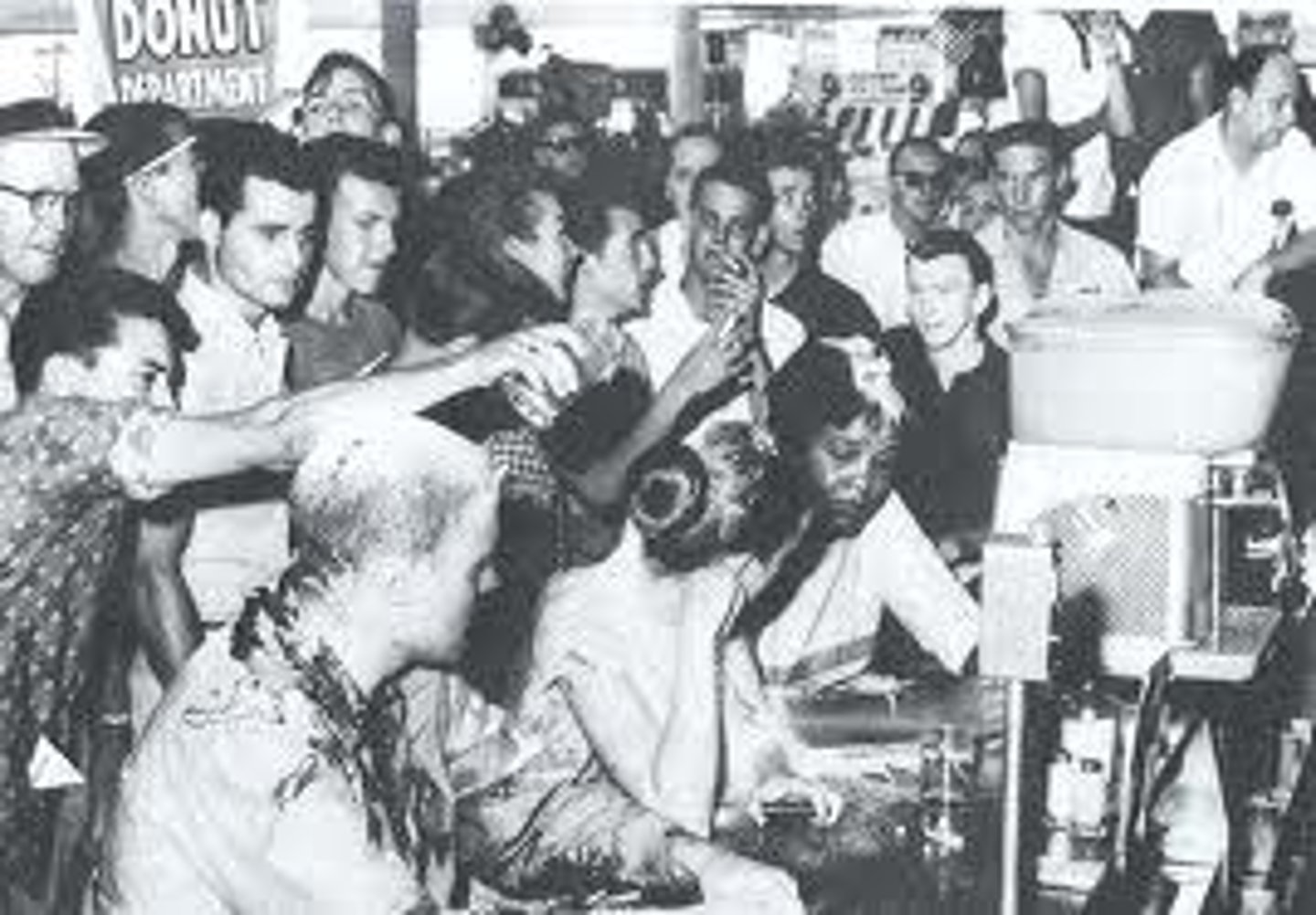
sit-in
An organized passive protest, in which people occupy seats prohibited to them, like in restaurants and other public places

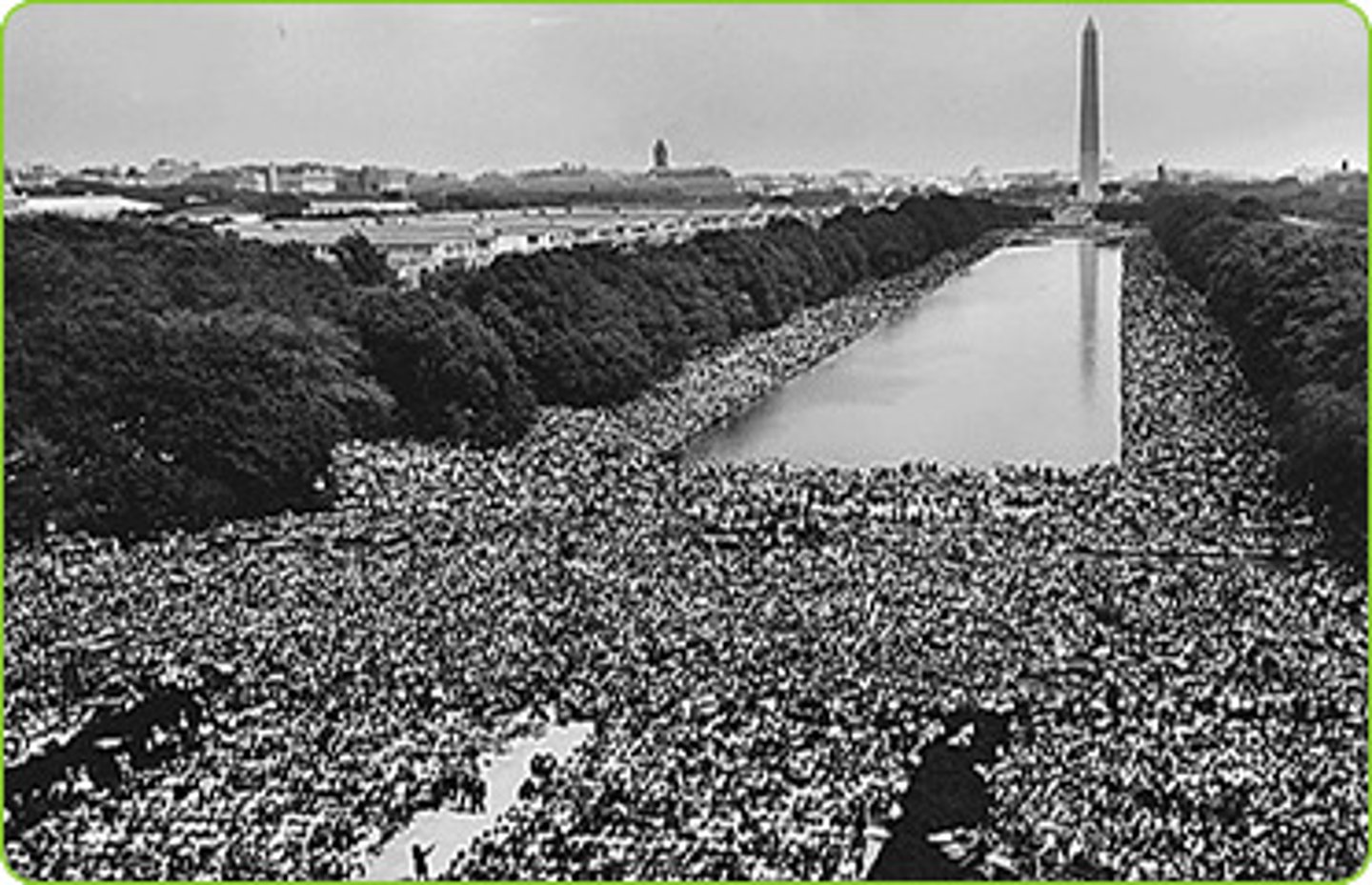
march
A nonviolent protest where large groups of people march on a street to bring attention to an issue and to inspire change.

Rosa Parks
A black woman who broke the bus segregation law that started the Montgomery bus boycott.

just / justice
fair / fairness
demonstrator / protester
A person who takes part in a public protest or march
activist
A person who fights for social or political change
unjust
unfair
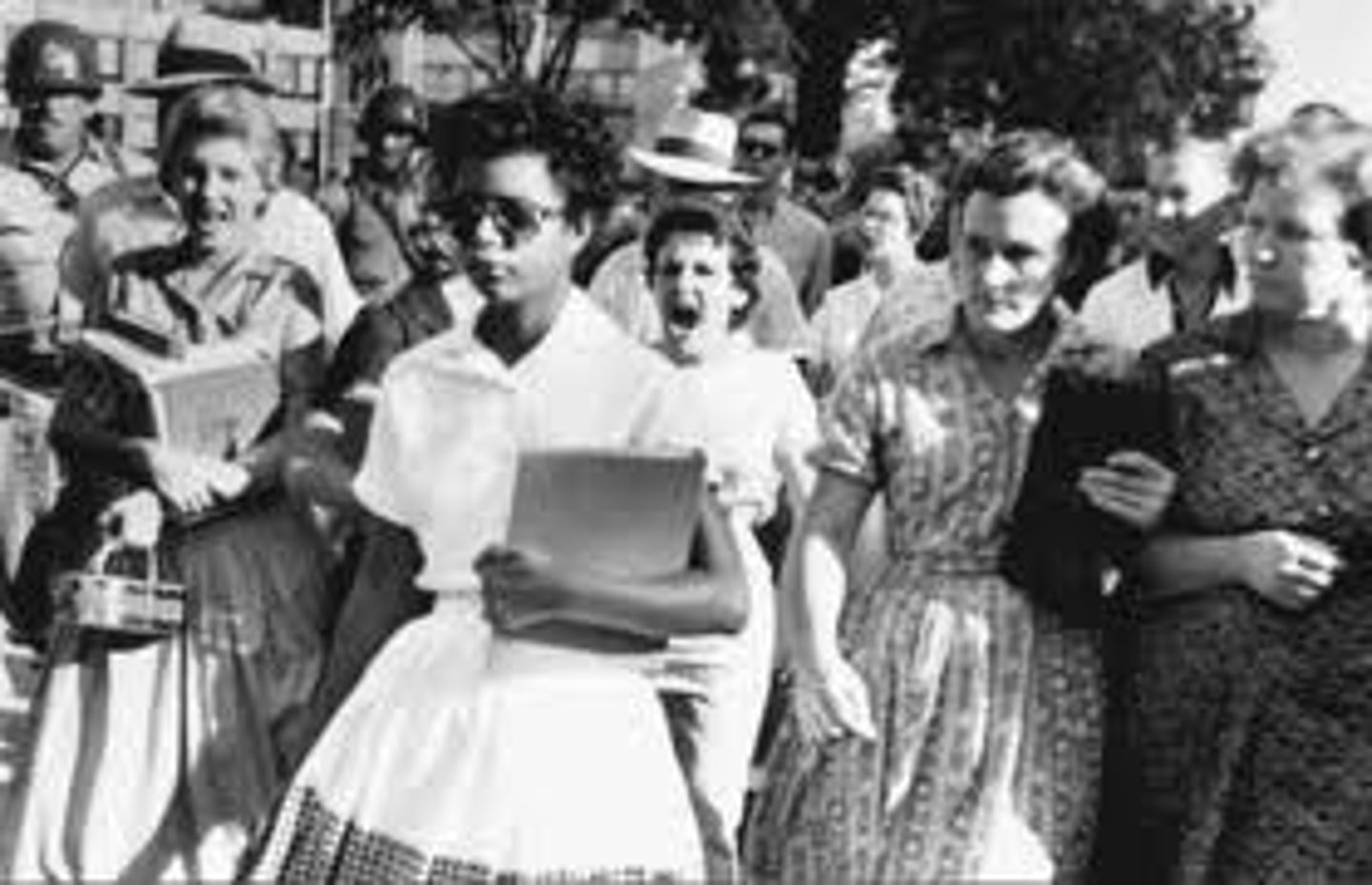
Little Rock 9
Nine black students who were banned from going to a white school by Governor Faubus in Arkansas, even after the Brown v. BOE decision. President Eisenhower send federal troops to escort the black students into the school.

SCLC: Southern Christian Leadership Conference
An organization led by Martin Luther King Jr., starting in 1957, to organize nonviolent action of local protest groups throughout the South
SNCC: Student Nonviolent Coordinating Committee
An organization of students that protested segregation through nonviolent means, such as sit-ins

NAACP: National Association of the Advancement of Colored People
A group founded in the early 1900s that brought lawsuits and organized actions to end racial discrimination during this time period
discrimination
the unjust or prejudicial treatment of different groups of people, especially based on race, age, or sex
Stokely Carmichael
head of the SNCC making a separatist philosophy of black power as the official objective of the organization

Fannie Lou Hamer (1917-1977)
American civil rights activist; she was a prominent leader of the Mississippi Freedom Democratic Party

Heart of Atlanta Motel v. US
1964
*A motel operator refused to serve an African American customer
*The Supreme Court upheld the Civil Rights Act of 1964, which outlawed discrimination in schools, places of work, voting sites, public accommodations, and public areas

The Feminine Mystique (1963)
Best-selling book by feminist thinker Betty Friedan. This work challenged women to move beyond the drudgery of suburban housewifery and helped launch what would become second-wave feminism.

Roe v. Wade (1973)
The court legalized abortion by ruling that state laws could not restrict it during the first three months of pregnancy. Based on 4th Amendment rights of a person to be secure in their persons.

Equal Pay Act of 1963
An amendment to the Fair Labor Standards Act, this act requires equal pay for men and women doing equal work.

Brown Power Movement
Started in the 1960's to get changes in America. Bilingual Education Act was a law that provided funds for schools to develop bilingual and cultural heritage programs for non-English speaking children.

Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA)
A special education law that requires schools to educate students with disabilities in least restrictive environments to the greatest extent of their abilities using plans tailored to the individual needs of the students.
Mapp v. Ohio (1961)
Evidence illegally gathered by the police may not be used in a criminal trial

Gideon v. Wainwright (1963)
Ordered states to provide lawyers for those unable to afford them in criminal proceedings. Warren Court's judicial activism in criminal rights.

Miranda v. Arizona (1966)
Established Miranda warnings of counsel and silence. Must be given before questioning. Warren Court's judicial activism in criminal rights.

Immigration Act of 1965
Abolished the national-origins quotas and providing for the admission each year of 170,000 immigrants from the Eastern Hemisphere and 120,000 from the Western Hemisphere

Stonewall Inn Riots (1969)
A two-day riot by Stonewall Inn patrons after the police raided the gay bar in New York's Greenwich Village in 1969; the event contributed to the rapid rise of a gay liberation movement.

Silent Spring (1962)
Book written by Rachel Carson, a Marine biologist who warned of the misuse of pesticides and their negative affects on the environment. The book is credited with starting the modern environmental movement.

Clean Air Act of 1970
The law aimed at combating air pollution, by charging the EPA with protecting and improving the quality of the nation's air.

Tinker v. Des Moines (1969)
Students in an Iowa school were suspended for wearing black armbands to protest the Vietnam war. Ruled that this suspension was unconstitutional, and that public school students do not "shed their constitutional rights at the schoolhouse door."

New Jersey v. TLO (1985)
addresses the constitutionality of a search of a public high school student for contraband after she was caught smoking. A subsequent search of her purse revealed drug paraphernalia, marijuana, and documentation of drug sales. The U.S. Supreme Court, in a 6-3 ruling, held that the search was reasonable under the Fourth Amendment.
